Слайд 1 RICKETTSIOSES
Identification. It`s the group of acute transmissible illnesses
of the man caused by the rickettssia and characterized by
the expressed intoxication and generalized panvasculitis, which result is the lesion of the CNS, internal bodies and spotty-papular exanthema at majority of them.
Rickettsia ( F. Rickettsiacae.) They were divided on three kinds: Rickettsia, Coxiella, Rochalimea.
Rickettsia are Gram (-), rod-shaped, spherical or pleo-morphic organisms smaller than bacteria and have a size from 0.3 – 0.5 up to 3 - 4 microns.
They occupy the intermediate position between viruses and bacteria.
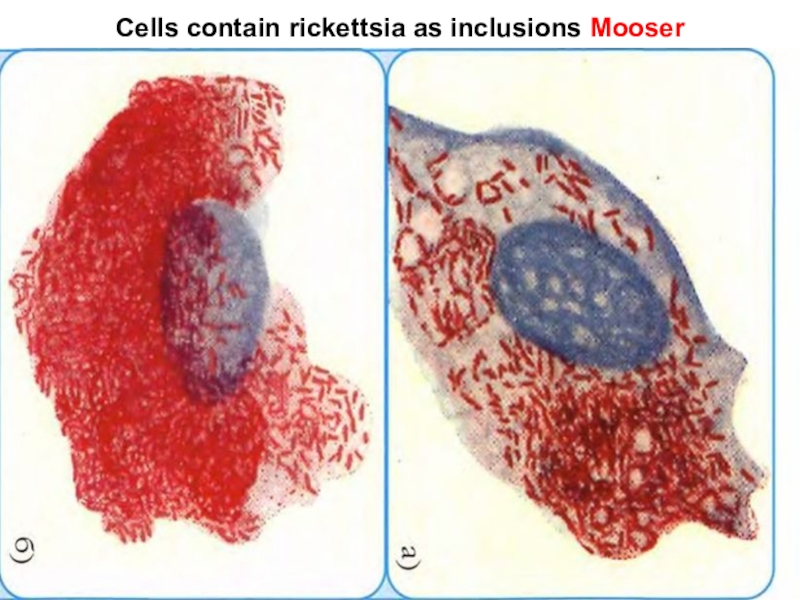
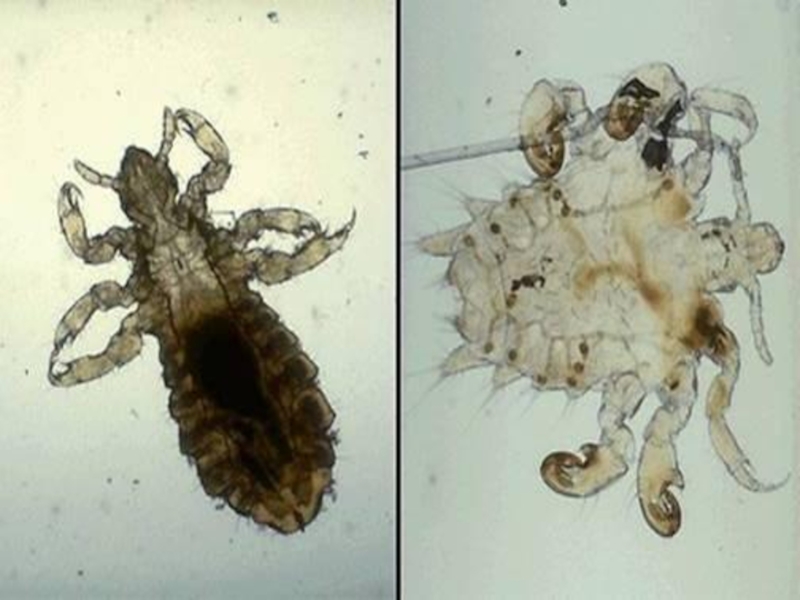
Слайд 2Cells contain rickettsia as inclusions Mooser
Слайд 3
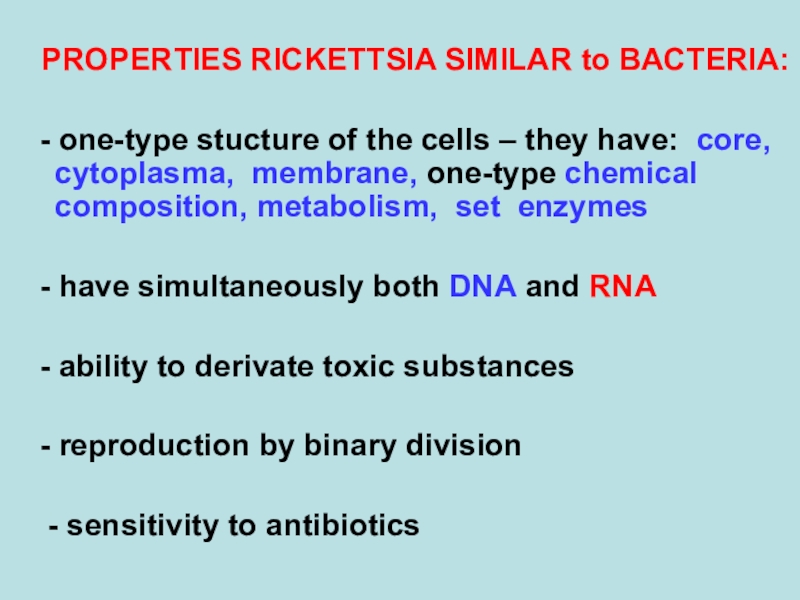
PROPERTIES RICKETTSIA SIMILAR to BACTERIA:
- one-type stucture of the cells
– they have: core, cytoplasma, membrane, one-type chemical composition, metabolism,
set enzymes
- have simultaneously both DNA and RNA
- ability to derivate toxic substances
- reproduction by binary division
- sensitivity to antibiotics
Слайд 4
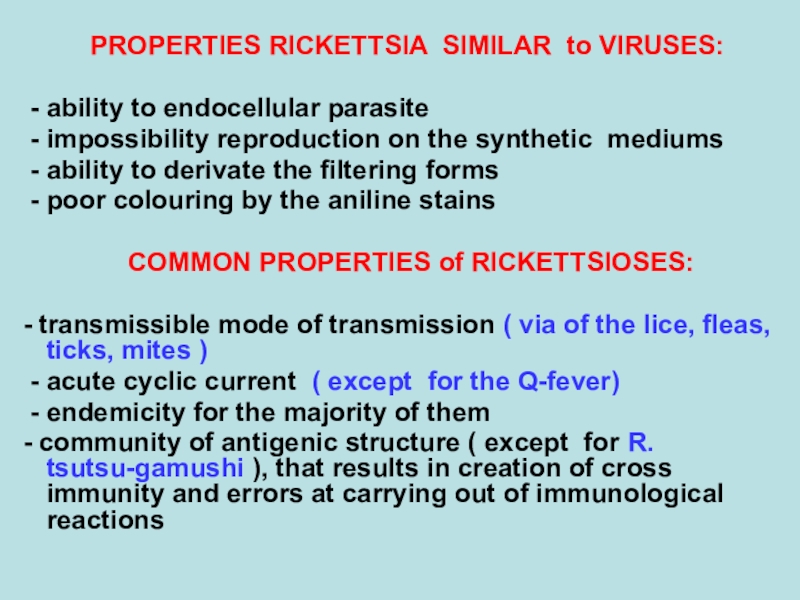
PROPERTIES RICKETTSIA SIMILAR to VIRUSES:
- ability to endocellular
parasite
- impossibility reproduction on the synthetic mediums
- ability
to derivate the filtering forms
- poor colouring by the aniline stains
COMMON PROPERTIES of RICKETTSIOSES:
- transmissible mode of transmission ( via of the lice, fleas, ticks, mites )
- acute cyclic current ( except for the Q-fever)
- endemicity for the majority of them
- community of antigenic structure ( except for R. tsutsu-gamushi ), that results in creation of cross immunity and errors at carrying out of immunological reactions
Слайд 5
Rickettsia in the environment are not enough steady:
- at
warming up to 60 d. C – are survived some
minutes
- at boiling - are perished instantly
- formalinum 0.5 %, phenolum 5 %, alcohol and aether - fast inactivate their
