Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
PSYCHOTROPIC DRUGS
Содержание
- 1. PSYCHOTROPIC DRUGS
- 2. Слайд 2
- 3. Sedative - a drug that subdues excitement
- 4. Слайд 4
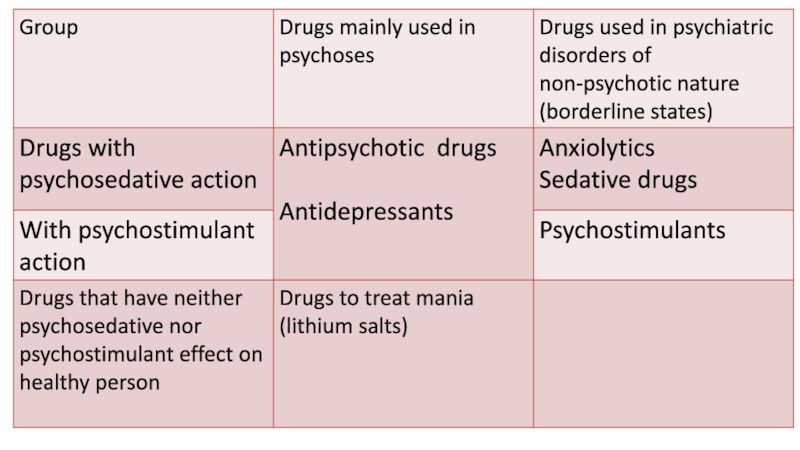
- 5. Anxiolytics (tranquilizers) The main effect of these drugs
- 6. BDZs activate their receptor, which is an
- 7. Слайд 7
- 8. Слайд 8
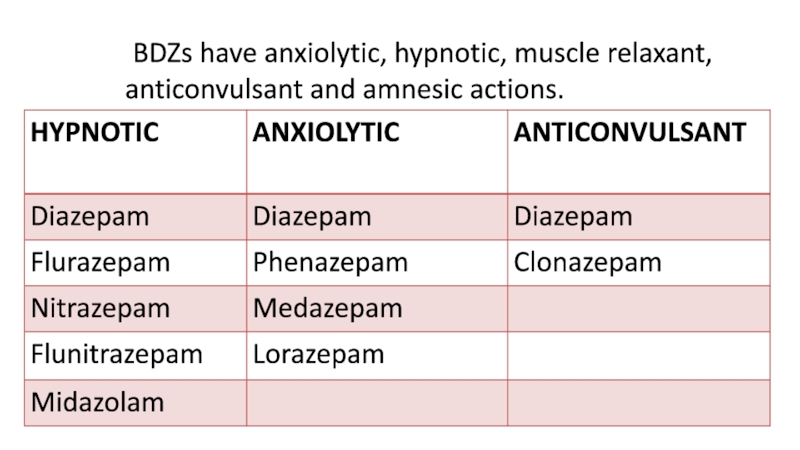
- 9. BDZs have anxiolytic, hypnotic, muscle relaxant, anticonvulsant and amnesic actions.
- 10. Long-term action (t1/2 =24-48 h): Diazepam, Phenazepam,
- 11. BDZs have marked anxiolytic and sedative properties.
- 12. BDZs cause muscle relaxation due to the
- 13. BDZs are well absorbed from the digestive
- 14. Side effectsIn high doses they can cause
- 15. Buspironе is the agonist of serotonin receptors.
