Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Biological bases of Parasitism and Class Sarcodina
Содержание
- 1. Biological bases of Parasitism and Class Sarcodina
- 2. ParasitologyParasitology is the study of parasites, their
- 3. ParasitismIn evolutionary ecology, parasitism is a symbiotic
- 4. The following are several of the broad
- 5. Слайд 5
- 6. Medical parasitologyMedical parasitology is the subject that
- 7. These include organisms such as- Plasmodium spp., the
- 8. Слайд 8
- 9. Слайд 9
- 10. Слайд 10
- 11. Class SarcodinaSarcodine, any protozoan of the superclass
- 12. Слайд 12
- 13. Слайд 13
- 14. Слайд 14
- 15. Слайд 15
- 16. Слайд 16
- 17. Слайд 17
- 18. Pathogenicity
- 19. Слайд 19
- 20. IMPORTANT LINKShttps://youtu.be/4pex9y8slCI https://youtu.be/gfCunkjxkMo https://youtu.be/4pex9y8slCI
- 21. Слайд 21
- 22. Скачать презентанцию
ParasitologyParasitology is the study of parasites, their hosts, and the relationship between them. As a biological discipline, the scope of parasitology is not determined by the organism or environment in question
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Parasitology
Parasitology is the study of parasites, their hosts, and the
relationship between them. As a biological discipline, the scope of
parasitology is not determined by the organism or environment in question but by their way of life. This means it forms a synthesis of other disciplines, and draws on techniques from fields such as cell biology, bioinformatics, biochemistry, molecular biology, immunology, genetics, evolution and ecology.Слайд 3Parasitism
In evolutionary ecology, parasitism is a symbiotic relationship between species,
where one organism, the parasite, lives on or in another
organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life.Слайд 4The following are several of the broad areas in which
parasitologists work: Medical Parasitology. … Agriculture, Aquaculture, and Veterinary Parasitology. … Wildlife and
Fisheries Parasitology. … Ecological and Systematic Parasitology. … Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Parasites. … Immunoparasitology. … Parasitology Educators.Слайд 6Medical parasitology
Medical parasitology is the subject that deals with the
parasites that infect humans, the diseases caused by them, clinical
picture and the response generated by humans against them. It is also concerned with the various methods of their diagnosis, treatment and finally their prevention & control. A parasite is an organism that live on or within another organism called the host.Слайд 7These include organisms such as- Plasmodium spp., the protozoan parasite which
causes malaria. The four species infective to humans are P.
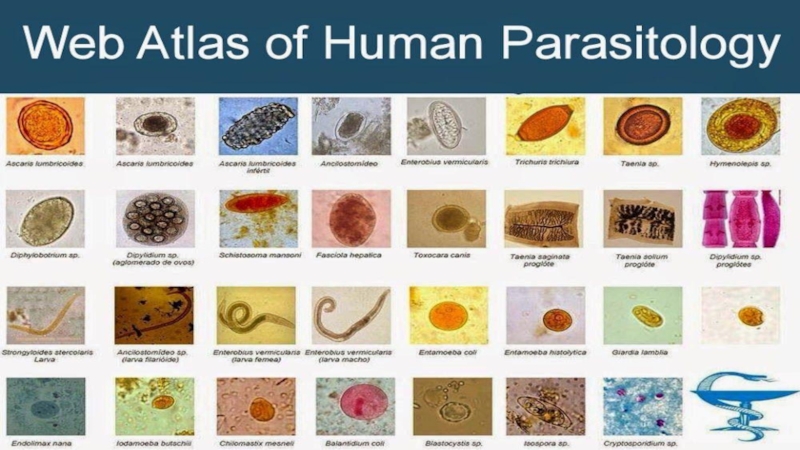
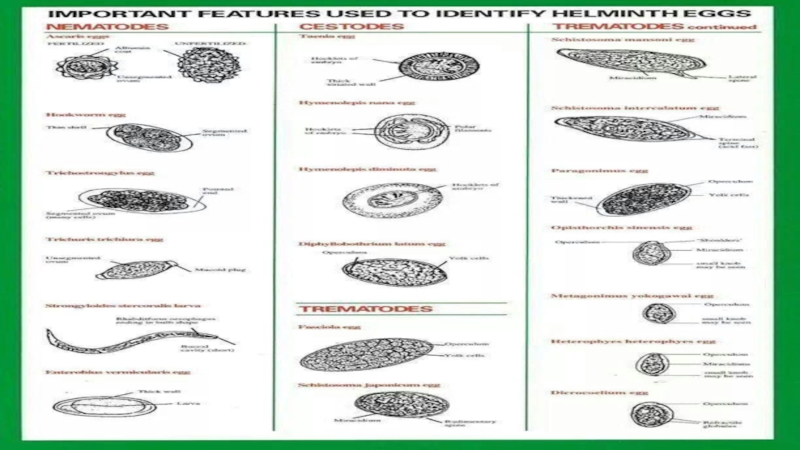
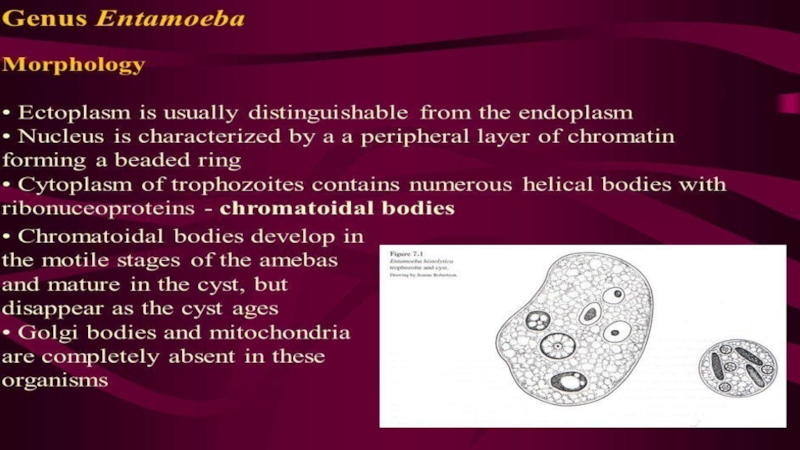
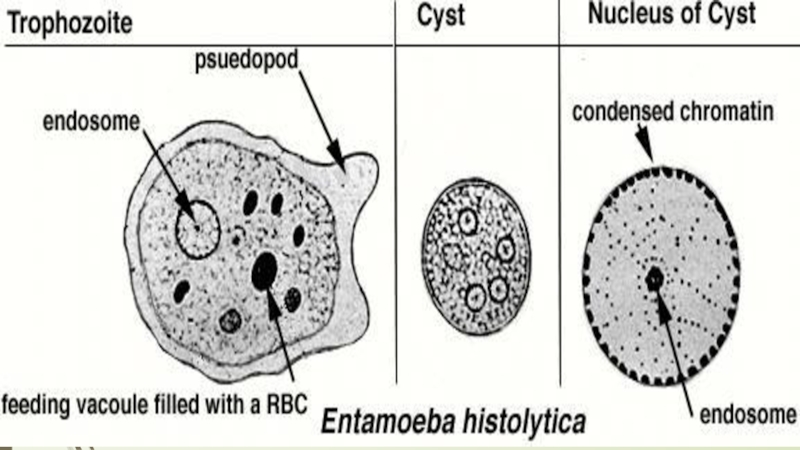
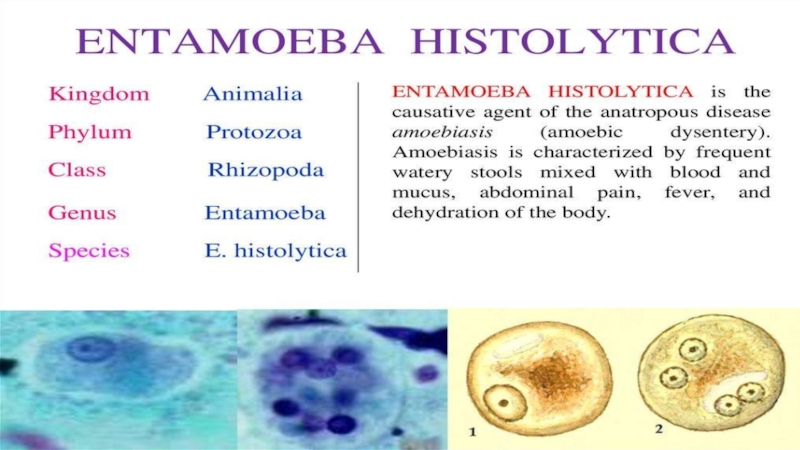
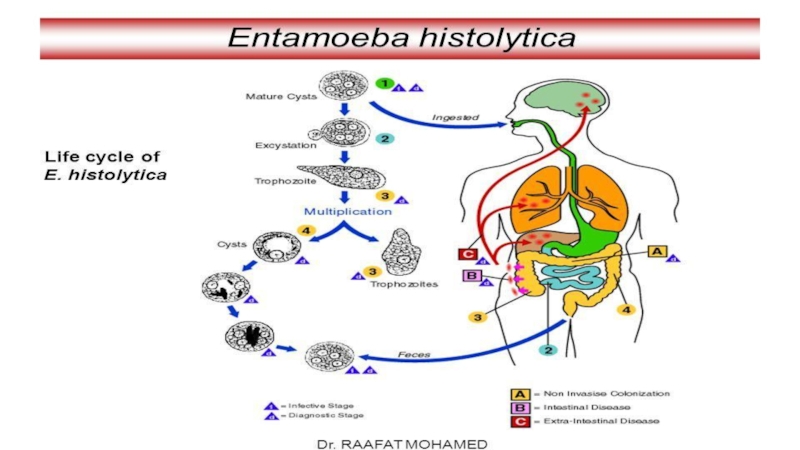
falciparum, P. malariae, P. vivax and P. ovale. Leishmania, unicellular organisms which cause leishmaniasis Entamoeba and Giardia, which cause intestinal infections (dysentery and diarrhoea) Multicellular organisms and intestinal worms (helminths) such as Schistosoma spp., Wuchereria bancrofti, Necator americanus (hookworm) and Taenia spp. (tapeworm) Ectoparasites such as ticks, scabies and lice Medical parasitology can involve drug development, epidemiological studies and study of zoonoses.Слайд 11Class Sarcodina
Sarcodine, any protozoan of the superclass (sometimes class or
subphylum) Sarcodina. These organisms have streaming cytoplasm and use temporary
cytoplasmic extensions called pseudopodia in locomotion (called amoeboid movement) and feeding.Sarcodina (phylum Protozoa, subphylum Sarcomastigophora) A superclass of protozoa which form pseudopodia for feeding and locomotion. There are three classes, and many orders. The majority of species live in marine aquatic environments but some occur in fresh water (and are important members of the soil fauna) and some are parasitic in the intestinal tracts of vertebrates and invertebrates. The superclass includes the Radiolaria, known from the Cambrian, and the Heliozoa, which are exclusively freshwater and have a fossil record that extends back only to the Pleistocene.