Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
BRAZIL The Unknown Giant Luiz Amaral
Содержание
- 1. BRAZIL The Unknown Giant Luiz Amaral
- 2. GeographyTerritory: 8,514,215.3 km² (3,287 357 mi²)Coastline: 7,367
- 3. GeographyMain cities with population in 2005: São
- 4. North 45.27% of the Brazilian territory. 7
- 5. North-East 18.26% of the Brazilian territory. 45
- 6. Center-West 18.86% of the Brazilian territory. 11
- 7. South 6.75% of the Brazilian territory. 24
- 8. South-East 10.85% of the Brazilian territory. The
- 9. São Paulo Over 34 000 000 inhabitants.
- 10. History Brazilian History is divided into three
- 11. Brazilian Territory
- 12. Democracy and dictatorship in modern Brazilian History1889
- 13. Juscelino Kubitschek (JK) (1956 – 1961)Fifty years
- 14. Jânio Quadros (Jan 31 – Aug 25,
- 15. João Goulart (Jango) (1961 - 1964)Left-wing vice
- 16. Castelo Branco(1964 – 1967)Costa e Silva(1967 –
- 17. The Economy1964 – 1967: Economic RecuperationPrograma de
- 18. Redemocratization1974: Gen. Geisel becomes president and promises
- 19. Tancredo Neves (1985)Minister of Justice during Getúlio
- 20. José Sarney (1985 - 1990)Ex-member of the
- 21. Fernando Collor de Melo (1991-1992)First president democratically
- 22. Itamar Franco (1992 - 1994)Vice-president of Collor;
- 23. Fernando Henrique Cardoso (1995 - 2002)FHC consolidated
- 24. Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva (2003 -
- 25. Social Issues in BrazilThe Brazilian economy had
- 26. Racial Issues in BrazilBrazil has a multi-racial
- 27. Improvements in Social IssuesInfant mortality rates dropped
- 28. CURIOSITIES:Orange Pipeline (Sucoduto) 30% of the orange
- 29. CURIOSITIES:How do we vote?www.tse.gov.br/eleicoes/urna_eletronica/simulacao_votacao/UrnaApplet2.htm 100% electronic voting.
