Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
LECTURE № 5 Colligative Properties of Solutions
Содержание
- 1. LECTURE № 5 Colligative Properties of Solutions
- 2. QUIZ MENEXT1 What is it a true
- 3. QUIZ MENEXT2 The amount of a solute
- 4. QUIZ ME3 What is the molar concentration
- 5. QUIZ ME4 What is the molality of
- 6. Nature of SoluteNon-electrolytic are substances that do
- 7. SOLUTION OF Electrolyte – solution that
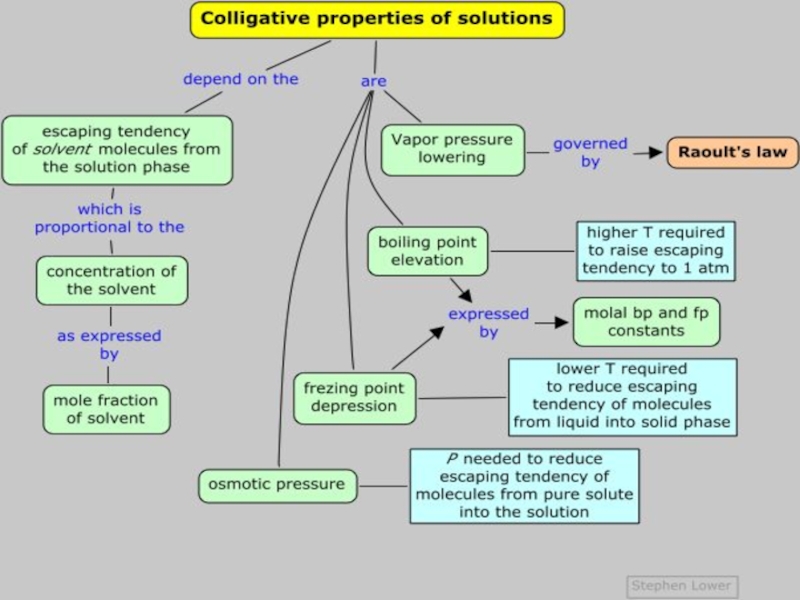
- 8. Colligative PropertIES Colligative properties are the set of
- 9. 1) Vapor Pressure Lowering (1st Raoult’s Law)Related
- 10. The vapor pressure of water (P0) is the pressure
- 11. Vapor pressure depends on various factors: the
- 12. Vapor Pressure LoweringPure waterAqueous solution of nonvolatile solute>
- 13. As solute molecules are added to a
- 14. The extent to which a nonvolatile solute
- 15. The temperature at which vapor pressure is
- 16. The 2nd Raoult’s Law One consequence of Raoult's
- 17. ebulioscopic constant of solventThe boiling temperature of non-electrolytes solutionebulioscopic method
- 18. where Esvt is boiling point elevation constant,
- 19. krioscopic constant of solventThe freezing temperature of non-electrolytes solutionkrioscopic method
- 20. where Ksvt is the freezing point depression
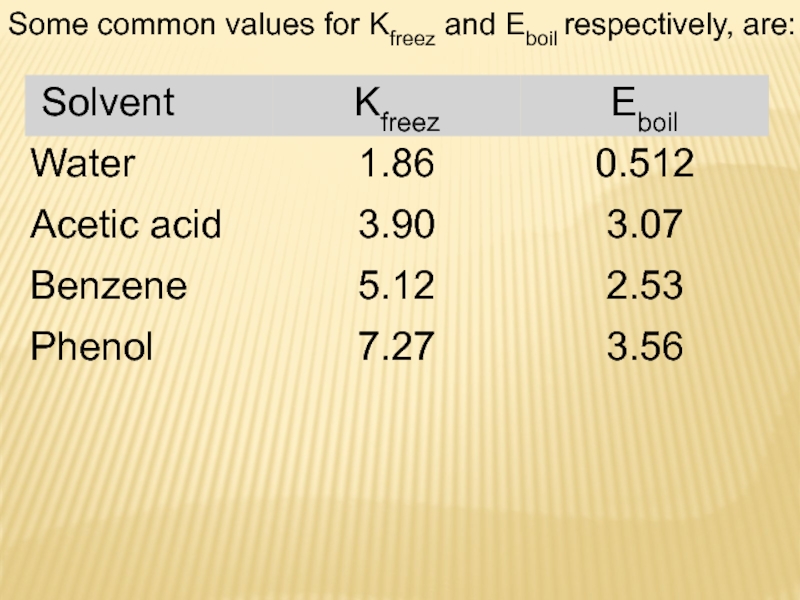
- 21. Some common values for Kfreez and Eboil respectively, are:
- 22. In 1784, the French physicist Jean Antoine
- 23. Jean-Antoine Nollet first documented observation of osmosis in
- 24. Net transfer of solvent molecules into the
- 25. Osmotic Pressureh
- 26. (a) A dilute solution of glucose in
- 27. The osmotic pressure of a solution is
- 28. Molarirty units are most appropriate in calculating
- 29. Types of Solutions Based on Solute Concentration…Hypotonic
- 30. Non-electrolyte:1 М sugar solutionElectrolyte:1 М NaCl salt
- 31. The degree of dissociation is associated with an isotonic factor by next ratio:For Electrolyte Solution:
- 32. If equal numbers of moles of each
- 33. SUMMARY OF FACTS AND CONCEPTS 1. Colligative properties
- 34. 7. In electrolyte solutions, the interaction between
- 35. Слайд 35
- 36. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 3QUIZ ME
NEXT
2 The amount of a solute dissolved in a
given amount of solvent is represented by the …
Volume of
the solutionMass of the solute
Mass of the solution
Concentration of the solute
Слайд 4QUIZ ME
3 What is the molar concentration of solution?
the number
