Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Kinesio Taping : An Introduction on Technique and Results
Содержание
- 1. Kinesio Taping : An Introduction on Technique and Results
- 2. OverviewIntroduction to Kinesio TapingPropertiesTheoretical BenefitsTypes of ApplicationApplication
- 3. Kinesio Tape Properties
- 4. Properties of Kinesio TapeMimics skin qualitiesTape is
- 5. Theoretical Benefits
- 6. Theoretical BenefitsAnalgesic AffectMechanoreceptorsCreate space for areas of
- 7. Theoretical BenefitsCorrect MalalignmentPositional stimulus Align fascia tissuesScar TissueBreaks adhesionsReduce irritation
- 8. Types of Application
- 9. Types of ApplicationYIXFanWebDonut
- 10. Types of Application: YUsed to surround muscleEither
- 11. Type of Application: IUsed for more acute
- 12. Type of Application: X and Donut XUsed when
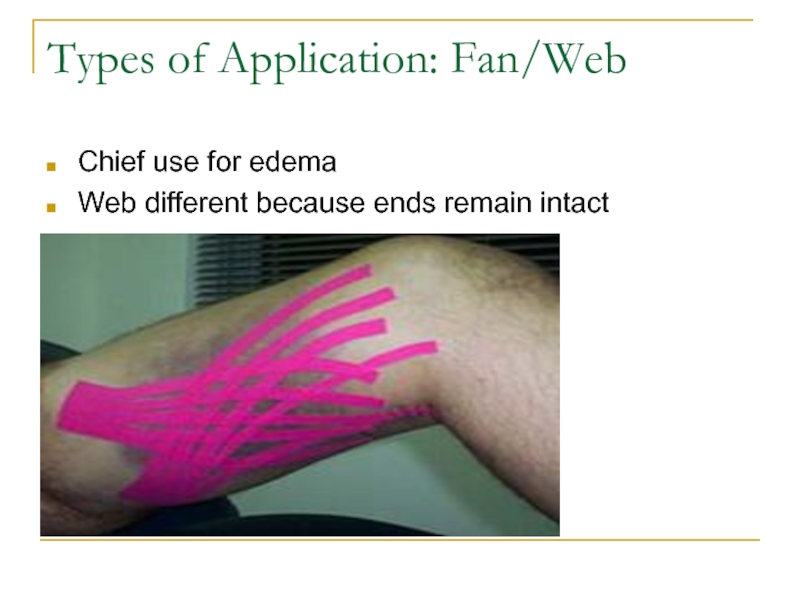
- 13. Types of Application: Fan/WebChief use for edemaWeb different because ends remain intact
- 14. Type of Application StretchMuscle should be elongated
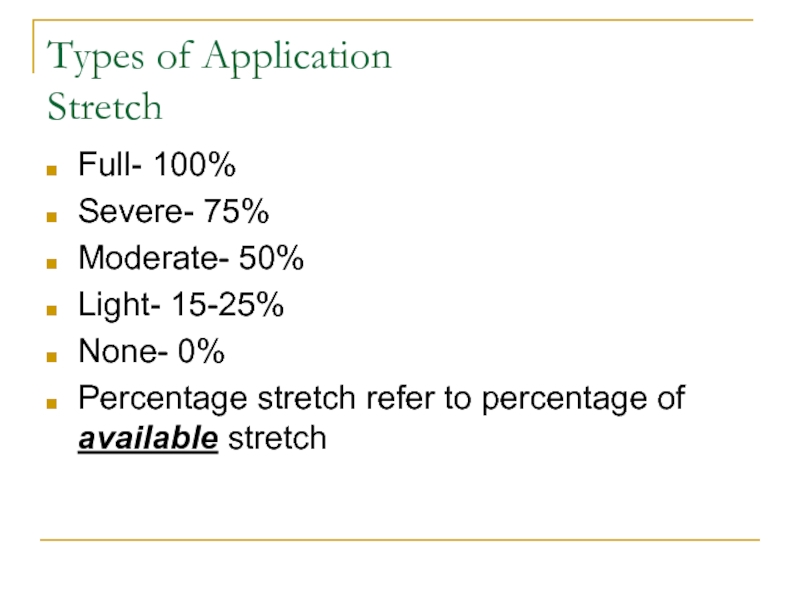
- 15. Types of Application Stretch Full- 100%Severe- 75%Moderate- 50%Light- 15-25%None- 0%Percentage stretch refer to percentage of available stretch
