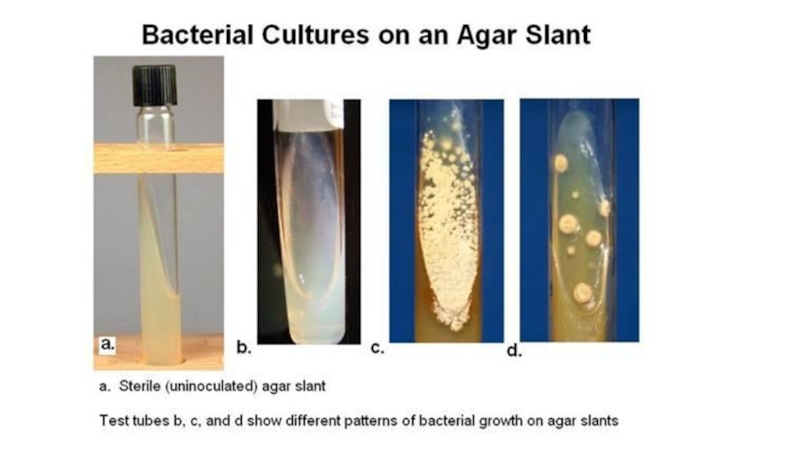
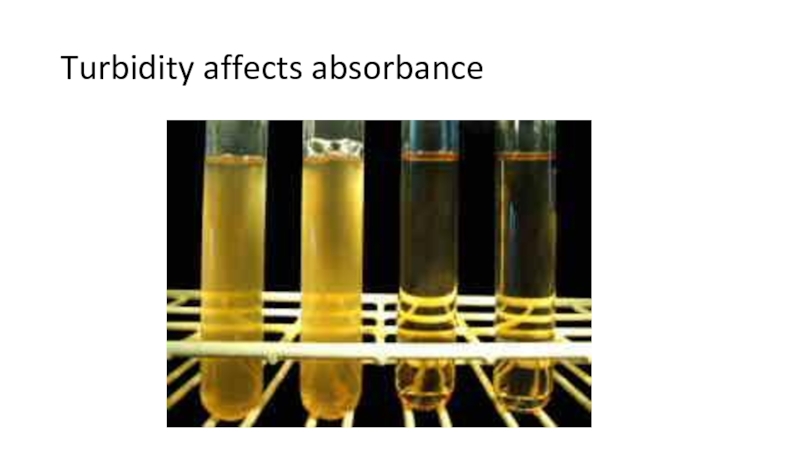
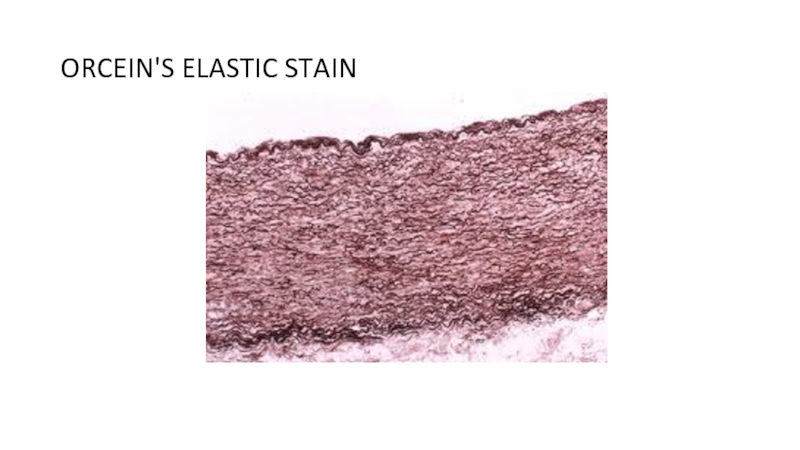
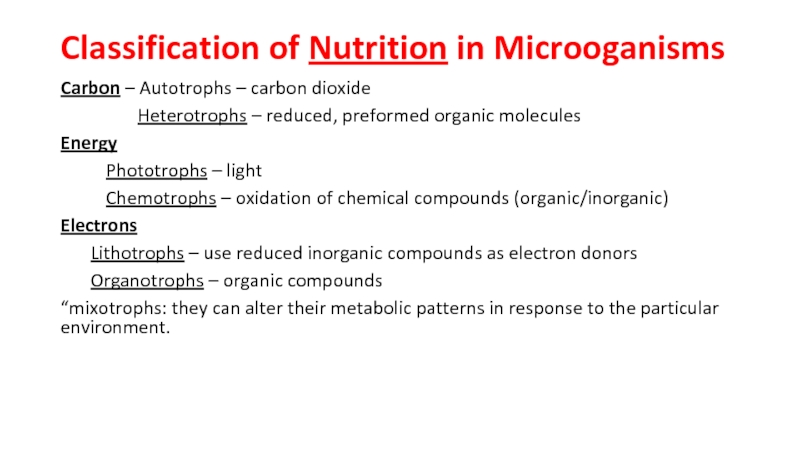
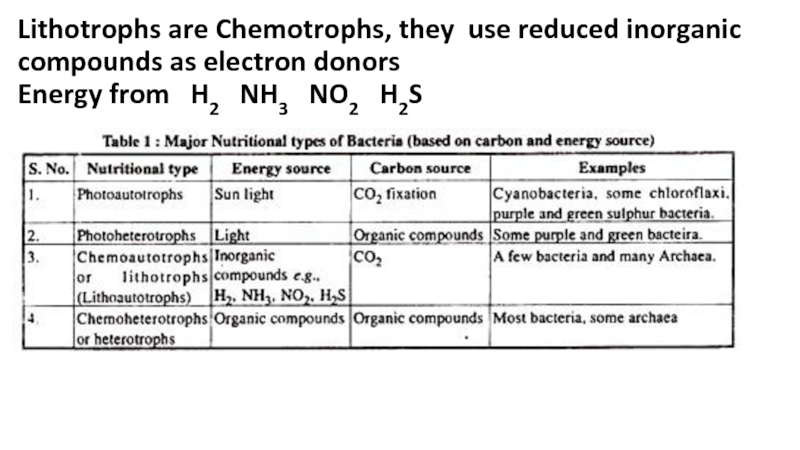