of equivalent-moles of solute per 1 liter of solution
the gram
of a solute per 1 milliliter of solutionthe number of moles of solute per 1 kilogram of solvent
the number of moles of solute per 1 liter of solution
Слайд 5QUIZ ME
4 What is the molality of solution?
the number of
equivalent-moles of solute per 1 liter of solution
the gram of
a solute per 1 milliliter of solutionthe number of moles of solute per 1 kilogram of solvent
the number of moles of solute per 1 liter of solution
Слайд 6Nature of Solute
Non-electrolytic are substances that do not form ions
and do not conduct electricity when placed in water.
An electrolyte
is a substance that, when dissolved in water form ions, as results a solution can conduct electricity: NaCl => Na+ + Cl-
cation anion
Слайд 7SOLUTION OF
Electrolyte – solution that conducts electricity
ionic compounds
in polar solvents dissociate (break apart) in solution to make
ionsmay be strong (100% dissociation) or weak (less than 100%)
Strong Electrolyte – all or almost all of compound dissociates; example: strong acids (H2SO4, HNO3, HClO4, HCl, HBr, HI)
Weak Electrolyte – small amount of compound dissociates; example – weak acids (HF, CH3COOH, H3PO4)
Nonelectrolyte – solution that does not conduct electricity
solute is dispersed but does not dissociate
Example: sugar (dissolves but does not dissociate), organic acids (contain carboxyl groups)
Слайд 8Colligative PropertIES
Colligative properties are the set of properties that depend
only on the concentration of solute particles (ions or molecules)
in the solution and not the type. In other words, it doesn’t matter if it is salt, sugar, gasoline, or tennis balls – it will behave the same way!
Слайд 91) Vapor Pressure Lowering (1st Raoult’s Law)
Related to boiling point
2)
Freezing Point Depression
Salt on the road
Anti-freeze in your radiator
And Boiling
Point Elevation (2nd Raoult’s Law)Anti-freeze in your radiator
3) Osmotic Pressure (Van’t Hoff’s Law)
Membrane diffusion
The Great Sugar Fountain
Colligative PropertIES:
Слайд 10 The vapor pressure of water (P0) is the pressure at which water vapor is in
thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed state.
When ↑t , ↑p0
H2O:00C – 4,6 mm Hg
200C – 17,4 mm Hg
1000C – 760 mm Hg
P0
Слайд 11 Vapor pressure depends on various factors:
the nature of the
liquid,
the presence of dissolved substances in the liquid or
solid. According to Raoult's law, the vapor pressure of a pure liquid or solid is lowered by the addition of a solute.
