Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Department of Theoretical Mechanics, Engineering and Robotic Systems (202)
Содержание
- 1. Department of Theoretical Mechanics, Engineering and Robotic Systems (202)
- 2. Theoretical mechanics. Lecture1. IntroductionTheoretical mechanics is the
- 3. Слайд 3
- 4. Statics Statics is concerned with bodies that are
- 5. 1. Basic conceptions: rigid body, particle, force,
- 6. Example of rigid body system: the mechanism
- 7. A particle (материальная точка) If the dimensions of
- 8. Force (сила) Force is one of
- 9. Force classification The physical nature of forces is
- 10. A force is vector value.It has three
- 11. System of forces (система сил) A set of
- 12. Equivalent force systems (эквивалентные системы сил) Two force
- 13. A resultant of a force system is
- 14. Balanced force system (equilibrated force system) (уравновешенная
- 15. 2. Axioms of staticAxiom 1. A rigid
- 16. Axiom 2. The action of a given
- 17. Слайд 17
- 18. Principle of transmissibility: A force point of application
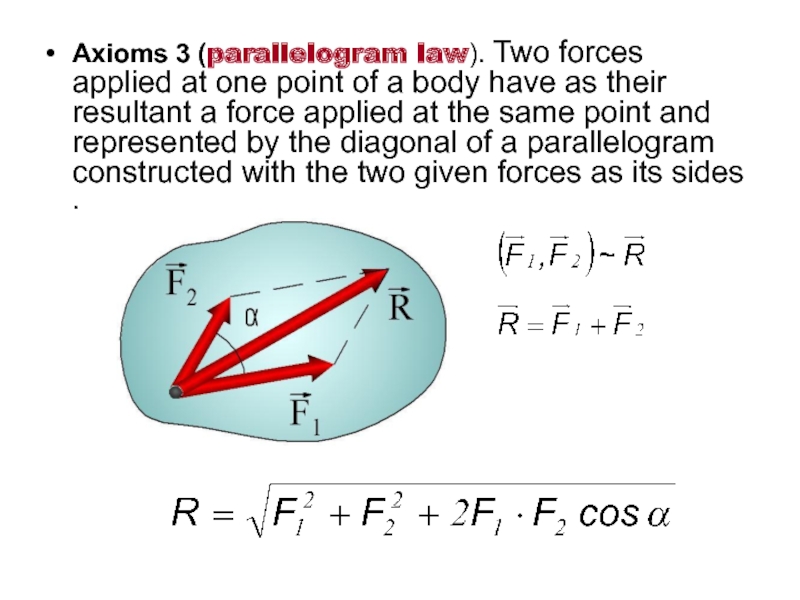
- 19. Axioms 3 (parallelogram law). Two forces applied
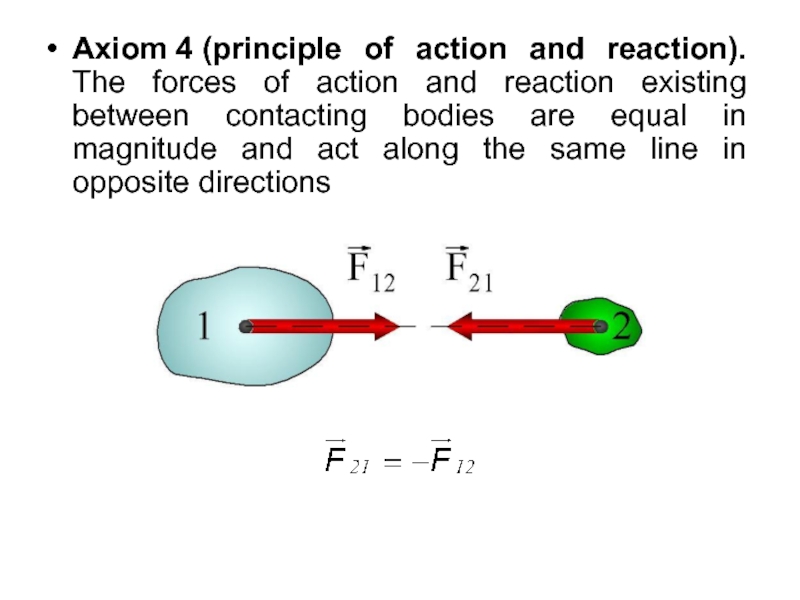
- 20. Axiom 4 (principle of action and reaction).