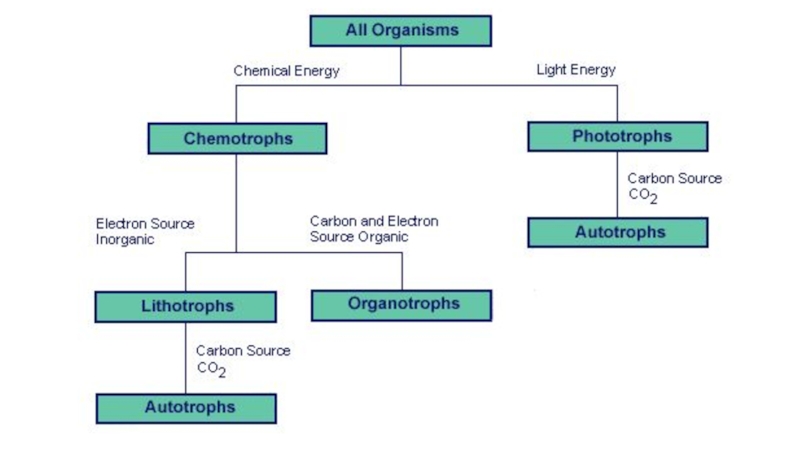
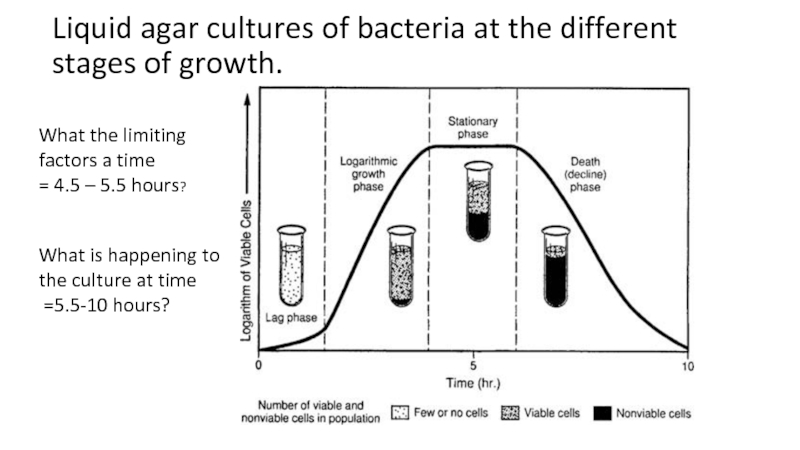
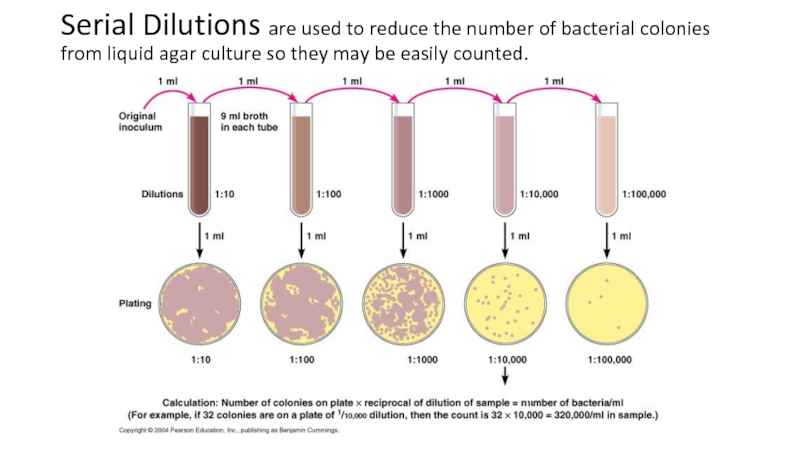
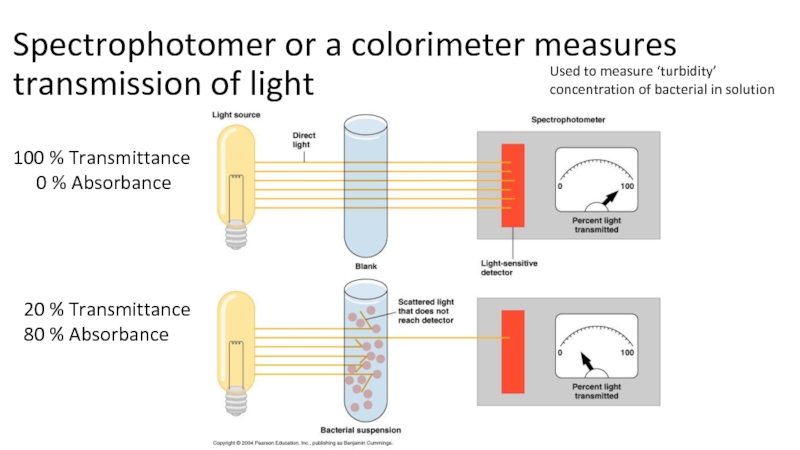
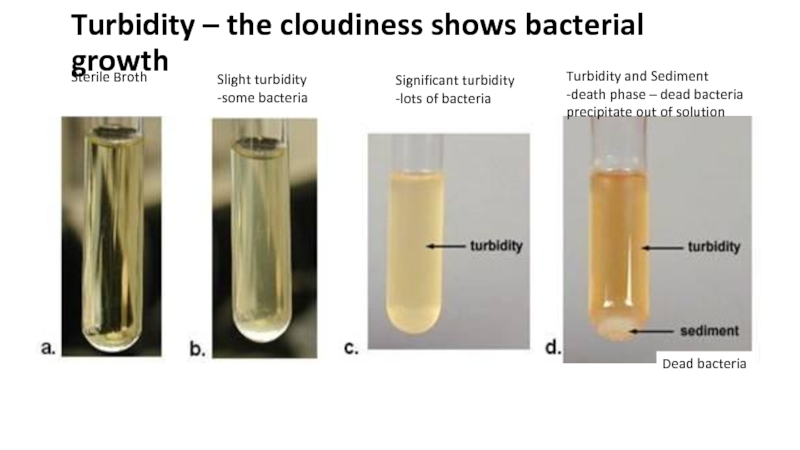