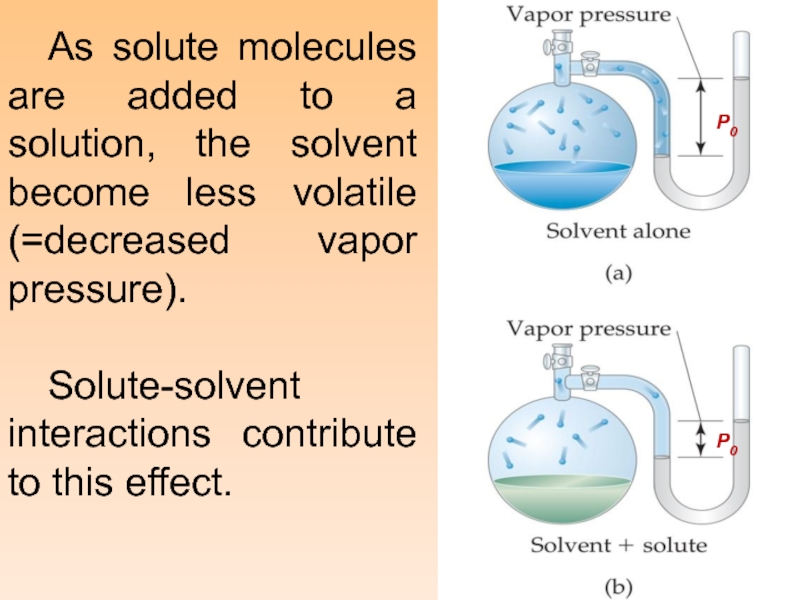
Слайд 13 As solute molecules are added to a solution, the solvent
become less volatile (=decreased vapor pressure).
Solute-solvent interactions contribute to this
effect.P0
P0
Слайд 14 The extent to which a nonvolatile solute lowers the vapor
pressure is proportional to its concentration. This was discovered by
French chemist Francois Raoult (1830-1907).1st Raoult’s law states that for non-electrolyte solutions, the partial vapor pressure of a solvent over a solution (P1) is equal to the vapor pressure of the pure solvent (P0) multiplied by the mole fraction of the solute (X2). This law is mathematically expressed as:
the number of dissolving solute moles
the number of solvent mole
the mole fraction
Слайд 15 The temperature at which vapor pressure is equal to the
atmospheric pressure (p0= pаtm) is called boiling point
The temperature at
which vapor pressure of solvent in its liquid and solid phase become equal is called freezing pointat 00C water is freezing,
and at 1000C water is boiling
Слайд 16The 2nd Raoult’s Law
One consequence of Raoult's law is that
the boiling point of a solution made of a liquid