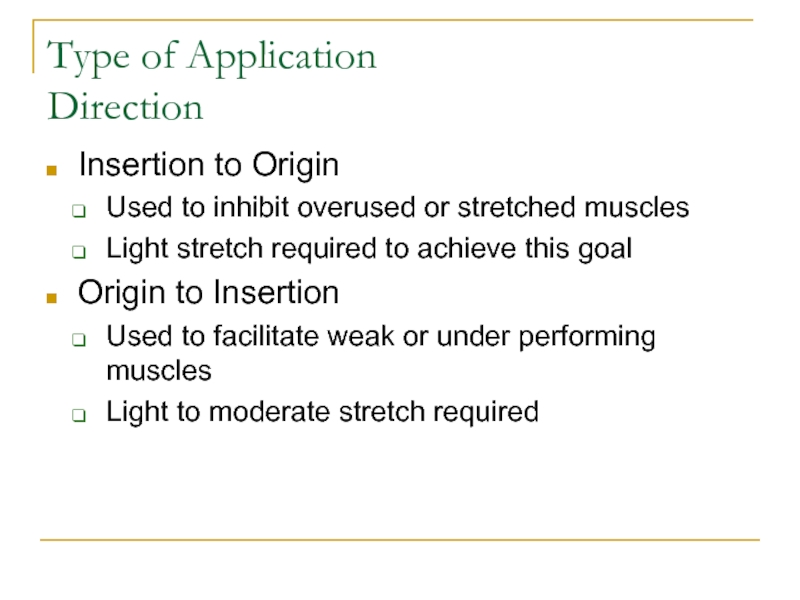
- 16. Type of Application DirectionInsertion to OriginUsed to
- 17. Application Guidelines
- 18. Application GuidelinesShave hair if interfering with adhesiveNo
- 19. Application GuidelinesMeasure appropriate length- allowing for desired
- 20. Evidence Based Practice
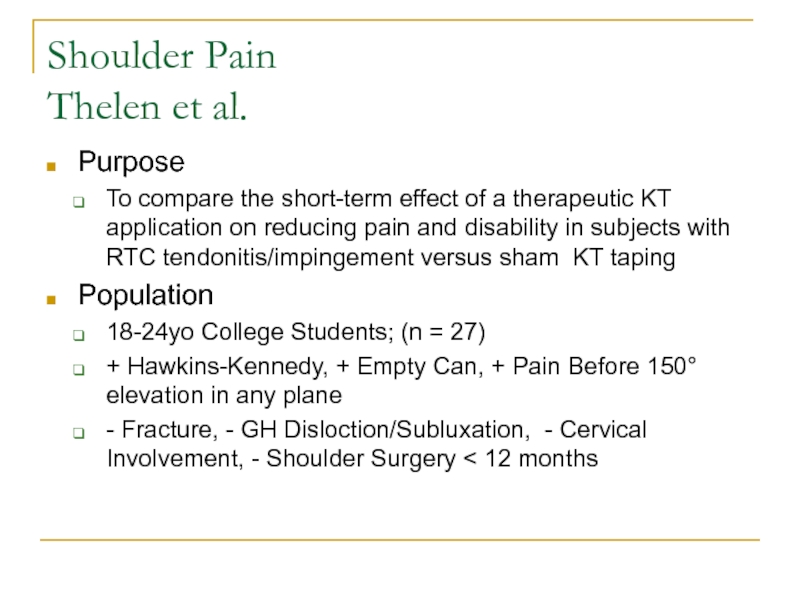
- 21. Shoulder Pain Thelen et al.PurposeTo compare the
- 22. Intervention15-25% Stretch Y-Strip for Supraspinatus15-25% Stretch Y-Strip
- 23. Lower Trunk ROM Yoshida et al.PurposeTo determine
- 24. InterventionCross-over Study15-25% stretch with Y-StripPlace base above
- 25. Traumatic Patellar Dislocation OsterhuesPurposeTo demonstrate the use
- 26. Intervention10% Stretch Y-Strip from the insertion to
- 27. KT effect on Peds Yasukawa et alPurposeTo
- 28. InterventionWide variety of KT techniques, IndividualizedOutcomeMelbourne Assessment16
- 29. Clinical Implications
- 30. Clinical ImplicationsLevel of evidenceWeak- only one RCT
- 31. Clinical ImplicationsWhy use itTool in the toolboxTreats
- 32. Clinical Implications Athletic Taping v Kinesio TapingBragg article
- 33. RTC Impingement Taping
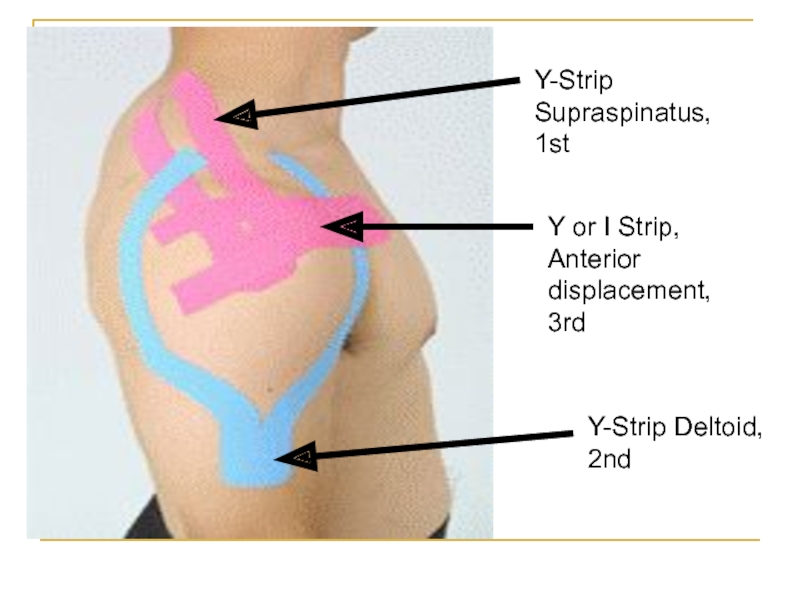