- at temperature is lower - 20 d.C or quick desiccation
are survived from 1 to 3 years
- the rickettssia form a toxic substance with properties both exotoxin and endotoxin wich is extremely unstable and nonseparable from a cell envelope
Слайд 6
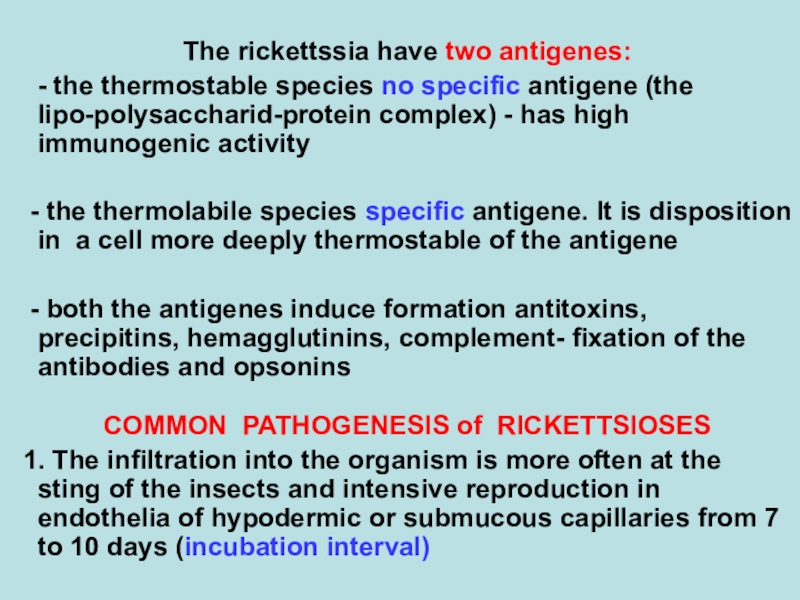
The rickettssia have two antigenes:
- the thermostable species no
specific antigene (the lipo-polysaccharid-protein complex) - has high immunogenic activity
- the thermolabile species specific antigene. It is disposition in a cell more deeply thermostable of the antigene
- both the antigenes induce formation antitoxins, precipitins, hemagglutinins, complement- fixation of the antibodies and opsonins
COMMON PATHOGENESIS of RICKETTSIOSES
1. The infiltration into the organism is more often at the sting of the insects and intensive reproduction in endothelia of hypodermic or submucous capillaries from 7 to 10 days (incubation interval)
Слайд 7
2.The primary affect as the infiltrate with scab or without
can be shaped in a place of implantation of the
rickettsia.
3.A hematogenic dissimination of the rickettsia from the primary center with lesion of the endothelium of the larger vessels with development vasculitis and perivascular mononuclear infiltrates occur through 7 - 10 days.
Affected cells may contain rickettsia as inclusions Mooser (e.g. Epidemic typhus)
4. At repeated dissiminations of the rickettsia, the lesion of vessels become generalized and it shows clinical:
- enanthema and spotty-papular exanthema
- wide-spread thrombosis with both the ischemia and
necrosises in perivascular tissues in many bodies
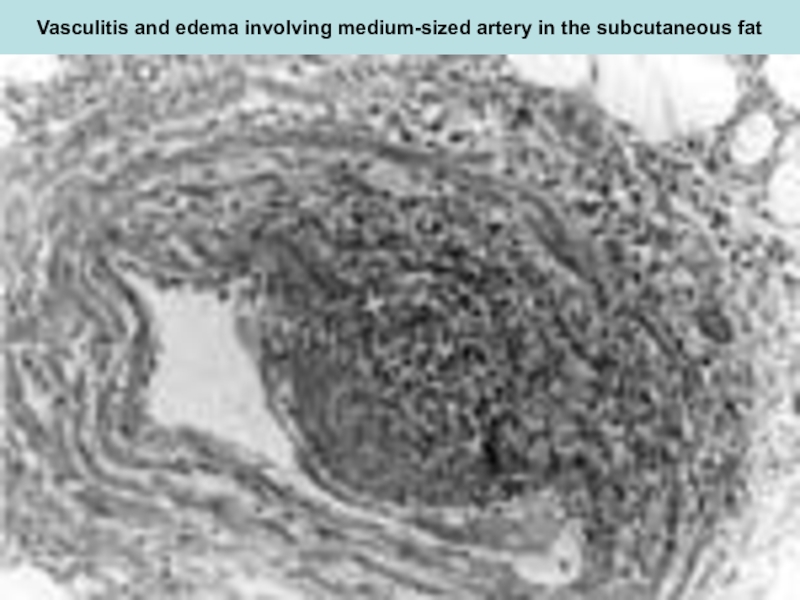
Слайд 8Vasculitis and edema involving medium-sized artery in the subcutaneous fat
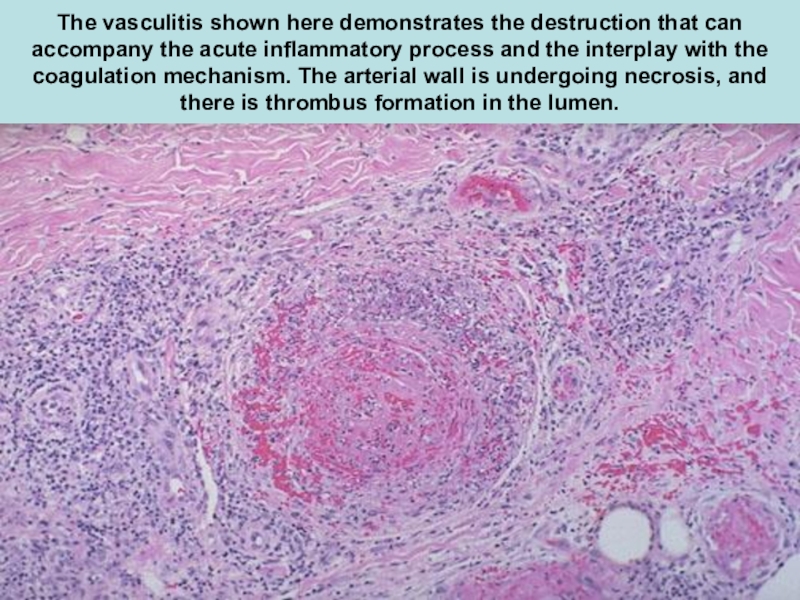
Слайд 9The vasculitis shown here demonstrates the destruction that can accompany
the acute inflammatory process and the interplay with the coagulation
mechanism. The arterial wall is undergoing necrosis, and there is thrombus formation in the lumen.