- 21. Axiom 5 (principle of solidification) (принцип отвердевания) If
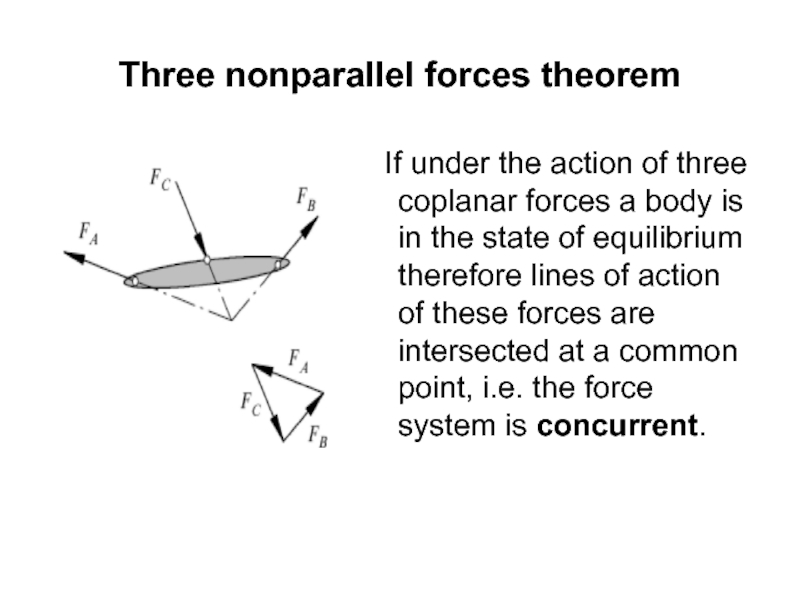
- 22. Three nonparallel forces theorem If under the action
- 23. Скачать презентанцию
Theoretical mechanics. Lecture1. IntroductionTheoretical mechanics is the branch of the physical sciences that deals with the mechanical motion of bodies, i.e. changing of relative position of bodies in space in the
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Department of
Theoretical Mechanics, Engineering
and Robotic Systems
(202)
Methodic room
227 m.b.
Слайд 2Theoretical mechanics.
Lecture1.
Introduction
Theoretical mechanics is the branch of the physical sciences
that deals with the mechanical motion of bodies, i.e. changing
of relative position of bodies in space in the course of time.Слайд 4Statics
Statics is concerned with bodies that are at rest or
have uniform motion. Such bodies are said to be in
equilibrium.Statics provides methods for determination of support reactions and relationships between internal force distribution and external loads for structures.
Слайд 51. Basic conceptions:
rigid body, particle, force, force system,
rigid body equilibrium
A
rigid body (абсолютно твердое тело)
A body is called rigid if
the distance between any two points of the body does not change during its interaction with other solids. Consequently, the angle between any two straight lines in the body remains constantA rigid body system (система твердых тел)
A set of rigid bodies connected among themselves is called rigid body system
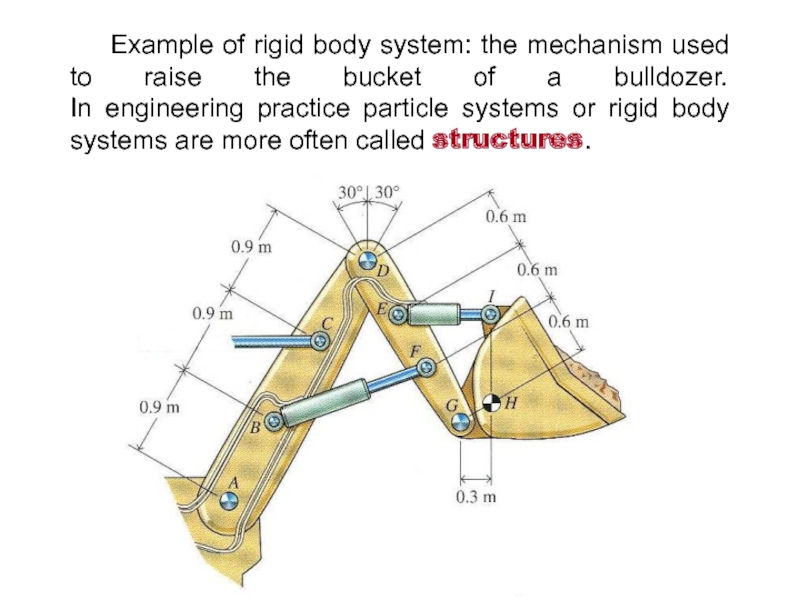
Слайд 6 Example of rigid body system: the mechanism used to raise
the bucket of a bulldozer. In engineering practice particle systems or
rigid body systems are more often called structures.Слайд 7A particle (материальная точка)
If the dimensions of a body are
irrelevant to the description of its position the body may
by treated as aparticle.
