Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Option B – Medicine and Drugs
Содержание
- 1. Option B – Medicine and Drugs
- 2. Pharmaceutical ProductsA drug or medicine is any
- 3. Placebo effect:A pharmacologically inert substance (often a
- 4. Research and Development:Development of a new drug
- 5. Thalidomide Early 1960’s given to pregnant women
- 6. Methods of Administering Drugs:OrallyEffect varies because absorption
- 7. Parenteral (injection)SubcutaneousBeneath the skinSlow absorptionIntra-muscularUsed when immediate
- 8. More about drugsFat-soluble drugs are more easily
- 9. ToxicityLD50 is the dose (in mg of
- 10. Tolerance and DependenceDrugs may result in physical
- 11. AntacidsBases (metal oxides, metal hydroxides, metal carbonates,
- 12. AnalgesicsPain relievers act by interfering with pain
- 13. Mild analgesicsAspirin (acetyl salicylic acid or ASA)
- 14. Uses of salicylic acid and its derivatives:
- 15. Aspirin substitutesAcetaminophen ( paracetemol)Does not upset stomach
- 16. Strong analgesicsOpium alkaloids (morphine, heroin, codeine)Belong to
- 17. Слайд 17
- 18. Advantages of Opiates:Pharmacological effectsMajor effects on:Nervous systemThe
- 19. Disadvantages:Psychological effectsDrowsiness, mood change, mental fogginess, nausea
- 20. DepressantsDrugs that calm and relax the central
- 21. AlcoholSmall, fat-soluble organic molecule – readily penetrates
- 22. Long-termAlcoholism is caused by an inability to
- 23. Alcohol interacts with other drugsCan produce coma
- 24. Breathalyzer testSubject breathes into an analyzer containing
- 25. Gas Liquid ChromatographyMore precise than breathalyzerUses a
- 26. Слайд 26
- 27. Infra-Red SpectroscopyIR light does not promote electrons
- 28. Слайд 28
- 29. Other DepressantsDiazepam (Valium) is a tranquilizer used
- 30. StimulantsStimulate brain and central nervous systemCause increased alertness and awarenessInclude amphetamines, nicotine, and caffeine
- 31. AmphetaminesHave structures similar to adrenalineBoth are derived from
- 32. NicotineInitial stimulant effect, followed by depression, which
- 33. Smoking can also lead toLung cancerCancer of
- 34. CaffeineIncreases rate of cellular metabolism and therefore
- 35. Caffeine, like nicotine, contains a tertiary amine
- 36. AntibacterialsAntibacterials are selective: they attack infectious bacteria
- 37. Penicillins:Produced from fungi (penicillium genus)Accidentally discovered by
- 38. StructurePenicillins all have a certain structural feature
- 39. Penicillins differ only in their type of side chain
- 40. Penicillins function by interfering with the cross-links
- 41. Disadvantages of penicillinsAbout 10% of the population
- 42. Broad vs. Narrow Spectrum Antibiotics:Broad spectrumEffective against
- 43. Antibiotics in animal feedAntibiotics are added to
- 44. AntiviralsViruses are submicroscopic, non-cellular infectious particles that
- 45. Controlling virusesAntibacterials may be effective if they
- 46. Many antiviral drugs work to inhibit the
- 47. Stereochemistry in Drug Action and Design (HL
- 48. Geometric isomers have: different physical properties, including
- 49. Optical isomers:Different from geometric isomers:The molecules are
- 50. Слайд 50
- 51. An equimolar mixture of both enantiomers (racemic
- 52. Synthetic drugs, when chiral, are usually produced
- 53. Synthesis of non-racemic mixtures is difficult, as
- 54. Combinatorial chemistryAs drug R & D is
- 55. Libraries of a vast amount of related
- 56. Combi-chem began in the 1960’sMost importantly: Solid-phase
