Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Optical fiber
Содержание
- 1. Optical fiber
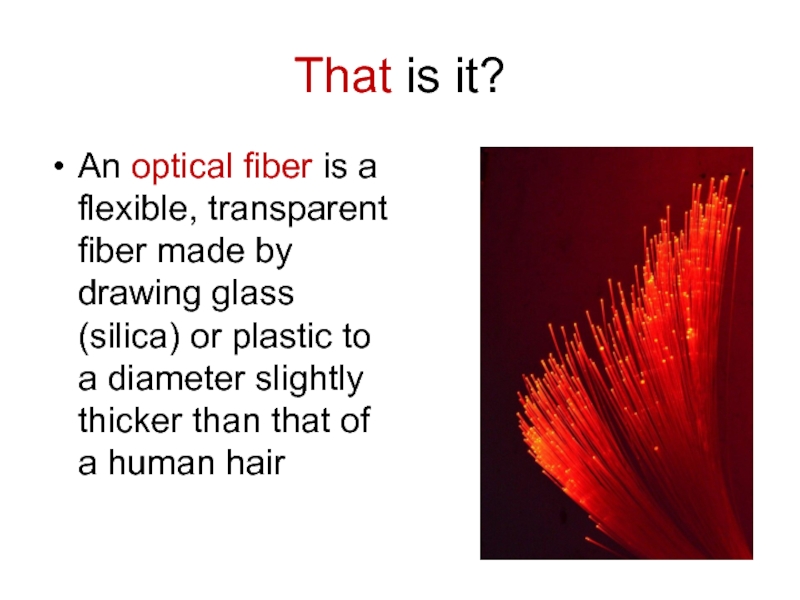
- 2. That is it?An optical fiber is a
- 3. USED FOR…Optical fibers are used most often
- 4. USED FOR…Fibers are used instead of metal
- 5. illuminationFibers are also used for illumination and
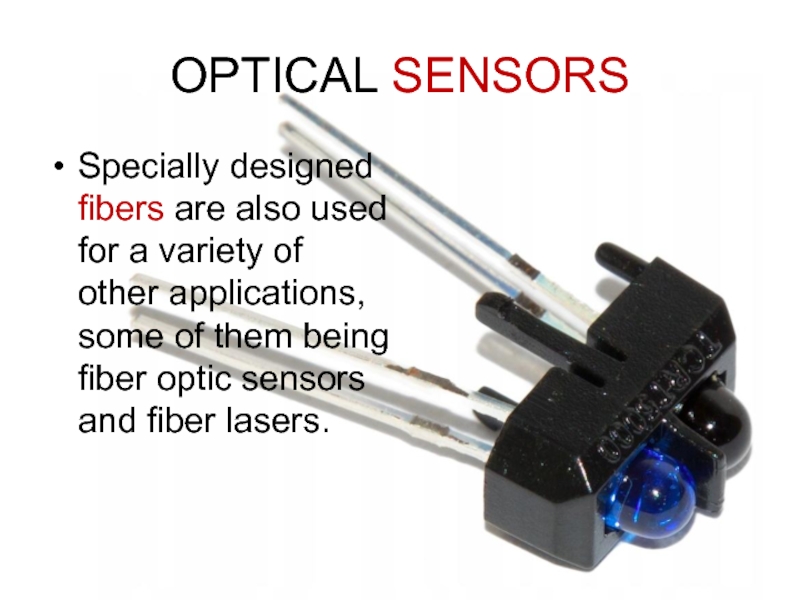
- 6. OPTICAL SENSORSSpecially designed fibers are also used
- 7. HISTORY OF MADE Guiding of light by
- 8. CommunicationOptical fiber is used as a medium
- 9. Advantages over copper wiring High bandwidth A
- 10. ManufacturingMaterialsGlass optical fibers are almost always made
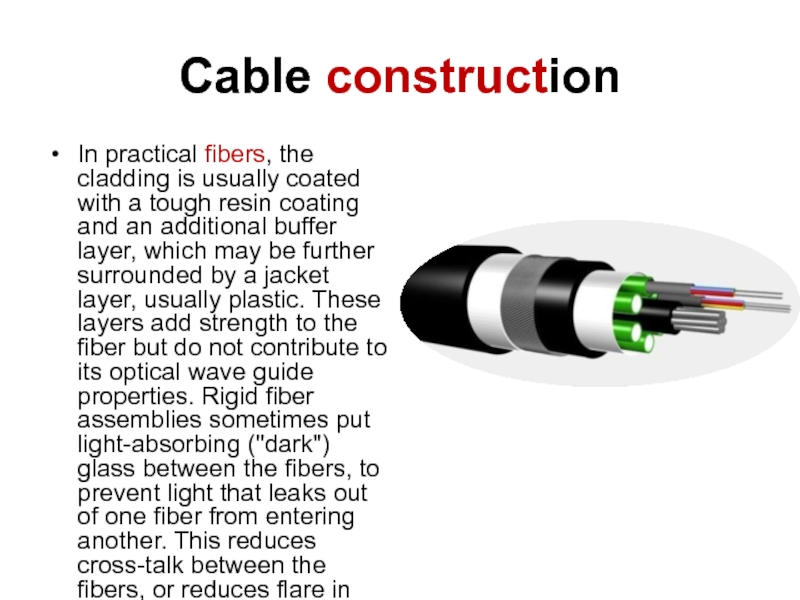
- 11. Cable constructionIn practical fibers, the cladding is
- 12. Thanks for attention
- 13. Скачать презентанцию
That is it?An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 3USED FOR…
Optical fibers are used most often as a means
to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber
and find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths (data rates) than electrical cables.Слайд 4USED FOR…
Fibers are used instead of metal wires because signals
travel along them with less loss; in addition, fibers are
immune to electromagnetic interference, a problem from which metal wires suffer.Слайд 5illumination
Fibers are also used for illumination and imaging, and are
often wrapped in bundles so they may be used to
carry light into, or images out of confined spaces, as in the case of a fiberscope.Слайд 6OPTICAL SENSORS
Specially designed fibers are also used for a variety
of other applications, some of them being fiber optic sensors
and fiber lasers.Слайд 7HISTORY OF MADE
Guiding of light by refraction, the principle
that makes fiber optics possible, was first demonstrated by Daniel
Colladon and Jacques Babinet in Paris in the early 1840s. John Tyndall included a demonstration of it in his public lectures in London, 12 years later.Tyndall also wrote about the property of total internal reflection in an introductory book about the nature of light in 1870:The first working fiber-optical data transmission system was demonstrated by German physicist Manfred Börner at Telefunken Research Labs in Ulm in 1965, which was followed by the first patent application for this technology in 1966.NASA used fiber optics in the television cameras that were sent to the moon. At the time, the use in the cameras was classified confidential, and employees handling the cameras had to be supervised by someone with an appropriate security clearance.Слайд 8Communication