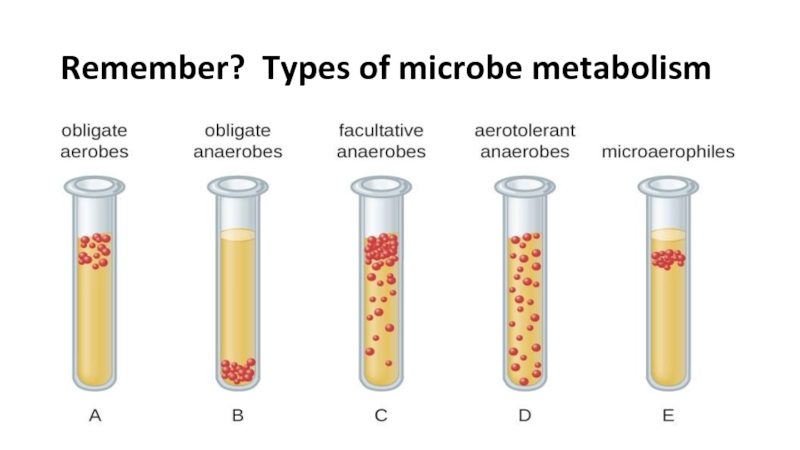
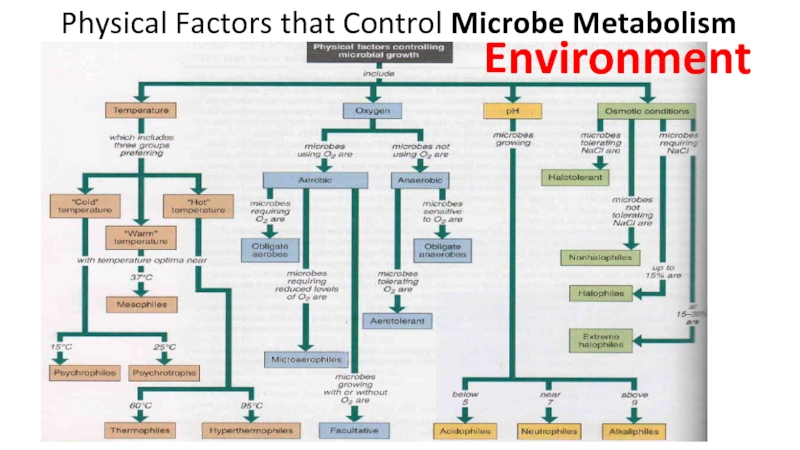
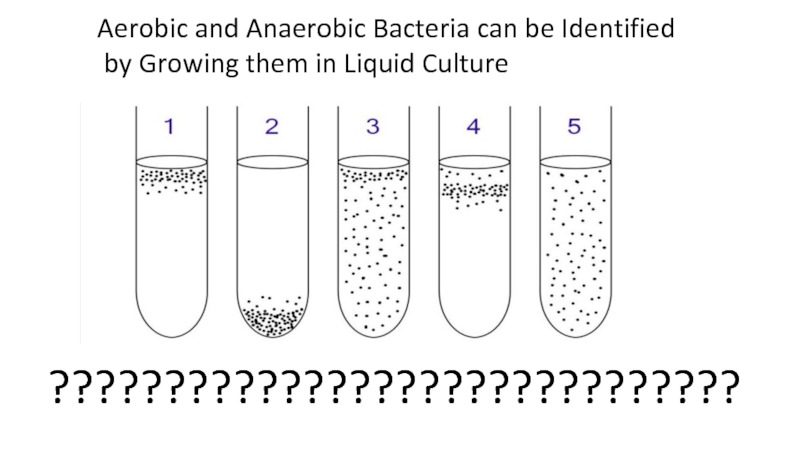
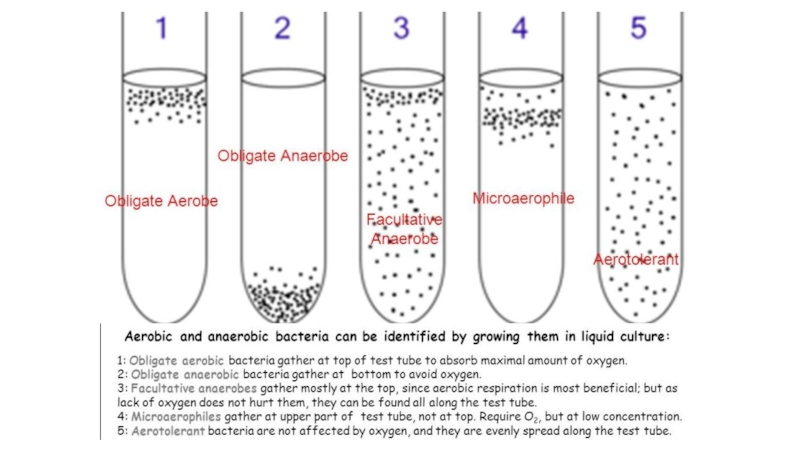
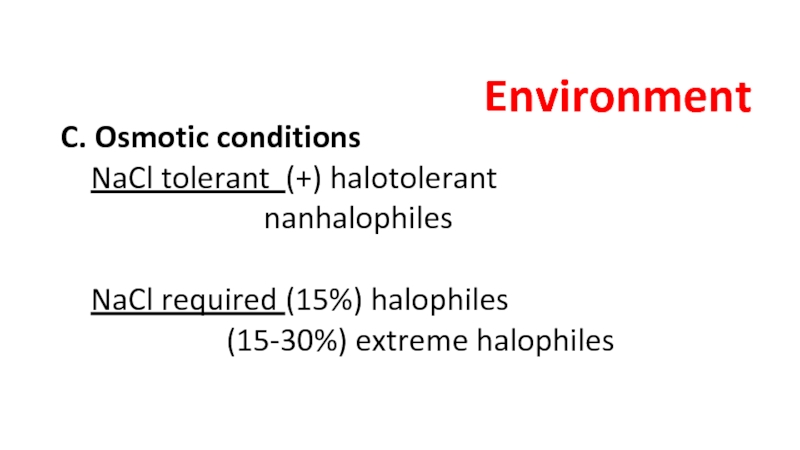