- 30. CURIOSITIES:EMBRAER Embraer has become one of the
- 31. CURIOSITIES:BOSSA NOVA (The new beat) Bossa nova
- 32. Web resources http://www.mre.gov.br/cdbrasil/itamaraty/web/ingles/index.htm http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_Brazil http://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/br.html http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Luiz_In%C3%A1cio_Lula_da_Silva http://www.ibge.gov.br/ (not everything is available in English) http://ww2.aegis.com/news/ct/2003/CT030601.html http://www.embraer.com.br/english/content/home/ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bossa_nova
- 33. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
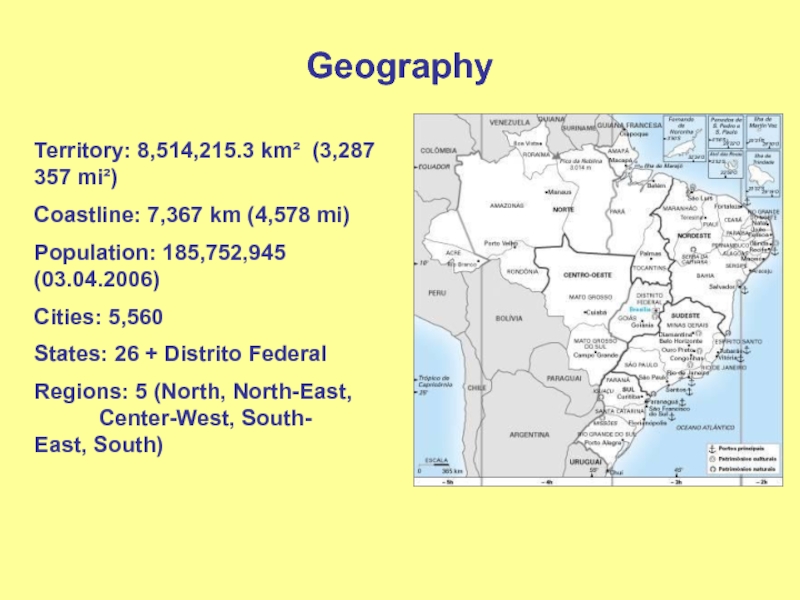
Слайд 2Geography
Territory: 8,514,215.3 km² (3,287 357 mi²)
Coastline: 7,367 km (4,578 mi)
Population:
185,752,945 (03.04.2006)
North-East, Center-West, South- East, South)Слайд 3Geography
Main cities with population in 2005:
São Paulo –
SP (10,927,985)
Rio de Janeiro – RJ (6,094,183)
Salvador –
BA (2,673,560)Belo Horizonte – MG (2,375,329)
Fortaleza – CE (2,374,944)
Brasília – DF (2,333,108)
Curitiba – PR (1,757,904)
Manaus – AM (1,644,690)
Recife – PE (1,501,008)
Porto Alegre – RG (1,428,696)
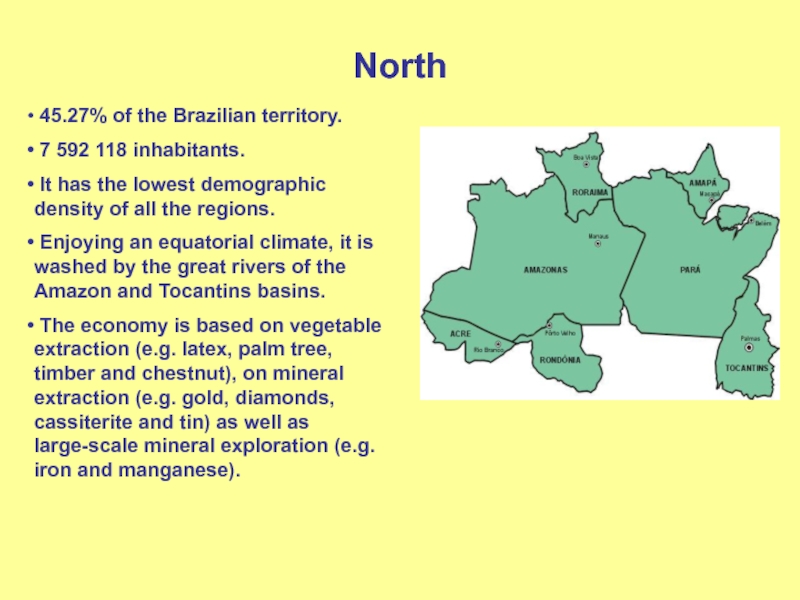
Слайд 4North
45.27% of the Brazilian territory.
7 592 118 inhabitants.
It has the lowest demographic density of all the regions.
Enjoying an equatorial climate, it is washed by the great rivers of the Amazon and Tocantins basins.The economy is based on vegetable extraction (e.g. latex, palm tree, timber and chestnut), on mineral extraction (e.g. gold, diamonds, cassiterite and tin) as well as large-scale mineral exploration (e.g. iron and manganese).
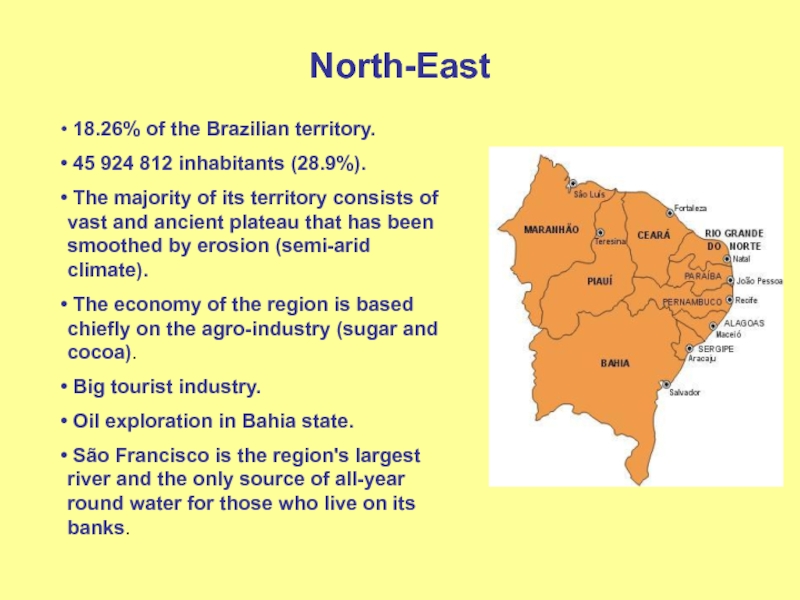
Слайд 5North-East
18.26% of the Brazilian territory.