Optical fiber is used as a medium for telecommunication and
computer networking because it is flexible and can be bundled
as cables. It is especially advantageous for long-distance communications, because light propagates through the fiber with much lower attenuation compared to electrical cables. This allows long distances to be spanned with few repeaters.Слайд 9Advantages over copper wiring
High bandwidth A single optical fiber can
carry over 3,000,000 full-duplex voice calls or 90,000 TV channels.
Immunity
to electromagnetic interference Light transmission through optical fibers is unaffected by other electromagnetic radiation nearby. The optical fiber is electrically non-conductive, so it does not act as an antenna to pick up electromagnetic signals. Information traveling inside the optical fiber is immune to electromagnetic interference, even electromagnetic pulses generated by nuclear devices.Low attenuation loss over long distances Attenuation loss can be as low as 0.2 dB/km in optical fiber cables, allowing transmission over long distances without the need for repeaters.
Electrical insulator Optical fibers do not conduct electricity, preventing problems with ground loops and conduction of lightning. Optical fibers can be strung on poles alongside high voltage power cables.
Material cost and theft prevention Conventional cable systems use large amounts of copper. Global copper prices experienced a boom in the 2000s, and copper has been a target of metal theft.
Security of information passed down the cable Copper can be tapped with very little chance of detection
Слайд 10Manufacturing
Materials
Glass optical fibers are almost always made from silica, but
some other materials, such as fluorozirconate, fluoroaluminate, and chalcogenide glasses
as well as crystalline materials like sapphire, are used for longer-wavelength infrared or other specialized applications. Silica and fluoride glasses usually have refractive indices of about 1.5, but some materials such as the chalcogenides can have indices as high as 3. Typically the index difference between core and cladding is less than one percent.Plastic optical fibers (POF) are commonly step-index multi-mode fibers with a core diameter of 0.5 millimeters or larger. POF typically have higher attenuation coefficients than glass fibers, 1 dB/m or higher, and this high attenuation limits the range of POF-based systems.