- 16. SedativesBromide salts, valerian and motherwort preparations belong
- 17. Bromism – chronic poisoning This is manifested
- 18. Antipsychotic drugs (neuroleptic drugs) have antipsycotic and
- 19. Antipsychotic effect reduces the productive symptoms of
- 20. Psychosedative action is characterized by general sedation
- 21. Parkinsonism The inhibition of the nigrostriatal transmission and
- 22. Other effectsHypnotic effect: superficial sleep, which is
- 23. Chlorpromazine inhibits the center of termoregulation. The
- 24. Cardiovascular system: Chlorpromazine decreased arterial pressure. This
- 25. Слайд 25
- 26. Side effects. Extrapyramidal disturbancesParkinsonism with typical manifestations—
- 27. Side effects.CNS: Drowsiness, lethargy, mental confusion;Hyperprolactinemia (due
- 28. UseAntipsychotics drugs are administered in psychoses with
- 29. Lithium salts are mainly used to manage
- 30. Lithium carbonate differs from the other antipsychotic
- 31. Скачать презентанцию
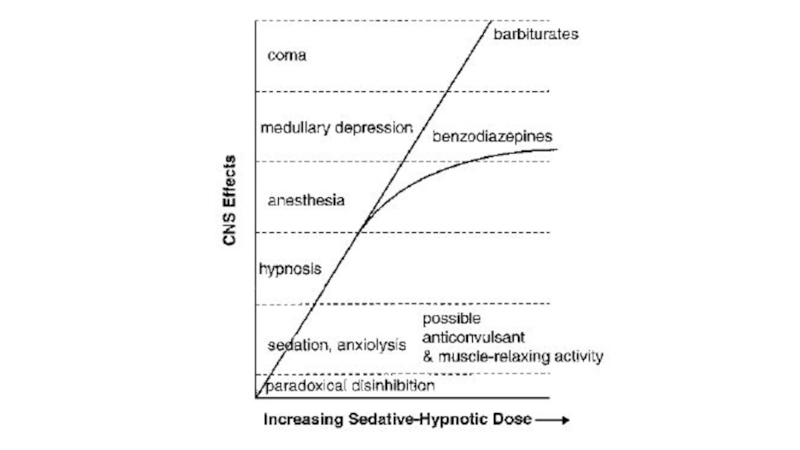
Sedative - a drug that subdues excitement and calms the subject without inducing sleep, though drowsiness may be produced.Drugs: benzodiazepines, barbiturates and alcohols Cause dose-dependent CNS depression that extends from sedation
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1PSYCHOTROPIC DRUGS
Drugs of this group are used for the treatment
of mental illness:
fear, anxiety.Слайд 3Sedative - a drug that subdues excitement and calms the
subject without inducing sleep, though drowsiness may be produced.
Drugs: benzodiazepines,
barbiturates and alcohols Cause dose-dependent CNS depression that extends from sedation to respiratory depression and death
BZs reach a plateau in CNS depression, barbiturates and alcohol do not.
Слайд 5Anxiolytics (tranquilizers)
The main effect of these drugs is the anxiolytic
one. It results in a decrease of internal tension, elimination
of nervousness, anxiety and fear. Besides, most anxiolytics have a sedative action. They do not affect the autonomic innervations; they do not induce extrapyramidal disorders.Anxiolytics are divided into groups:
Agonists of benzodiazepine receptors
Agonists of serotonin receptors (Buspirone)
Drugs of different action types.
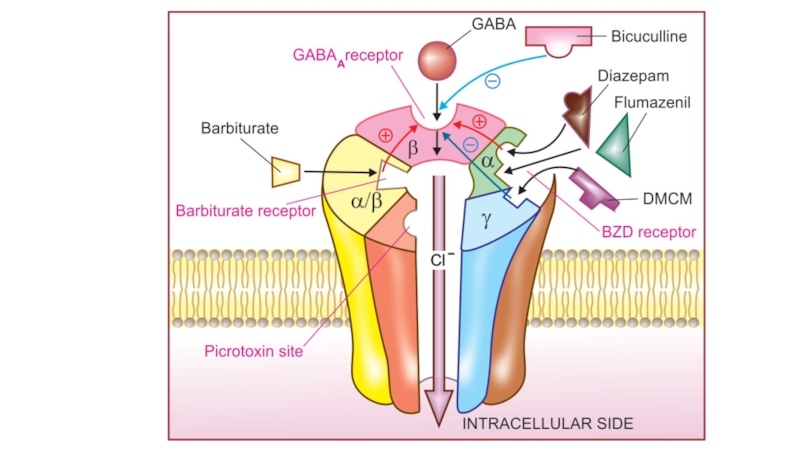
Слайд 6BDZs activate their receptor, which is an integral part of
the GABA receptor–Cl¯ channel complex in limbic system.
Occupation of the
BDZ sites by BDZ receptor agonists causes a conformational change in the GABA receptor. This increases the affinity of GABA binding and enhances the actions of GABA on the Cl− conductance of the neuronal membrane. GABA activates ↑ CL- influx, which results in hyperpolarisation.Barbiturates act at the another binding site and similarly enhance the action of GABA .
In the absence of GABA, BDZs and low doses of barbiturates do not affect Cl− conductance.
