Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
KIMEP Department of General Education
Содержание
- 1. KIMEP Department of General Education
- 2. Lecture 5 Food and Agriculture
- 3. Thou shouldst eat to live; not live to eat. Sokrates, Ancient Greek philosopher
- 4. OutlineFood and NutritionMajor Food SourcesSoil: A Renewable ResourceOther Agricultural ResourcesNew Crops and Genetic EngineeringSustainable Agriculture
- 5. World food supplies: 1950 versus 2000Richer countries:
- 6. World Famines: large-scale food shortages, massive
- 7. Essential NutrientsMalnourishment - a
- 8. Protein Deficiency DiseasesKwashiorkor –
- 9. Overnutrition -
- 10. MAJOR FOOD SOURCESWheat, rice, maize are
- 11. Rational NutritionNutrition – intake of food needed
- 12. 6 Main Nutrition ComponentsProteins, Fats, Carbohydrates –
- 13. Eating a Balanced Diet - Food Pyramid
- 14. Meat, Milk, and SeafoodMilk & meat: highly
- 15. Environmental Issues with Raising BeefEvery 16 kg
- 16. SOIL - A VALUABLE RESOURCESoil - a
- 17. Soil OrganismsWithout soil organisms, the earth would be covered with sterile mineral particles.
- 18. - Soils are stratified into horizontal layersTogether they make up the soil profileSoil Profile
- 19. WAYS WE USE & ABUSE SOILMuch potential
- 20. ErosionErosion: the process
- 21. OTHER AGRICULTURAL RESOURCESWaterFertilizerEnergy Pesticides Agriculture is the
- 22. FertilizersNitrogen (N), potassium (K), and phosphorus (P)
- 23. Up to 90% of all pesticides never reach target organisms.
- 24. NEW CROPS & GENETIC ENGINEERING~3,000 plant
- 25. Green Revolution "Miracle Crop" YieldThey are "High
- 26. Genetic EngineeringGenetic engineering is the splicing a
- 27. SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURESustainable agriculture (regenerative
- 28. Organic and Locally Grown Foods
- 29. Sustainable agriculture aims to produce food and
- 30. Sustainable farming:
- 31. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 4Outline
Food and Nutrition
Major Food Sources
Soil: A Renewable Resource
Other Agricultural Resources
New
Crops and Genetic Engineering
Sustainable Agriculture
Слайд 5World food supplies: 1950 versus 2000
Richer countries: the most common
dietary problem is over-nutrition (obesity)
Sub-Saharan Africa: food production has not
kept pace with rapid population growthAsia: most rapid increase in crop production and this accompanied rapid population growth
Chronic Hunger - within families that don't get enough to eat, women and children have the poorest diets.
Nutrition and Food Supplies
Слайд 6World Famines: large-scale food shortages, massive starvation.
Causes are:
Environmental conditions - natural disasters, drought, insects
National politics - corruption, oppression
Armed conflict
Economics - price gouging, poverty, landlessness
Слайд 7 Essential Nutrients
Malnourishment - a nutritional imbalance caused
by a lack of specific dietary components (wrong ratio of
nutrients)polished rice is low in nutrients
Undernourishment – < 90% of min caloric intake needed
NUTRIENT DEFICIENCY:
Protein deficiency diseases - kwashiorkor, marasmus.
Iron deficiency (anemia) - most common in the world and most severe in India.
Iodine deficiency - thyroid problems (goiter, etc) (problem in Almaty)
Selenium deficiency – thyroid and heart problems (typical for China)
Vitamin A deficiency – blindness, eye problems (beta-carotene – precursor of vit A)
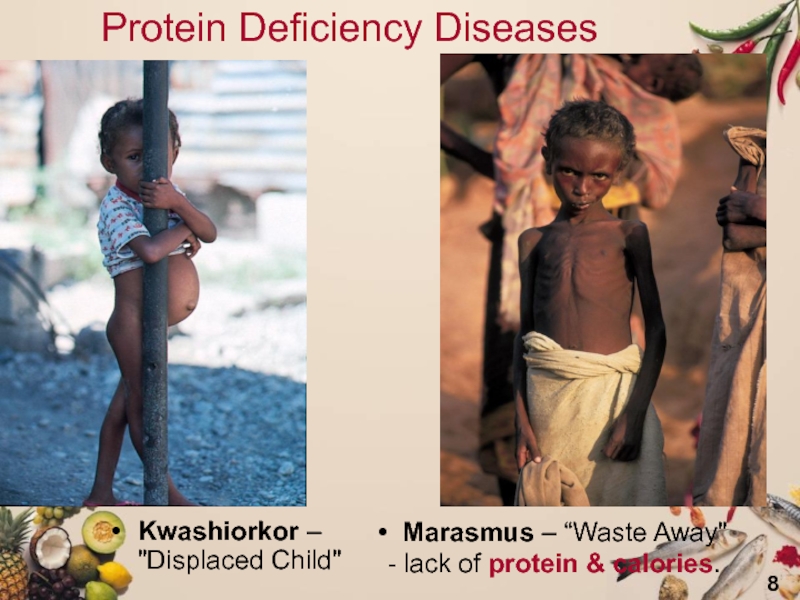
Слайд 8Protein Deficiency Diseases
Kwashiorkor – "Displaced Child"
Marasmus – “Waste Away" - lack of protein &
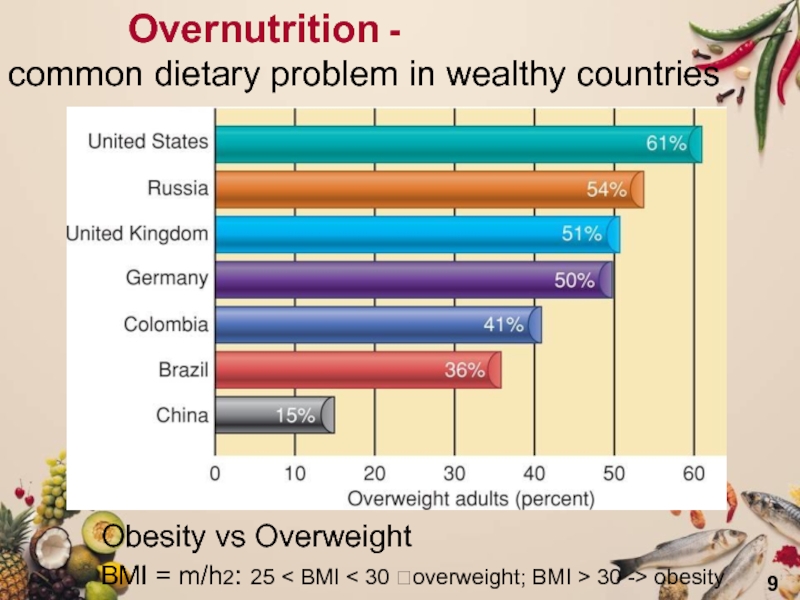
calories.Слайд 9 Overnutrition -
common dietary problem in wealthy countries
Obesity vs Overweight
BMI = m/h2: 25 < BMI < 30 overweight; BMI > 30 -> obesity
Слайд 10 MAJOR FOOD SOURCES
Wheat, rice, maize are food staples in
the world.
Wheat, rice, potatoes are staples in Russia and Kazakhstan.
Potatoes,
barley, oats and rye are staples in cool, moist climates.Cassava, sweet potatoes, other roots/ tubers are staples in warm wet climates.
Fruits and vegetables contain high levels of vitamins, minerals, fiber and complex carbohydrates.
Staple food – основные продукты питания
Crops
Слайд 11Rational Nutrition
Nutrition – intake of food needed to support life
Rational
Nutrition – nutrition that meets energy requirements of organism, providing
necessary metabolism at optimal regime of food intake.Main components of Rational Nutrition:
Balance (optimal amount and ratio of food components)
Nutrition Timetable
Energy Balance
~ 2,000 kcal per day needed for a female,
2,550 kcal – for a male.
Слайд 126 Main Nutrition Components
Proteins, Fats, Carbohydrates – Energy!
Fiber, Vitamins, Minerals
& Water – no E!
Fuel value of food:
Energy value:
Fat =
9 kcal per gramProtein = 4 kcal per gram
Carbohydrates = 4 kcal per gram
Note: Alcohol: =7 kcal /g!
∆E = Ein - Econs ≤ 5%
Daily nutrients ratio:
Carbohydrates 40 to 60%
Fat 20 to 30%
Protein 10 to 15%
Слайд 14Meat, Milk, and Seafood
Milk & meat: highly prized, but inequitable
distribution. Developed countries: 20% of world population, but consume 80%
of meat & milk production. LDCs produce 60% of world's milk & meat.~90% of the grain grown in North America used to feed cattle, hogs, poultry, & other animals!
Seafood is an important protein source in many countries. This food source is threatened by over-harvesting and habitat destruction.
Слайд 15Environmental Issues with Raising Beef
Every 16 kg of grain &
soybeans fed to cattle in feedlots produce 1 kg of
edible beef.If we ate grain directly, we would obtain 21 times more calories and 8 times > protein than we get eating the beef.
Слайд 16SOIL - A VALUABLE RESOURCE
Soil - a complex mixture of
weathered minerals, partially decomposed organic matter and living organisms
We depend
on soil for life, yet tend to take this living resource for granted.> 25,000 different soil types: different parent material, time, topography, climate, organisms
30-50% of the world's croplands are losing topsoil faster than it can be replaced
Soil is a renewable resource (in the long run).
Слайд 17Soil Organisms
Without soil organisms, the earth would be
covered with
sterile mineral particles.
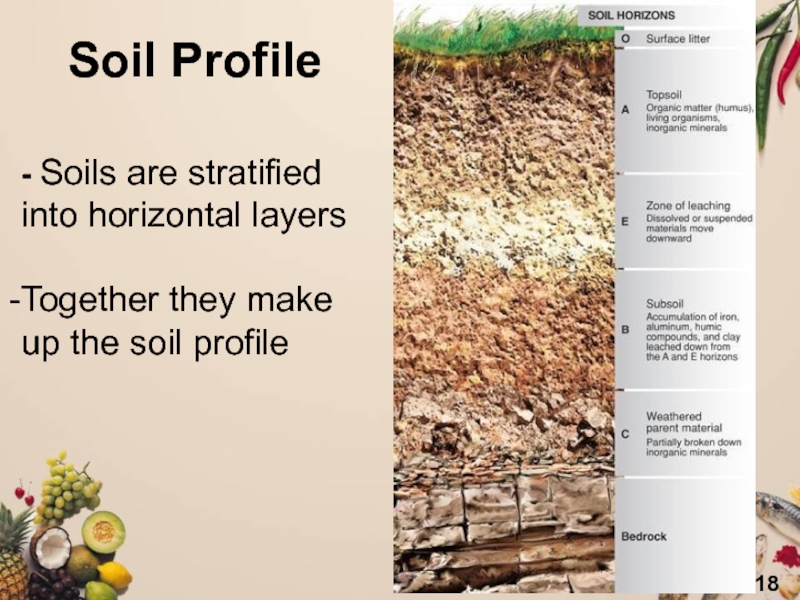
Слайд 18- Soils are stratified
into horizontal layers
Together they make up
the soil profile
Soil Profile
Слайд 19WAYS WE USE & ABUSE SOIL
Much potential cropland suffers from
constraints.
~11% of the earth's land area is currently in agricultural
production.Up to four times as much could potentially be converted to agricultural use.
Much of this additional land suffers from constraints.
Слайд 20 Erosion
Erosion: the process by which topsoil
(most fertile & productive) is removed and moved elsewhere.
Erosion: natural
process carried out by gravity, water, wind.Erosion - a disaster: since it reduces the productive capacity of the land.
Erosion reduces crop production by ~1% of world cropland per year.
Wind Erosion -> Kazakhstan
Слайд 21OTHER AGRICULTURAL RESOURCES
Water
Fertilizer
Energy
Pesticides
Agriculture is the biggest global consumer
of water, but there are ways to reduce water use
(above - sprinklers deliver water efficiently).Слайд 22Fertilizers
Nitrogen (N), potassium (K), and phosphorus (P) are major macronutrients
for plants
Lack of N, K, and P often limits plant
growth.Adding nutrients via fertilizer usually stimulates growth and increases crop yields.
1950 - ~20 kg/ha fertilizer used.
2000 - ~90 kg/ha fertilizer used – much more than needed!!.
Manure and nitrogen-fixing bacteria are alternative methods of replenishing soil nutrients.
Слайд 24 NEW CROPS & GENETIC ENGINEERING
~3,000 plant species are used
for food, but most world food comes from 16 crops..
Many
new or unconventional varieties might be valuable food supplies.Progress in farm production comes from technological advances and modification of a few well-known species.
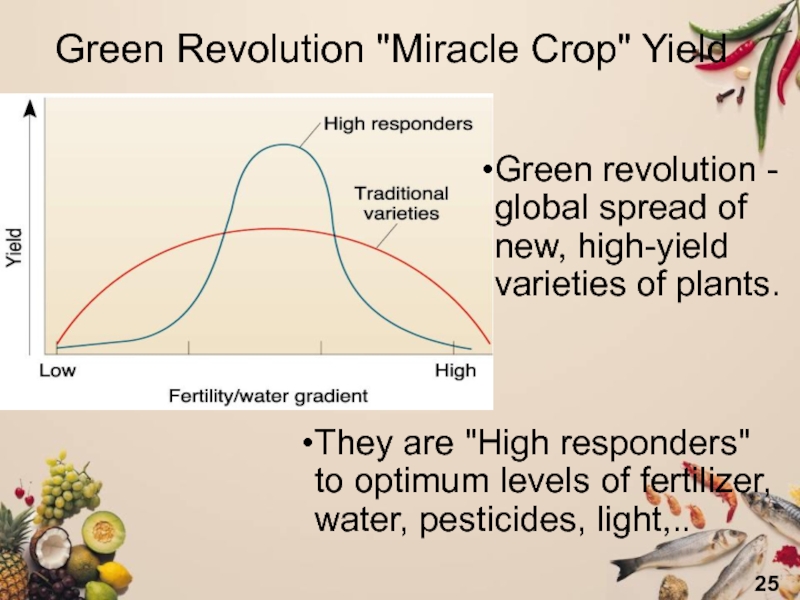
Слайд 25Green Revolution "Miracle Crop" Yield
They are "High responders"
to optimum levels of fertilizer, water, pesticides, light,..
Green revolution -
global spread of new, high-yield varieties of plants. Слайд 26Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering is the splicing a gene from one
organism into the chromosome of another.
These Transgenic organisms are called
Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) producedThese new genes result in plants with pest resistance, built in weed control and wider tolerances
Opponents fear traits could spread to wild varieties, and increased expense would largely hurt smaller farmers.
Слайд 27 SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE
Sustainable agriculture (regenerative farming) - goal
is to produce food and fiber on a sustainable basis
and to repair damage caused by destructive practices. Soil is essential to sustainable agriculture.Soil conservation - land management, ground cover, climate, soil type and tillage system are important elements in soil conservation.