- 34. Y-Strip Supraspinatus, 1stY or I Strip, Anterior displacement, 3rdY-Strip Deltoid, 2nd
- 35. Quadriceps Taping
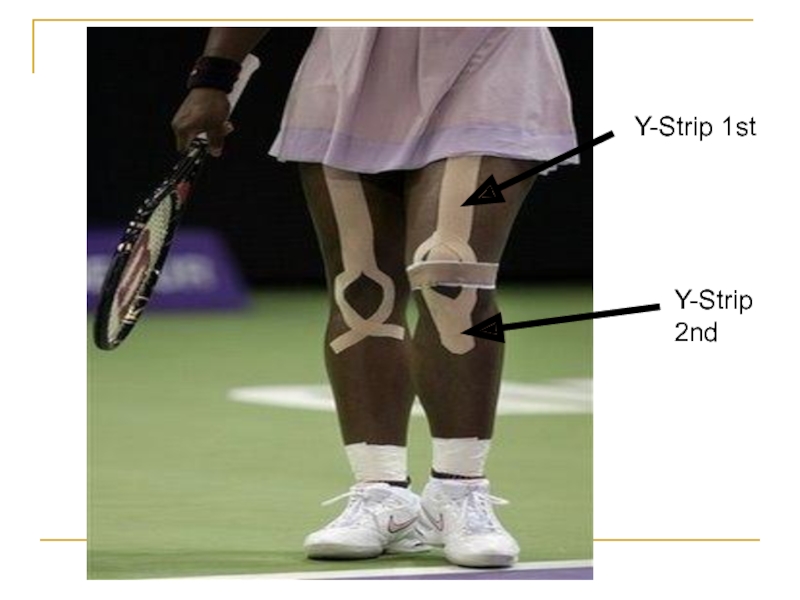
- 36. Y-Strip 1stY-Strip 2nd
- 37. ReferencesClinical Theraputic Applications of the Kinesio Taping
- 38. Скачать презентанцию
OverviewIntroduction to Kinesio TapingPropertiesTheoretical BenefitsTypes of ApplicationApplication GuidelinesCurrent EvidenceShoulder PainLower Trunk ROMLateral Patella DislocationAcute Pediatrics PopulationClinical ImplicationsApplication of Kinesio TapeRTC Impingement TapingQuadriceps Facilitation Taping
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Kinesio Taping:
An Introduction on Technique and Results
Chris Keating SPT
Thomas Jefferson
University
Слайд 2Overview
Introduction to Kinesio Taping
Properties
Theoretical Benefits
Types of Application
Application Guidelines
Current Evidence
Shoulder Pain
Lower
Trunk ROM
Lateral Patella Dislocation
Acute Pediatrics Population
Clinical Implications
Application of Kinesio Tape
RTC
Impingement TapingQuadriceps Facilitation Taping
Слайд 4Properties of Kinesio Tape
Mimics skin qualities
Tape is replicating hands on
the patient
Sensiomotor stimulation
Allows longitudinal stretch of 30-40% of its resting