45 924 812 inhabitants
(28.9%).
The majority of its territory consists of vast and
ancient plateau that has been smoothed by erosion (semi-arid climate).The economy of the region is based chiefly on the agro-industry (sugar and cocoa).
Big tourist industry.
Oil exploration in Bahia state.
São Francisco is the region's largest river and the only source of all-year round water for those who live on its banks.
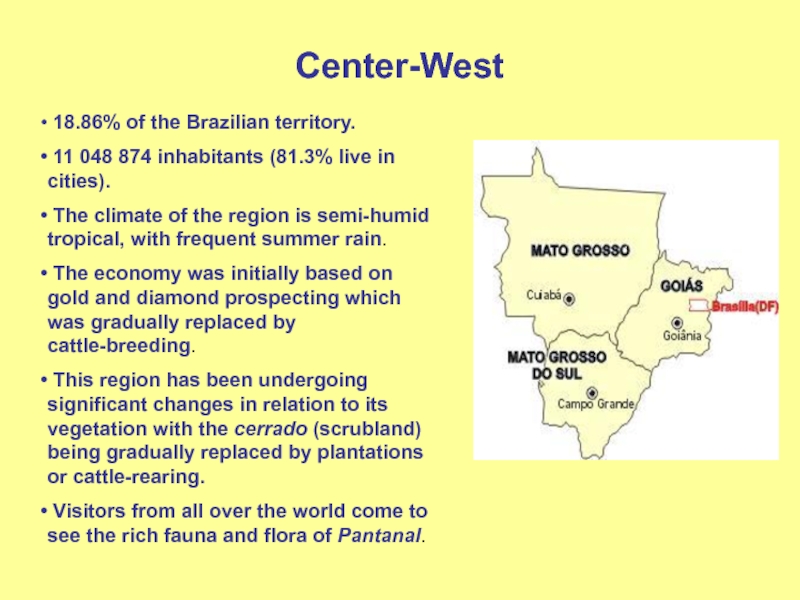
Слайд 6Center-West
18.86% of the Brazilian territory.
11 048 874 inhabitants
(81.3% live in cities).
The climate of the region is
semi-humid tropical, with frequent summer rain.The economy was initially based on gold and diamond prospecting which was gradually replaced by cattle-breeding.
This region has been undergoing significant changes in relation to its vegetation with the cerrado (scrubland) being gradually replaced by plantations or cattle-rearing.
Visitors from all over the world come to see the rich fauna and flora of Pantanal.
Слайд 7South
6.75% of the Brazilian territory.
24 223 412 inhabitants
(74.1% live in cities).
It has a sub-tropical climate, except
in the northern region of the state of Paraná where a tropical climate predominates.The region was colonized by German, Italian, and Azorean immigrants.
Initially based on cattle-rearing, the economy of the South has developed a significant industrial base over recent decades.
Agricultural production makes use of modern cultivation techniques (wheat, soy, rice, maize, beans and tobacco).
Слайд 8South-East
10.85% of the Brazilian territory.
The region has the
largest population: 69 174 339 inhabitants (88% live in cities).
Its typical landscape consists of rounded mountain formations.Its economy is the most developed and industrialized in the country.
Biggest oil basin in Brazil (state of Rio de Janeiro).
Car manufacturers (Volkswagen, Ford, Fiat, Mercedes, Chevrolet, Citroen, Toyota, Honda).
It is the most visited region in Brazil.
Main international airports (Guarulhos – SP, Galeão – RJ).
Слайд 9São Paulo
Over 34 000 000 inhabitants.
Responsible for 35%
of Brazilian GDP.
Its GDP is bigger than the GDP
of any other country in Latin America except Mexico.Its GDP is twice the Argentinean GDP.
It has the best research institutions in Latin America (USP and UNICAMP).