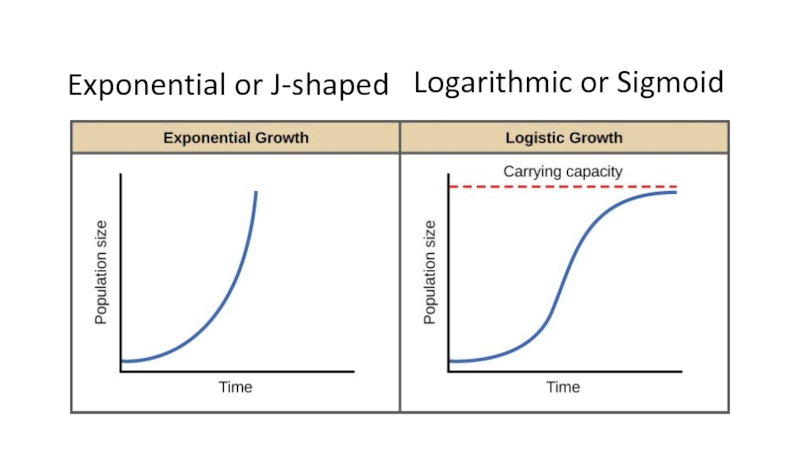
the main types of nutrition in microorganisms
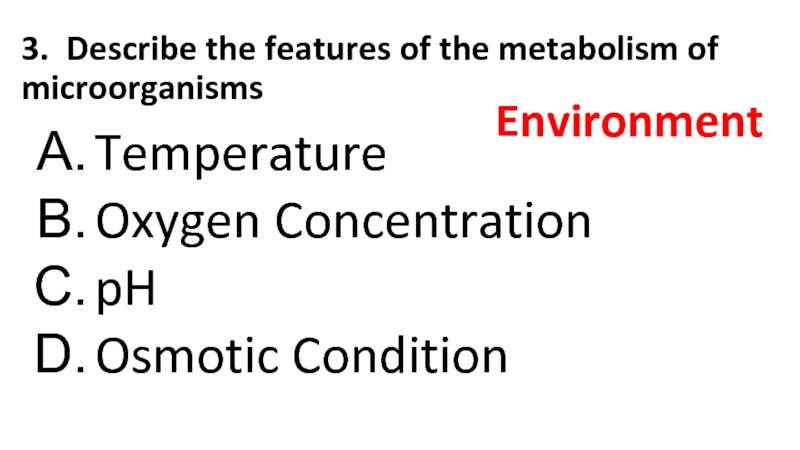
11.4.3.2 Describe the features
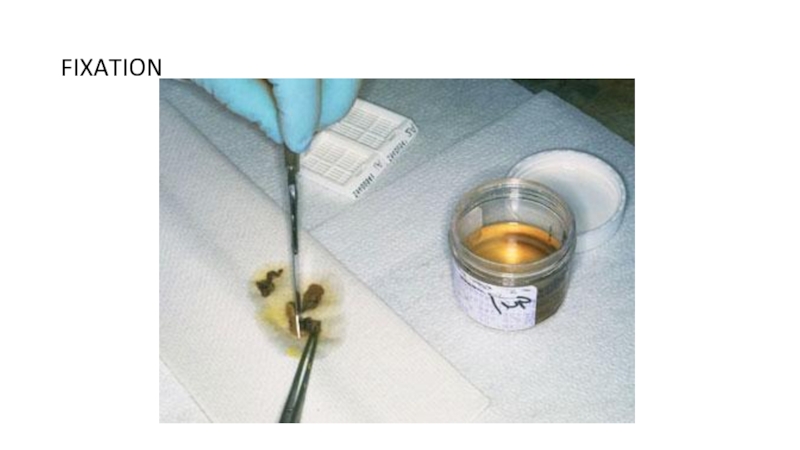
