Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Lecture subject :
Содержание
- 1. Lecture subject :
- 2. Atherosclerosis - is a chronic disease, appearing
- 3. Atherosclerosis etiology:Metabolic factors (exo- and endogenic) Hormonal factorsHemodynamic factorsNeural factorVascular factorHereditary and ethnic factors
- 4. Risk factors:HyperlipidemiaHypodynamiaArterial hypertensionDiabetes mellitusHypothyroidismHeredity
- 5. Слайд 5
- 6. Слайд 6
- 7. Atherogenic and anti-atherogenic substancesLow-density (LDLP) and very
- 8. Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis Etiologic factors lead to
- 9. Слайд 9
- 10. Morphology and morphogenesis: Macroscopic and microscopic stages of atherosclerosis have to be distinguished.
- 11. Stages of atherosclerosis (macroscopic):Fat stains and stripes
- 12. Слайд 12
- 13. Слайд 13
- 14. Stages of atherosclerosis (microscopic): Prelipidic stageLipoidosis (corresponds
- 15. Stages of atherosclerosis (microscopic): Prelipidic stage (macro:
- 16. Слайд 16
- 17. Слайд 17
- 18. Слайд 18
- 19. Слайд 19
- 20. Слайд 20
- 21. Слайд 21
- 22. Atherosclerotic plaque (scheme)1 – cover, 2 –
- 23. Clinicopathologic forms of atherosclerosis:Atherosclerosis of aortaAtherosclerosis of
- 24. In case of atherosclerosis of any localization
- 25. Atherosclerosis of aorta
- 26. Слайд 26
- 27. Слайд 27
- 28. Слайд 28
- 29. Слайд 29
- 30. Слайд 30
- 31. Слайд 31
- 32. Слайд 32