- 57. “linking group” is attached to a plastic
- 58. Procedure can be extended so that the
- 59. AnaestheticsLocal vs. GeneralLocal anaesthetics block pain in
- 60. Cocaine, procaine, and lidocaine all contain a benzene ring and a tertiary amine group
- 61. Cocaine, besides acting as a local anaesthetic,
- 62. General anaesthetics act on the brain and
- 63. Слайд 63
- 64. Слайд 64
- 65. Dalton’s Law of partial pressures can be
- 66. Mind-altering drugsPsychedelic drugs or psychotomimetics (simulate madness)Cause
- 67. LSDPowerful hallucinogenEffect depends on:DosePhysiological conditionPsychological conditionExpectationsMagnifies perceptionDestroys
- 68. MescalineProduces color hallucinationsLasts approximately 12 hoursPsilocybinMagnified perceptionLow
- 69. LSD, mescaline, and psilocybin all contain a
- 70. Слайд 70
- 71. Cannabiscannabis sativa, contains pharmacologically active compounds (cannabinoids)Legalization
- 72. Скачать презентанцию
Pharmaceutical ProductsA drug or medicine is any chemical which:Alters sensory sensationsAlters mood or emotionsAlters physiological state (consciousness, activity level, or coordination)
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Pharmaceutical Products
A drug or medicine is any chemical which:
Alters sensory
sensations
coordination)Слайд 3Placebo effect:
A pharmacologically inert substance (often a sugar pill) produces
a significant reaction because the patient expects, desires, or was
told it would happenUsed as a control in clinical trials
Highlights the body’s natural healing powers
Слайд 4Research and Development:
Development of a new drug is a very
costly, lengthy process controlled by the government:
In 1970, 3620 drugs
were tested. 16 came on the market at an average cost of $20 millionOnly 1 in 2000 drugs eventually make it to the market
Phase I: Initial clinical trials on volunteers after the drug has proven safe when given to animals
Phase II: Thorough clinical investigation to eliminate investigator bias
Phase III: Extended clinical evaluation
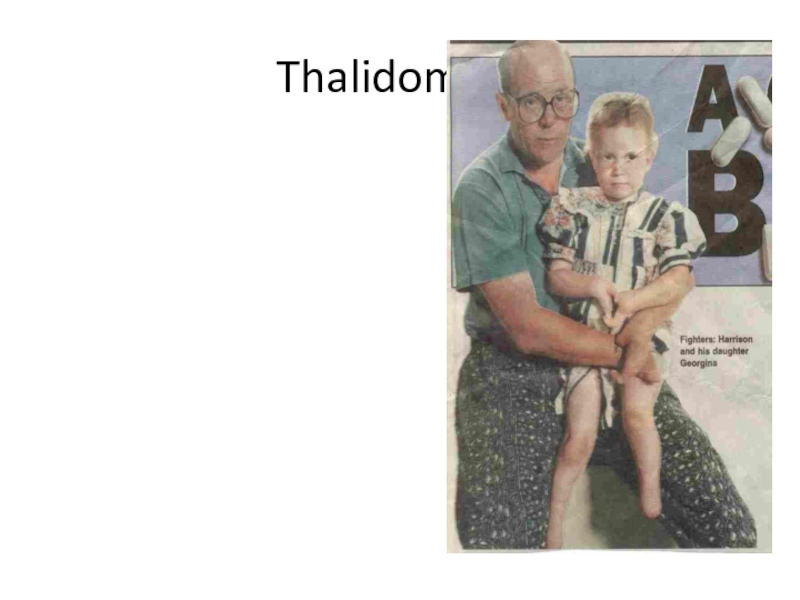
Слайд 5Thalidomide
Early 1960’s given to pregnant women to treat morning
sickness
Later found to cause major birth defects
One isomer controls morning
sickness, the other leads to birth defects (optical isomers)Слайд 6Methods of Administering Drugs:
Orally
Effect varies because absorption is affected by
stomach content and drug concentration
Primary site of absorption is the
small intestineRectally
Effective if a drug cannot be taken orally or if a drug is pH sensitive
Inhalation
Rapid, systemic administration due to extensive network of blood vessels in lungs
Слайд 7Parenteral (injection)
Subcutaneous
Beneath the skin
Slow absorption
Intra-muscular
Used when
immediate response is not
required
Used for large volumes of drug injection
Intravenous
Near instantaneous effect
Concentration not
affected by stomach content Слайд 8More about drugs
Fat-soluble drugs are more easily absorbed, since blood
vessels contain a fatty layer
Capillaries of brain are denser and
prevent diffusion of many substances into the brain (blood-brain barrier)Drugs are broken down by the kidneys and liver
Half-life is the time required for half of the drug to be eliminated
Слайд 9Toxicity
LD50 is the dose (in mg of substance per kg
of body mass) that is lethal to to 50% of
laboratory animalsThe lower the LD50, the more toxic the substance
Lowest LD50 rating known as of yet: botulism toxin (BoTox) – most toxic substance known LD50 of roughly 0.005-0.05 µg/kg
Слайд 10Tolerance and Dependence