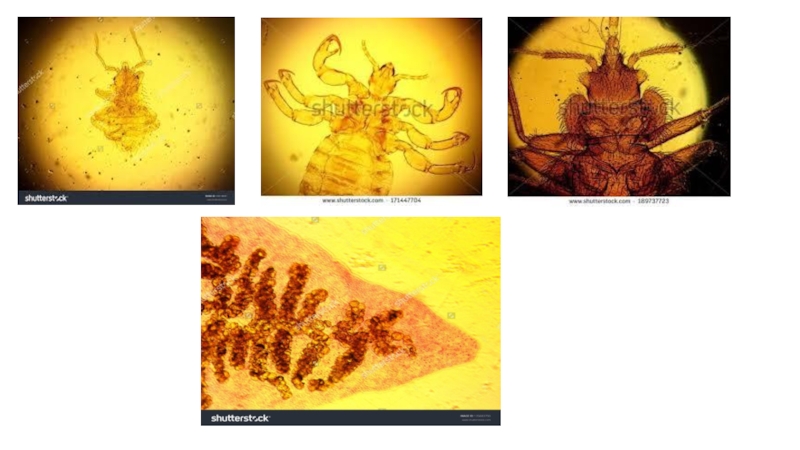
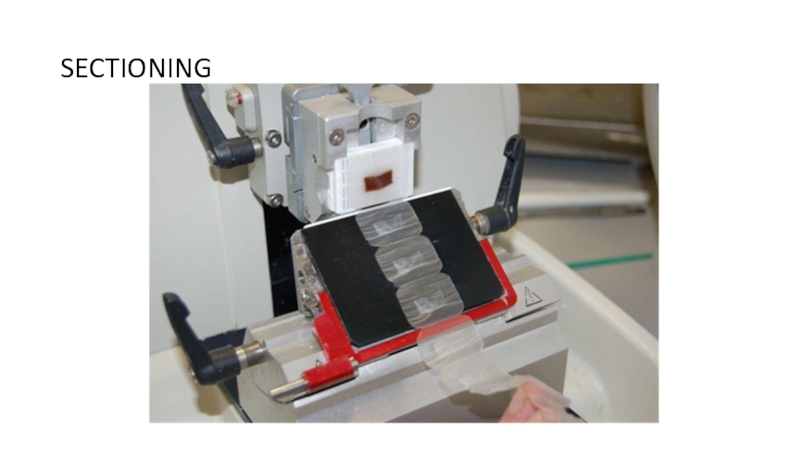
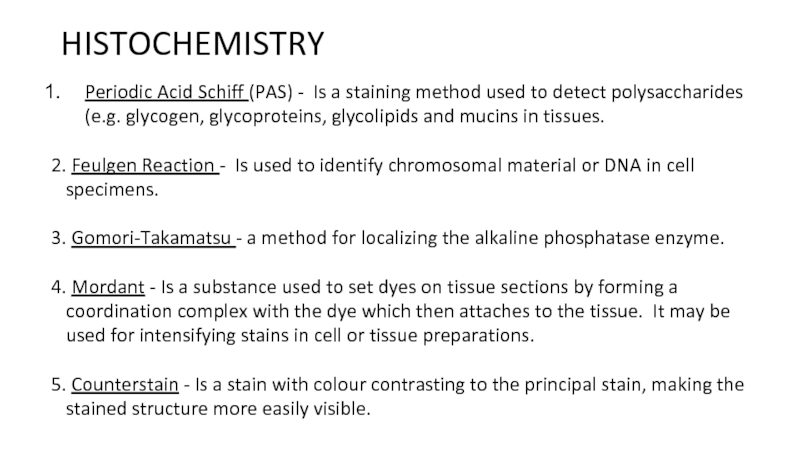
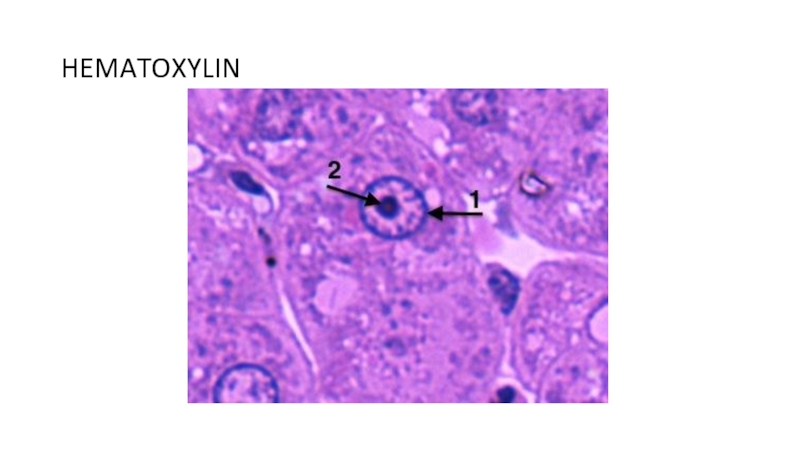
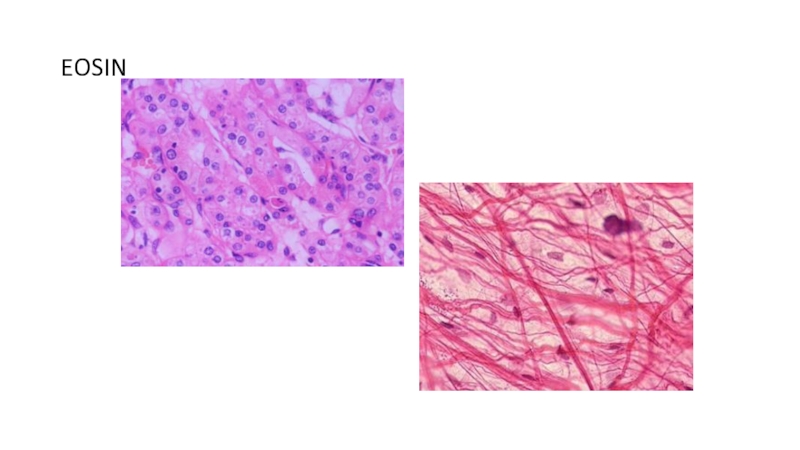