solvent with a nonvolatile solute is greater than the boiling point of the pure solvent. The boiling point of a liquid or is defined as the temperature at which the vapor pressure of that liquid equals the atmospheric pressure. For a solution, the vapor pressure of the solvent is lower at any given temperature. This pattern applies to the freezing point of the solution. Therefore, a higher temperature is required to boil the solution and a low temperature – to freeze the solution than the pure solvent.Слайд 17ebulioscopic constant of solvent
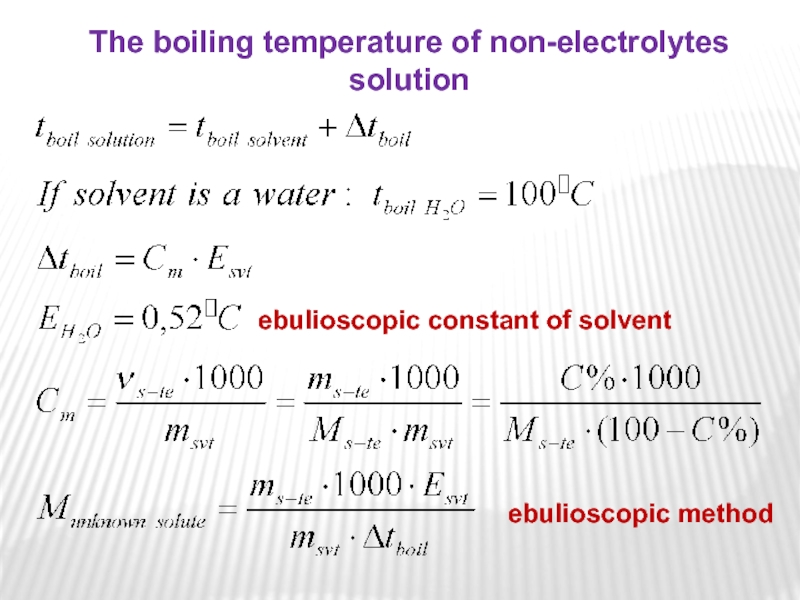
The boiling temperature of non-electrolytes solution
ebulioscopic method
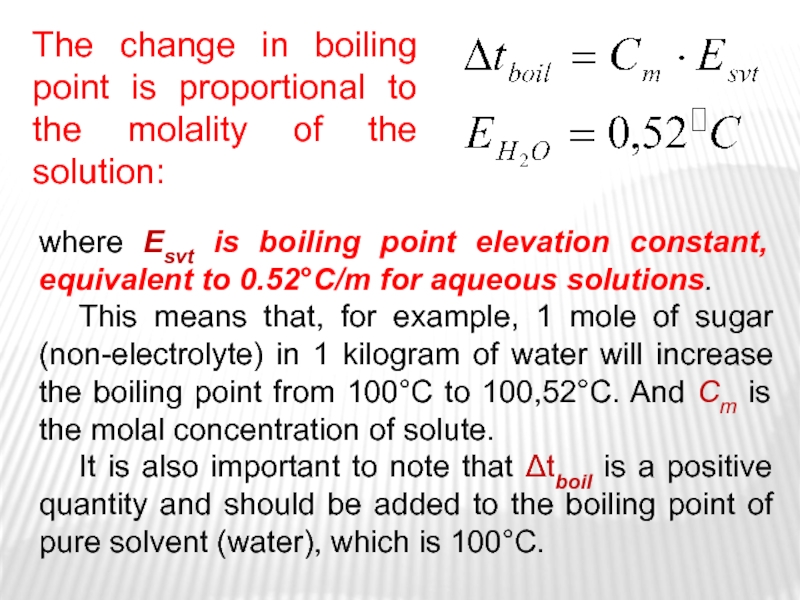
Слайд 18where Esvt is boiling point elevation constant, equivalent to 0.52C/m
for aqueous solutions.
This means that, for example, 1 mole
of sugar (non-electrolyte) in 1 kilogram of water will increase the boiling point from 100C to 100,52C. And Cm is the molal concentration of solute. It is also important to note that Δtboil is a positive quantity and should be added to the boiling point of pure solvent (water), which is 100C.
The change in boiling point is proportional to the molality of the solution:
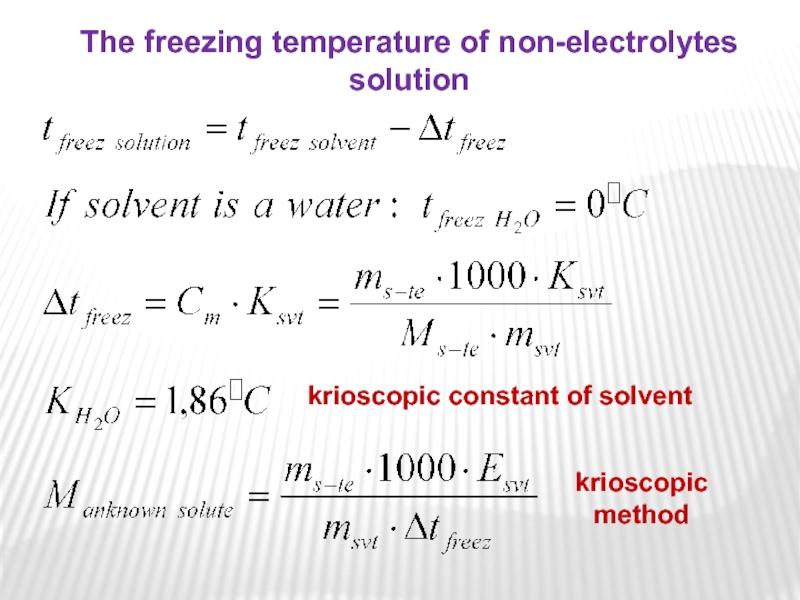
Слайд 19krioscopic constant of solvent
The freezing temperature of non-electrolytes solution
krioscopic
method
Слайд 20where Ksvt is the freezing point depression constant equivalent to
-1,86C/m for aqueous solutions.