lengthEffective for 3-5 days of constant use
Latex free and heat activated adhesive
Acrylic adhesive applied in wave fashion to allow for moisture escape
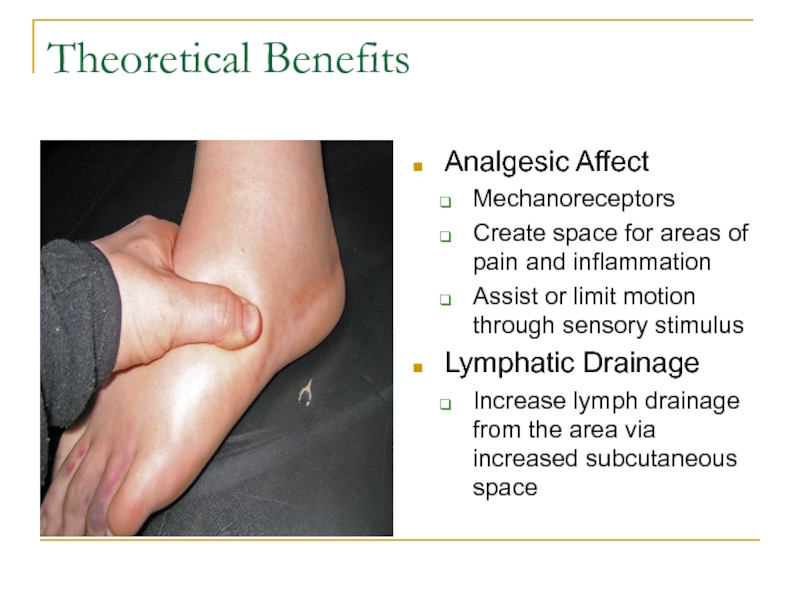
Слайд 6Theoretical Benefits
Analgesic Affect
Mechanoreceptors
Create space for areas of pain and inflammation
Assist
or limit motion through sensory stimulus
Lymphatic Drainage
Increase lymph drainage from
the area via increased subcutaneous spaceСлайд 7Theoretical Benefits
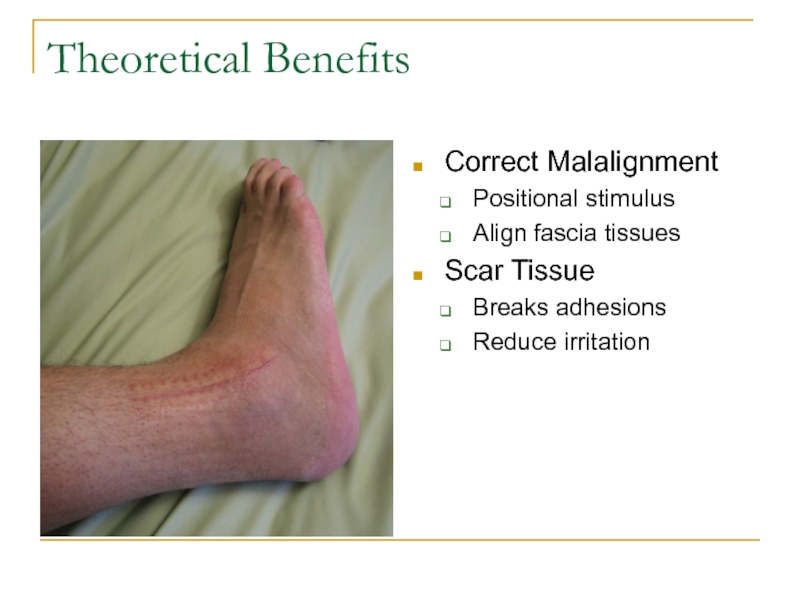
Correct Malalignment
Positional stimulus
Align fascia tissues
Scar Tissue
Breaks adhesions
Reduce irritation
Слайд 10Types of Application: Y
Used to surround muscle
Either to facilitate or
inhibit muscle stimuli
Should be 2 inches longer than target muscle
Teres
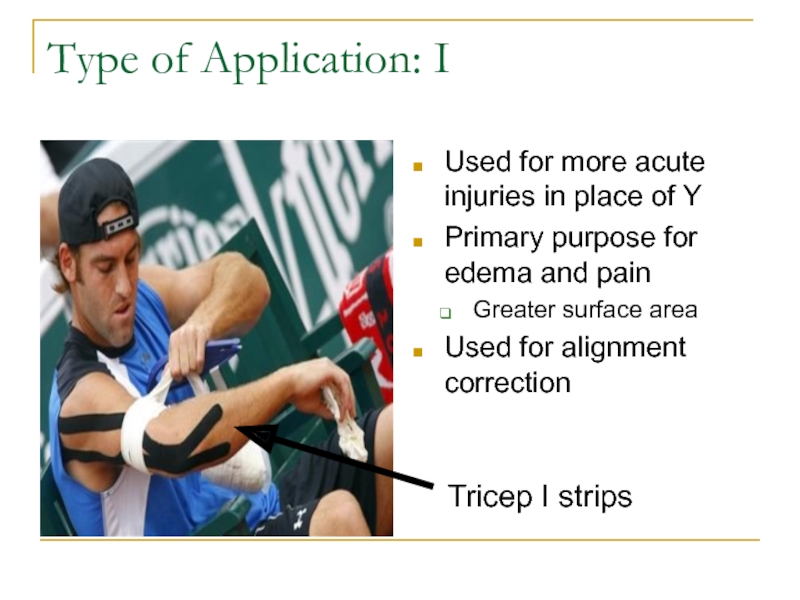
Minor YСлайд 11Type of Application: I
Used for more acute injuries in place
of Y
Primary purpose for edema and pain
Greater surface area
Used for
alignment correctionTricep I strips
Слайд 12Type of Application: X and Donut
X
Used when origin and insertion
change depending on movement (Rhomboids)
Donut
Specifically used for edema
Use overlapping strips
and the center is cut out over area of focusСлайд 14Type of Application
Stretch
Muscle should be elongated prior to application
KT requires
none to partial stretch
Stretch results in skin convolutions whether they
are visible or not they are presentWould rather have too little than too much stretch
This is not athletic taping, do not take up full stretch*
Слайд 15Types of Application
Stretch
Full- 100%
Severe- 75%
Moderate- 50%
Light- 15-25%
None- 0%
Percentage stretch refer
to percentage of available stretch
Слайд 16Type of Application
Direction
Insertion to Origin
Used to inhibit overused or stretched
muscles
Light stretch required to achieve this goal
Origin to Insertion
Used to
facilitate weak or under performing musclesLight to moderate stretch required
Слайд 18Application Guidelines
Shave hair if interfering with adhesive
No oils or lotions
on skin
If wet, pat dry
Do not use hair dryer on
tapeUse alcohol to prep skin if needed
Слайд 19Application Guidelines
Measure appropriate length- allowing for desired stretch
Remove tape carefully
in order not to touch or increase application difficulty
Rub tape
after application to activate adhesiveAllow 20 mins for adhesive to take effect
If KT doesn’t reduce pain than D/C treatment after 20 mins
Слайд 21Shoulder Pain
Thelen et al.