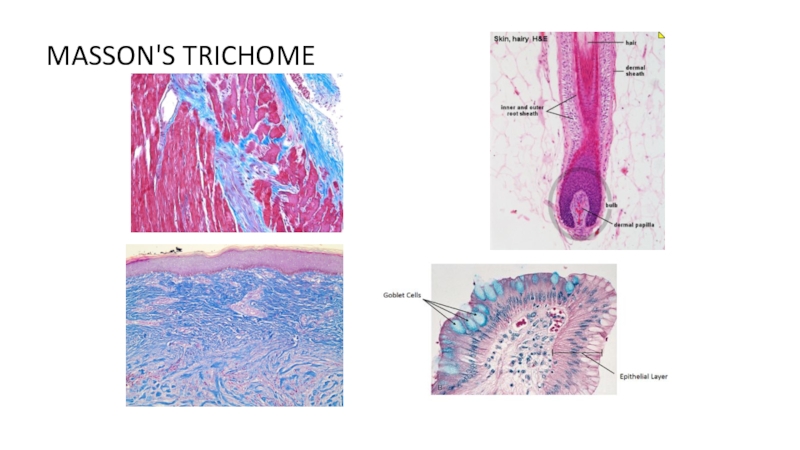
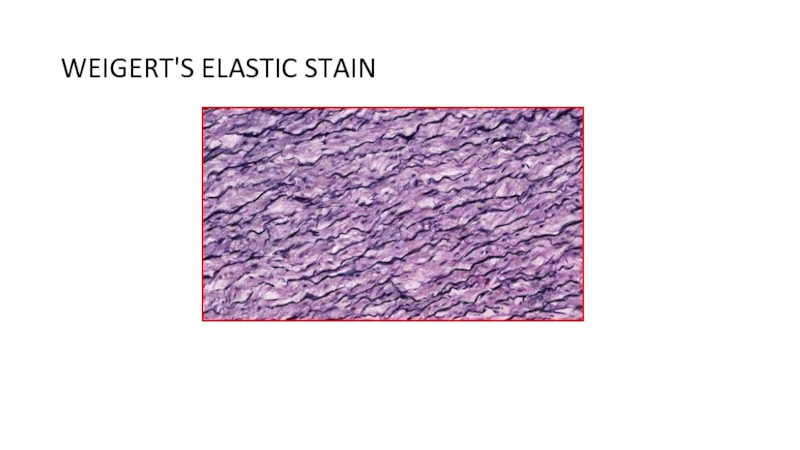
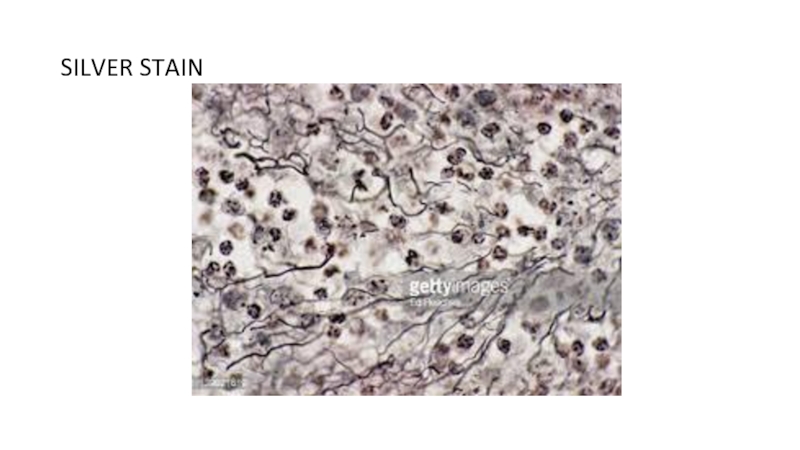
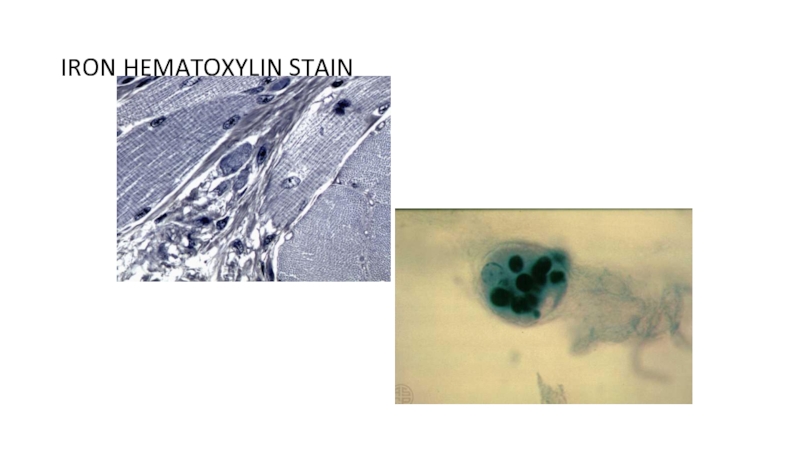
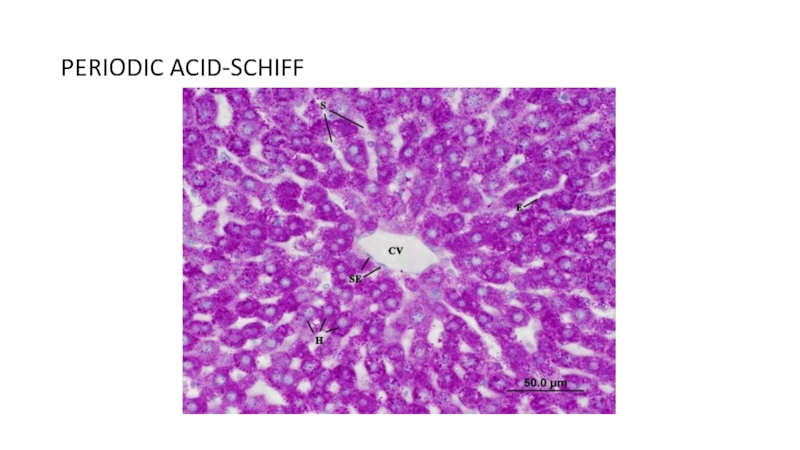