Drugs may result in physical or psychological dependence
Tolerance
means that over time, an individual requires an increased amount
of the drug to achieve the same physiological effectСлайд 11Antacids
Bases (metal oxides, metal hydroxides, metal carbonates, or metal hydrogencarbonates)
that react with excess stomach acid to adjust pH
Stomach acid
helps suppress growth of harmful bacteria and aids in digestionOften combined with alginates and anti-foaming agents to prevent reflux
Consumption of too much antacid results in alkalosis (basic stomach)
Слайд 12Analgesics
Pain relievers act by interfering with pain receptors
Mild analgesics work
by blocking the production of prostaglandins
Prostaglandins:
Constrict blood vessels
Affect hypothalamus (region
of brain controlling heat regulationIncrease permeability of capillaries to allow for swelling
Strong analgesics work by binding to receptors in the brain
Prevents transmission of pain impulses without depressing the central nervous system
Слайд 13Mild analgesics
Aspirin (acetyl salicylic acid or ASA) produced from salicylic
acid (relatively strong acid, difficult to take)
Addition of acetyl group
lowers acidity – less irritating to stomachASA is called a prodrug: a less active form that is converted to the active form after administration
ASA can also be used to produce alka-seltzer and other drugs by further modification
Слайд 14Uses of salicylic acid and its derivatives:
Relief from minor aches
and pains
Fever reduction (antipyretic)
Anti-inflammatory agent
Anti-clotting agent
Disadvantages of aspirin:
Can cause upset
stomach and ulcerationRisk of severe gastrointestinal bleeding following alcohol consumption
Small risk of allergy (.5% of population)
Accidental infant poisoning; small correlation to Reye’s syndrome in children
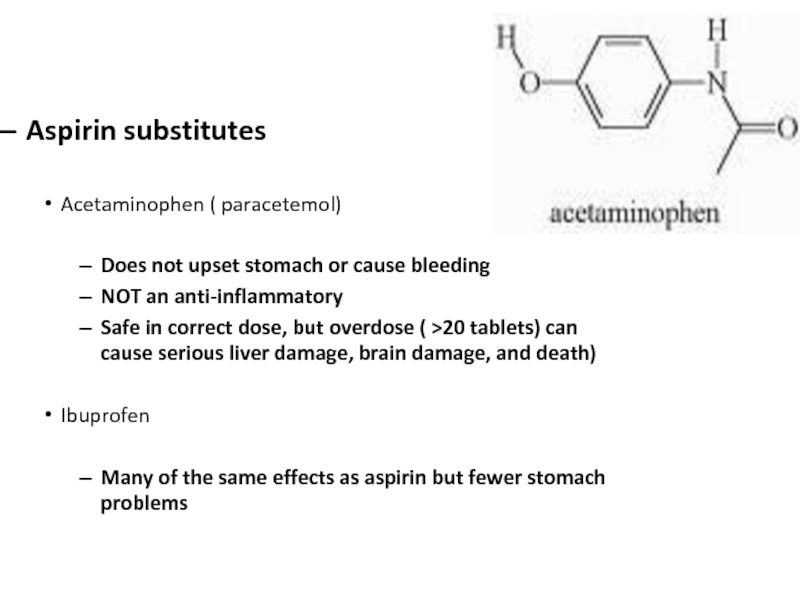
Слайд 15Aspirin substitutes
Acetaminophen ( paracetemol)
Does not upset stomach or cause bleeding
NOT
an anti-inflammatory
Safe in correct dose, but overdose ( >20 tablets)
can cause serious liver damage, brain damage, and death)Ibuprofen
Many of the same effects as aspirin but fewer stomach problems
Слайд 16Strong analgesics
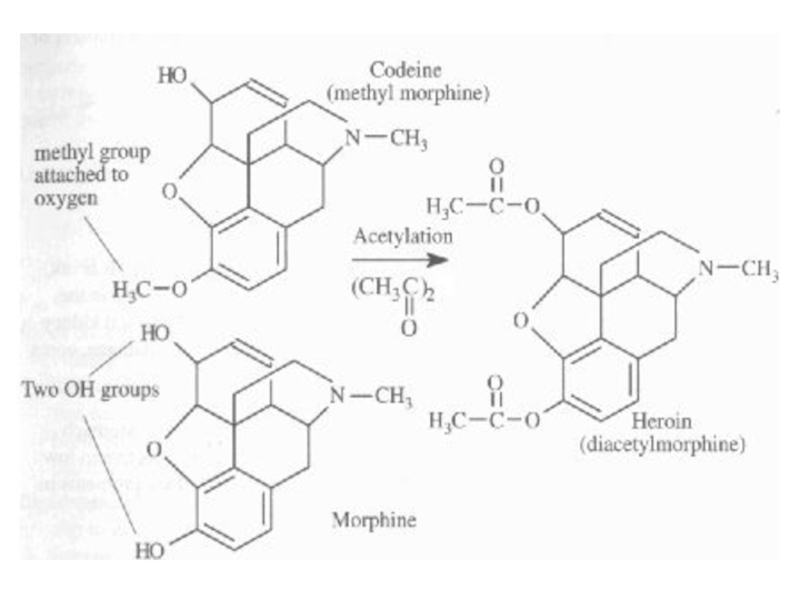
Opium alkaloids (morphine, heroin, codeine)
Belong to “opiate” class (drug
that exerts actions on the body similar to morphine) or
“narcotics” (drug that produces a narcotic (sleep-inducing) effect as well as an analgesic (pain relieving) effect)Morphine is principal alkaloid, making up about 10% by mass of raw opium
Codeine is about .5% of raw opium
Heroin is synthesized from morphine (semi-synthetic drug) via a simple acetylation
Слайд 18Advantages of Opiates:
Pharmacological effects
Major effects on:
Nervous system
The eye
GI tract
Uses:
Strong analgesic
for relieving severe pain
Treatment of diarrhea (produces constipation)
Cough suppressant
Слайд 19Disadvantages:
Psychological effects
Drowsiness, mood change, mental fogginess, nausea and vomiting
Anxiety, fear,
lethargy, sedation, lack of concern, inability to concentrate
Tolerance and Dependence
Cross-tolerance
can occur (users tolerant to one opiate will be tolerant to other opiates)Users may not function properly without the drug, experience withdrawal symptoms (addiction)
Слайд 20Depressants
Drugs that calm and relax the central nervous system
Tranquilizers
Alcohol, valium,
librium (Reduce distress but do not produce sleep)
Sedatives
Barbiturates (Reduce distress
but do not produce sleep, stronger than tranquilizers)Hypnotics
Chloral hydrate (produces sleep in larger doses)