Слайд 10
5. The generalized lesion of the endothelium results to a
hyperpermeability of vessels with escaping them of water and electrolytes
(appearance of edemas) and erythrocytes (appearance hemorrhage) with development of the hypo-volemic shock in severe cases.
6. The lesion of the endothelium results in activation of the coagulating system of blood with possible outcome in DIC (disseminated intravascular coagulopathy)
7. Main causes of death at rickettsioses - acute heart failure, the lesion a CNS or circulatory disturbance indirect resulting in heart failure, hypovolemic shock, DIC.
Слайд 11
BASIC GROUPS of RICKETTSIOSES:
Organisms Vectors
1.Group of a typhus:
- epidemic typhus and illness Brill R. Prowazekii - Human body louse
- endemic ( murine) typhus R. Mooseri Rat flea
2. Group of spotty fevers:
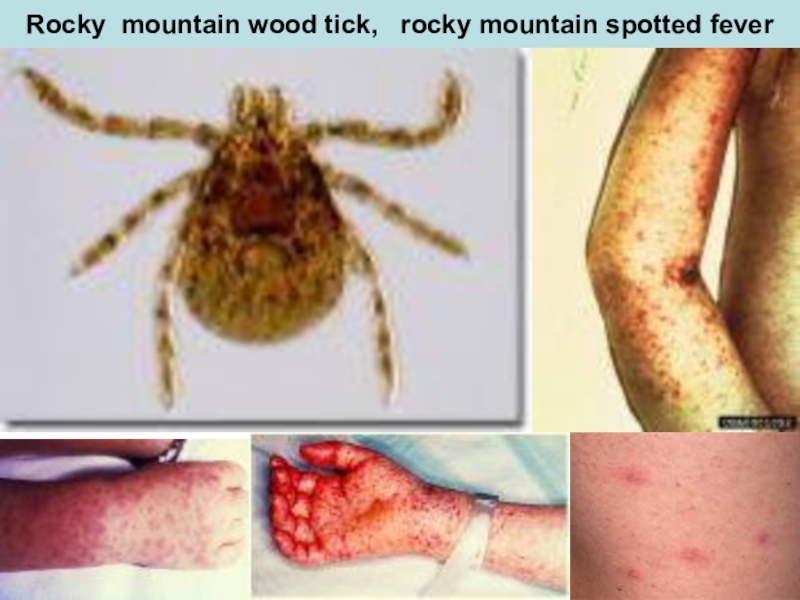
- Fever of rocky mountains R. Rickettsii Hard tick
- Marseilles fever( African tick typhus) R. Conori Hard tick
- North-Asian typhus R.sibirica Hard tick
- North-Australian typhus R. Australis Hard tick
- Varioliform rickettsiosis (Ricketsial pox) R. Akari Mite
3. Group tsutsugamushi R. Tsutsugamusi Trombiculid
(scrub typhus) larval mite
4. Group of the Q-fever - Q-fever Coxiella burnetti Hard tick
5. Group paroxysmal of rickettsioses: Rochalimaea
- trench fever (volynian fever) quintana Human body louse
Слайд 12
All rickettsioses are subdivided on 2 groups:
Anthroponoses rickettsioses:
-
epidemic typhus.
- trench fever
Cycle of circulation of
the rickettsia:
the sick man > human body louse > next the man
All other rickettsioses – zoonozes
Cycle of circulation of the rickettsia:
the sick animal >lice, fleas, ticks >next animal or the man
Слайд 13
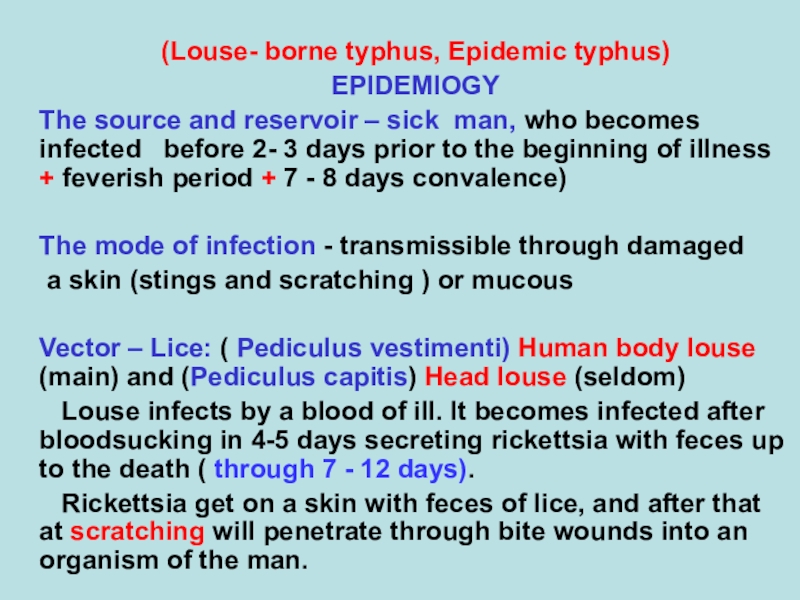
(Louse- borne typhus, Epidemic typhus)
EPIDEMIOGY
The source and reservoir –
sick man, who becomes infected before 2- 3 days
prior to the beginning of illness + feverish period + 7 - 8 days convalence)
The mode of infection - transmissible through damaged
a skin (stings and scratching ) or mucous
Vector – Lice: ( Pediculus vestimenti) Human body louse (main) and (Pediculus capitis) Head louse (seldom)
Louse infects by a blood of ill. It becomes infected after bloodsucking in 4-5 days secreting rickettsia with feces up to the death ( through 7 - 12 days).