The state houses many of the largest Brazilian and international companies and foreign banks with head-offices in the country.
It is also the headquarters of the eighth largest stock market in the world and the second largest future market.
http://www.latinbusinesschronicle.com/statistics/gdp/ranking.htm
Слайд 10History
Brazilian History is divided into three periods:
Colony (1500
– 1822)
Empire (1822 – 1889)
Republic (1889 – present)
Brazilian CapitalsSalvador (1549 – 1773)
Rio de Janeiro (1773 – 1960)
Brasília (1960 – present)
Political Organization
Hereditary captaincies (colony)
States (previous provinces) with more local power
States as part of a federative republic
Слайд 12Democracy and dictatorship in modern Brazilian History
1889 – 1930: Constitutional
Democracy.
1930 – 1945: Military coup places Getúlio Vargas in power.
1930 – 1937: Vargas interim presidency.1937 – 1945: Estado Novo (New State).
1945 – 1964: Democratic period.
1964 – 1985: Military Dictatorship.
1985 – present: Modern Democracy.
Слайд 13Juscelino Kubitschek (JK)
(1956 – 1961)
Fifty years in five.
Building of Brasília.
Era
of great hope.
Influx of international investments.
The economy boomed, but at
some cost.Inflation and devaluation of the currency.
Слайд 14Jânio Quadros
(Jan 31 – Aug 25, 1961)
Elected with no congressional
support.
Polemic figure (prohibited bikinis in Copacabana).
Right-wing president who established relations
with Cuba and Russia.Resigned in an attempt to gain political power.
His resignation created a political crisis.
Слайд 15João Goulart (Jango)
(1961 - 1964)
Left-wing vice president.
1961 – 1963: Parliamentary
system.
1963 – 1964: Presidential system.
Nationalist reforms to face social problems.
Nationalization
of companies.Increase of organized social groups.
Nationalism vs Imperialism.
Слайд 16Castelo Branco
(1964 – 1967)
Costa e Silva
(1967 – 1969)
Emílio Médici
(1969 –
1974)
Ernesto Geisel
(1974 - 1979)
João Baptista Figueiredo
(1979 - 1985)
Brazilian Military Presidents
Слайд 17The Economy
1964 – 1967: Economic Recuperation
Programa de Ação Econômica do
Governo (PAEG)
Reduced budget, deficit, salaries, inflation. GDP grew again.
1969 –
1973: The Brazilian Miracle GDP grew 11% a year.
Growth was based on more debts and external dependency.
Salaries were very low, and social benefits were lost.
1973 – 1979: Economic Problems
Increase of internal and external debts.
1978 : Strikes in São Paulo.
1980’s: “The lost decade”
Inflation soared, the debt destroyed the Brazilian economy.
IMF imposed a painful austerity program on Brazil.
Слайд 18Redemocratization
1974: Gen. Geisel becomes president and promises democracy.
1979: Gen. Figueiredo
becomes president and promises to finish Geisel’s work.
1979: General amnesty
(including those who tortured civilians).New political parties are allowed to exist.
1982: General elections for governors and state representatives.
1984 – Diretas Já! – Direct (vote) now! A civil movement for direct presidential elections.
Слайд 19Tancredo Neves
(1985)
Minister of Justice during Getúlio Varga’s government (1935).
Prime Minister
of Jango (1961).
Jan 15, 1985: elected president by the congress.
Died
in Mar 15, 1985.Tancredo was the hope for a new country.
Слайд 20José Sarney
(1985 - 1990)
Ex-member of the ARENA, vice-president of Tancredo.
His
government faced several economic problems: huge foreign debt, and inflation.
Plano
Cruzado (economic plan) did not work.1986: Elections for congress.
1988: New constitution.
Слайд 21Fernando Collor de Melo
(1991-1992)
First president democratically elected since 1961.
He was
a good looking candidate that promised to end corruption and
to modernize the country.Involved in many scandals, he was impeached in 1992.
Several rallies occurred throughout the country against him.
Слайд 22Itamar Franco
(1992 - 1994)
Vice-president of Collor; formally took office in
Dec 1992.
Inflation reached 6000% in 1993.
Franco managed to unite several
political parties and create a successful economic plan (Plano Real) in 1994 that reduced inflation to a single digit.His minister of Economy was elected president in 1994.