Слайд 21Alcohol
Small, fat-soluble organic molecule – readily penetrates cell membrane and
is easily absorbed from the GI tract
Social effects:
Costs
Sickness and death
associated with abuseCrime and traffic costs
Physiological effects
Short term:
Reduces anxiety and inhibitions
Impairs attention, judgment, and control
Violent or aggressive behavior
Loss of motor function
Effect depends on body mass and concentration of alcohol in the blood
Слайд 22Long-term
Alcoholism is caused by an inability to reduce alcohol intake
Withdrawal
symptoms (nausea, sweating, anxiety, hypertension
Tolerance
Cirrhosis (scarring) and cancer of the
liver (the major detoxification organ)Heart disease
Hypertension
Strokes
Gastritis
Ulcers
Depression
Birth defects
Слайд 23Alcohol interacts with other drugs
Can produce coma or death when
combined with sleeping pills or barbiturates
Can cause stomach bleeding with
aspirinCan inhibit breakdown of other drugs
Measuring blood alcohol concentration (BAC)
Mass (g) of ethanol per 100 cm3 of blood
.08% is legal limit in US (.080 g per 100 cm3 of blood)
Ethanol is easily absorbed from the stomach to the blood, where it is exhaled by the lungs (ethanol is fairly volatile)
C2H5OH(l) C2H5OH(g)
The alcohol vapor can be detected by a number of methods
Слайд 24Breathalyzer test
Subject breathes into an analyzer containing an oxidizing agent
and a detector
Potassium dichromate (K2CrO4)is the oxidizing agent
Oxidizes ethanol to
ethanoic acidThis is an oxidation-reduction reaction that involves an electron transfer
This electron transfer generates an electric current which can be detected by the machine
Unreliable in legal cases
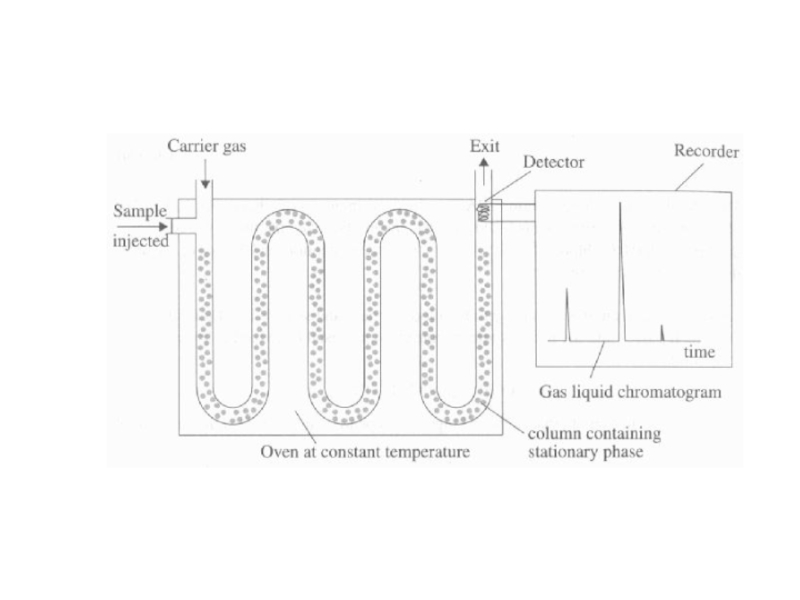
Слайд 25Gas Liquid Chromatography
More precise than breathalyzer
Uses a stationary phase (non-volatile
liquid or solid support) and a mobile phase (inert gas,
like N2)Breath components (CO2, H2O, and alcohol vapor) are injected into the machine and partitioned (divided) between the stationary and mobile phases
Components exit at different intervals (each substance has a different affinity and bond strength for the two phases, and thus move through at different rates)
Components are detected
Retention time for each component is measured (time taken for each component to pass through the column)
Blood alcohol’s retention time is compared to the retention time for a standard ethanol sample
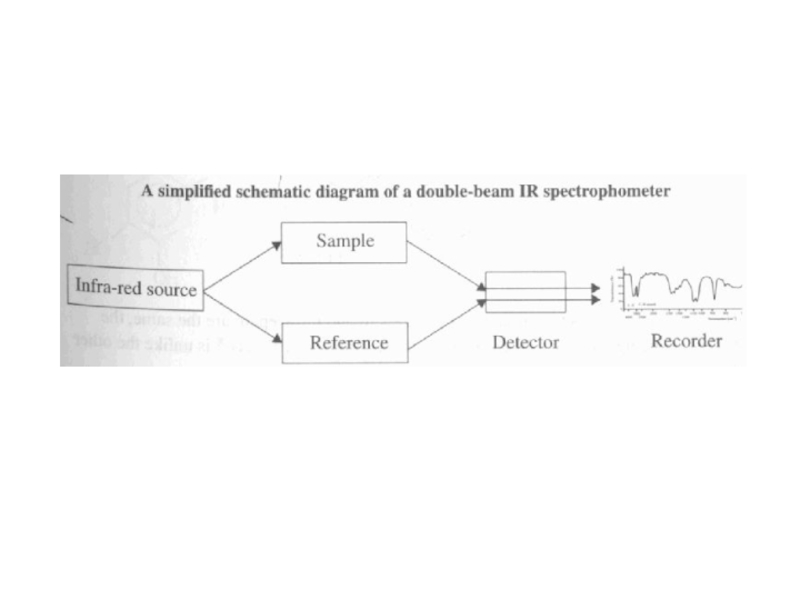
Слайд 27Infra-Red Spectroscopy
IR light does not promote electrons to higher levels,
but does provide enough energy to make molecules “vibrate”
Vibrational motion
depends on the mass of the molecule and the types of bonds presentIR spectrum therefore depends on types of molecules present (“molecular fingerprint”)
Scale is based on wavenumber (1/wavelength)
Police use intoximeter (IR spectrometer) to confirm breathalyzer test
IR radiation is passed through breath sample
C-H group in alcohol absorbs a certain frequency of IR light
% transmittance of the C-H frequency is determined, indicating amount of alcohol present
Слайд 29Other Depressants
Diazepam (Valium) is a tranquilizer used to relieve anxiety
and tension
Nitrazepam (Mogadon) is a hypnotic drug used to induce
sleepFluoxetine hydrochloride (Prozac) is used to treat mental depression by increasing activity of serotonin (a neurotransmitter)
Слайд 30Stimulants
Stimulate brain and central nervous system
Cause increased alertness and awareness
Include
amphetamines, nicotine, and caffeine
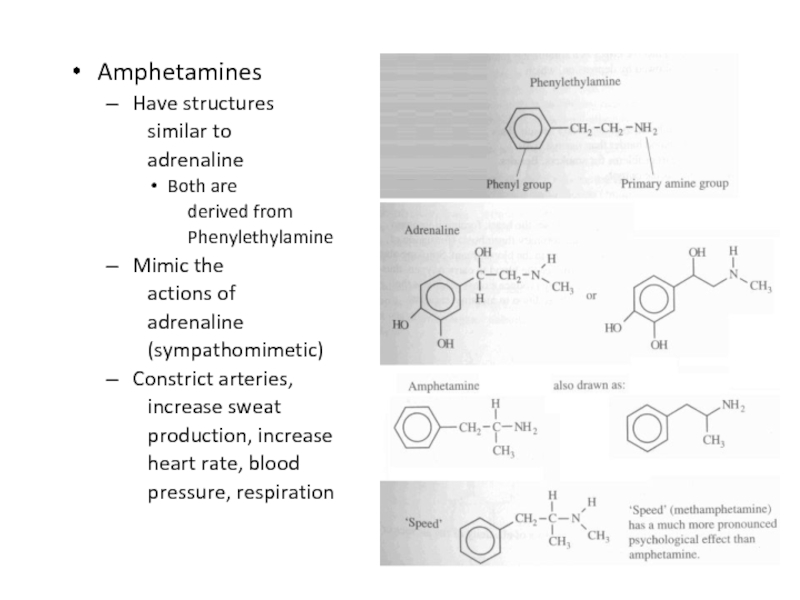
Слайд 31Amphetamines
Have structures