Purpose
To compare the short-term effect of a
therapeutic KT application on reducing pain and disability in subjects
with RTC tendonitis/impingement versus sham KT tapingPopulation
18-24yo College Students; (n = 27)
+ Hawkins-Kennedy, + Empty Can, + Pain Before 150° elevation in any plane
- Fracture, - GH Disloction/Subluxation, - Cervical Involvement, - Shoulder Surgery < 12 months
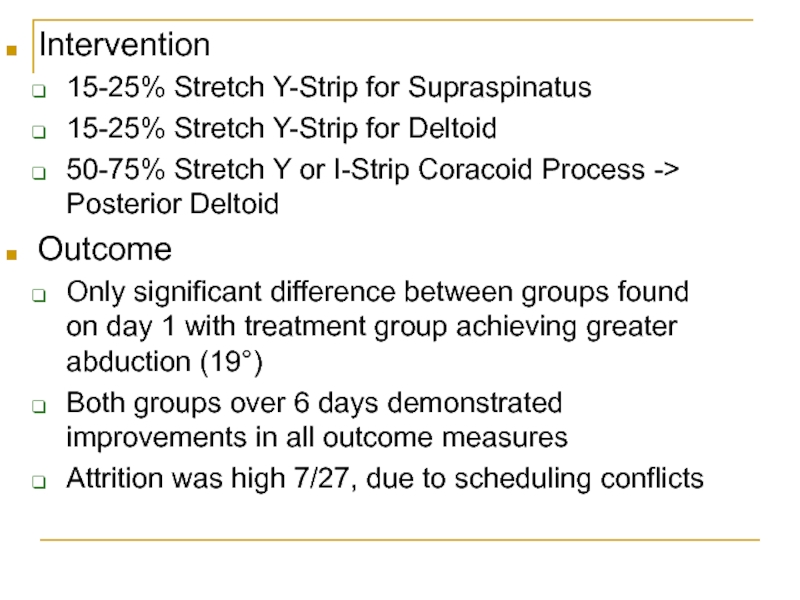
Слайд 22Intervention
15-25% Stretch Y-Strip for Supraspinatus
15-25% Stretch Y-Strip for Deltoid
50-75% Stretch
Y or I-Strip Coracoid Process -> Posterior Deltoid
Outcome
Only significant difference
between groups found on day 1 with treatment group achieving greater abduction (19°)Both groups over 6 days demonstrated improvements in all outcome measures
Attrition was high 7/27, due to scheduling conflicts
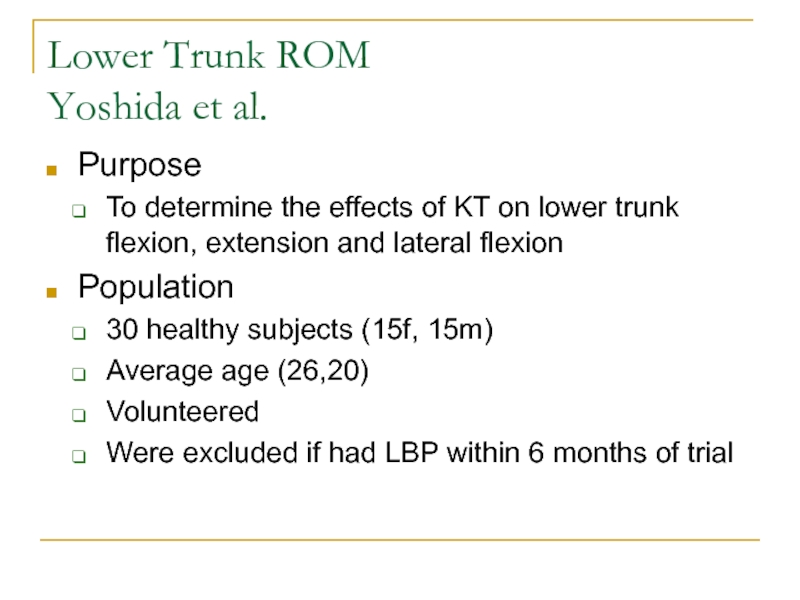
Слайд 23Lower Trunk ROM
Yoshida et al.