Слайд 10Long-term action (t1/2 =24-48 h): Diazepam, Phenazepam, Medazepam
Medium-term action (t1/2=6-24
h): Lorazepam, Alprazolam
Short-term action (t1/2 ˂6 h): Midazolam
Flumazenil is a
specific antagonist of BDZs. It blocks the BDZs receptors and eliminates fully or decreases the intensity of the most central effects of BDZs. Слайд 11BDZs have marked anxiolytic and sedative properties. By reducing emotional
tension, they also promote the onset of sleep. They are
used in the treatment of neuroses, neurosis-like conditions and insomnia.There are BDZs with marked anxiolytic action and none or minimal sedative-hypnotic action. Such drugs are called “Day-time anxiolytics (tranquilizers)”. For example Medazepam.
Слайд 12BDZs cause muscle relaxation due to the depression of the
spinal polysynaptic reflexes and disturbance of its supraspinal regulation. These
drugs are called central muscular relaxants and used in neurology.BDZs have anticonvulsant activity. They are effective in status epilepticus.
They potentiate the CNS inhibition caused by drugs with non-selective CNS depressants action. They are administered for premedication before surgical interventions.
Слайд 13BDZs are well absorbed from the digestive tract, easily pass
through the blood-brain barrier and other biological barriers.
They undergo metabolism.
Some metabolites have marked and long-term anxiolytic effect.They bind with the plasma proteins and are deposited in the fatty tissues.
The kidneys are the main elimination route for the metabolites and conjugates of BDZs.
Слайд 14Side effects
In high doses they can cause amnesia.
Drowsiness, delayed motor
response, memory impairment, weakness, diplopia, headache, nausea, vomiting, dysmenorrhea, skin
rashes.During long-term therapy: tolerance and drug dependence (psychological and physical, withdrawal syndrome).
Teratogenic effect.
Слайд 15Buspironе is the agonist of serotonin receptors. It has marked
anxiolytic activity. After its administration the effects develops slowly (over
1-2 weeks).It has not sedative, anticonvulsive and muscle-relaxing action.
It has a low tendency to induce tolerance and drug dependence.
Side effects: nervousness, dizziness, headache, paresthesias, nausea, diarrhea.
Слайд 16Sedatives
Bromide salts, valerian and motherwort preparations belong to the sedative
drugs. They have a moderate calming action. They are administered
for the treatment of neuroses, increased irritability and sleeplessness.Sodium bromide and potassium bromide are the most widely used bromides. Their main action is associated with the intensification of the inhibitory processes in the brain cortex. The effect of bromide depends on the type of nervous system (weak and strong type).
Слайд 17Bromism – chronic poisoning
This is manifested by general lethargy,
apathy, memory disorder, skin lesions. The irritating action of bromide
leads to the inflammation of the mucous membranes, which is associated with the cough, rhinitis, conjunctivitis and diarrhea.The treatment: discontinuation of bromide intake, administration of large amount of sodium chloride, drinking a lot of water, introduction of diuretics.
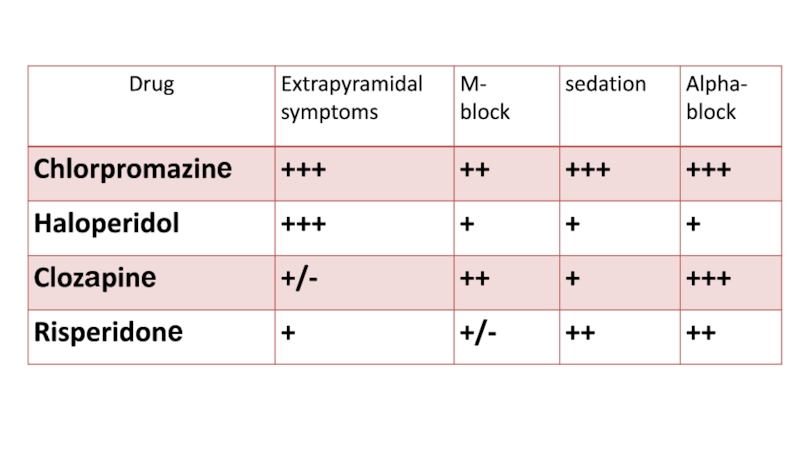
Слайд 18Antipsychotic drugs (neuroleptic drugs) have antipsycotic and sedative action.
Classification
1.Typical antipsychotic
drugs
Phenothiazine derivatives: Chlorpromazinе, Trifluoperazinе
Butyrophenone derivatives: Haloperidol, Droperidol
2. Atypical antipsychotic
drugs: Clozаpinе, Risperidonе
Слайд 19Antipsychotic effect reduces the productive symptoms of psychoses (delusions, hallucinations)
and delays further progression of schisophrenia.
The effect is associated with
the block of postsynaptic dopamine D2-receptors of mesolimbic and mesocortical systems.Haloperidol > Trifluoperazinе > Chlorpromazinе
Risperidonе blocks D2 and 5-НТ 2А receptors.
Слайд 20Psychosedative action
is characterized by general sedation – elimination of
affective reactions, reduction of anxiety, nervousness, decrease in motor activity.
is associated with their effect on the ascending reticular formation of the brainstem, limbic system, hypothalamus. They block α-adrenoceptors, H-receptors, serotonin receptors and M-cholinoceptors.
Chlorpromazinе, Haloperidol, Droperidol
But Trifluoperazinе has psychostimulant action.
Слайд 21Parkinsonism
The inhibition of the nigrostriatal transmission and reduction of the
suppression of the striatum of the substantia nigra lead to
a change of the effect of the striatum on motor activity control. This results in the enhancement of the activity of the spinal cord α-motoneurons, increase in muscular tone and development of drug-indused parkinsonism (hypokinesia, rigidity, tremor).Typical antipsychotics cause parkinsonism.
Atypical antipsychotics cause very rarely.
Слайд 22Other effects
Hypnotic effect: superficial sleep, which is easily interrupted by
external stimuli.
Ability to potentiate action of a number of neurotropic
drugs, such as general anesthetics, hypnotics and opioid analgetics.Antiemetic effect, which is associated with the block of the dopamine receptors of the trigger zone, located at the bottom of the 4th ventricle. They can prevent vomiting caused by antiblastomic drugs.
Слайд 23Chlorpromazine inhibits the center of termoregulation. The outcome depends on
the temperature of the surrounding environment. Often an insignificant hypothermia
is observed (due to an increase in heat loss).If Chlorpromazine is applied under low temperatures (physical cooling), there is a marked fall in the body temperature. This effect is used in surgery.
Chlorpromazine has a typical muscle relaxing effect, which results in a reduction of motor activity. It is associated with the inhibition of supraspinal regulation of muscular tone.
Слайд 24Cardiovascular system: Chlorpromazine decreased arterial pressure. This effect is associated
with the inhibition of hypothalamic centres, with the α-adrenoceptors blocking
effect and spasmolytic properties. Hypotension is commonly associated with reflex tachycardia.Chlorpromazine possesses some M-cholinoceptors blocking (atropine-like) properties. They result in mild suppression of salivary, bronchial and digestive gland secretion and also tachycardia.
Слайд 26Side effects. Extrapyramidal disturbances
Parkinsonism with typical manifestations— rigidity, tremor, hypokinesia,
mask like facies, disorders of gait;
Malignant neuroleptic syndrome : It
occurs rarely with high doses of potent agents. The patient develops marked rigidity, immobility, tremor, hyperthermia, semiconsciousness, fluctuating BP and heart rate; myoglobin may be present in blood. The syndrome lasts 5–10 days after drug withdrawal and may be fatal.Слайд 27Side effects.
CNS: Drowsiness, lethargy, mental confusion;
Hyperprolactinemia (due to D2 blockade),
amenorrhoea, infertility, galactorrhoea and gynaecomastia;
CVS Postural hypotension, tachycardia;
Dry mouth,
blurring of vision, constipation, urinary retention in elderly males;Cholestatic jaundice;
Skin rashes, urticaria, contact dermatitis, photosensitivity;
Agranulocytosis.
Слайд 28Use
Antipsychotics drugs are administered in psychoses with marked excitation, affective
reactions, aggressiveness, delirium, hallucinations.
In complex with other drugs when treating
drug dependence (opioid analgetics, alcohol)Phenothiazine and Haloperidole are used as antiemetic drugs and in persistant hiccups.
They are used with general anesthetics, hypnotics and opioid analgetics besause they can potentiate actions.
Слайд 29Lithium salts are mainly used to manage and prevent mania
and bipolar (manic depressive) disorder.
The mechanism of antimanic and mood
stabilizing action of lithium:Li+ partly replaces body Na+ and is nearly equally distributed inside and outside the cells; this may affect ionic fluxes across brain cells or modify the property of cellular membranes.
Lithium decreases the presynaptic release of NA and DA.
Слайд 30Lithium carbonate differs from the other antipsychotic drugs by a
slowly onset of effect (2-3 weeks), more selective action on
manias, and a lack of sedative effect (listlessness and apathy).The low therapeutic window has to be considered.
Side effects: dyspeptic disorders, muscle weakness, tremor, polyuria, thirst.
Acute poisoning with the lithium salts: vomiting, diarrhea, ataxia, disarthria, and cramps.