similar to
adrenaline
Both are
derived from
Phenylethylamine
Mimic the
actions
of
adrenaline
(sympathomimetic)
Constrict arteries,
increase sweat
production, increase
heart rate, blood
pressure, respiration
Слайд 32Nicotine
Initial stimulant effect, followed by depression, which encourages frequent use
Short
term effects:
Increased heart rate and blood pressure, putting stress on
the heartReduces urine output
Long term effects
Increased risk of heart disease and blood clot (thrombosis)
Inhibits oxygen-carrying capacity of blood
Increased risk of peptic ulcers
Слайд 33Smoking can also lead to
Lung cancer
Cancer of the larynx and
mouth
Heart and blood vessel disease
Empyhsema
Chronic bronchitis
Air pollution
Fires!!
Stained fingers and teeth
Bad
breathVery easy to develop dependence on nicotine compared to alcohol or barbiturates
Withdrawal symptoms: weight gain, nausea, insomnia, irritability, fatigue, depression, and inability to concentrate
Слайд 34Caffeine
Increases rate of cellular metabolism and therefore respiration
In low doses,
enhances wellbeing, alertness, energy, and motivation
In large amounts, physical coordination
and timing are affected, and sleeplessness may also result.Weak diuretic (increases urine flow)
Tolerance occurs, but no physical dependence
Vasoconstrictor (blood vessel constriction), so can help in treating migraines
Can help newborn babies to breathe as it increases respiration
Слайд 35Caffeine, like nicotine, contains a tertiary amine group (nitrogen atom
attached to three organic [i.e. carbon-containing] substituents):
Слайд 36Antibacterials
Antibacterials are selective: they attack infectious bacteria rather than human
cells
Can be
Bacteriostatic (inhibit bacterial cell division) or
Bacteriocidal (directly kill bacteria)
Normally
ineffective against viruses because viruses live within host cell, which are unaffected by most antibioticsСлайд 37Penicillins:
Produced from fungi (penicillium genus)
Accidentally discovered by Alexander Fleming, who
noticed that bacteria did not grow around a spot of
penicillium notatum mold on a culture plateFleming could not isolate the “penicillin,” and later gave up the research
Florey and Chain, at Oxford, renewed the research and started administering the drug to humans
Awarded the Nobel Prize
Thousands of lives were saved during WWII
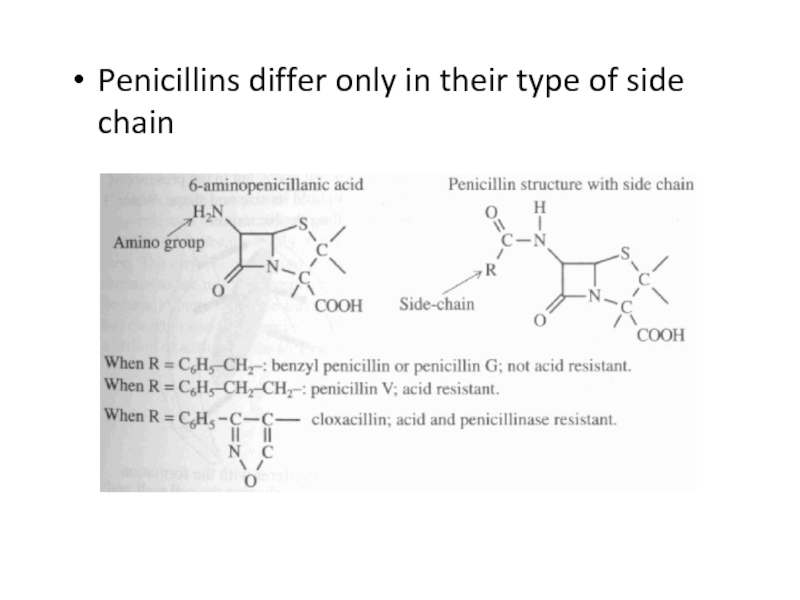
Слайд 38Structure
Penicillins all have a certain structural feature in common, the
6-APA group
(6-aminopenicillic acid)
Structure has no effect on bacterial growth,
but when an extra side chain is added to the amino (NH2) group, it becomes “active”Side chain varies between different types of penicillin:
Penicillin G, the first type created, is not acid-resistant, and must be injected to bypass the stomach
Penicillin V is acid-resistant
Cloxacillin is acid and penicillinase (bacteria-produced enzyme that breaks down penicillin) resistant
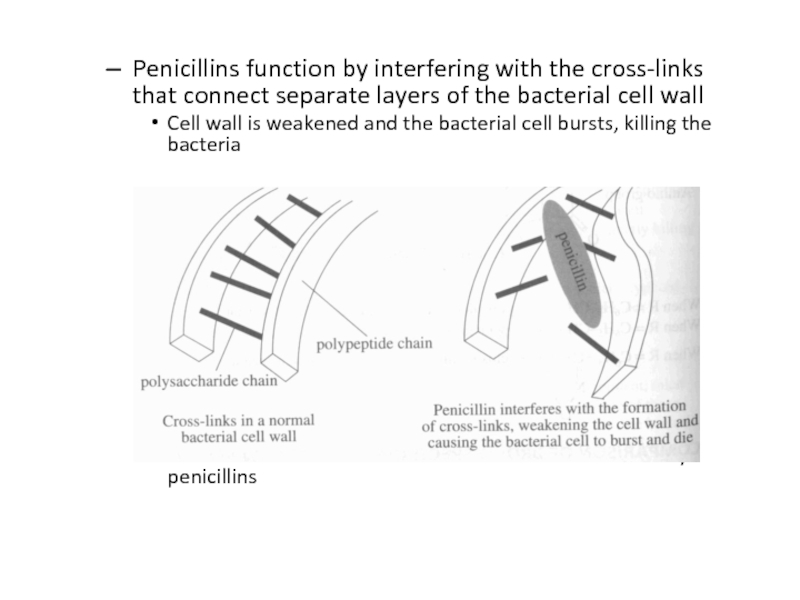
Слайд 40Penicillins function by interfering with the cross-links that connect separate
layers of the bacterial cell wall
Cell wall is weakened and
the bacterial cell bursts, killing the bacteriaHumans do not have cell walls and are thus unaffected by penicillins
Слайд 41Disadvantages of penicillins
About 10% of the population is allergic
Side effects
include fever, body rash, shock, and death
Overprescription can result in
destruction of harmless bacteria in the digestive tract, allowing harmful bacteria to colonizeOverprescription leads to genetics resistance over time, rendering the antibiotic eventually useless
Thus, antibiotics should only be prescribed when there is no other option that can reduce suffering or save a life
Слайд 42Broad vs. Narrow Spectrum Antibiotics:
Broad spectrum
Effective against a wide variety
of bacteria
Tetracyclines (Aureomycin, Terramycin)
Repeated use may wipe out harmless bacteria
in the digestive tract, which may be replaced by harmful strainsNarrow spectrum
Effective against only certain types of bacteria
Penicillins
Typically, a broad spectrum is initially prescribed until the bacteria can be identified, at which point a narrow spectrum is prescribed
Слайд 43Antibiotics in animal feed
Antibiotics are added to animal feed to
prevent the spread of infection throughout livestock
However, this can encourage
the development of drug-resistant bacteria that humans will eventually be exposed toСлайд 44Antivirals
Viruses are submicroscopic, non-cellular infectious particles that can only reproduce
inside a living host cell
Unlike bacteria, which have a cellular
structure, viruses have no nucleus, cytoplasm, or cell membraneThis limits the effectiveness of antibacterial drugs on viruses
Слайд 45Controlling viruses
Antibacterials may be effective if they block the transfer
of genetic information, although few do
Vaccination is primary method of
preventionPatient is exposed to weakened or inert viral particles to stimulate immune system
Immune system produces antibodies, crucial in the immune response, specific to that virus
Future exposure to active viral particles is more easily controlled because antibodies have already been produced against it
Слайд 46Many antiviral drugs work to inhibit the function of replication-specific
enzymes
Latent viruses are viruses that inject their genetic material into
a host cell, but the material is not expressed until a later dateHerpes simplex virus, certain types of cancer
AIDS virus
Attacks immune system by binding to a receptor glycoprotein (CD4) on T4 immune cells
Difficult to fight because of:
its ability to mutate (thus rendering a previous treatment ineffective)
Its metabolism is similar to human cells
Слайд 47Stereochemistry in Drug Action and Design (HL only)
Stereoisomers are isomers
with the same molecular formula AND the same structural formula,
but a different arrangement of atoms in space.Geometric isomers:
If a pair of stereoisomers contains a double bond, cis and trans arrangements can exist:
cis: substituents are on the same side of the double bond
trans: substituents are on opposite sides of the double bond
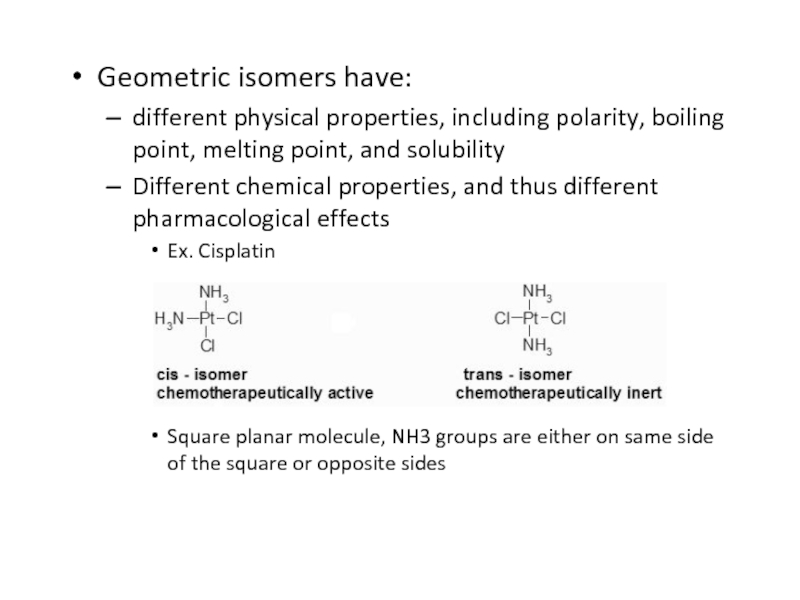
Слайд 48Geometric isomers have:
different physical properties, including polarity, boiling point,
melting point, and solubility
Different chemical properties, and thus different pharmacological
effectsEx. Cisplatin
Square planar molecule, NH3 groups are either on same side of the square or opposite sides
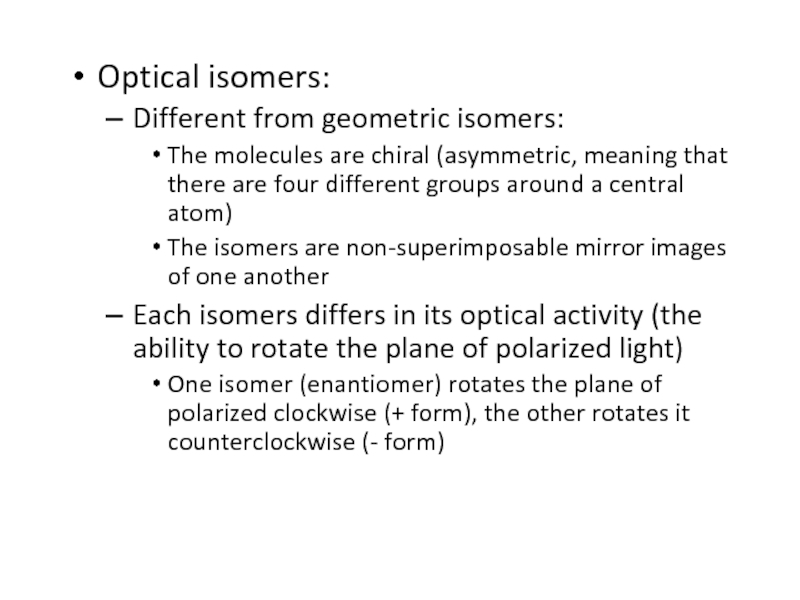
Слайд 49Optical isomers:
Different from geometric isomers:
The molecules are chiral (asymmetric, meaning
that there are four different groups around a central atom)
The
isomers are non-superimposable mirror images of one anotherEach isomers differs in its optical activity (the ability to rotate the plane of polarized light)
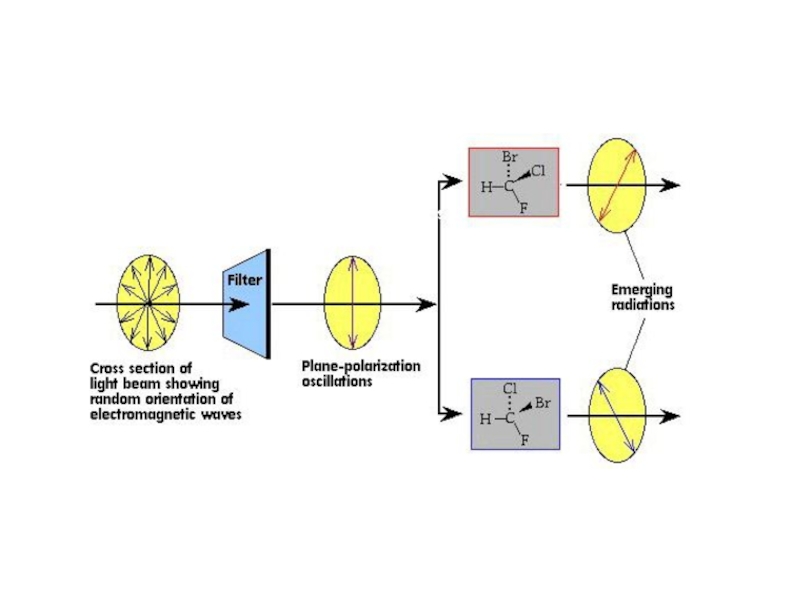
One isomer (enantiomer) rotates the plane of polarized clockwise (+ form), the other rotates it counterclockwise (- form)
Слайд 51An equimolar mixture of both enantiomers (racemic mixture) will not
rotate the plane and is said to be optically inactive
Drugs