- 33. Atherosclerosis of arteries of heart and cerebral
- 34. Слайд 34
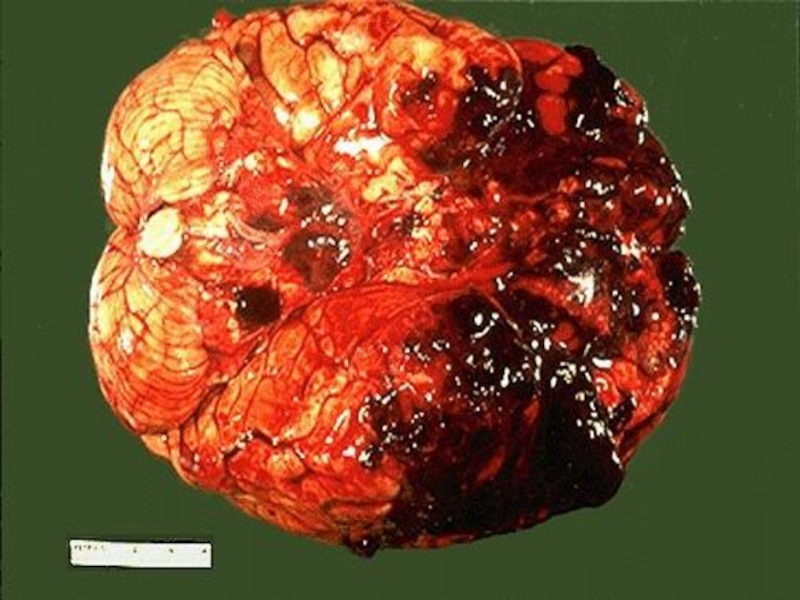
- 35. Atherosclerosis of renal arteries leads to the development of atherosclerotic macrotuberous kidney
- 36. Atherosclerotic nephrosclerosis
- 37. Atherosclerosis of arteries of low extremities leads
- 38. Слайд 38
- 39. Слайд 39
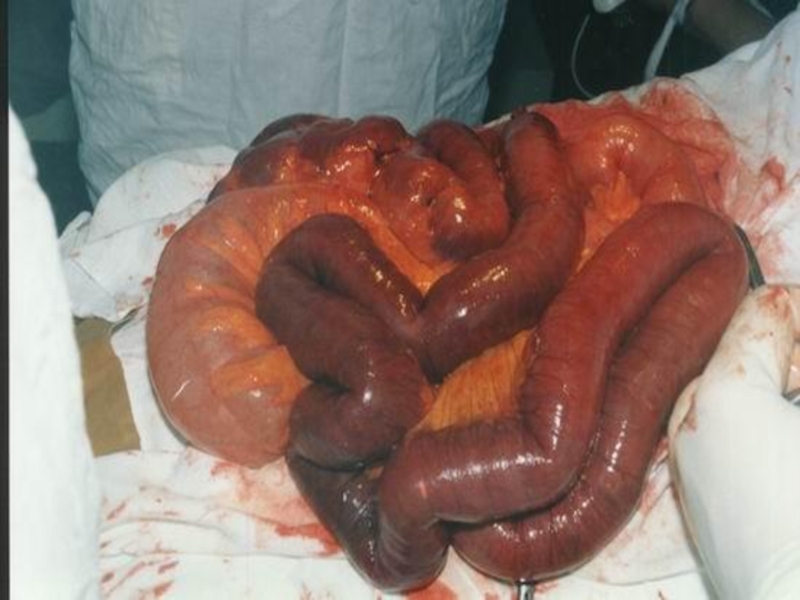
- 40. Atherosclerosis of mesenteric arteries leads to the bowels gangrene
- 41. Слайд 41
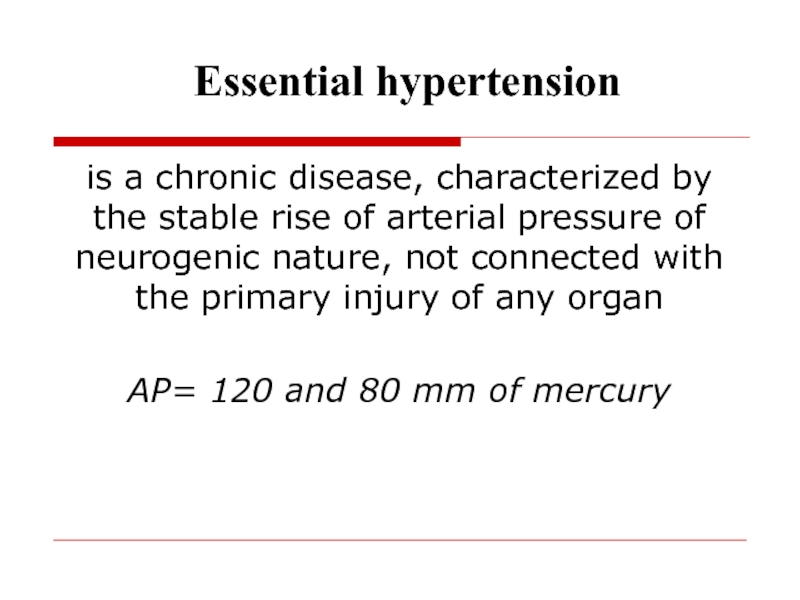
- 42. Essential hypertension
- 43. Essential hypertension is a chronic disease, characterized
- 44. Risk factors: Stress, psychoemotional overstrain HeredityIncreased use of sodium chloride (table salt)
- 45. Hypertension course: malignantbenign
