Слайд 1Lecture 3. ENGLISH VOCABULARY AS A SYSTEM
In a simple code
each sign has only one meaning, and each meaning is
associated with only one sign. This one-to-one relationship is not realised in natural languages.
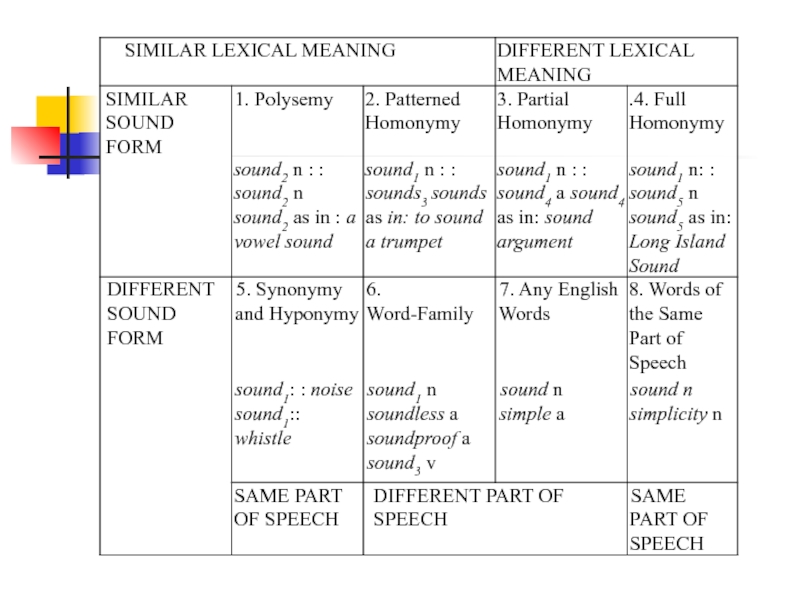
When several related meanings are associated with the same group of sounds within one part of speech, the word is called polysemantic, when two or more unrelated meanings are associated with the same form — the words are homonyms, when two or more different forms are associated with the same or nearly the same denotative meanings — the words are synonyms.
Слайд 3Homonyms
According to the degree of identity:
homonyms proper
match (спичка) –
match (матч)
Homophones
sale – sail
Homographs
lead – lead (свинец)
and homoforms
found (the
Past Indefinite of find) – to found
patterned homonymy
silence – to silence
Слайд 4According to the type of distinguishing meaning
lexical
seal (тюлень) – seal
(печать)
lexico-grammatical
rose (поднялся) – rose (роза);
Grammatical
boys – boy’s – boys’
Слайд 5Professor Smirnitsky’s classification
Full homonyms
bank (банк) – bank (берег
(реки, озера)).
Partial homonyms (this type of homonymy is characteristic of
words belonging to different lexico-grammatical classes)
a seal (an animal) – to seal (to close tightly)
Слайд 6The sources of homonymy
convergent sound development (звуковая конвергенция)
sound (OE gesund)
– sound (sonus)
split of polysemy / divergent sense development –
(распад полисемии)
board (доска) – board (питание, стол) – board (комиссия)
borrowing words
rite (ритуал) (Lat) – write, right (Native)
Conversion and shortening
to drive – a drive; rep (repertory) – rep (representative)
Слайд 7Discrimination of homonymy and polysemy
the semantic proximity of the LSVs
(cf. spring (season; a twisted piece of metal, a place
where water comes up from the ground)
their derivation capacity (cf. deep-voiced, voicing against the candidate, the Active voice of the verb)
the range of collocability
Слайд 8Synonyms
Ex.: to kill-to slay - to waste
According to the degree
of equivalence:
full (absolute): semasiology – semantics, scarlet fever –
scarlatina
partial (relative)
Слайд 9Difference between synonyms
1. close in meaning (but not totally interchangeable)
to glitter (with anger) - to sparkle (with joy)
different
in meaning considerably
journey – voyage – trip
2. The degree of the quality expressed
want, desire, long for
3. Evaluative connotations
loving, devoted – doting (безумно любящий; слепо обожающий)
Слайд 10Difference between synonyms
4. Stylistic colouring
maid – girl, talkative – loquacious
5.
Stylistic colouring + difference in emotional colouring and evaluation: visage
– face – phiz – snout (морда, рыло животного) – mug.
Contextual synonyms: buy – get (I’ll go to a shop and get some bread)
Слайд 11Euphemism (Gr euphemismos < eu ‘good’ and pheme ‘voice’)
referring to
something unpleasant by using milder words and phrases so that
a formerly unoffensive word receives a disagreeable meaning
more or less ‘pleasant or at least inoffensive connotation becomes synonymous to one that is harsh, obscene, indelicate or otherwise unpleasant
mad, graveyard, water-closet → insane, cemetery, lavatory → God's Acre, lady’s/men’s room/restroom, etc.
Слайд 12Paronyms
(not be confused with synonyms)
words that sound alike but
are different in meaning and usage.
affect – effect, cause
– course, ingenious [i] (находчивый, изобретательный, умелый) – ingenuous [e] (бесхитростный).
Слайд 13Antonyms
lexical units of opposite meaning.
dull – interesting; dull
(of a blade) – sharp, dull (of a pain) –
acute
Iron - ?
Слайд 14Classifications of antonyms
root and affixational ones:
good – bad,
happy – unhappy.
phraseological antonyms
big fish – small fry.
Semantically:
1) contrary
(контрарные) cold (cool and warm) hot
2) contradictory (контрадикторные) not alive – dead
3) conversive (конверсивные) buy – sell, give – receive
4) antonyms of opposite direction (векторно-разнонаправленные) East-West, know-forget, left-right
Слайд 15Neologisms
New words and expressions that are created for new things
1)
neologisms proper: cyberpunk
2) transnominations : edutainment (education+entertainment)
3) semantic innovations (переосмысление)
: switched-on (well-informed, efficient)
Слайд 16Phonological neologisms (often onomatopoeical)
Dude, nylon, zap
Morphological neologisms
Affixation: racketeer,
neatnik (чистюля), foodie
composition: trouble-shooter job-hopper
Shortening: urb ← urban, TOEFL
Conversion: to
garage a card
Blending: vegelate (vegetable+chocolate), vegeburger).
Слайд 17Semantic neologisms
metaphoric or metonymic transfer metaphore: spam
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M_eYSuPKP3Y
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PDvZ_zyoCHY
Borrowed neologisms
karoshi – (in Japan) death caused by overwork Etymology: from
Japanese ka “excess” + ro “labour” + shi “death”
Слайд 18Occasionalisms, or author’s neologisms
simple structure knowhownik - специалист, умелец, nofoodnik,
re-fusenik (человек, которому отказали в получении визы)
multiple attributive structures (поликомпонентные
атрибутивные цепочки): breakfast-in-the-bedder
There is a sort of Oh-what-a-wicked-world-this-ls-and-how-I-wish-i-could-do-something-to-make-it-better-and nobler expression about Mont-morency. (Jerome K- Jerome)