Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Teacher: Kamilova Irina Kaharovna Prepared By: Sulur PerumalSwamy Venkatesh
Содержание
- 1. Teacher: Kamilova Irina Kaharovna Prepared By: Sulur PerumalSwamy Venkatesh
- 2. WHAT ISBREECH?Malpresentation is apresentation that is not
- 3. INCIDENCEThis presentation occurs in:3-4% of term pregnancies.7%
- 4. TYPES OF BREECHFRANK BREECHFOOTLING BREECHCOMPLETE BREECHExtended or
- 5. WHY ARE SOME BABIES BREECH?Sometimes it’s just
- 6. PREDISPOSING FACTORSMATERNALFETAL / PLACENTALFibroidsCongenital uterine abnormalitiesUterine surgeryMultiple GestationPrematurityPlacenta praeviaAbnormality, e.g. anencephaly or hydrocephalusFetal neuromuscular conditionOligohydramniosPolyhydramnios
- 7. DIAGNOSISThe diagnosis of breech presentation may be
- 8. CLINICALDIAGNOSISPalpationFundal grips; the head is felt with
- 9. WHAT CANBE DONE?AFFAN
- 10. MANAGEMENTEXTERNAL CEPHALIC VERSIONVaginal deliveryLower segment caesarean section
- 11. MANAGEMENT1. EXTERNAL CEPHALIC VERSIONECV is a relatively straightforward
- 12. MANAGEMENT1. EXTERNAL CEPHALIC VERSIONThe procedure is performed at
- 13. MANAGEMENT
- 14. RISK OF ECVPlacental abruptionPremature rupture of membrane (PROM)Cord accidentTransplacental hemorrhageFetal bradycardia
- 15. CONTRAINDICATIONSFetal abnormality (e.g. hydrocephalus)Placenta praeviaOligohydramnios or polyhydramniosHistory
- 16. Pros and consADVANTAGESDISADVANTAGESReduction in breech presentation in
- 17. CHOICESFORBIRTH?WHAT ARE MY
- 18. VAGINAL BREECH DELIVERY2 MODE OF DELIVERY
- 19. INDICATIONSPresentation should be either extended or flexedNo evidence of feto pelvic disproportionEstimated
- 20. MANAGEMENTDURING LABOURFetal well being and progress of
- 21. TECHNIQUEDescent of the buttocks occurs until the
- 22. TECHNIQUE
- 23. TECHNIQUE3. Delivery of SHOULDERSBaby will be lying the
- 24. TECHNIQUE
- 25. TECHNIQUE4. Delivery of THE HEADDelivered using the Mauriceau-
- 26. TECHNIQUE
- 27. COMPLICATIONSThe greatest fear with a vaginal breech
- 28. 3 MODE OF DELIVERY.CESAREAN SECTION
- 29. Hannah ME, HofmeyrGJ TrialStudies had proven that
- 30. INDICATIONSClinically inadequate pelvisFootling or kneeling breech presentationLarge
- 31. PROCEDUREInformed consentSurgical basisThe pfannenstiel incisionThe infra-umbilical incisionUterine incision
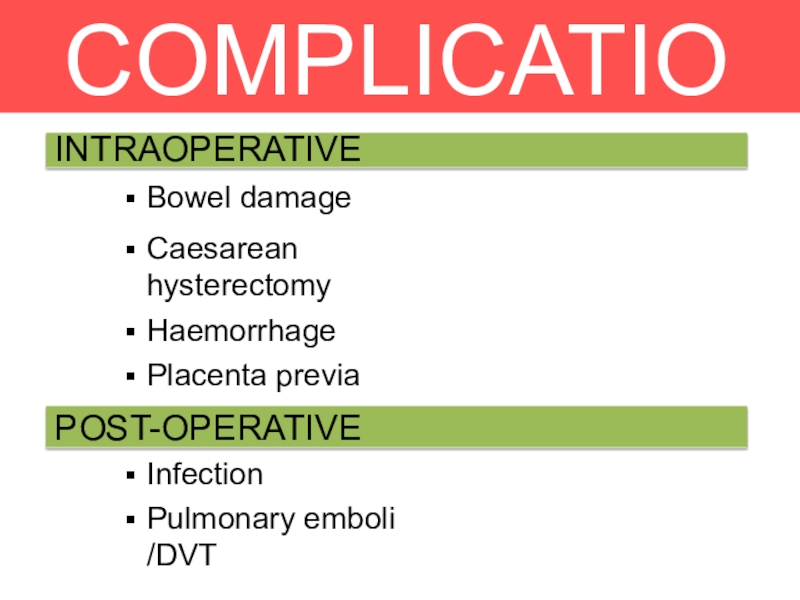
- 32. COMPLICATIONSInfectionPulmonary emboli /DVTINTRAOPERATIVEBowel damageCaesarean hysterectomyHaemorrhagePlacenta previaUrinary tract damagePOST-OPERATIVE
- 33. THANK YOU FOR ATTENTION !!!
