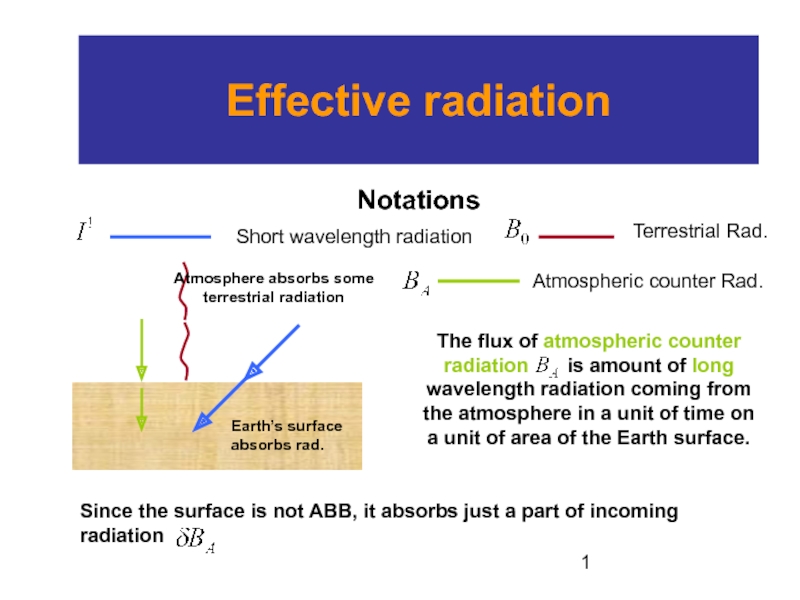
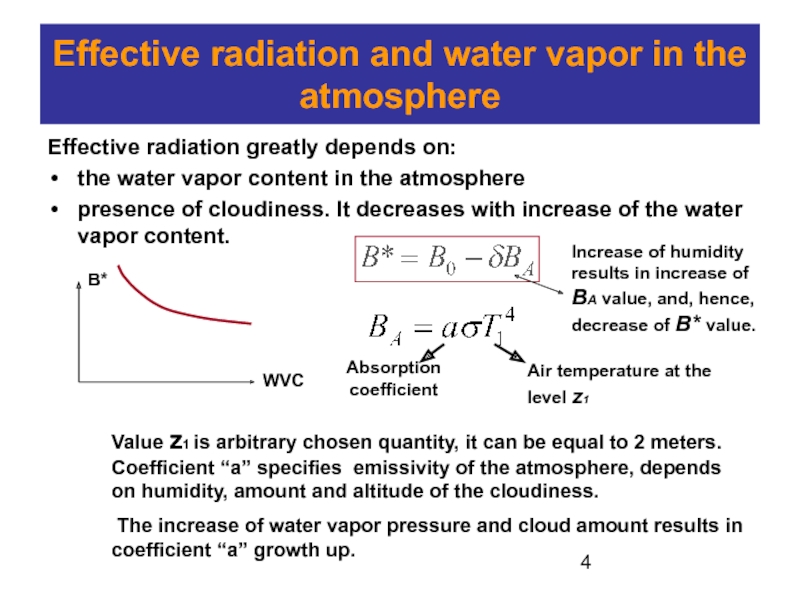
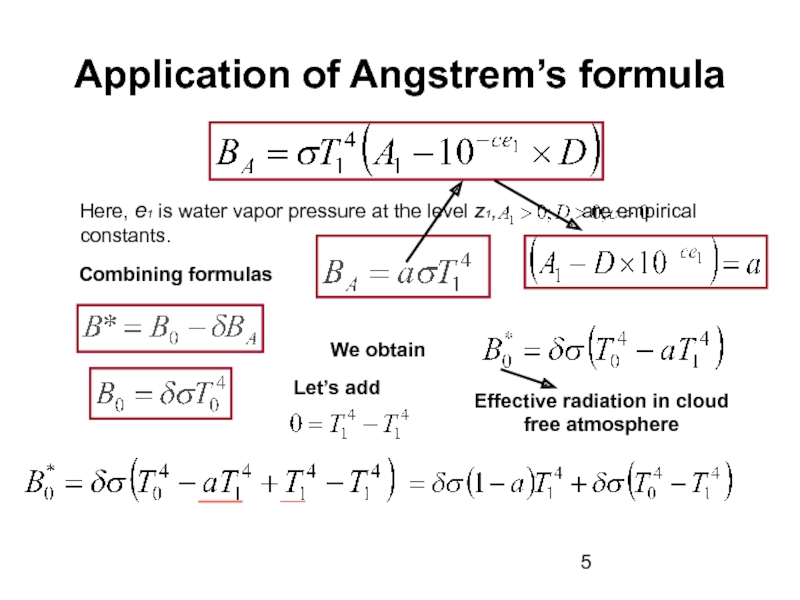
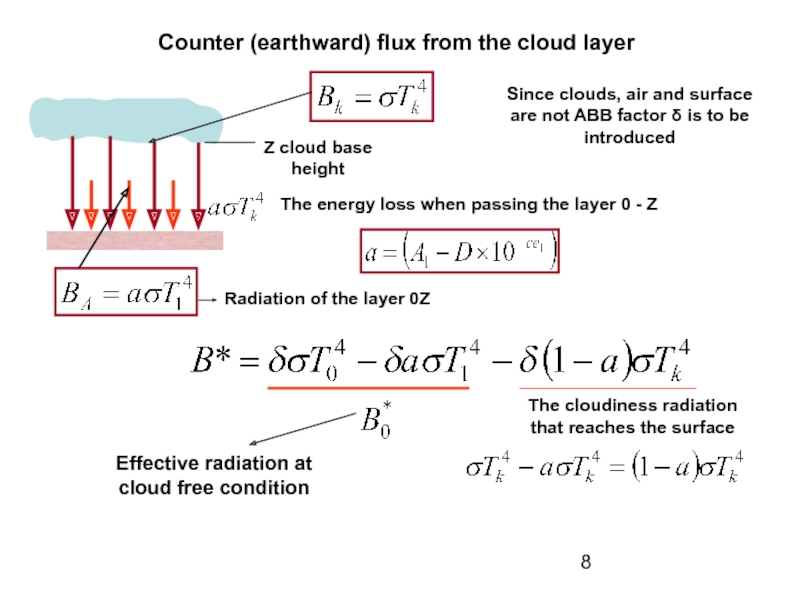
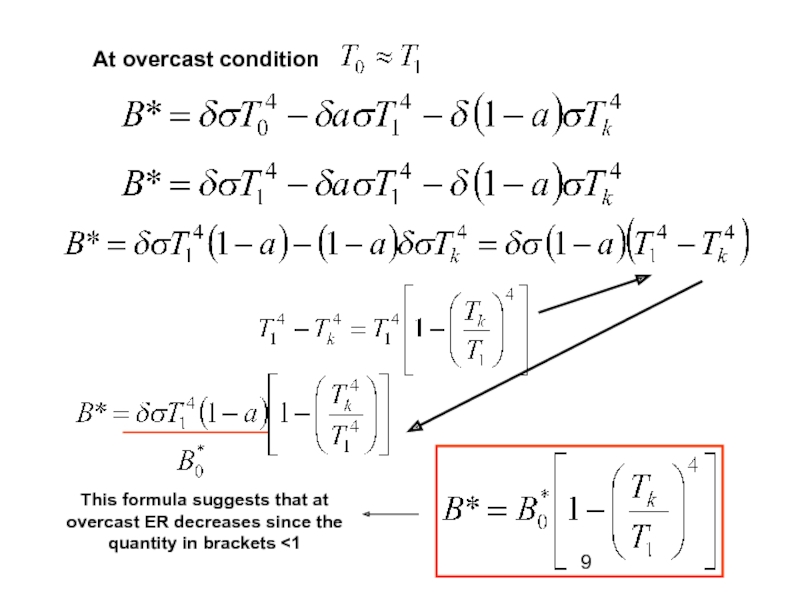
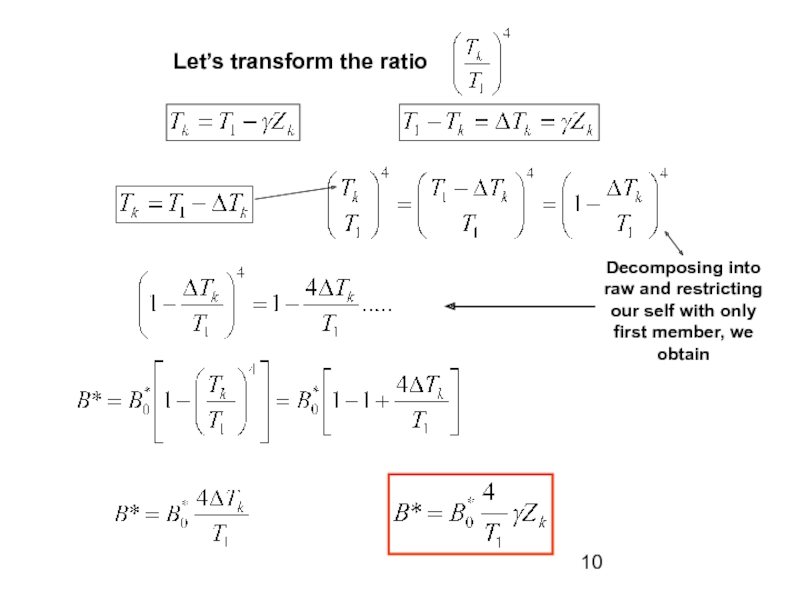
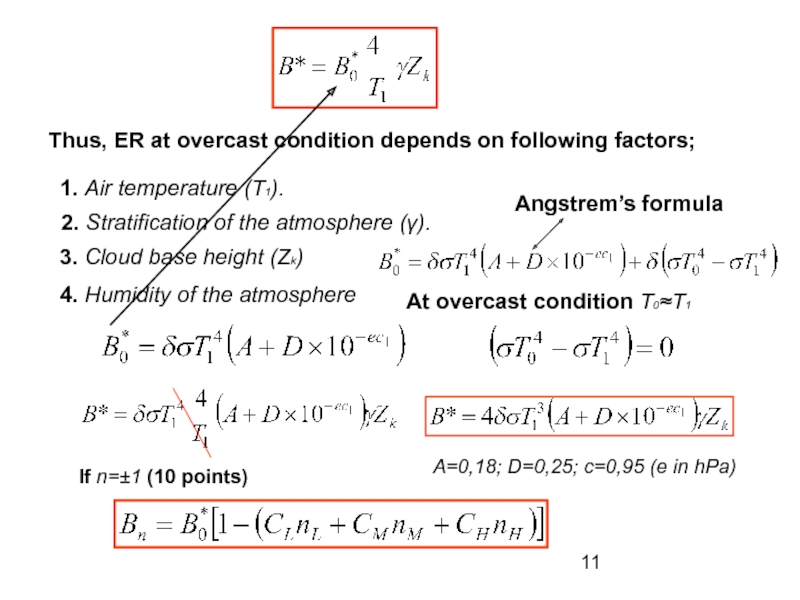
absorbs some terrestrial radiation
The flux of atmospheric counter radiation
is amount of long wavelength radiation coming from the atmosphere in a unit of time on a unit of area of the Earth surface.Since the surface is not ABB, it absorbs just a part of incoming radiation