Again, for example, 1 mole of
sugar (non-electrolyte) in 1 kilogram of water will decrease the freezing point from 0C to -1,86C. And since we have already established that the freezing point of the solution is less than that of the pure solvent, then Δtfreez is a negative quantity and should be subtracted from the freezing point of pure solvent (water), which is 0C.
The change in freezing point can be found similarly:
Слайд 22 In 1784, the French physicist Jean Antoine Nollet discovered that
a pig's bladder filled with a concentrated solution of alcohol
in water expanded when it was immersed in water. The bladder acted as a semipermeable membrane, which allowed water molecules to enter the solution, but kept alcohol molecules from moving in the other direction. Movement of one component of a solution through a membrane to dilute the solution is called osmosis, and the pressure this produces is called the osmotic pressure ().Osmotic pressure can be demonstrated with the apparatus shown in the figure below. A semipermeable membrane is tied across the open end of a thistle tube. The tube is then partially filled with a solution of sugar or alcohol in water and immersed in a beaker of water. Water will flow into the tube until the pressure on the column of water due to the force of gravity balances the osmotic pressure driving water through the membrane.
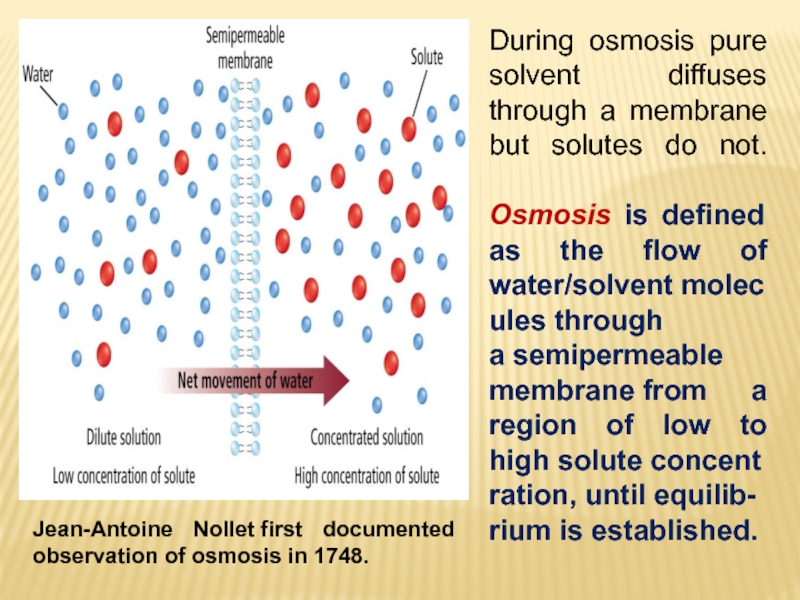
Слайд 23Jean-Antoine Nollet first documented observation of osmosis in 1748.
During osmosis pure
solvent diffuses through a membrane but solutes do not.
Osmosis
is defined as the flow of water/solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane from a region of low to high solute concentration, until equilib-rium is established.