Rickettsia get on a skin with feces of lice, and after that at scratching will penetrate through bite wounds into an organism of the man.
Слайд 14
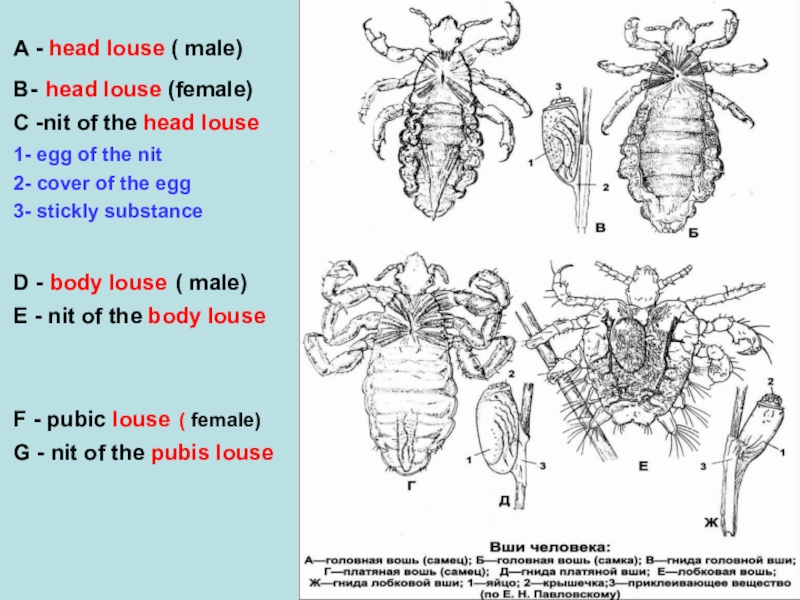
A - head louse ( male)
B- head louse
(female)
C -nit of the head louse
1- egg of
the nit
2- cover of the egg
3- stickly substance
D - body louse ( male)
E - nit of the body louse
F - pubic louse ( female)
G - nit of the pubis louse
Слайд 16They are nits of the Human head lice
Слайд 17The Human head louse, Pediculus humanus capitis, has an elongated
body and narrow anterior mouthparts. Human body louse look
similar but lay their eggs (nits) on clothing fibers instead of hair fibers.
Слайд 18
Aerborne mode of transmission is possible - as in
dry feces of the lice rickettsia can survive about 1
year!
The patient without lice is not dangerous for contact ,
though for him in a blood rickettsia are present!
Susceptibility general !
The case rate is enlarged in January - March
Has no true endemic of the centers (as against other rickettsioses), but more often meets in the countries in the South and North of Africa, central and South America
Wars and the disasters - rise a case rate
Outside of epidemics - the sporadic case rate supports for the endemic illness Brill- Zinsser.
The mortality in cases, nontreated by antibiotics, makes
10 - 60 %!!!
Слайд 19
CLINIC
Can proceed typically : as mild, middle-severe, severe
and fulminant forms.
But can proceed atypically: as asymptomatically, abortical,
the erased forms
Periods of illness:
Incubation - 12 - 14 days ( from 6 to 23 days)
Initial (4 - 5 days) - from a beginning of a fever - up to the exanthema
Peak (4 - 10 days)- from an exanthema - up to normal temperature
Convalescence - 2 - 3 weeks
Initial period:
- acute beginning with fast rise of the temperature up to 39-
40 d.C
- obstinate headache, myalgia, arthralgia, insomnia
Слайд 20
- thirst, anorexia, weakness, giddiness
- common anxiety, euphoria,
irritability, the verbiage
- acoustical, visual, tactile hypersensivite
OBJECTIVE:
- the
red, edematic face, scleritis – s-m Kjary - Aucyne
- enanthema on a soft palate, tongue – s- m of Rosenberg
- raised fragility of capillaries
- tachycardia (more than 130 -140 in minutes - poor
forecast!!)
- dull of cardiac sounds, hypotonia
- tongue dry, impose by white fur
- the temperature curve has of the constant type
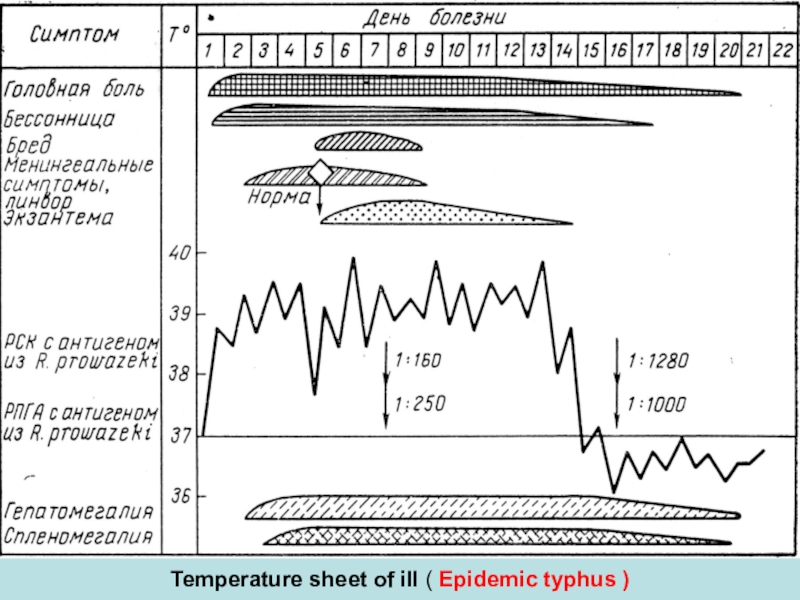
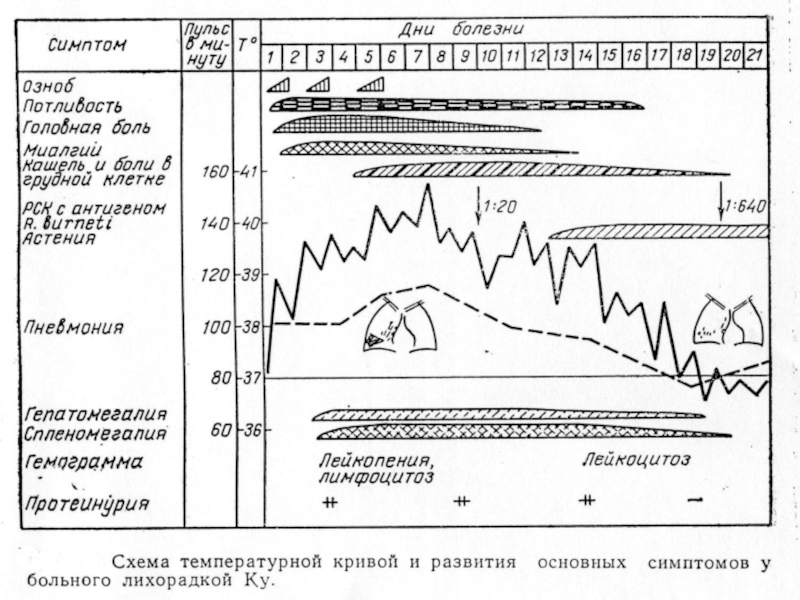
Слайд 21Temperature sheet of ill ( Epidemic typhus )
Слайд 22
PEAK PERIOD of ILLNESS:
- short-term lowering of temperature (
on some clocks )
for the
4th – 5th days of illness (appearance of the
exanthema)
and on the 9th – 10th day (disappearance of the
exanthema)
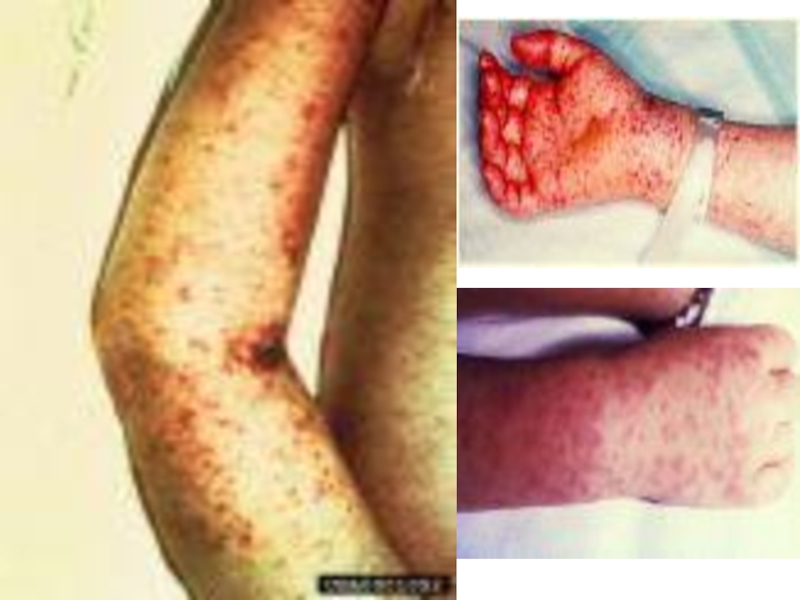
- appearance plentiful, roseolous or petechial of the
exanthema on a skin of a breast, back, abdomen, thighs,
arms. Exanthema appearance only once, does not rise
above the level of the skin
- intensifying of the headache and intoxication, transition
from a stage of exitation in "the typhous status " ( 6 - 8
days of illness) with appearance of hallucinations
frightening character and development of a psychosis
Слайд 23
- tachycardia, arrhythmia, falling B/P (70/40 mm Hg.)
signs of
a meningocephalitis, s- ms: Kerniga, Govorov- Godejae, dysarthria, dysphagia, convulsive
seizures - have been revealed. CSF- clear, with normal dynamics and chemical constituens Coma and muscular rigidity may occur.
The lesion peripheral NS – as neuritises, neuralgia,
polyradiculoneurites, plexites with subsequent
by violation of the trophicity of the tissues as necrosises
and ulcers of the skin and the mucous
The lesion ANS ( autonomic nervous system) appears by change: hyperemia of the face on his paleness, tachy-cardia on a bradycardia, red dermographism on white etc.
Слайд 24
The lesion of kidneys - glomerulonephritis, ischuria paradoxa, involuntary
emiction, oliguria, anuria, azotemia ( commonly occurs in the
sireously or criticaly ill patients)
- May be enlarged of the spleen and the liver (since 4-6 days of illness), but jaundice is unusual, the hypoproteinemia with reduction in the albumin fraction.
violation in a liver keratin of exchange (appearance icterus
only of the skin of palms and soles - s-m of Filippovich)
Respiratory tract:
- rhinites, laryngitises, tracheites, localized pneumonitis.
The fever has of a constant type is replaced on remittent
and since 12- 14 days is reduced critically or lytic
Слайд 25
STAGE of CONVALESCENCE:
- temperature is normalized during 2 -
3 weeks
- the intoxication and signs of the lesion
NS disappears
- the liver and lien diminution
- the hypotension and asthenic syndrome is durably saved
- the mental activity is normalized after all
Complications of a louse- born typhus:
- cardiovascular unsufficiency, myocardites, endocardites,
myocardiosclerosis
- tromboses, thromboembolism, thrombophlebites
- pneumonia, otites, mumps, stomatites
- decubituses, gangrene of the extremities, phlegmon
hypodermic fats etc.
Слайд 26
ILLNESS Brill- Zinsser (Recurrent typhus fever)
- the absence of lice
in clothes and hair of ill patient
- senior age of
the patients, which have transferred earlier
louse-born typhus !!
- less expressed fever (in limits 38 - 39 гр. С) and
intoxication
- enanthema only for 20 % of the patients
- scanty exanthema for 60 - 90 % of the patients
- Increase of a liver and spleen - nonconstant s-m!!
- damage NS corresponds mild or middle severe forms of
the louse-born typhus
- Complication - thromboses of surface veins, pneumonia
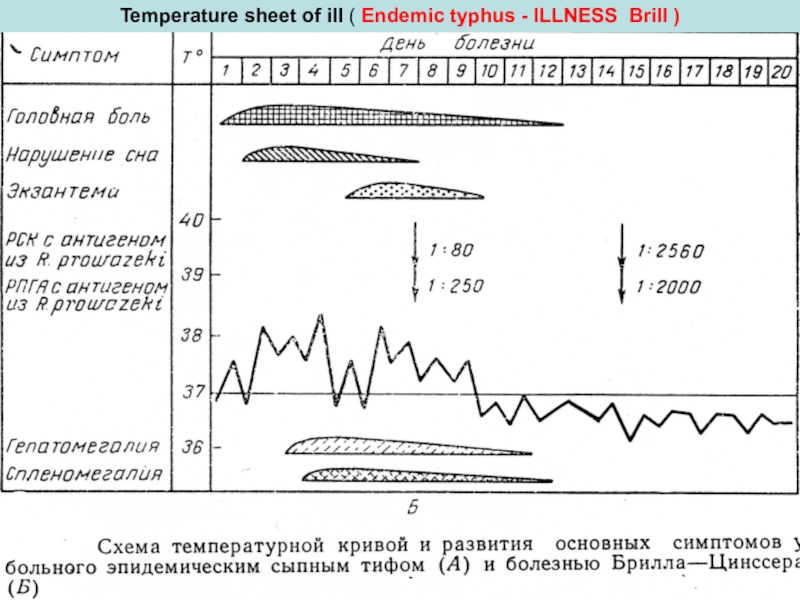
Слайд 27Temperature sheet of ill ( Endemic typhus - ILLNESS Brill
Слайд 28
SPECIFIC DIAGNOSIS:
- CFT (+) with 5 -7 days
of illness for 40 - 50 % of the patients,
but over
2-3 weeks of illness for 100 % diagnostic titer 1:160)
(In a titer 1:10 - 1:20 many years can be saved!!
HАT (+) with 5-7 days for the majority of the patients, and about 2
weeks for 100 % (diagnostic titer 1:40 - 1:80)
- PHAT(+) with 3 - 4 days of illness (diagnostic titer 1:1000 1:2000)
- IFA - at a louse-born typhus at once occur in a blood IgM, and at Brill
in a blood it are found out IgG and IgM, and the titer CFT raises
up to considerable values (1: 10240)
- Weil-Felix reaction with an antigene Proteus ОХ-19, but it occurs
only since the second week, gives a decussation of response with
other rickettsioses.
Слайд 29
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS:
In initial period - influenza and ARVD, pneumonia,
meningacoccal
infection, hemorrhagic fevers
In peak of disease - other typhoids and rickettsioses, measles, ornithosis, mononucleosis, sepsis, trichinosis, canicola fever, a phlebotomus fever, medicinal Illness, lues
TREATMENT:
Hospitalization after a disinfestation (except for Brill)
Diet, bed rest regimen, maintenance behind a skin and
mucous
Anti-infectious therapy- the primary drugs:
tetracyclini 5 - 8 mg/kg РО in q6h
doxycyclini 1,5 mg/kg РО in q12h
metacyclini 4 - 8 mg/kg РО in q12h
oletetrini 5 – 8 mg/kg РО in q4h
The alternative drugs –laevomycetin, erythromicin, ciprofloxacin, rifampicin but they are less effective!!
Слайд 30
Duration of treatment - all period of a fever +
2 - 3 days!
- Desintoxication
- Antiferment drugs
-
Anticoagulants
- Antioxidants
- Glucocorticoids
- Cardiac glycosides, antipyretics
- Sedative etc.
PROPHYLAXIS:
- Isolation both disinfestation of the patient and his clothes
- Overseeing by the center 71 days (at Brill 25 days)
- Revealing and hospitalization in the center all patients
with the fever by duration more than 5 days
- Vaccination under the special indications (dry « chemical»
a vaccine in a dose 0,5 mls)
Слайд 31
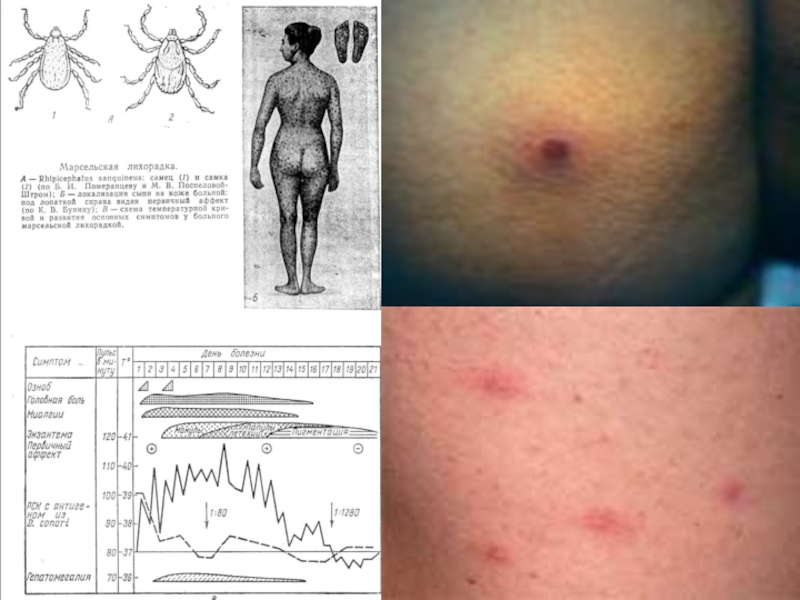
THE MARSEILLES FEVER
( Mediterranean fever, African tick typhus, spotty
fever ) :
Acute transmissible disease with good-quality
current appearing by a primary dermal affect, by regional the lymphadenitis and by the maculopapular eruption
The infectious agent - R. conori
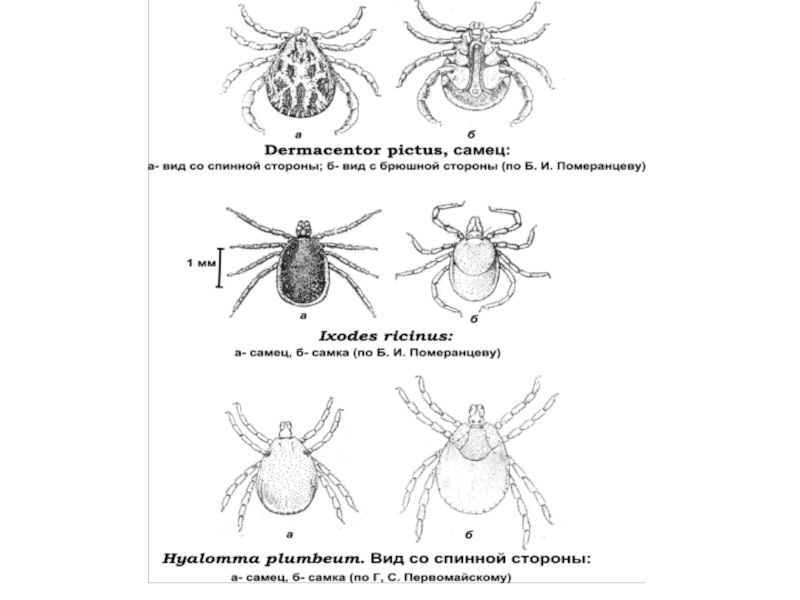
Carrier and source – dog tick (Rhipicephalus sanguineus) with transphase and transovarial transmission of the infectious agent
The mechanism of infection - sting tick or rubbing in of its hemolymph through broken of a skin or mucosas
Слайд 32
Season uprise - May - October
Susceptibility - general, more often meets in seaside cities
of the Black and Mediterranean seas
Clinic
- incubation interval 3 - 7 days
- Acute beginning with chill and fever 38 - 39 d.C
- Strong headache, but meningocephalitis and
the typhous status does not develop
- Arthralgia and myalgia, insomnia, weakness
- Appearance of a primary affect from 3 to 10 mm with
necrosis and crust in a place of a sting tick, ( but without
subjective sensations )- prior to a fever 5-7 days!!!
- regional lymphadenitis and maculopapular eruption on
to all body and palms and soles with 2 - 4 days for 100 %
the patients!!!
Слайд 35
- Increase of a liver and spleen
- Extension
of boundaries of heart, dull of its tones,
bradycardia
- Leukopenia, lymphomonocytosis, rise moderate ESR Complications - thrombophlebites, bronchites, broncho-
pneumonias is (rare)
Laboratory diagnosis –CFT with 5 - 7 days of illness
in titer (1:46 - 1:60) or PHAT in titer (1:800 - 1:3200)
Treatment - as at the mild forms of a louse-born typhus
Prophylaxis – antitick processing of dogs
- disinfestation in the centers and microcenters (box dog)
- isolation of vagrant dogs
- preventing an attack ticks on the people!!!
Слайд 36FEVER Q (Q- fever)
Zoonotic rickettsiosis with
acute good-quality current, fever, intoxication and polymorphism of clinical
manifestations.
The infectious agent - Coxiella burnetii- is well saved in the external environment: at 4 (+) d.C survives about one year, in meat - more than month, warming up to 90 гр. C maintain about one hour, but at boiling perishes in 10 minutes.
The source - numerous animals and birds, infected which reaches from 10 up to 33 %!!
Ways of transmission - aerogenic, contact, nutritional and transmissible (70 sorts of ticks )
The infectious agent circulates in natural and urban the centers
Слайд 39
Susceptibility general, but a cattle-breeders are sick in spring-year's period
( lambing, superactivity ticks) more
Incubation interval 12 - 19 days
(3 - 32 days)
The clinical forms of disease:
- Acute for 75 - 80 % of the patients, (duration 2 - 3 weeks),
- Subacute for 15 - 20 % of the patients (more than 4
weeks)
- Chronic for 2-5 % of the patients (about one year),
Initial period of disease:
- Acute beginning, ferver up to 39 – 40 d.C, headache,
weakness, sweating, anorexia
- Arthralgia, myalgia, pain in all body
- The fever can be remittent, continued, intermittent
duration up to 2 weeks with lowering for the type crisis -
lisis
Слайд 40
Peak of illness:
- All manifestations of illness amplify, can
be encephalitis
with delirium and hallucinations
- Maculo-papular eruption for 6-8 days for 3- 4 % the
patients
- Bradycardia or tachycardia, dull cardiac sounds
- The pneumonias for 12 % (are more often on the right)
tracheitis, bronchitis
- hepatolienmegaly for 65 - 85 % of the patients
- Duration of illness 10 - 13 days
- The relapses arise for 3 - 7 % of the patients, no more than
3 times!!
- Diagnostics - CFT (diagnostic titer 1:8 - 1:16)
- Treatment as at a exantomatic typhus
- Prophylaxis - common sanitary measures, vaccination
on epidemiological indication
Слайд 42
SCRUB TYPHUS
Identification. Acute zoonotic rickettsiosis described by the high
fever, the intoxication, formation of primary affect in the place
of introduction of the infected mite, occurrence spotty–papular exanthema, general panvasculitis, interfering activity CN and cardiovascular systems. For the first time it is described in 1810 in Japan.
The endemic countries : Japan, Korea, China, Burma, Vietnam, New Guinea, Australia, Sri Lanka, Malaysia, Pakistan, Tadjikistan, the Far East Russia.
The infectious agent - Rikettsia tsutsugamushi (orientalis).
Слайд 43Epidemiology
- the natural reservoir- rodents (mice, rats, hares, etc.)
and them ectoparasites (mites of family Trimbiculidae)
Mode of transmission- only
infected larvae mites. Adult mites and nymphs - do not feed on the vertebrate hosts
Susceptibility high in all age groups, but the agricultural workers and visitors is more often are ill. Biotype of the centers are valleys of the rivers
Seasonal prevalence depends on climatic conditions, but always coincides with a maximum of number infected larvae mites.
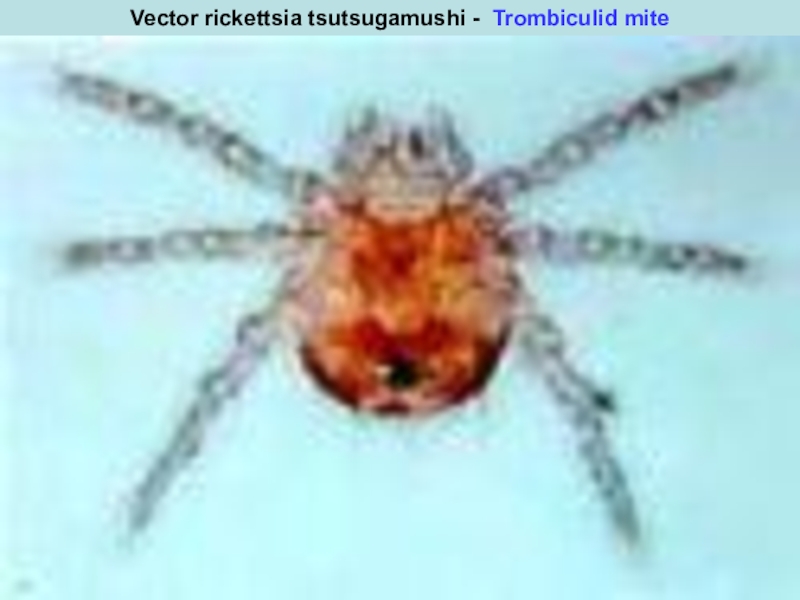
Слайд 44rickettsia tsutsugamushi
Vector rickettsia tsutsugamushi - Trombiculid mite
Слайд 45
Pathogenesis and Pathomorphology:
- the primary affect is formed on
the skin in a place of introduction of the agent.
The specific intoxication leads to to damage of a fine vascular network as panvasculitis as well as at the typhus but less expressed.
- at pathomorphologic research attributes myocarditis, glomerulonephritis, interstitial pneumonias, meningo-encephalitis, hemorrhagic a syndrome are found out
Clinic
incubation period from 7 to 20 days (on the average 10 - 12
days)
Disease begins abrupt:
- fever, myalgia, intensive headache, insomnia
- the temperature to the 3th - to the 4th day reaches 39- 40 dg.C. It is kept 14-16 days (sometimes 3 weeks and more) and comes to the end accelerated lysis
Слайд 46
Objectively:
- hyperemia and edema of the face, conjuctival injection,
profuse sweating, relative bradycardia
primary affect on the
skin of a trunk or extremities as: macula of 0,3- 2 sm > vesicula > ulcer > black scab + regional lymphadenitis
- macular rash on the skin about 5th -8th day of illness (the breast, abdomen, extremities (except for palms and soles) In some days turns in maculo-papular and disappears
- the period of occurrence of the rash is accompanied by amplification of the intoxication - intensive headache, insomnia, delirium, hyperkinesis, meningeal syndrome.
Слайд 47
СV system - hypotonia, tachycardia, expansion of borders of heart
and dullness of its tones, pancarditis (less often)
Lungs- bronchites, the
interstitial pneumonia
Moderate splenomegaly
Kidney - attributes of “toxic kidney“ or glomerulonephritis
The general analysis of blood – has nonspecific changes
Variants of current – from severe (in Japan and among visitors in endemic areas) - to easy and erased
Lethality - without antibiotic therapy from 1 % (islands Peskadorskie) up to 60 % (Japan and Taiwan)
Complications: myocarditis, meningoencephalitis, glomerulonephritis acute cardiovascular insufficiency
Слайд 48Diagnosis:
- Luminescent method and biological (infection of mice)
- HA
with antigene Proteus OXK about 2-nd weeks of disease
- Complement-fixation
test
Specific diagnosis is complicated because of an antigenic variety strains the infectious agent
Differential diagnosis - others rikettsiosises, a fever
dengue, medicinal and infectious erythema
Treatment - as at a typhus
Preventive maintenance:
- processing place in endemic areas acariasides
- carrying of special clothes
- use of mite repellents
Active immunization by the weakened vaccines ( seldom) - no currently available vaccine is effective
The isolation, the current disinfection, quarantine, immunization and inspection contact are not carried out
Слайд 4925
Clinic of a epidemic typhus (H. Fracastoro, 1546 г)
… At first illness is expressed weakly, … but soon
there are malignant signs, because, though the high temperature on a nature of these fevers and is not felt by the patient, some is noted inside disorder, breakdown in all body, as at fatigue.
Decubituses on a back, the head grow heavy, sensivity is killed also consciousness, more by a part, after 4-7 days is blacked out, the patient speaks many words (delirates)
The eyes have reddened. Pulse infrequent and weak. The urine, is usual in the beginning paleish, but dense, then soon becomes reddish and turbid, similar on pomegranate wine. A feces corrupt, mephitic.
About 4 - 7 days on arms back and breast break out red, frequently and purple spots, similar to stings fleas, quite often and greater size reminding lentil.
Sleepiness, sometimes insomnia, sometimes alternately that and another sometimes prevails. The similar state keeps in other cases about 7 days, in others up to 14, in others and is longer
Sometimes there is an ischuria, that is very poor sign ….

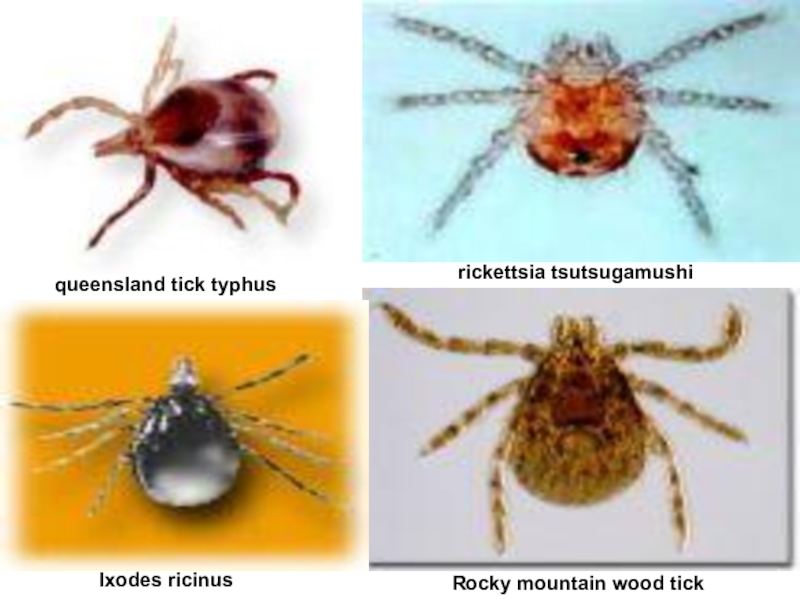
Слайд 51queensland tick typhus
rickettsia tsutsugamushi
Ixodes ricinus
Rocky mountain wood tick
Слайд 52Rocky mountain wood tick, rocky mountain spotted fever
Слайд 53The head louse, Pediculus humanus capitis, has an elongated body
and narrow anterior mouthparts. Body lice look similar but lay
their eggs (nits) on clothing fibers instead of hair fibers.