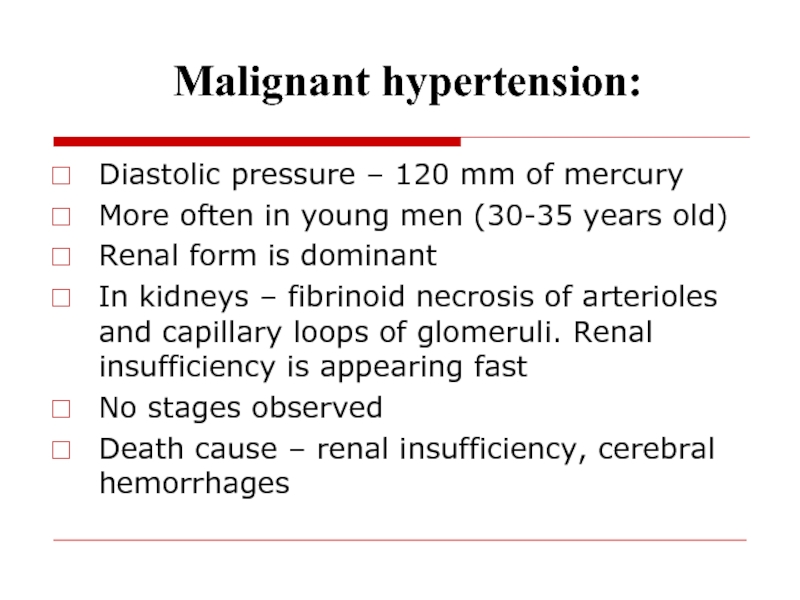
- 46. Malignant hypertension: Diastolic pressure –
- 47. Слайд 47
- 48. Слайд 48
- 49. Слайд 49
- 50. Benign course of hypertension
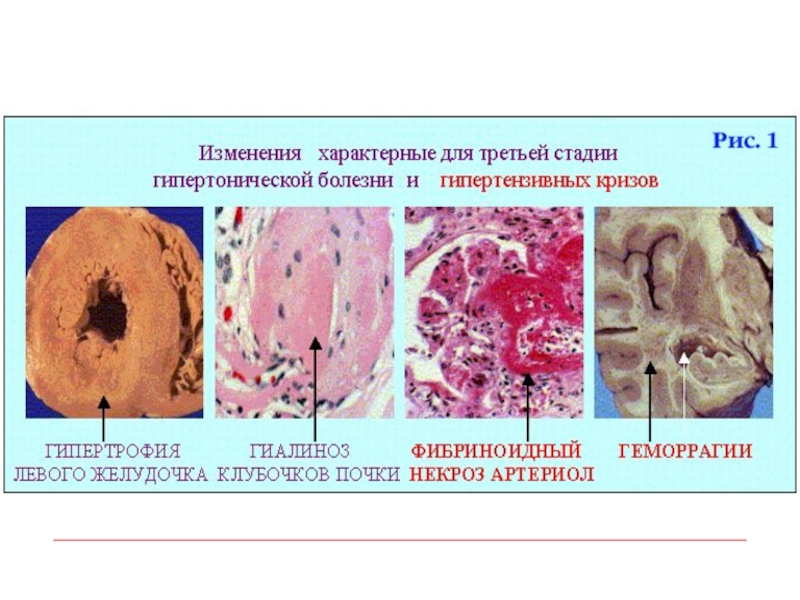
- 51. 3 stages: Pre-clinicalGeneralized changes of small arteries
- 52. Pre-clinical stage:Transient hypertension Hypertrophy of muscle layer
- 53. Слайд 53
- 54. Stage of the generalized changes of arteries:Stable
- 55. Слайд 55
- 56. Слайд 56
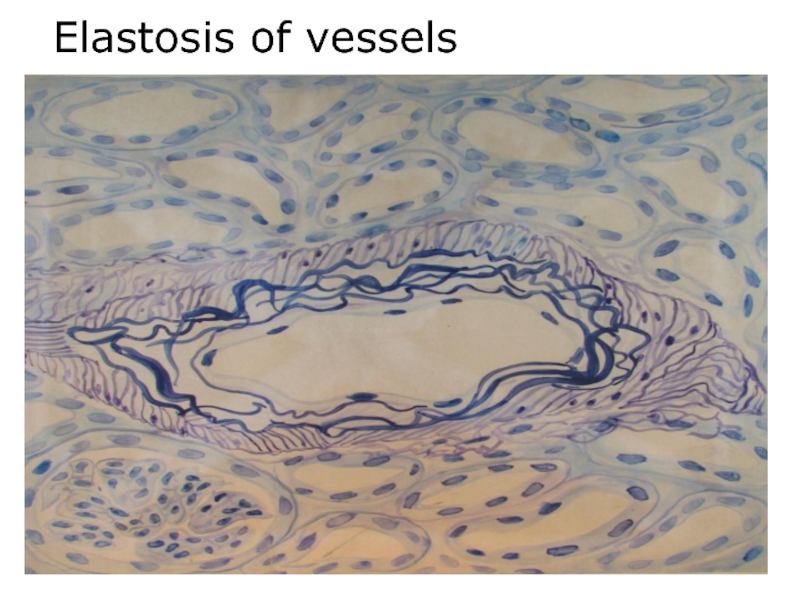
- 57. Elastosis of vessels
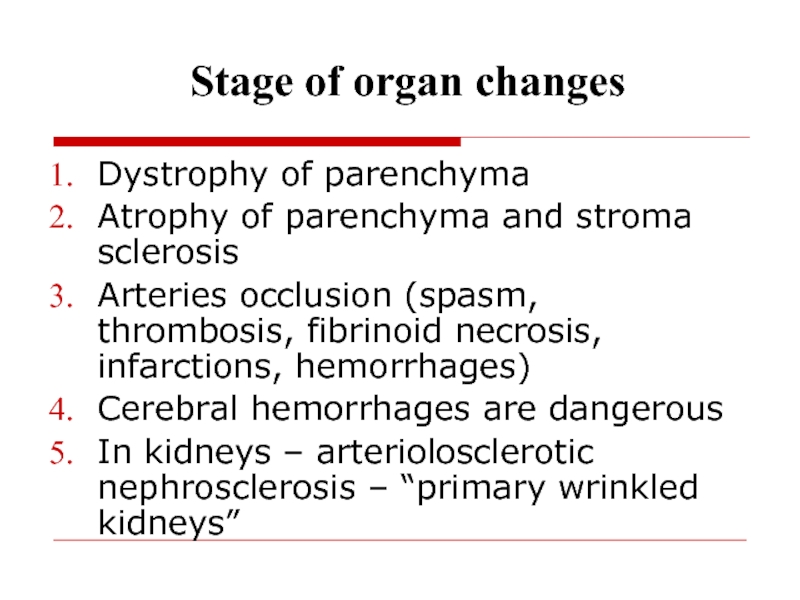
- 58. Stage of organ changes Dystrophy of
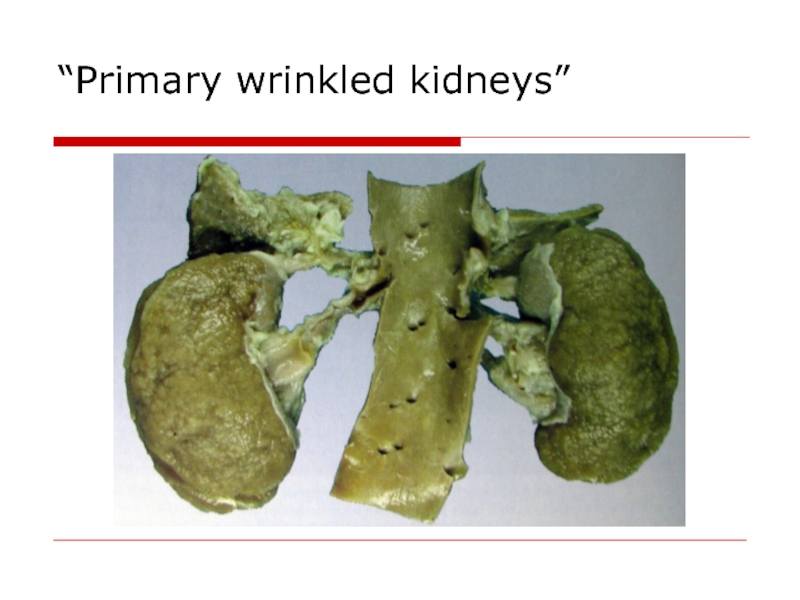
- 59. “Primary wrinkled kidneys”
- 60. Слайд 60
- 61. Слайд 61