Purpose
To determine the effects of KT
on lower trunk flexion, extension and lateral flexion
Population
30 healthy subjects
(15f, 15m) Average age (26,20)
Volunteered
Were excluded if had LBP within 6 months of trial
Слайд 24Intervention
Cross-over Study
15-25% stretch with Y-Strip
Place base above sacrum
Attach tails on
each erector spinae group with light tension
Outcomes
Taping significantly increased flexion
(17cm) over non-tapingNo control group
Needs more detailed measurements
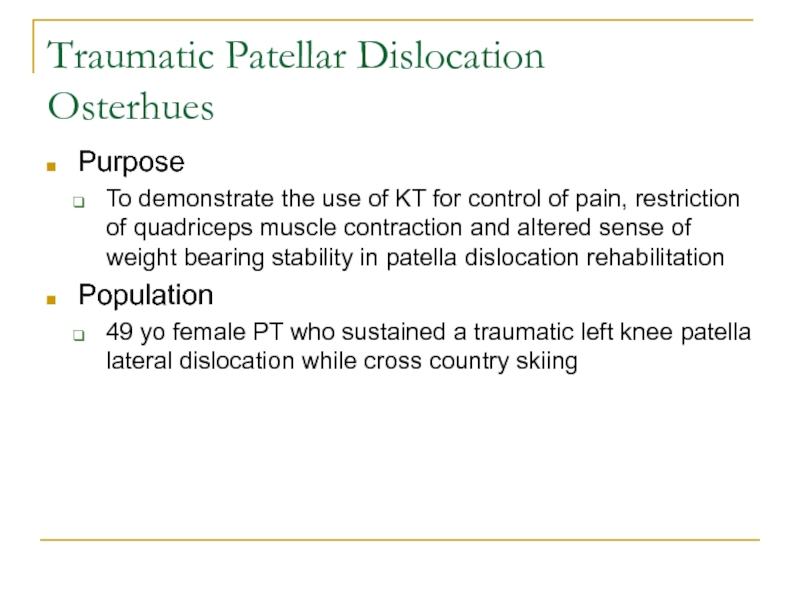
Слайд 25Traumatic Patellar Dislocation
Osterhues
Purpose
To demonstrate the use of KT for control
of pain, restriction of quadriceps muscle contraction and altered sense
of weight bearing stability in patella dislocation rehabilitationPopulation
49 yo female PT who sustained a traumatic left knee patella lateral dislocation while cross country skiing
Слайд 26Intervention
10% Stretch Y-Strip from the insertion to origin
Base placed
without tension
Tails across medial retinacular tissue and lateral quadriceps border
with paper off tension Treatment also included:
IFC, ice with compression, static and dynamic balance training, stationary bike, ROM exercises, massage
Outcome
Reduced pain with activity 4 weeks after injury with KT use function comparable to Atkin et al. (2000) study which put timetable at 6 months
Tests with NeuroCom Balance Master higher for taped condition than no taped, however both numbers outside (below) normal ranges
Слайд 27KT effect on Peds
Yasukawa et al
Purpose
To describe the functional arm
and hand skills for children admitted into a rehab program
subsequent use of KTPopulation
15 Children (10f, 5m) Ages 4-16
4 SCI, 2 TBI, 3 Brain Tumor, 2 CVA, Seizure, CP, 2 Birth Defects
+ muscle weakness or abnormal muscle tone
Grades of 3 or more on Mod. Ashworth were excluded
Trace on MMT or sensory issues were also excluded
No cognitive or motivation issues
Слайд 28Intervention
Wide variety of KT techniques, Individualized
Outcome
Melbourne Assessment
16 pt questionnaire measuring
upper limb function
Designed for CP population
Scores significantly improve pre-test to
post-test as well as 3 days after tapingIts hard to draw specific treatment from study
Overall function improved in group average immediately after taping limiting learning curve
Increase of 5 on MA immediately after application
Increase of 10 on MA 3 days after application
Слайд 30Clinical Implications
Level of evidence
Weak- only one RCT found (via Medline,
Cinahl, Cochrane, DARE, ACP)
Mainly case studies, presented were a sample
of the most PT relevantWhat does the evidence support
Increase in ROM
Increase in function
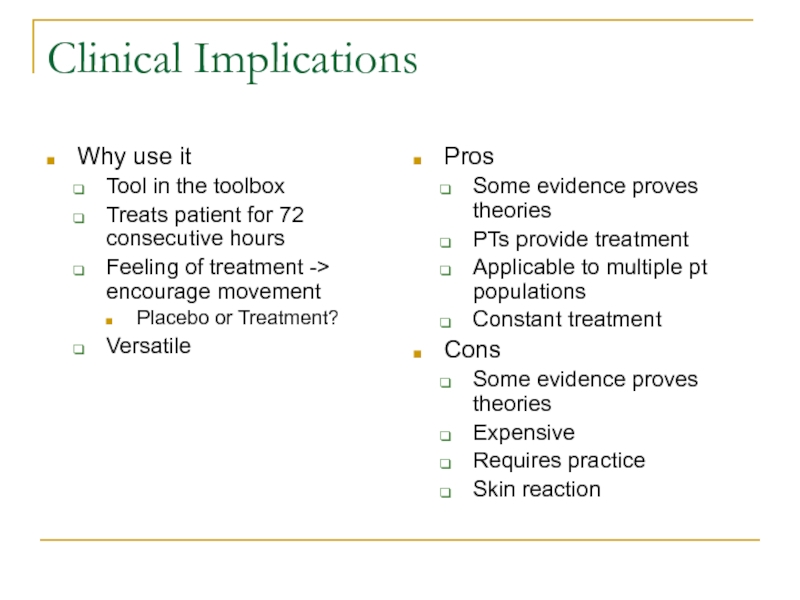
Слайд 31Clinical Implications
Why use it
Tool in the toolbox
Treats patient for 72
consecutive hours
Feeling of treatment -> encourage movement
Placebo or Treatment?
Versatile
Pros
Some
evidence proves theoriesPTs provide treatment
Applicable to multiple pt populations
Constant treatment
Cons
Some evidence proves theories
Expensive
Requires practice
Skin reaction
Слайд 32Clinical Implications
Athletic Taping v Kinesio Taping
Bragg article demonstrates AT decrease
in support within an hour of use
Since KT does not
focus on support its means of sensory stimulus to enforce movement may just be a better form of ATClinical Opinion
Kinesio Taping could be a useful tool for therapist who see patients only a handful of times during rehab
Little evidence supports its multiple theories, more research needed
May be a way to facilitate and encourage movement
Слайд 37References
Clinical Theraputic Applications of the Kinesio Taping Method; K. Kaze,
J. Wallis, T. Kase; Tokyo, Japan, 2003
The Clinical Efficacy of
Kinesio Tape for Shoulder Pain: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Clinical Trial; M. Thelen, J. Dauber, P. Stoneman; Journal of Orthopaedic and Sports Physical Therapy, 38:7 2008Pilot Study: Investigating the Effects of Kinesio Taping in an Acute Pediatic Rehabilitation Setting; A. Yasukawa, P. Patel, C Sisung; American Journal of Occupational Therapy, 60:1 2006
The Use of Kinesio Taping in the Management of Traumatic Patella Dislocation. A Case Study; D. Osterhues; Physiotherapy Theory and Practice; 20:4 2004
The Effect of Kinesio-Taping on Lower Trunk Range of Motions; A. Yoshida, L Kahanov; Research in Sports Medicine, 15 2007
Characteristics of Patients with Primary Acute Lateral Patellar Dislocation and Their Recovery Within the First Six Months of Injury; DM. Atkins, Dc Fithian, KS Marangi; The American Journal of Sports Medicine; 28:4 2000
Failure and Fatigue Characteristics of Adhesive Athletic Tape; Bragg, R.W, Macmahon, J.M, Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 34:3 2002