A particle system (система материальных точек, материальная система)
A particle system is a set of particles whose motions are interconnected. So, a position, velocity and acceleration of particle in the system are connected with same parameters of other particles.
The sample of particle system is system of planets that rotates about the Sun.
Слайд 8Force (сила)
Force is one of the main fundamental
quantities of mechanics.
A force is measure of mechanical interaction between
two bodies. So when we say “a force acts on the body” we know that there is another body acting as a source of the force.As a result of this interaction bodies can be accelerated or deformed.
Слайд 9Force classification
The physical nature of forces is not studied in
mechanics. We distinguish forces solely by the mode of their
interaction :a force may be exerted at a distance as in the case of gravitational or magnetic attraction (long-range interaction);
a force may act through actual contact as the lift force acting on the airplane wing in incident flow
(close-range interaction)
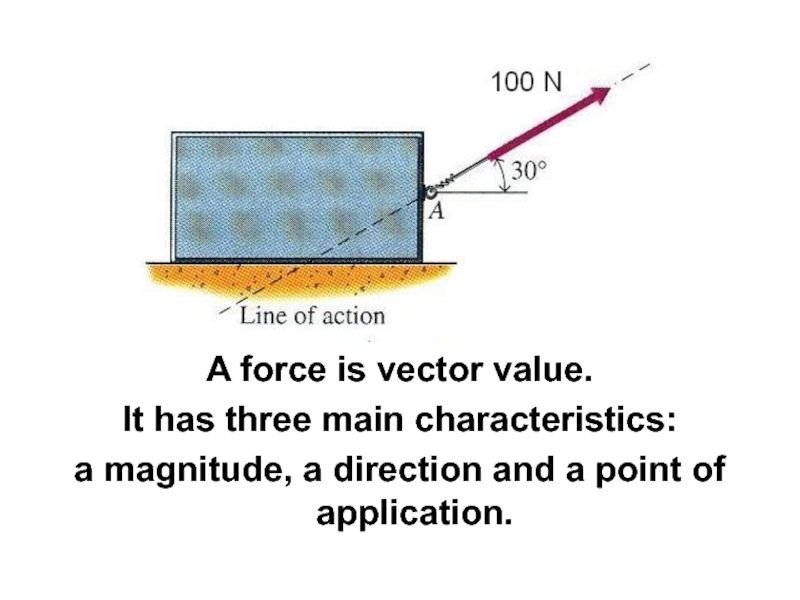
Слайд 10A force is vector value.
It has three main characteristics:
a
magnitude, a direction and a point of application.
Слайд 11System of forces (система сил)
A set of forces applied to
a material object (particle, rigid body, system of rigid bodies)
and treated as group is called system of forces.Example. Forces that act on an airplane: tractive force, lift force, weight, drag force.
Слайд 12Equivalent force systems (эквивалентные системы сил)
Two force systems are said
to be equivalent if they produce the same external effect
when applied in turn to a given body.Resultant of force system (равнодействующая системы сил)
If a force system is equivalent to only single force, this force is called a resultant.
Слайд 13 A resultant of a force system is the simplest equivalent
system to which the original system can be reduced.
The process
of reducing a force system to a simpler equivalent system is called composition (приведение).The process of expanding a force or a force system into a less simple equivalent system is called resolution (разложение на составные части) .
A component (компонента) of a force is one of the two or more forces into which the given force may be resolved.
Слайд 14Balanced force system (equilibrated force system) (уравновешенная система сил, система
сил эквивалентная нулю)
A system of forces is called balanced if
the force system resultant is zero.A rigid body under the action of balanced force system is in the state of equilibrium, i.e. body is at the rest or moves translational with uniform velocity along straight line.
Слайд 152. Axioms of static
Axiom 1. A rigid body which is
acted upon by two forces will be in equilibrium if
and only if the two forces have the same magnitude and the same line of action but opposite sense.Слайд 16Axiom 2. The action of a given force system on
a rigid body remains unchanged if another balanced force system
is added to, or subtracted from, the original system. In a special case, in accordance with Axiom 1, this balanced force system can consist of two equal and opposite forces acting along the common line .It follows from Axiom 2 (corollary) that a force may be applied at any point on its given line of action without altering the resultant effects of the force, external to the rigid body on which it acts. The corollary is named the principle of transmissibility.
Слайд 18Principle of transmissibility:
A force point of application can be shifted
along force’s line of action without change to the state
of the body.Force is sliding vector.
Без изменения состояния тела
точка приложения силы может быть перемещена вдоль линии действия силы.
Сила – скользящий вектор