from natural sources are usually chiral and are generally found as a single enantiomerEx. Penicillin V
Opposite enantiomer can only be produced artificially and is pharmacologically inactive
Слайд 52Synthetic drugs, when chiral, are usually produced as racemic mixtures
Ex.
: Ibuprofen
One enantiomer is pharmacologically inactive
Drug still produced as a
racemic mixture to reduce costsThalidomide
One enantiomer alleviates morning sickness, the other can cause birth defects
Unknown before it was prescribed in the 1970’s
Racemic mixture (“bad” and “good” enantiomers) can still be sold as a treatment for leprosy
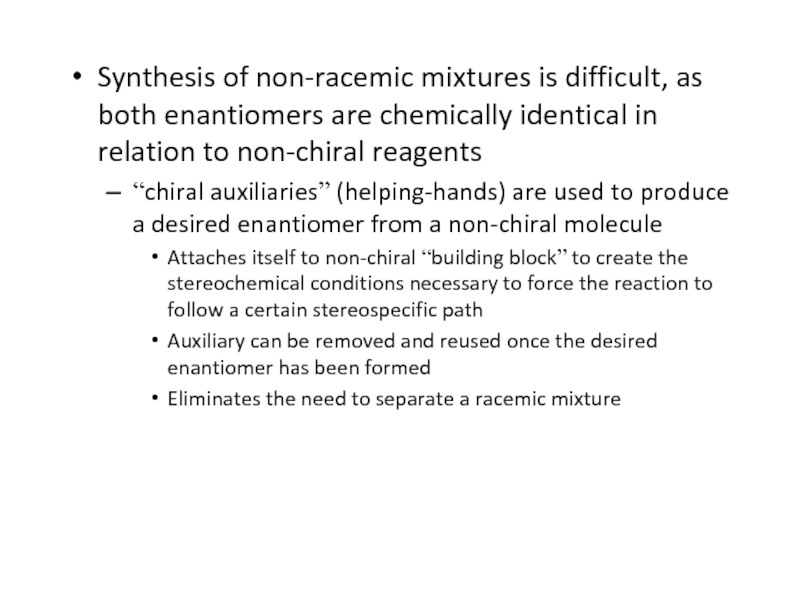
Слайд 53Synthesis of non-racemic mixtures is difficult, as both enantiomers are
chemically identical in relation to non-chiral reagents
“chiral auxiliaries” (helping-hands) are
used to produce a desired enantiomer from a non-chiral moleculeAttaches itself to non-chiral “building block” to create the stereochemical conditions necessary to force the reaction to follow a certain stereospecific path
Auxiliary can be removed and reused once the desired enantiomer has been formed
Eliminates the need to separate a racemic mixture
Слайд 54Combinatorial chemistry
As drug R & D is very costly and
time-consuming, most drug research begins with a “lead compound,” (not
lead as in metal, but “leed) whose main structure is left unaltered but other parts are changed to produce more effective drugs.Combinatorial chemistry (combi-chem) involves creating a large number of molecules and quickly testing them for desirable biological activity
Sometimes compounds are “virtually tested” by computer simulation
Combi-chem involves reacting a set of starting materials in all possible combinations
Uses same methods as basic organic synthesis, but uses technology and computers to make very large libraries of related chemicals
Increases the chances of finding better drugs
Слайд 55Libraries of a vast amount of related compounds are produced
using robotics to perform repetitive work (ex. adding a fixed
volume of a substance to a collection of chemicals) (parallel synthesis)Products of these reactions are then tested, without animals, by studying their effects on enzymes
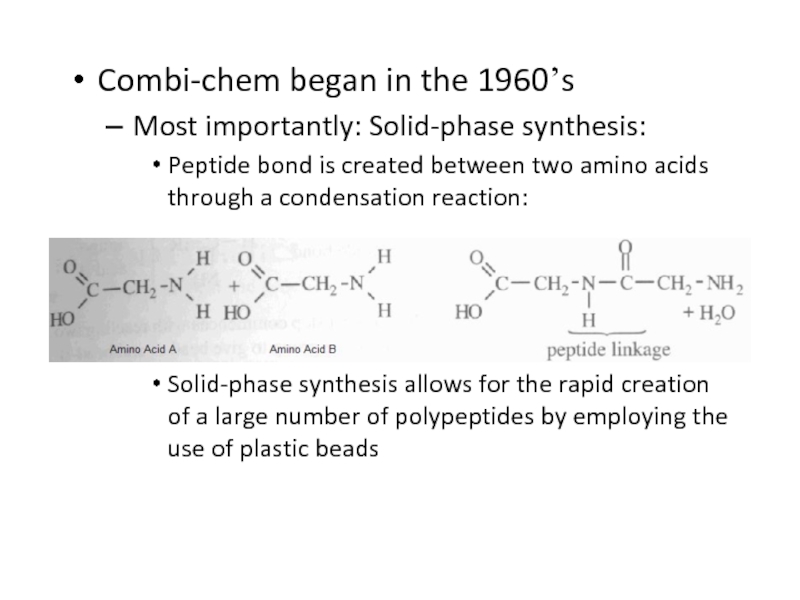
Слайд 56Combi-chem began in the 1960’s
Most importantly: Solid-phase synthesis:
Peptide bond is
created between two amino acids through a condensation reaction:
Solid-phase synthesis
allows for the rapid creation of a large number of polypeptides by employing the use of plastic beads Слайд 57
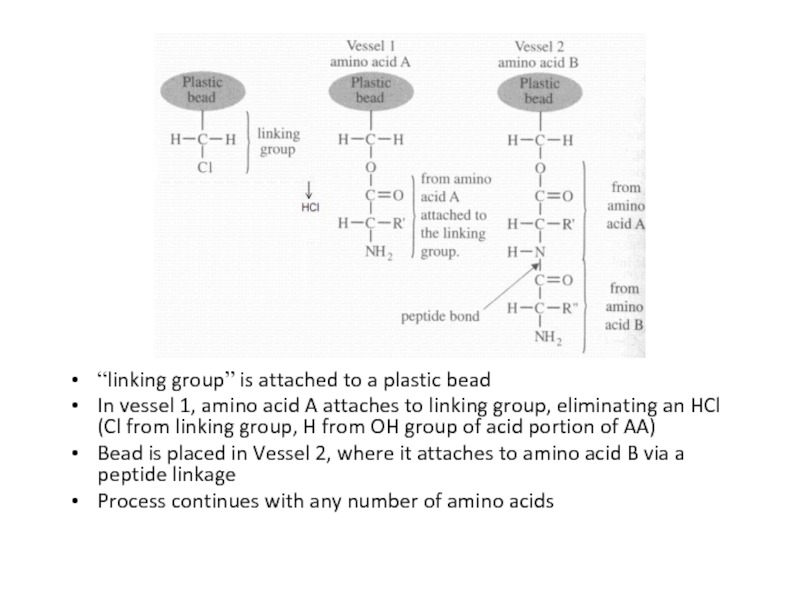
“linking group” is attached to a plastic bead
In vessel 1,
amino acid A attaches to linking group, eliminating an HCl
(Cl from linking group, H from OH group of acid portion of AA)Bead is placed in Vessel 2, where it attaches to amino acid B via a peptide linkage
Process continues with any number of amino acids
Слайд 58Procedure can be extended so that the first step reacts
two amino acids, A and B, to produce bead A
and bead BThese can be split into separate containers so that each now contains beads A and B, in a half and half mixture
In the second stage, one container is reacted with amino acid A to produce bead A-A and bead B-A
the other container is reacted with amino acid B to produce bead A-B and bead B-B
This two amino acid, two stage process produces 4 (22 ) amino acids (A-A, B-A, A-B, and B-B)
Starting with 3 amino acids in a 2 stage process would produce 32 (9) peptides, 10 amino acids in a 4 stage process would produce 104 (10,000 polypeptides) etc.
