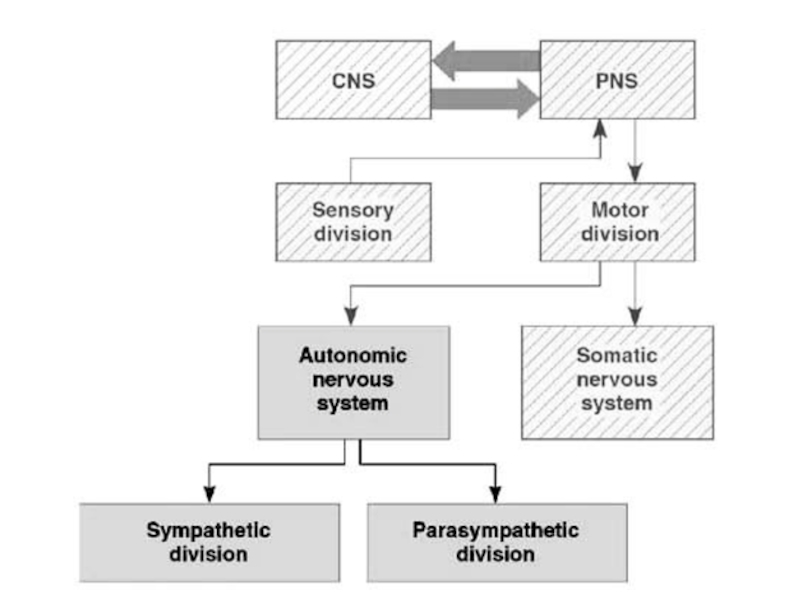
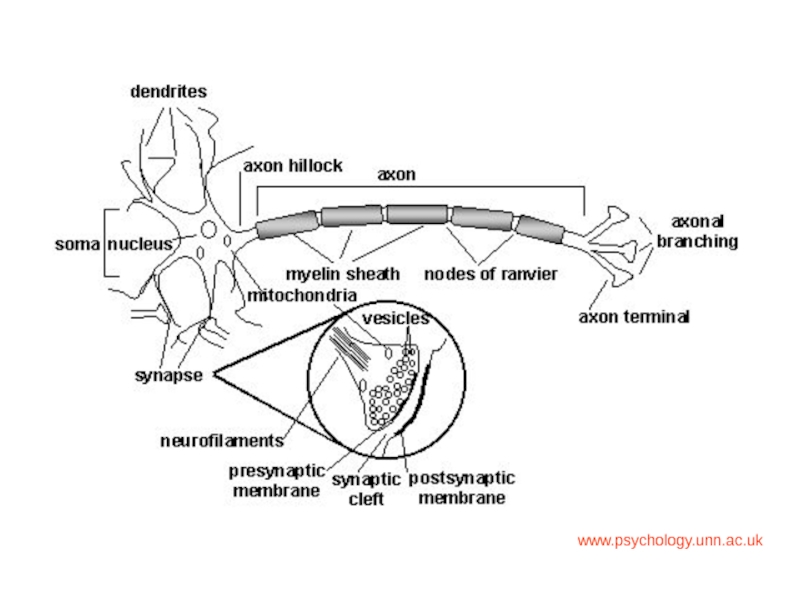
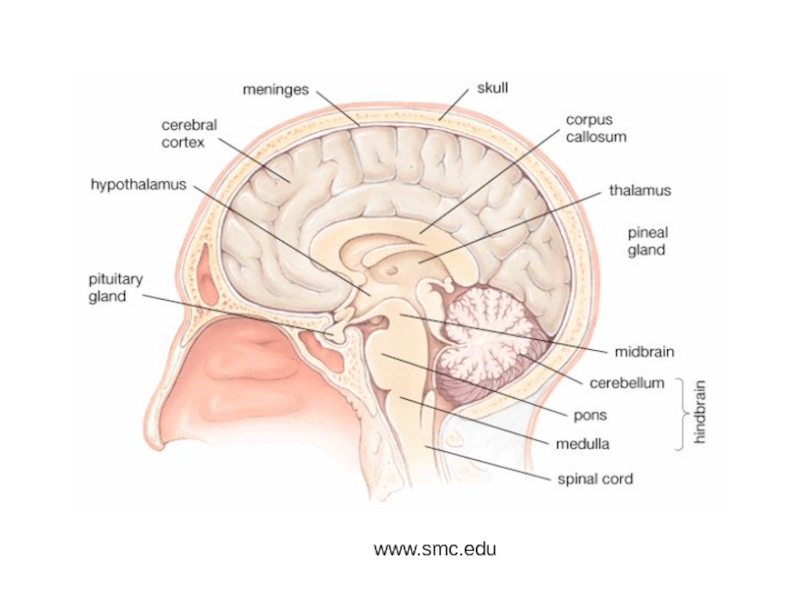
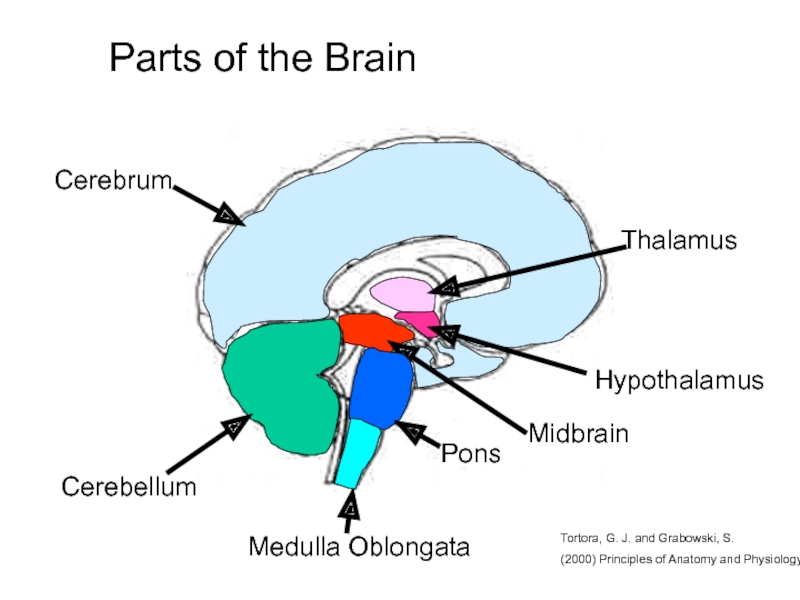
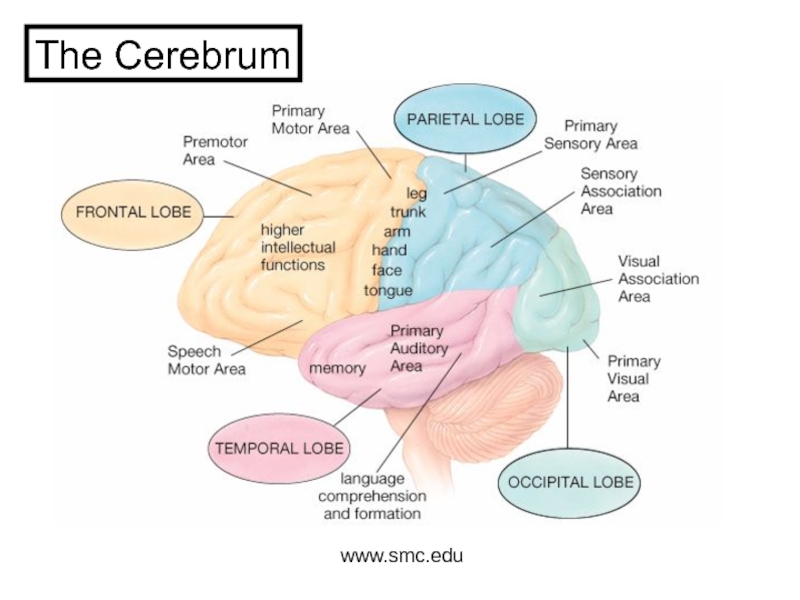
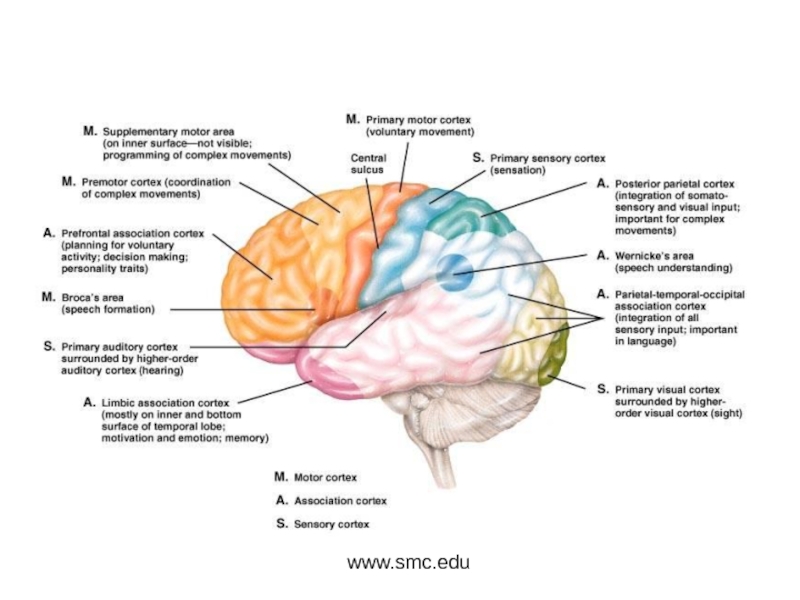
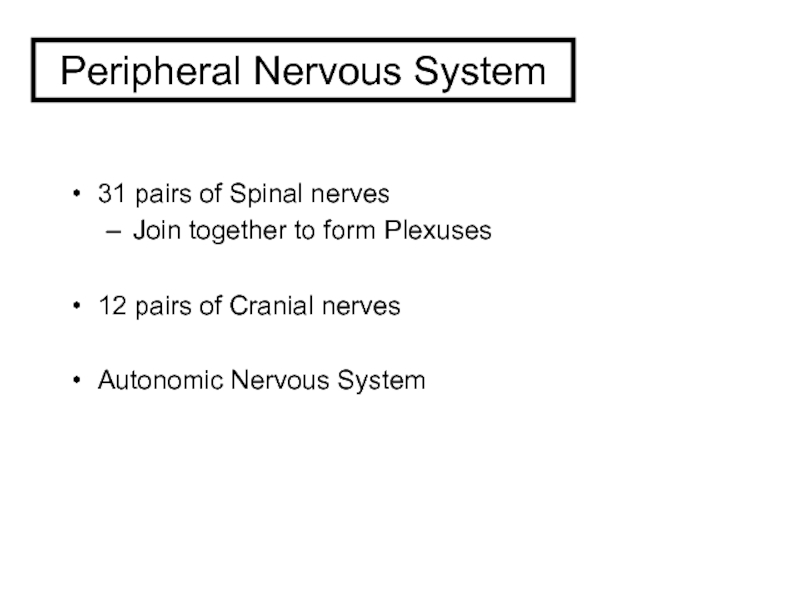
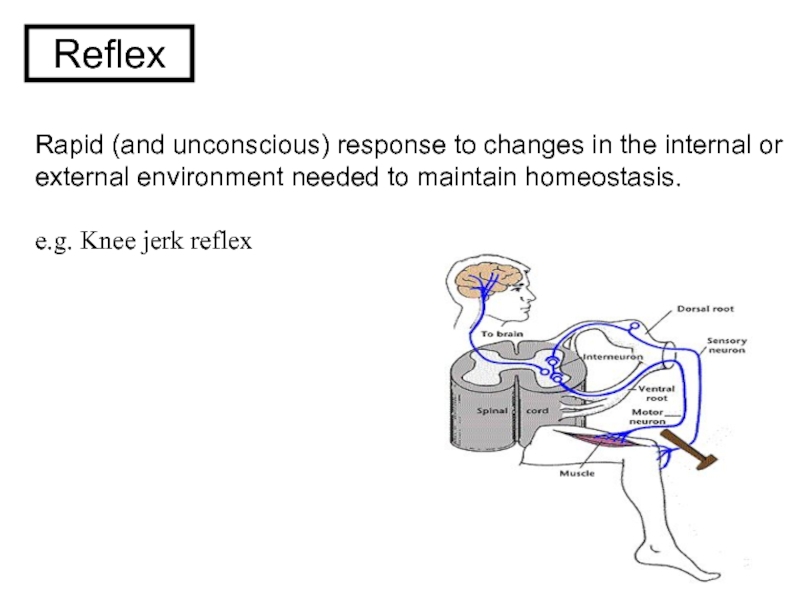
and Autonomic Nervous systems.
To understand the functions of these components.
To
explain how a nervous impulse is transmitted.To explain the underlying physiology behind the lesions/damage that occurs in the nervous system.