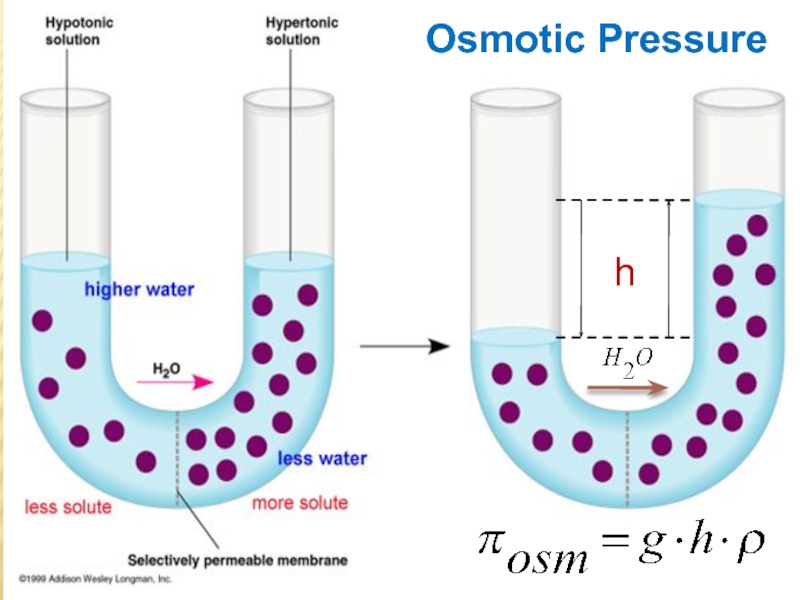
Слайд 24 Net transfer of solvent molecules into the solution until the
hydrostatic pressure equalizes the solvent flow in both directions.
Because the
liquid level for the solution is higher, there is greater hydrostatic pressure on the solution than on the pure solvent .Osmotic Pressure:
The excess hydrostatic pressure on the solution compared to the pure solvent.
Слайд 26(a) A dilute solution of glucose in water is placed
in the right arm of a U-tube, and the left
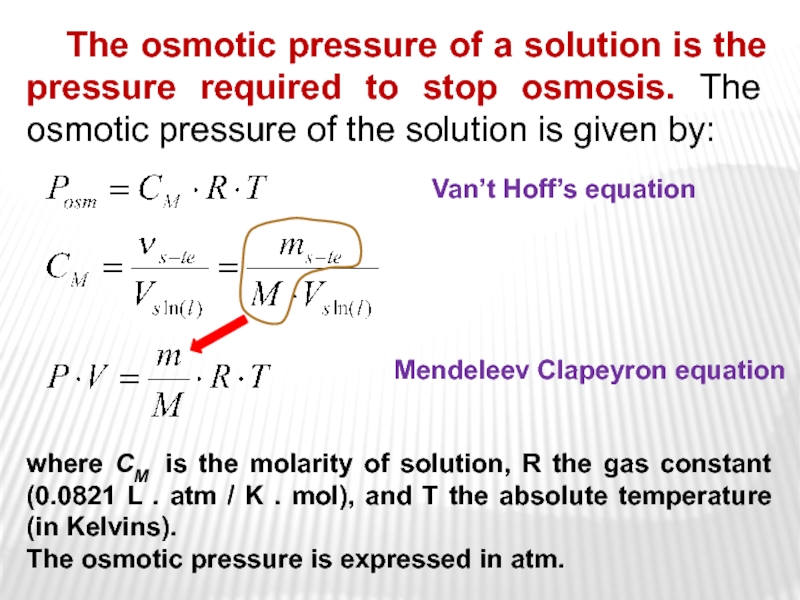
arm is filled to the same height with pure water; a semipermeable membrane separates the two arms. Because the flow of pure solvent through the membrane from left to right (from pure water to the solution) is greater than the flow of solvent in the reverse direction, the level of liquid in the right tube rises. (b) At equilibrium, the pressure differential, equal to the osmotic pressure of the solution (Πsoln), equalizes the flow rate of solvent in both directions. (c) Applying an external pressure equal to the osmotic pressure of the original glucose solution to the liquid in the right arm reverses the flow of solvent and restores the original situation.Слайд 27 The osmotic pressure of a solution is the pressure required
to stop osmosis. The osmotic pressure of the solution is
given by:where CM is the molarity of solution, R the gas constant (0.0821 L . atm / K . mol), and T the absolute temperature (in Kelvins).
The osmotic pressure is expressed in atm.
Van’t Hoff’s equation
Mendeleev Clapeyron equation
Слайд 28 Molarirty units are most appropriate in calculating which of the
following?