A large polypeptide library can therefore be quickly produced
Process can also be extended to other molecules besides peptides to produce very extensive chemical libraries
Слайд 59Anaesthetics
Local vs. General
Local anaesthetics block pain in a specific area
(injected under the skin or applied topically)
Cocaine, procaine, benzococaine, lidocaine
Block
nerve conduction and decrease blood supply Procaine and lidocaine do not affect the brain, but cocaine does
Слайд 61Cocaine, besides acting as a local anaesthetic, can also stimulate
the central nervous system
Only used medically as a surface application
in oral surgery, extremely dangerous when injected because it is a vasoconstrictorProduces a strong psychological addiction, although no physical dependence or tolerance
Procaine gives prolonged pain relief and immediate loss of feeling prior to dental surgery
Applied through injection and is short-lasting
Lidocaine produces loss of feeling and is applied topically
More potent than procaine
Itching and swelling are side effects
Слайд 62General anaesthetics act on the brain and produce unconsciousness, which
can be readily reversed
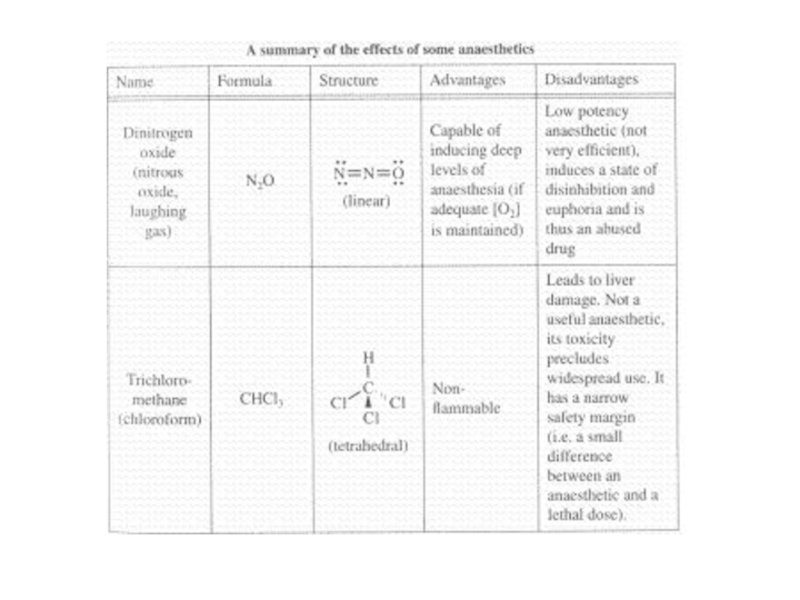
Nitrous oxide (N2O), diethyl ether (C2H5-O-C2H5), chloroform
(CHCl3), cyclopropane (C3H6), and halothane (CHClBrCF3)Some disadvantages:
Nitrous oxide is not very potent
Trichloromethane (chloroform) can lead to liver damage
Ethoxyethane and cyclopropane are highly flammable
Halothane is harmful to the ozone layer
Слайд 65Dalton’s Law of partial pressures can be used to calculate
partial pressures of component gases in an anaesthetic mixture
Ideal gas
law says: PtotalV=ntotalRTPtotal = Pa + Pb + Pc
Ntotal = na + nb + nc
Example: Isoflourane, a halogenated volatile anaesthetic, is used with nitrous oxide to sustain anaesthesia during surgery. If the concentrations of isoflourane, N2O, and O2 are 2.0%, 70%, and 28% respectively, calculate the partial pressure of each gas in the sample at 25C and 1.0 atm.
Pisoflourane = 2% x 1.0 atm = .02 x 1.0 atm = .02 atm
PN2 = 70% x 1.0 atm = .70 x 1.0 atm = .70 atm
PO2 = 28% x 1.0 atm = .28 x 1.0 atm = .28 atm
See examples on pg. 452 of LGB
Слайд 66Mind-altering drugs
Psychedelic drugs or psychotomimetics (simulate madness)
Cause hallucinations and distortion
of senses
LSD (lysergic acid)
Mescaline
Psilocybin (peyote mushrooms)
THC (tetrahydrocannabinol in marijuana)
Слайд 67LSD
Powerful hallucinogen
Effect depends on:
Dose
Physiological condition
Psychological condition
Expectations
Magnifies perception
Destroys sense of judgment
Produces
flashbacks without taking LSD
Does not produce physical addition but can
produce tolerance and psychological additionСлайд 68Mescaline
Produces color hallucinations
Lasts approximately 12 hours
Psilocybin
Magnified perception
Low doses produce relaxation,
high doses produce effects similar to LSD
THC (marijuana)
Mild hallucinogen
Causes silliness
and excitement at low dosesAs dosage increases, perception changes and hallucinations result
Can cause extreme anxiety, depression, uneasiness, panic attack and fearfulness in high doses
Driving and other tasks requiring thinking are difficult
Psychological dependence is possible
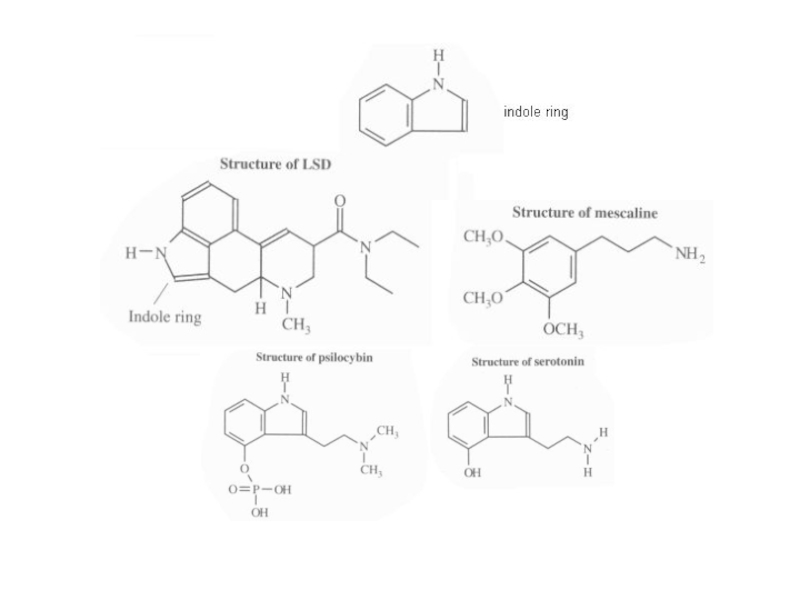
Слайд 69LSD, mescaline, and psilocybin all contain a benzene ring (6
carbon); LSD and psilocybin contain an indole ring (6 carbon
benzene ring fused to a 5-membered ring containing a secondary nitrogen)LSD is fat-soluble and easily diffuses into the brain
Psilocybin mimics the structure of the brain hormone serotonin
Слайд 71Cannabis
cannabis sativa, contains pharmacologically active compounds (cannabinoids)
Legalization is a hotly
contested issue
Arguments for:
Relieves symptoms from AIDS, cancer (allows for weight
gain by suppressing nausea), and glaucoma (alleviates harmful pressure in the eye)Arguments against:
Leads to respiratory ailments
Suppresses immune system
Decreases fertility
Causes brain damage and chromosomal damage leading to birth defects
“Gateway drug”
Users of marijuana and other drugs obtain them by illegal sources, leading to a host of crimes (prostitution, theft, murder, etc.)





























![Option B – Medicine and Drugs Caffeine, like nicotine, contains a tertiary amine group (nitrogen atom attached Caffeine, like nicotine, contains a tertiary amine group (nitrogen atom attached to three organic [i.e. carbon-containing] substituents):](/img/thumbs/a1aebd426323823f6ee85775ea818fed-800x.jpg)