Слайд 23Fernando Henrique Cardoso
(1995 - 2002)
FHC consolidated the political and economic
stability.
He privatized several companies (including CSN, and EMBRATEL).
After some
years of economic growth, Brazil’s economy suffered the consequences of world economic crisis. FHC was reelected in 1998.
Слайд 24Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva
(2003 - present)
He had a very
poor childhood. At age 12 he worked as a shoeshine
boy and street vendor.In 1978, he was elected president of the Steel Workers' Union of São Bernardo.
In 1980, he and a group of academics, union leaders and intellectuals founded the Labor Party (Partido dos Trabalhadores - PT).
During the 1990’s PT shifted from a left-wing party to more center-left position.
LULA was elected president in 2002.
Instead of deep social changes (as proposed in the past) his government chose a reformist line, passing new retirement, tributary, labor, and judicial laws, and discussing a university reform.
Слайд 25Social Issues in Brazil
The Brazilian economy had a belated flourishing,
even for Latin American standards.
During the 19th century Brazil
was poorer than Peru and growth was slow. During the 20th century the South and South-East regions developed much faster. This created the migration problem.
In the 20th century an educational system had to be built.
The quality of public education is still questionable in some areas.
Before 1950 there were no good public hospitals, and very few public health campaigns.
Слайд 26Racial Issues in Brazil
Brazil has a multi-racial society.
Mulatos
Caboclos
Cafuzos
Brazil was
the last country in the Americas to end slavery (1888).
Social
integration of African-Brazilians and other minorities (caboclos, cafuzos, etc) has been a slow process.The first affirmative action policies were introduced in the last ten years.
Racial minorities still have less access to good school, and good health system.
Different developing rates among different geographic regions increased the problem.
Слайд 27Improvements in Social Issues
Infant mortality rates dropped from 41.1% in
1992 to 27.5% in 2003 (15.18% in Argentina; 5.7% in
USA, but 14% among African Americans).97.3% of children (7 to 14) in school in 2003.
99.5% of homes have access to electricity, 89.6% receive public clean water.
17.5% have a computer at home, 13.2% have internet access (although Brazil represents 32% of internet access in Latin America).
“Fome Zero” (Zero Hunger) – A social program that distributes money to selected regions and cities whose inhabitants suffer severe difficulties.
“Bolsa Família” (Family Aid) – the program consists primarily of financial aid to families with incomes of less than US$40.00 per month. It demands that the families send their children to school and keep their vaccines up to date.
Aids program - Brazil's guarantee of access to free antiretroviral (ARV) drugs since 1996. The government promotes public campaigns to educate the population.
Слайд 28CURIOSITIES:
Orange Pipeline (Sucoduto)
30% of the orange produced in the
world (USA – 18%).
Brazil exports to Europe, USA, China,
Japan, Russia, India (among others).Слайд 29CURIOSITIES:
How do we vote?
www.tse.gov.br/eleicoes/urna_eletronica/simulacao_votacao/UrnaApplet2.htm
100% electronic voting.
We vote using
electronic voting machines.
Each candidate has one number.
We enter
the candidate’s number and see his/her picture and name on the screen.Official results in less than 24 hours.
Elections in Brazil are considered the most well organized in the continent.
Слайд 30CURIOSITIES:
EMBRAER
Embraer has become one of the largest aircraft manufacturers
in the world by focusing on specific market segments with
high growth potential in commercial, defense, and executive aviation.Embraer was Brazil’s largest exporter from 1999 to 2001 and the second largest in 2002, 2003 and 2004. It currently employs more than 16,500 people, 85.5% based in Brazil.
Слайд 31CURIOSITIES:
BOSSA NOVA (The new beat)
Bossa nova is a style
of Brazilian music invented in the late 1950s by a
group of middle-class students and musicians living in the Copacabana and Ipanema beachside districts of Rio de Janeiro.The music derives from samba but is more complex harmonically and less percussive.
Perhaps the best known bossa nova song is Antonio Carlos Jobim's “The Girl from Ipanema”.
Bossa Nova was popularized in the US by Stan Getz, João Gilberto, Tom Jobim, Frank Sinatra, and Vinicius de Moraes.