Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
ANCIENT INDIAN AND CHINESE PHILOSOPHY
Содержание
- 1. ANCIENT INDIAN AND CHINESE PHILOSOPHY
- 2. CONTENT OF THE LECTURE:EASTERN (ORIENTAL) PHILOSOPHYANCIENT INDIAN PHILOSOPHY -HINDUISM - BUDDHISM -JAINISM3. ANCIENT CHINESE PHILOSOPHY
- 3. EASTERN (ORIENTAL) PHILOSOPHYIn the West, the term
- 4. Слайд 4
- 5. EASTERN (ORIENTAL) PHILOSOPHYAncient eastern philosophy developed mainly
- 6. EASTERN (ORIENTAL) PHILOSOPHYConfucianism can be considered as
- 7. ANCIENT INDIAN PHILOSOPHY
- 8. ANCIENT INDIAN PHILOSOPHY
- 9. ANCIENT INDIAN PHILOSOPHY
- 10. ANCIENT INDIAN PHILOSOPHY
- 11. ANCIENT INDIAN PHILOSOPHY
- 12. ANCIENT INDIAN PHILOSOPHY
- 13. ANCIENT INDIAN PHILOSOPHY The development of
- 14. HINDUISMRig-Veda contains an extreme pluralism: the gods,
- 15. INDIAN SOCIETY’S CASTES:Head corresponds to the caste
- 16. INDIAN SOCIETY’S CASTES:
- 17. ANCIENT INDIAN PHILOSOPHICAL SCHOOLS:According to a
- 18. BUDDHISMreligious-philosophical doctrineteaching of awakening (ояну /пробуждение)at the
- 19. BUDDHISMIn Buddhism it’s proposed median (орталық/срединный) of
- 20. JAINISMpreaches(уағыздау/проповедовать)non-violence to all living beings in this
- 21. ANCIENT CHINESE PHILOSOPHY Considering all things
- 22. ANCIENT CHINESE PHILOSOPHY
- 23. ANCIENT CHINESE PHILOSOPHY
- 24. ANCIENT CHINESE PHILOSOPHY
- 25. ANCIENT CHINESE PHILOSOPHY
- 26. ANCIENT CHINESE PHILOSOPHICAL SCHOOLS:During this period, freely
- 27. CONFUCIANISMfocuses on the ethical rules, social norms
- 28. CONFUCIUS (551-479 BC)
- 29. CONFUCIANISMunderstood man in connection with his social
- 30. SCHOOL OF YIN AND YANG the
- 31. SCHOOL OF MOISM school was named after
- 32. SCHOOL OF NAMES examined the relations
- 33. LEGISMformed almost as a teaching that focused
- 34. TAOISMone of the major directions in Chinastudies
- 35. Lao Tzu (400 - ….. BC)
- 36. TAOISMthe purpose of thinking, in Taoism, is
- 37. Скачать презентанцию
CONTENT OF THE LECTURE:EASTERN (ORIENTAL) PHILOSOPHYANCIENT INDIAN PHILOSOPHY -HINDUISM - BUDDHISM -JAINISM3. ANCIENT CHINESE PHILOSOPHY
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2CONTENT OF THE LECTURE:
EASTERN (ORIENTAL) PHILOSOPHY
ANCIENT INDIAN PHILOSOPHY
-HINDUISM
- BUDDHISM
-JAINISM
3. ANCIENT
CHINESE PHILOSOPHY
Слайд 3EASTERN (ORIENTAL) PHILOSOPHY
In the West, the term Eastern (Oriental) philosophy
refers very broadly to the various philosophies of “the East”,
namely Asia, including China, India, Japan, Persia and other areasOne must take into account that this term ignores that these countries do not belong to a single culture
Слайд 5EASTERN (ORIENTAL) PHILOSOPHY
Ancient eastern philosophy developed mainly in India and
China
The Indian or Hindu schools of philosophy can be considered
the oldest schools of philosophyHindu philosophy is followed by the Buddhist and Jain philosophies
Слайд 6EASTERN (ORIENTAL) PHILOSOPHY
Confucianism can be considered as the oldest school
of philosophy in China
Confucianism developed in China around the same
time as Buddhism and Jainism developed in IndiaAnother school of philosophy, Taoism, developed in China around 200 BC
Слайд 13
ANCIENT INDIAN PHILOSOPHY
The development of ancient Indian philosophy consists of
two periods: Vedic and Classical
Rig-Veda is a collection of religious
hymns, the first known monument of Indian literatureThe word «veda» means «knowledge» and comes from the root «vid», that reconstructed from Proto-Indo-European root «weid», meaning «see» or «know»
Слайд 14HINDUISM
Rig-Veda contains an extreme pluralism: the gods, people, animals, plants,
elements, seasons, countries, qualities of body, spiritual abilities, etc.
They are
animate (жанды/одушевленные) substances, which are connected with each other and can transform into one another.The world and its phenomena are considered as the improvement of the primary entity (түп -тегі/сущность)(Purusha)
Purusha is also understood to be the first person, which consists of castes.
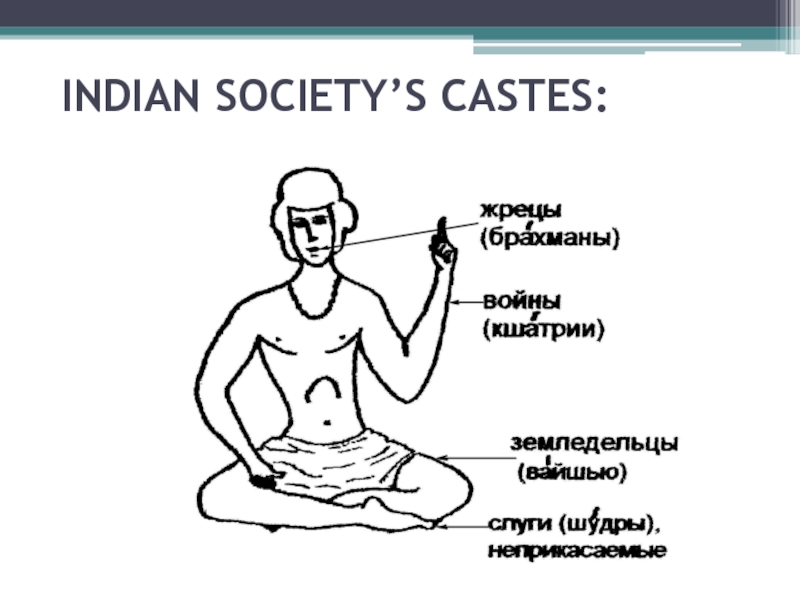
Слайд 15INDIAN SOCIETY’S CASTES:
Head corresponds to the caste of Brahmins (priests)
Hands
– to the caste of the Kshatriyas (the military or
ruling class)Feet – Vaisya caste (merchants, artisans)
Footsteps –Sudras caste (servants)
There were also Untouchables, that is, most lower of the castes
Слайд 17ANCIENT INDIAN
PHILOSOPHICAL SCHOOLS:
According to a traditional schools of Indian
philosophy (Brahmins) are divided into two broad classes, namely, orthodox
(astika) & heterodox (nastika)During next classical period, there appears an interest in ethical issues. Agnostics, materialists and fatalists oppose the Brahmins and the reformists
Слайд 18BUDDHISM
religious-philosophical doctrine
teaching of awakening (ояну /пробуждение)
at the core of Buddhism
is the doctrine of the four high-minded (мәртебелі/благородный) truths:
-
suffering,- the origin and causes of suffering
- a true cessation (тоқтату/прекращение) of suffering
- the true ways to stop suffering
Слайд 19BUDDHISM
In Buddhism it’s proposed median (орталық/срединный) of achieving Nirvana
This path
is directly related to the cultivation of three varieties of
virtues (ізгіліктер/добродетели):-morality (өсиет)
- concentration (шоғырлану)
- wisdom (даналық/мудрость)
Слайд 20JAINISM
preaches(уағыздау/проповедовать)
non-violence to all living beings in this
world
based primarily on
the cultivation of
soul to attain :
omniscience (білгендік/всеведение)
omnipotence (күдірет-күш/всесилие)
eternal bliss (рахат/блаженство)
Слайд 21
ANCIENT CHINESE PHILOSOPHY
Considering all things as a unity of opposites
(Yang – Yin), Chinese thinkers have explained the endless process
of moving through their dialectical interactionIn Chinese mythology, it is allocated the highest principle, which rules the world, the existence of things. This principle is sometimes understood as the highest personified ruler (Shang-di)
Слайд 26ANCIENT CHINESE PHILOSOPHICAL SCHOOLS:
During this period, freely and creatively there
were six major philosophical schools.
1) School of Confucians;
2) School of
Yin and yang;3) School of Moism (Mo-jia);
4) School of Names (Ming-jia);
5) School of Lawyers, legists (Fa-jia);
6) School of Ways and Power (Tao-jia)
Слайд 27CONFUCIANISM
focuses on the ethical rules, social norms and regulation control
Confucius
(551-479 BCE), his name is latinized version of the name
Kung Fu Tzu (teacher Kun)He is one of the first Chinese thinkers, philosophers
Слайд 29CONFUCIANISM
understood man in connection with his social function, and education
is to bring people to the execution (атқару/исполнение) of this
functionthe social order established through the ideal of universality, respect to nature and, especially, relations between people
this realization of functions and order based on the order leads to the manifestation of humanity
Слайд 30
SCHOOL OF YIN AND YANG
the central concept of Inyan Jia
- universal dualism forces of Yin-Yang
the cyclical nature of
interactions generated by these five elements: metal, wood, water, fire and earththis concept considers all of the developed of the world
Слайд 31SCHOOL OF MOISM
school was named after the founder Moe
Dee (479-391 BC)
the main attention was primarily paid to the
problems of social ethics, which is connected through a strict organization with the despotic power of the headthe whole meaning was to the ideas of universal love and mutual benefit of people
Слайд 32
SCHOOL OF NAMES
examined the relations of things and the very
expression of that relationship
examined the judgments and notions
Слайд 33LEGISM
formed almost as a teaching that focused primarily on issues
of socio-political change in the era of “warring states” (5-4
centuries BC)Слайд 34TAOISM
one of the major directions in China
studies nature, space and
people in movement
learns universe through direct penetration into the conceptual
nature of its existencethe world is in constant motion and change, evolving, living and acting on impulse (игерусіз/спонтанно)
Слайд 36TAOISM
the purpose of thinking, in Taoism, is “merger” (қосылуы/слияние) between
man and nature, because he is its part
Lao Tzu (old
teacher) is a senior contemporary of Confuciushe wrote the book “Tao Te Ching”, which became the basis for further development of Taoism