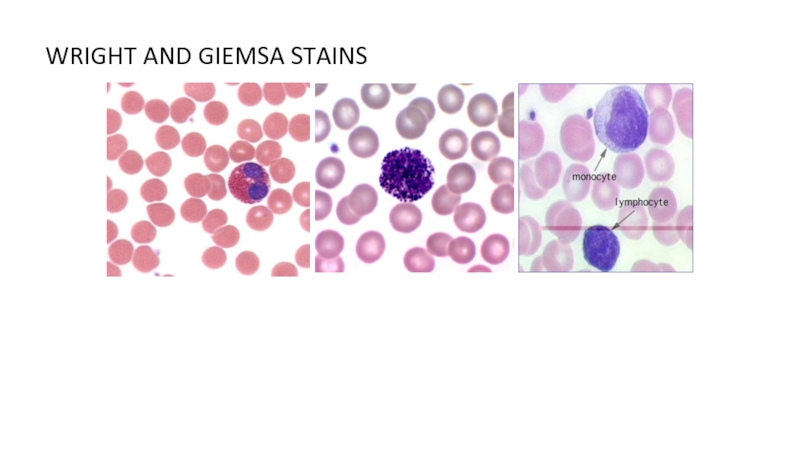
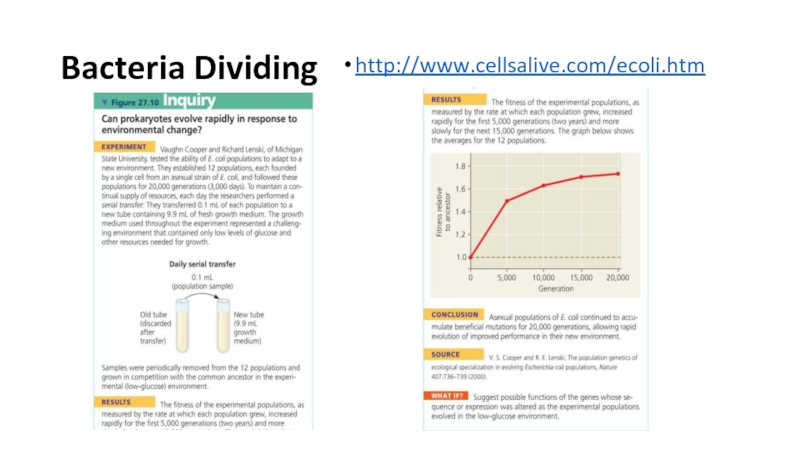
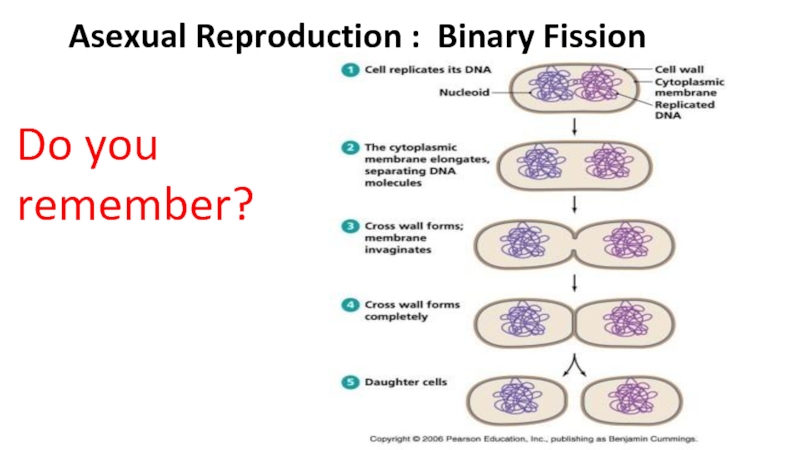
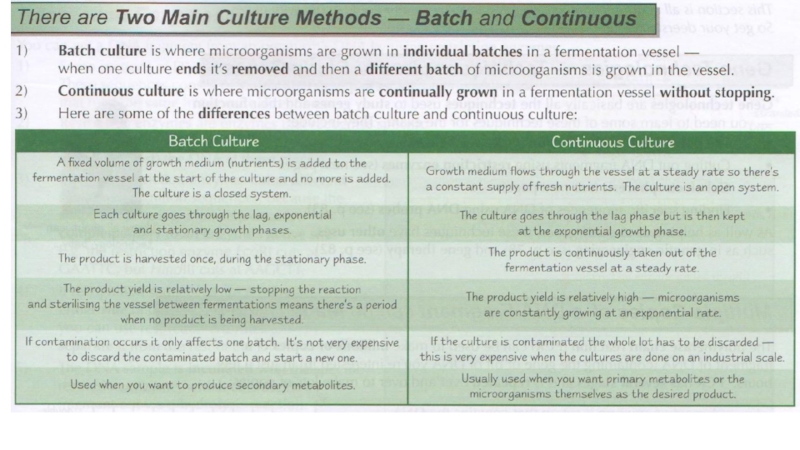
of metabolism of microorganisms11.4.3.3 Describe the methods for the preparation of permanent stains.
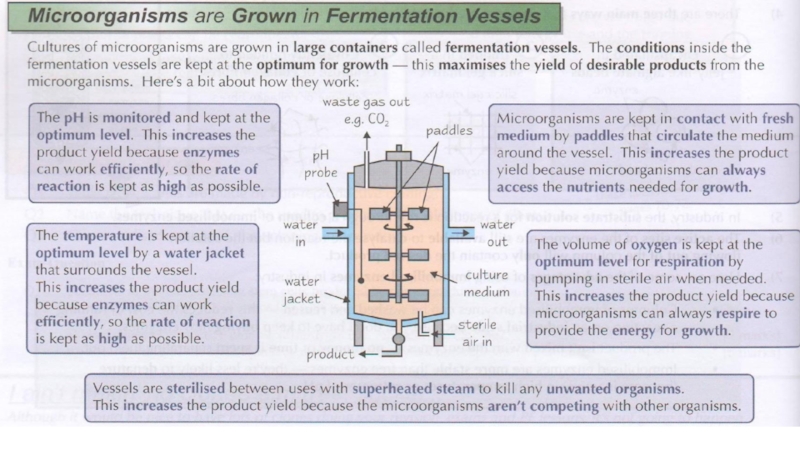
11.4.3.4 Describe the structure and the working principle of the fermenter
Success Criteria