- 34. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2WHAT IS
BREECH?
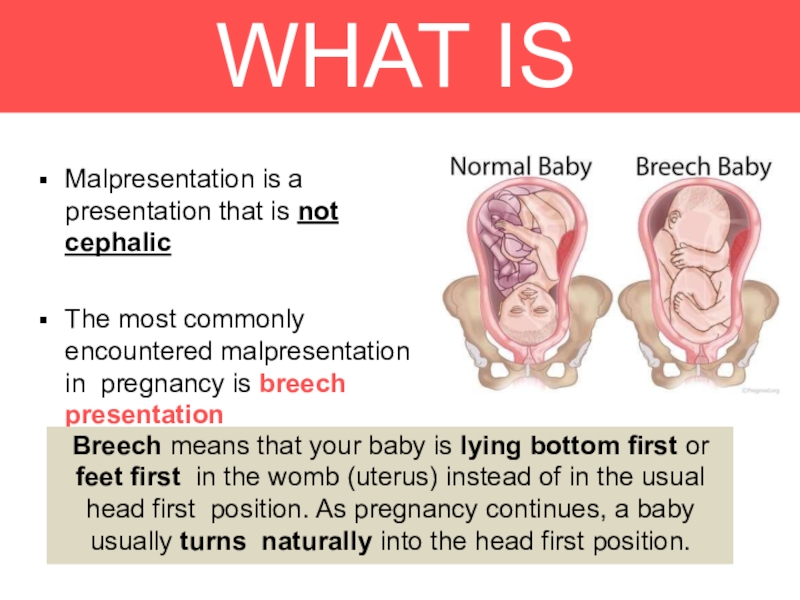
Malpresentation is a
presentation that is not cephalic
The most commonly
encountered malpresentation in pregnancy is breech presentation
Breech means that your
baby is lying bottom first or feet first in the womb (uterus) instead of in the usual head first position. As pregnancy continues, a baby usually turns naturally into the head first position.Слайд 3INCIDENCE
This presentation occurs in:
3-4% of term pregnancies.
7% of pregnancies at
32 weeks
25% of pregnancies of less than 28 weeks’
Слайд 4TYPES OF BREECH
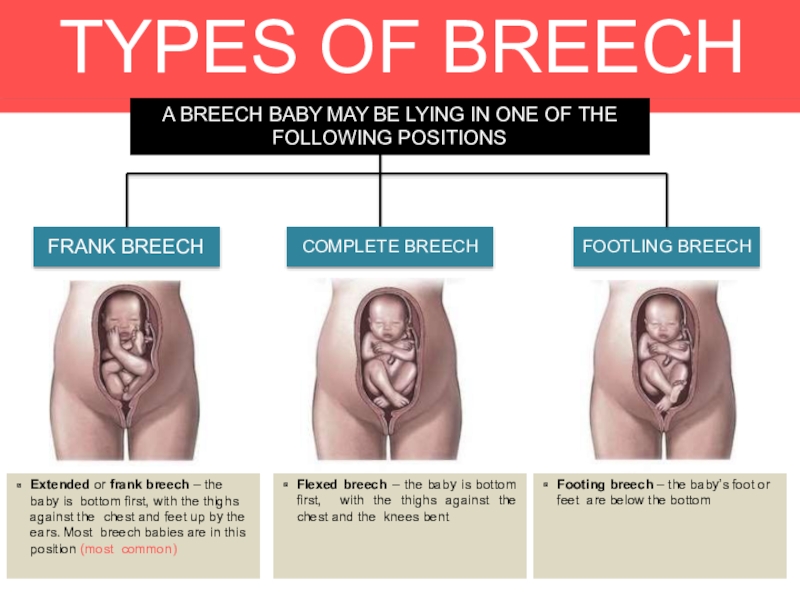
FRANK BREECH
FOOTLING BREECH
COMPLETE BREECH
Extended or frank breech –
the baby is bottom first, with the thighs against the
chest and feet up by the ears. Most breech babies are in this position (most common)Flexed breech – the baby is bottom first, with the thighs against the chest and the knees bent
Footing breech – the baby’s foot or feet are below the bottom
A BREECH BABY MAY BE LYING IN ONE OF THE FOLLOWING POSITIONS
Слайд 5WHY ARE SOME BABIES BREECH?
Sometimes it’s just a matter of
chance that a baby does not turn and remains the
breech position. At other times, certain factors make it difficult for a baby to turn during pregnancy. These might include the amount of fluid in the womb (either too much or too little), the position of placenta or if there’s any more than one baby in the womb.The vast majority of breech babies are born healthy. For a few babies, breech may be a sign of a problem with the baby
Слайд 6PREDISPOSING FACTORS
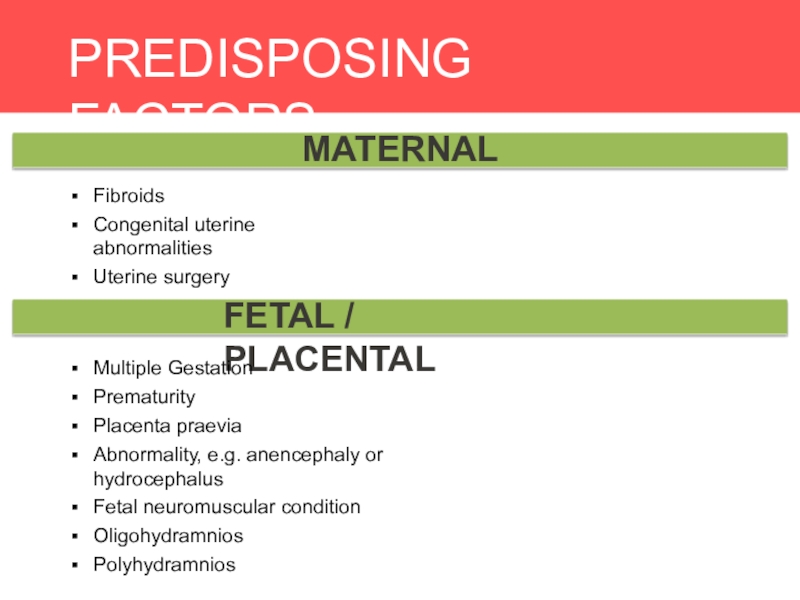
MATERNAL
FETAL / PLACENTAL
Fibroids
Congenital uterine abnormalities
Uterine surgery
Multiple Gestation
Prematurity
Placenta praevia
Abnormality, e.g.
anencephaly or hydrocephalus
Fetal neuromuscular condition
Oligohydramnios
Polyhydramnios
Слайд 7DIAGNOSIS
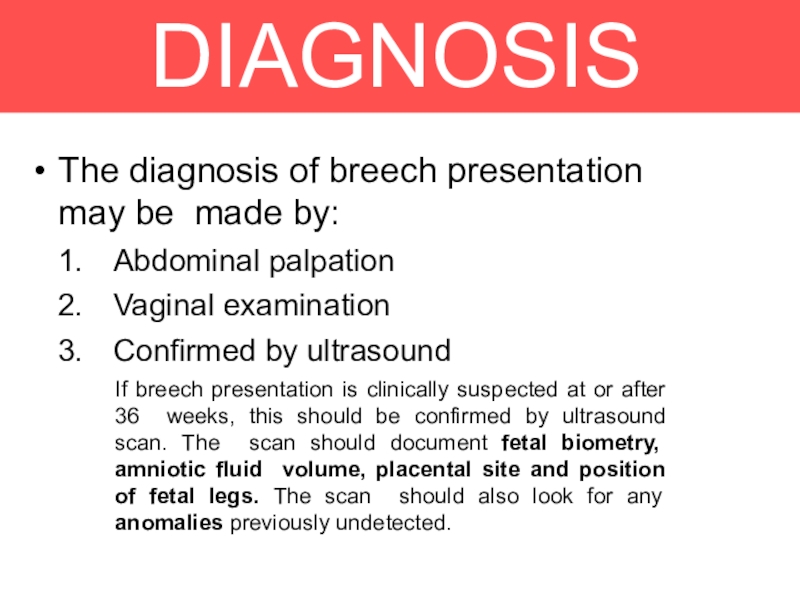
The diagnosis of breech presentation may be made by:
Abdominal palpation
Vaginal
examination
Confirmed by ultrasound
If breech presentation is clinically suspected at or
after 36 weeks, this should be confirmed by ultrasound scan. The scan should document fetal biometry, amniotic fluid volume, placental site and position of fetal legs. The scan should also look for any anomalies previously undetected.Слайд 8CLINICAL
DIAGNOSIS
Palpation
Fundal grips; the head is felt with its characters.
Pelvic grip;
the breech is felt, with its characters.
Auscultation
The fetal heart sounds
are head just at, or above the level of the umbilicusSlow dilatation of cervix
After rupture of the membranes, the presenting part is felt that is , the two buttocks with the anus in between , the genitalia on one side and the sacral spines on the opposite side.
In case of complete breech, the feet are felt on the same level as the buttocks.
In case of breech with extended legs, the buttocks only are felt.
In case of footling presentation, the feet are at a lower level than the buttocks.
In case of knee presentation, the knees are a lower level than the buttocks.
ABDOMINAL EXAMINATION
VAGINAL EXAMINATION
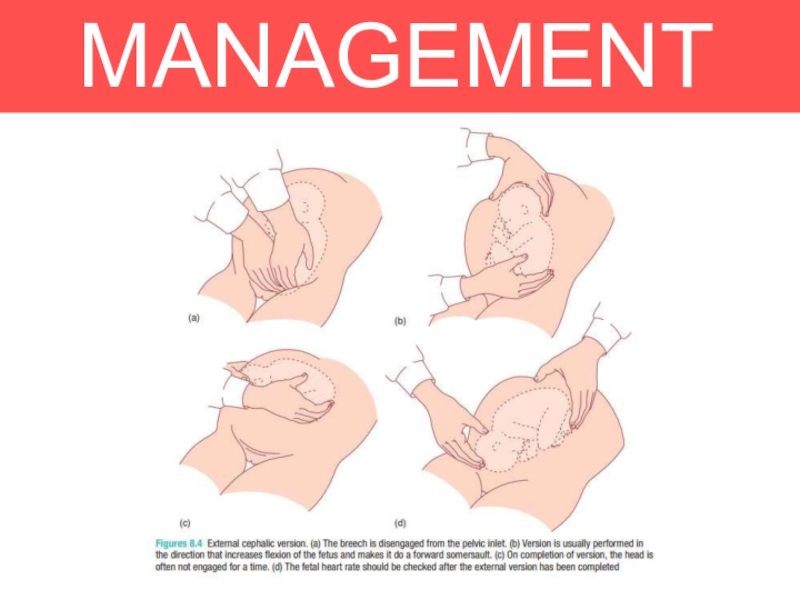
Слайд 11MANAGEMENT
1. EXTERNAL CEPHALIC VERSION
ECV is a relatively straightforward and safe technique
and has been shown to reduce the number of Caesarean
sections due to breech presentations.Should be offered at 36-37 weeks of pregnancy.
Success rate is around 50 per cent and are higher in multiparous women who tend to have more lax abdominal musculature. However it depends on the experience of the obstetrician.
A fetal heart rate trace must be performed before and after the procedure.
It is important to administer anti-D if the woman is Rhesus- negative.
Слайд 12MANAGEMENT
1. EXTERNAL CEPHALIC VERSION
The procedure is performed at or after 37
completed weeks by an experienced obstetrician.
ECV should be performed with
tocolytics (e.g. nifedipine) as this has been shown to improve the success rate.The woman is laid flat with a left lateral tilt having ensured that she has emptied her bladder and is comfortable.
HOW IS IT DONE?
With ultrasound guidance the breech is elevated from the pelvis and one hand is
used to manipulate this upward in the direction of a forward role, while the other hand applies gentle pressure to flex the fetal head and bring it down to the maternal pelvis.
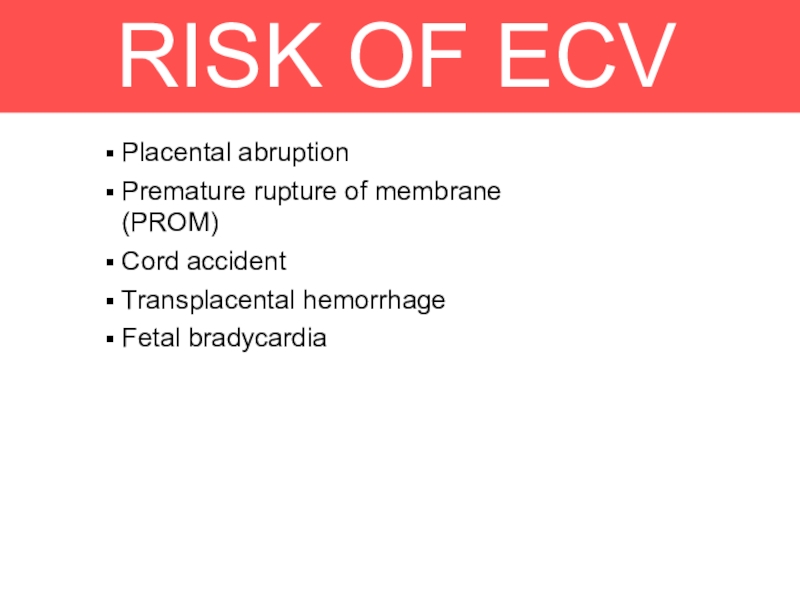
Слайд 14RISK OF ECV
Placental abruption
Premature rupture of membrane (PROM)
Cord accident
Transplacental hemorrhage
Fetal
bradycardia
Слайд 15CONTRAINDICATIONS
Fetal abnormality (e.g. hydrocephalus)
Placenta praevia
Oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios
History of antepartum haemorrhage
Previous
Caesarean or myomectomy scar on the uterus
Multiple gestation
Pre-eclampsia or hypertension
Plan
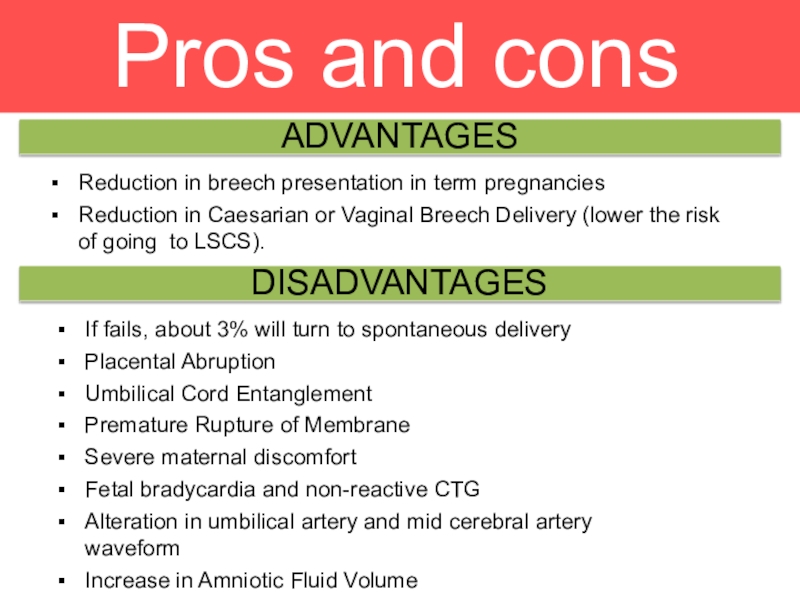
to deliver by Caesarean section anywayСлайд 16Pros and cons
ADVANTAGES
DISADVANTAGES
Reduction in breech presentation in term pregnancies
Reduction in
Caesarian or Vaginal Breech Delivery (lower the risk of going
to LSCS).If fails, about 3% will turn to spontaneous delivery
Placental Abruption
Umbilical Cord Entanglement
Premature Rupture of Membrane
Severe maternal discomfort
Fetal bradycardia and non-reactive CTG
Alteration in umbilical artery and mid cerebral artery waveform
Increase in Amniotic Fluid Volume
Слайд 19INDICATIONS
Presentation should be either extended or flexed
No evidence of feto pelvic disproportion
Estimated fetal weight
3.5 kg
No evidence of hyperextension of fetal head and fetal
abnormalities (hydrocephalus)No other obstetric complications.
Слайд 20MANAGEMENT
DURING LABOUR
Fetal well being and progress of labour should be
monitored
Epidural administration can prevent pushing before full dilatation
Fetal blood sampling to
monitor acid base statusOperator experienced in delivering breech babies should be available.
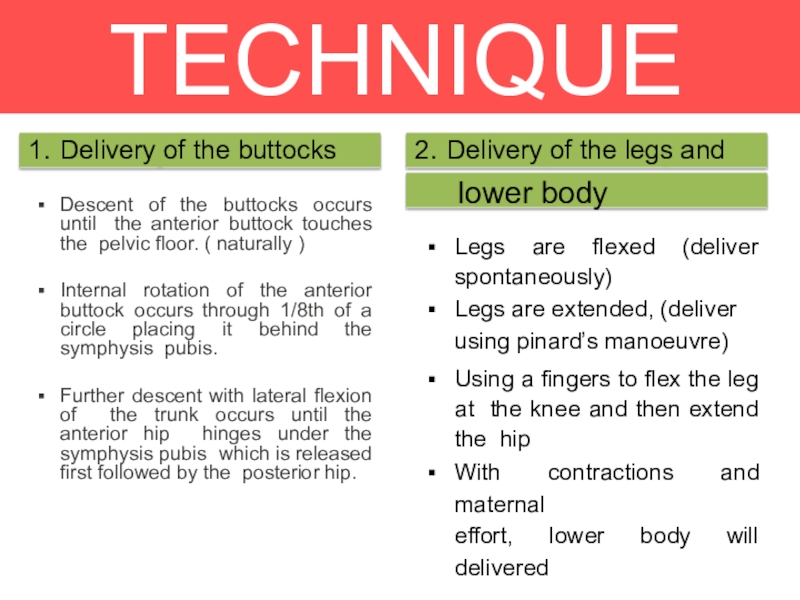
Слайд 21TECHNIQUE
Descent of the buttocks occurs until the anterior buttock touches
the pelvic floor. ( naturally )
Internal rotation of the anterior
buttock occurs through 1/8th of a circle placing it behind the symphysis pubis.Further descent with lateral flexion of the trunk occurs until the anterior hip hinges under the symphysis pubis which is released first followed by the posterior hip.
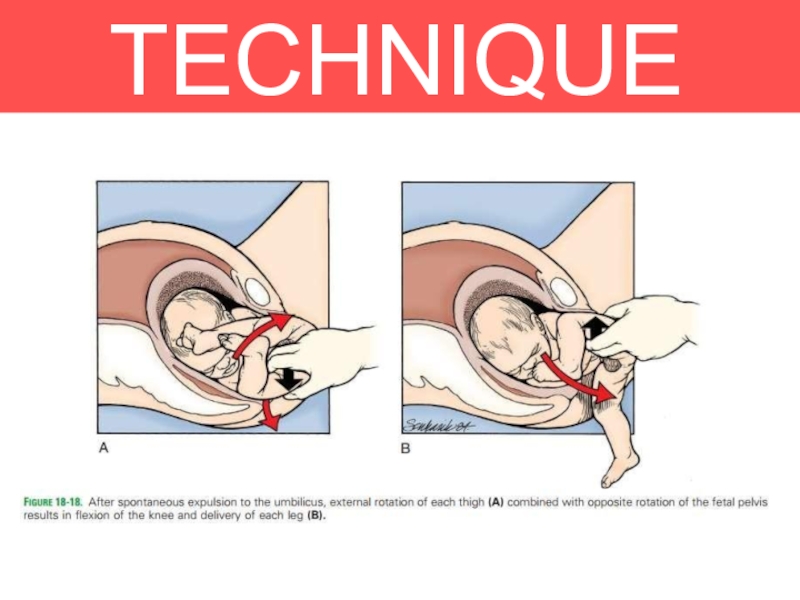
Legs are flexed (deliver spontaneously)
Legs are extended, (deliver
using pinard’s manoeuvre)
Using a fingers to flex the leg at the knee and then extend the hip
With contractions and maternal
effort, lower body will delivered
1. Delivery of the buttocks
2. Delivery of the legs and
lower body
Слайд 23TECHNIQUE
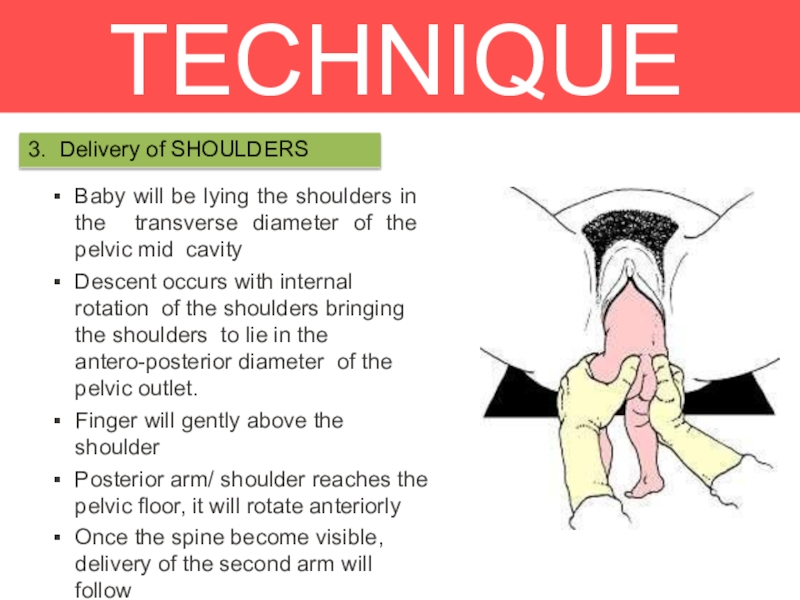
3. Delivery of SHOULDERS
Baby will be lying the shoulders in the
transverse diameter of the pelvic mid cavity
Descent occurs with internal
rotation of the shoulders bringing the shoulders to lie in the antero-posterior diameter of the pelvic outlet.Finger will gently above the shoulder
Posterior arm/ shoulder reaches the
pelvic floor, it will rotate anteriorly
Once the spine become visible, delivery of the second arm will follow
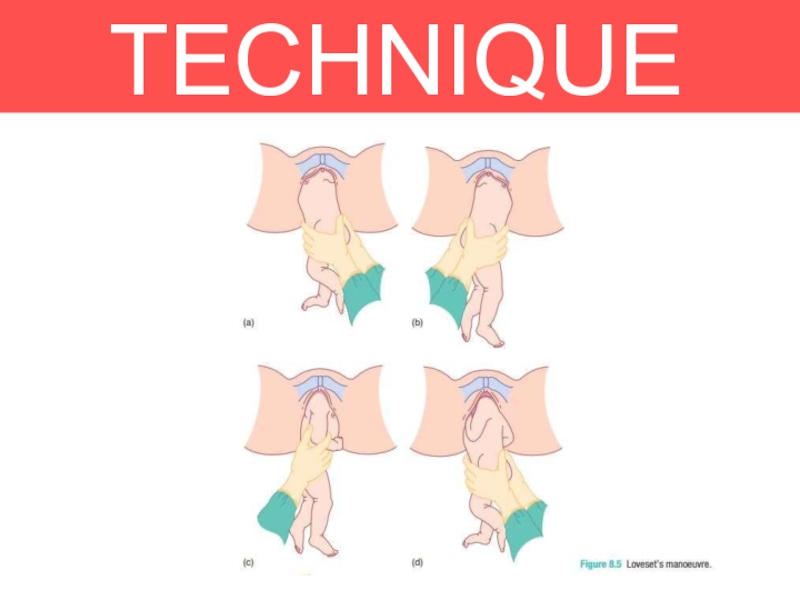
Loveset’s manoeuvre .
Слайд 25TECHNIQUE
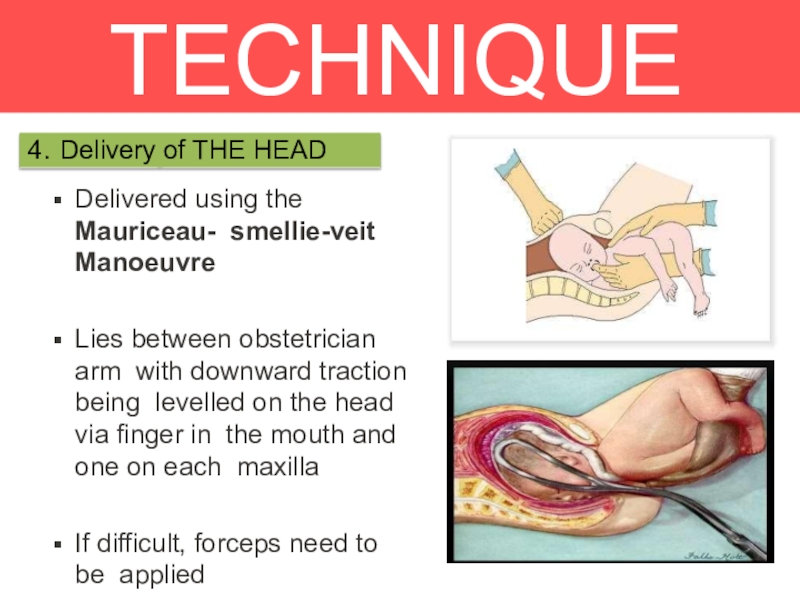
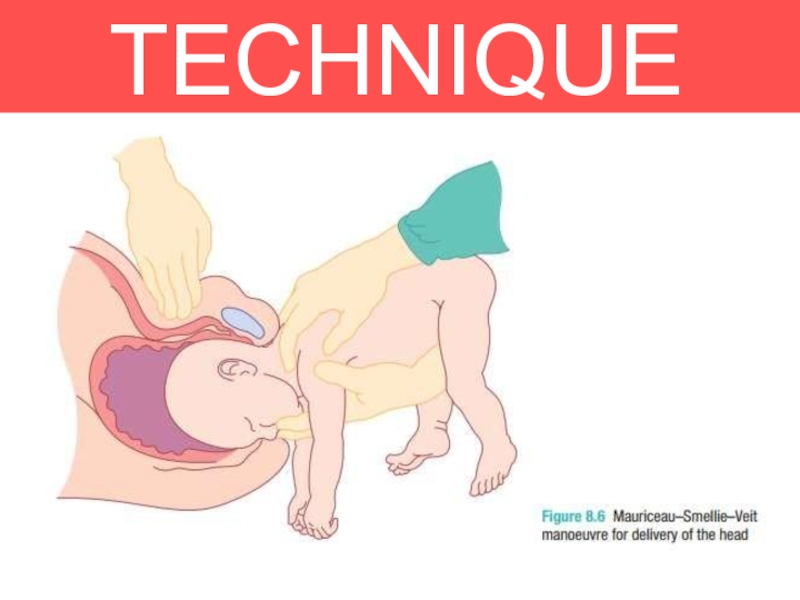
4. Delivery of THE HEAD
Delivered using the Mauriceau- smellie-veit Manoeuvre
Lies between
obstetrician arm with downward traction being levelled on the head
via finger in the mouth and one on each maxillaIf difficult, forceps need to be applied
Слайд 27COMPLICATIO
NS
The greatest fear with a vaginal breech is that the
baby will
get ‘stuck’.
Interference in the natural process by the inappropriate
use of oxytoxic agents or by trying to pull the baby out (breech extraction) will (paradoxically) increase the obstruction occuring.When delay occurs, particularly with delivery of the shoulders or head, the presence of an experienced obstetrician will reduce the risk of death or serious injury.
Слайд 29Hannah ME, Hofmeyr
GJ Trial
Studies had proven that a patient with
Breech presentation should go for C-Sect
“Planned C-sect is safe for
singleton term breech babies than planned vaginal birth, managed accordingly to a clinical protocol, but more complications for mothers.”The review of the this study showed that Planned C-sect was safer for the singleton breech baby at term than planned VBD.
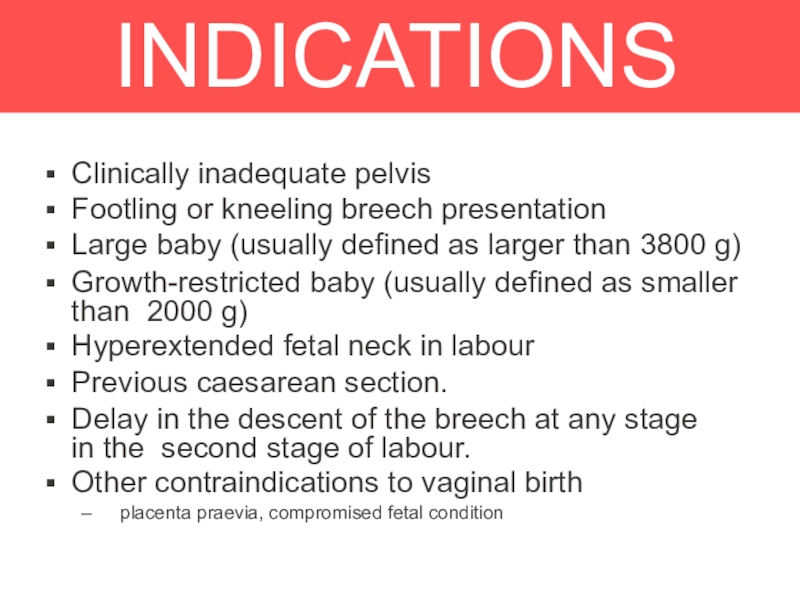
Слайд 30INDICATIONS
Clinically inadequate pelvis
Footling or kneeling breech presentation
Large baby (usually defined
as larger than 3800 g)
Growth-restricted baby (usually defined as smaller
than 2000 g)Hyperextended fetal neck in labour
Previous caesarean section.
Delay in the descent of the breech at any stage in the second stage of labour.
Other contraindications to vaginal birth
– placenta praevia, compromised fetal condition