QUIZ ME
A) freezingpoint depression
B) vapor pressure
C) boilingpoint evaluation
D) osmotic
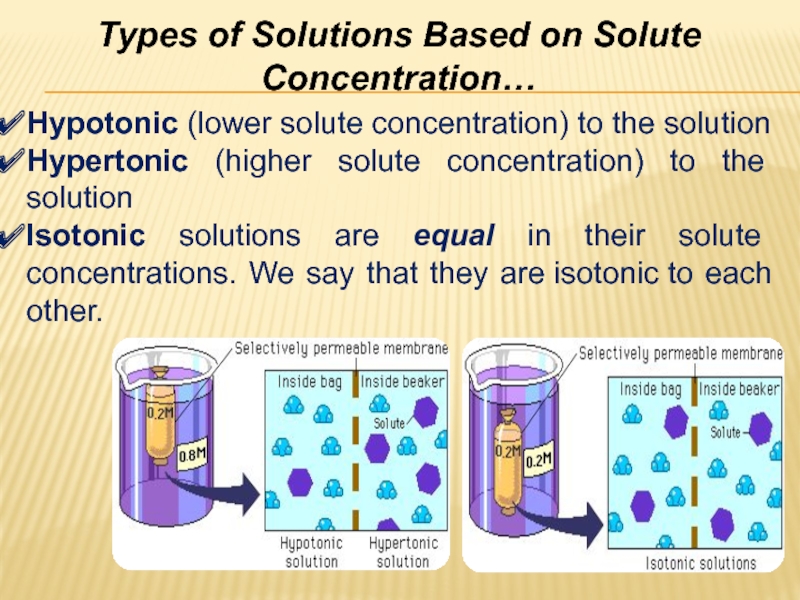
pressureСлайд 29Types of Solutions Based on Solute Concentration…
Hypotonic (lower solute concentration)
to the solution
Hypertonic (higher solute concentration) to the solution
Isotonic solutions
are equal in their solute concentrations. We say that they are isotonic to each other.Слайд 30Non-electrolyte:
1 М sugar solution
Electrolyte:
1 М NaCl salt solution
where i
is the Van’t Hoff factor, named after Jacobus Henricus Vant’
Hoff (1852-1911), who won the very first Nobel Prize in chemistry in 1901 for his work on colligative properties of solution.The i factor gives the number of particles per formula unit of the solute.
<<
i
Na+
Cl-
Слайд 31 The degree of dissociation is associated with an isotonic factor
by next ratio:
For Electrolyte Solution:
Слайд 32 If equal numbers of moles of each of the following
are dissolved in 1 kg of distilled water, the one
with the lowest boiling point will be:NaI
B) AlCl3
C) Mg(NO3)2
D) CH3COOH
E) C6H12O6
QUIZ ME
Слайд 33SUMMARY OF FACTS AND CONCEPTS
1. Colligative properties (or collective properties)
are properties that depend only on the number of solute
particles in solution and not on the nature of the solute particles.2. The four colligative properties of a solution are vapor pressure, osmotic pressure, boiling point and freezing point.
3. The change in vapor pressure where the solute is less volatile than the solvent is regulated by Raoult’s law, which states that the vapor pressure of a solvent over a solution is equal to the mole fraction of the solvent times the vapor pressure of pure solvent.
4. The osmotic pressure of a solution is the pressure required to stop osmosis.
5. The freezing point of the solution is always less than the freezing point of the pure solvent.
Слайд 34 7. In electrolyte solutions, the interaction between ions leads to
the formation of ion pairs. The Van’t Hoff factor (i)
provides a measure of the extent of dissociation of electrolytes in solution.8. Solutions can be classified as hypertonic, hypotonic or isotonic depending on the concentration of solute inside and outside the cell.
9. A hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of particle than the cell causing the cell to shrink.
10. A hypotonic solution has a lower concentration of particles than the cell causing the cell to swell.
11. An isotonic solution has the same osmotic strength on both sides of the semipermeable membrane.
12. Osmosis is the spontaneous net movement of solvent molecules through a semi-permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides.