Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
The main events of the 14 th -17 th centuries
Содержание
- 1. The main events of the 14 th -17 th centuries
- 2. The 14th century. The century of Plagues, war with France and conflicts in the elite
- 3. Scotland recognized, 1328 Robert the BruceEdward III
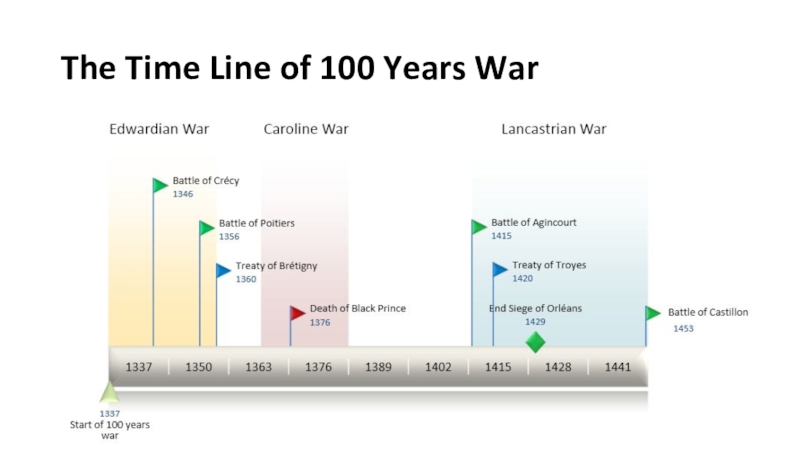
- 4. 100 Years War starts, 1337
- 5. The Time Line of 100 Years War
- 6. The Black Death sweeps 1/3 of English population, 1348-9
- 7. Wat Tyler’s Revolt, 1381
- 8. Chaucer starts “The Canterbury Tales”, 1386-9
- 9. Richard II deposed, 1399Richard IIHenry IV
- 10. The 15th century. The century of dynastic disputes
- 11. Scottish King James I Stewart taken hostage in England, 1406
- 12. The Battle of Agincourt, 1413
- 13. The Treaty of Troyes, 1420Agreement that Henry
- 14. Orleans lost, 1429
- 15. The Battle of Castillon and the Loss of the War, 1453
- 16. The Dynastic Struggle between the Lancasters and the Yorks begins, 1455
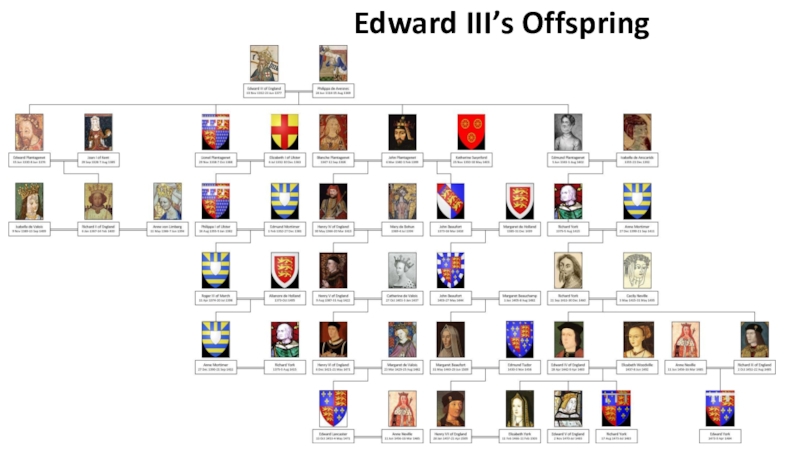
- 17. Edward III’s Offspring
- 18. Henry VI deposed, 1461. Edward IV becomes kingHenry VIEdward IV
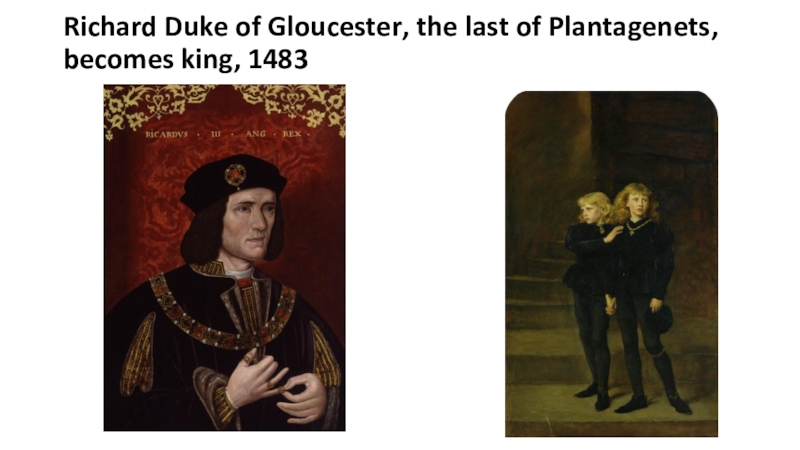
- 19. Richard Duke of Gloucester, the last of Plantagenets, becomes king, 1483
- 20. The Battle of Bosworth and coronation of Henry Tudor, 1485
- 21. The 16th century. The century of
- 22. Henry VIII breaks with Roman Catholicism, 1534 Henry VIIIDissolution of monastaries
- 23. Mary I returns Catholicism for 5 years, 1553-58
- 24. Francis Drake circumnavigates the Globe, 1577-80
- 25. Elisabeth I signs the death sentence on Mary Queen of Scots, 1587. James becomes king
- 26. The Spanish Armada defeated, 1588
- 27. The 17th century. The Crown and the Parliament are fighting about their prerogatives
- 28. James VI of Scotland becomes King James I of England, 1603. The Union of Crowns
- 29. Gunpowder Plot, 1605
- 30. Charles I launches the campaign against France , 1627-29The Siege of La Rochelle
- 31. 1628 - Petition of Rights:In return for
- 32. Anglo-Scottish Bishop’s War, 1639
- 33. The events which led to the 1st
- 34. The 1st Civil War, 1642-46
- 35. The 2nd Civil War, 1648-9Scots reach agreement
- 36. King Charles I executed, 1649
- 37. 3d English Civil War, 1649 - 51Cromwell
- 38. English Republic, 1649 - 1660Oliver Cromwell, 1653
- 39. Monarchy restored, 1660Charles II (ruled 1660 – 1685)James II (ruled 1685-88)
- 40. Restored Monarchy and Parliament1661 - Clarendon Code;
- 41. Major Political Events between 1679 and 16891679
- 42. New Age, New Monarchy1701 – The Act
- 43. Urquhart Castle, blown up in 1690Eilean Donan Castle, Demolished in 1719Jacobite Resistance in the Highlands
- 44. Bonnie Prince Charlie (Charles Edward Stuart) 1720 - 1788
- 45. Battle of Culloden, 1746
- 46. Скачать презентанцию
The 14th century. The century of Plagues, war with France and conflicts in the elite
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 13The Treaty of Troyes, 1420
Agreement that Henry V or his
heirs would be crowned as king of France after the
death of Charles VIСлайд 21The 16th century. The century of Reformation, absolute monarchy and
rise of England as a leading European power
Слайд 311628 - Petition of Rights:
In return for finances, Charles I
was forced to accept Parliament's statement of civil rights
Charles
I prorogues the Parliament and begins 11 years of personal rule, 1629;Слайд 33The events which led to the 1st Civil War
Short Parliament,
1640;
Irish Rebellion, Oct 1641;
Grand Remonstrance of Grievances, Dec. 1641;
Charles enters
Parliament to arrest its 5 rebellious leaders, Jan 4, 1642Charles leaves London to raise his army
Charles raises his royal standard in Nottingham, Aug 1642. The War begins
Слайд 35The 2nd Civil War, 1648-9
Scots reach agreement with Charles and
invade England, but already in Aug 1648 are defeated by
CromwellСлайд 373d English Civil War, 1649 - 51
Cromwell marches to Ireland
and harshly puts down the rebellion there;
Lands of Irish Catholics
confiscated and given to protestants;Charles II is crowned king in Scotland in 1651 and invades England, but defeated by Cromwell
Слайд 38English Republic, 1649 - 1660
Oliver Cromwell, 1653 – 1658 Lord
Protector
The Rump of the Long Parliament, dissolved in 1653, but
recreated in 1659Слайд 40Restored Monarchy and Parliament
1661 - Clarendon Code; "Cavalier" Parliament of
Charles II passes series of repressive laws against Nonconformists
1665 –
Great Plague1666 – Great Fire of London
Слайд 41Major Political Events between 1679 and 1689
1679 - Habeas Corpus
Act: forbidding imprisonment without trial; Charles II blocks the Parliament's
Bill of Exclusion against his Catholic brother James; Parliament dismissed; Charles II rejects petitions calling for a new Parliament; petitioners become known as Whigs; their opponents – as Tories1681 - Whigs reintroduce Exclusion Bill; Charles II dissolves Parliament;
1685 – Charles II dies and James becomes James II of England and VII of Scotland; rebellion by Charles II's illegitimate son, the Duke of Monmouth, against James II is put down;
1686 - James II lets Roman Catholics to be appointed to public office;
1687 - James II issues Declaration of Liberty of Conscience, extends toleration to all religions;
1688 - England's 'Glorious Revolution'; William III of Orange is invited to save England from Catholicism, lands in England, James II flees;
1689 - Convention Parliament issues Bill of Rights; establishes a constitutional monarchy in Britain; bars Roman Catholics from the throne; William III and Mary II become joint monarchs of England and Scotland (to1694), Toleration Act grants freedom of worship to dissenters in England
Слайд 42New Age, New Monarchy
1701 – The Act of Settlement;
1707 –
The Act of Union between England and Scotland
1714 – Queen
Ann dies and is followed by her German relative George Hanover (George I)1715-16 – Jacobite Rebellion
1721 – Robert Walpole becomes 1st Minister; the Age of Prime Ministers comes