- 62. Слайд 62
- 63. Слайд 63
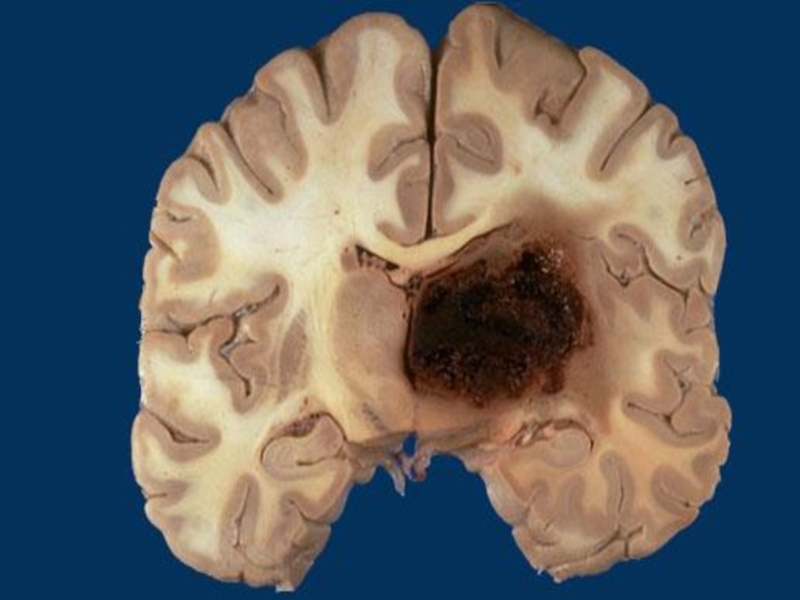
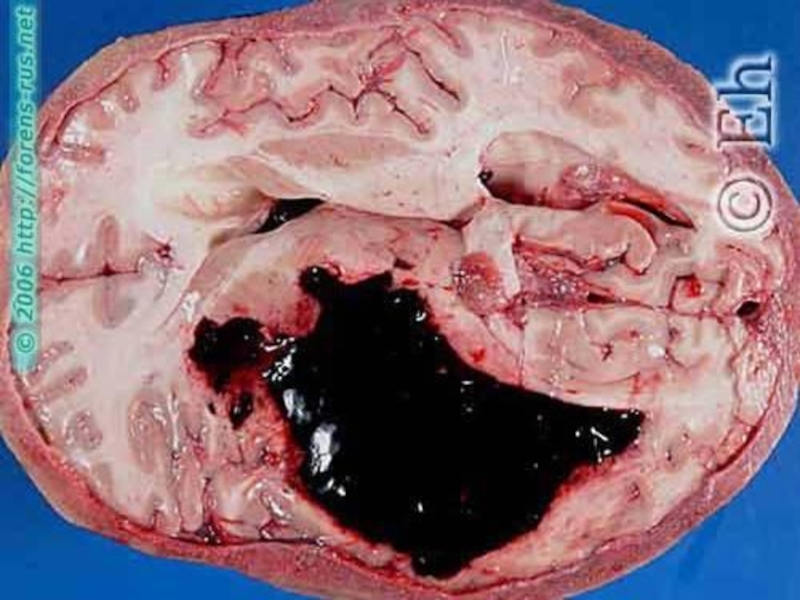
- 64. Types of cerebral hemorrhages: Without the structure
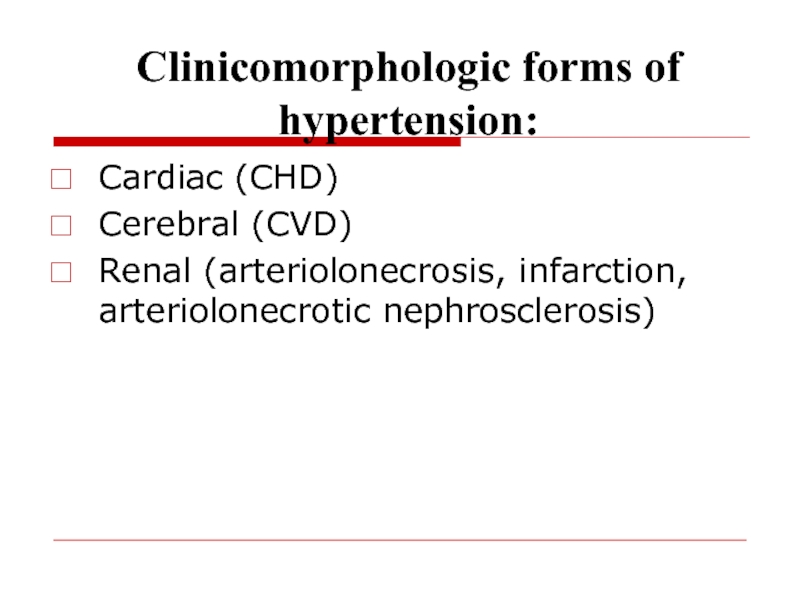
- 65. Clinicomorphologic forms of hypertension:Cardiac (CHD)Cerebral (CVD)Renal (arteriolonecrosis, infarction, arteriolonecrotic nephrosclerosis)
- 66. THANKS FOR YOURATTENTION!!!
- 67. Скачать презентанцию
Atherosclerosis - is a chronic disease, appearing as a result of lipid and protein metabolism derangement, characterized by arterial involvement of elastic and musculoelastic type in the form of focal deposition
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 3Atherosclerosis etiology:
Metabolic factors (exo- and endogenic)
Hormonal factors
Hemodynamic factors
Neural factor
Vascular
factor
Hereditary and ethnic factors
Слайд 4Risk factors:
Hyperlipidemia
Hypodynamia
Arterial hypertension
Diabetes mellitus
Hypothyroidism
Heredity
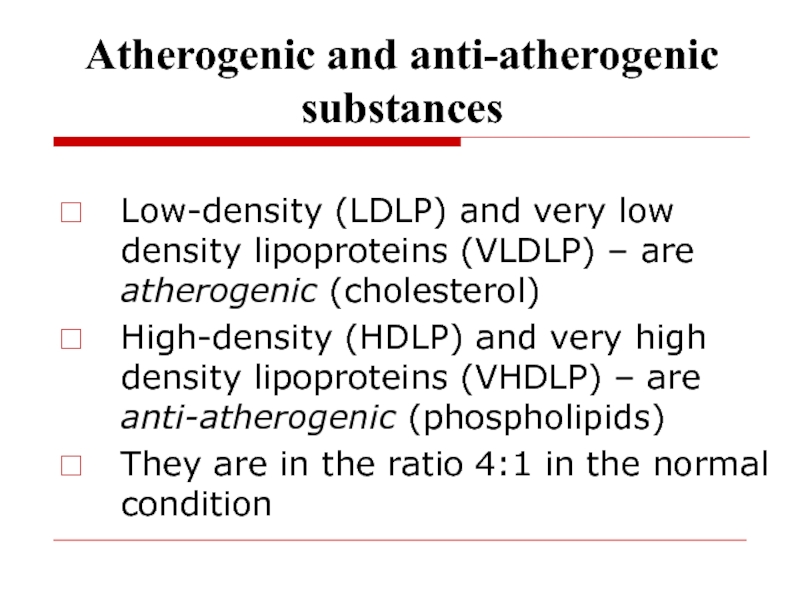
Слайд 7Atherogenic and anti-atherogenic substances
Low-density (LDLP) and very low density lipoproteins
(VLDLP) – are atherogenic (cholesterol)
High-density (HDLP) and very high
density lipoproteins (VHDLP) – are anti-atherogenic (phospholipids) They are in the ratio 4:1 in the normal condition
Слайд 8Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis
Etiologic factors lead to atherogenic lipoproteidemia and
increase of artery wall membranes permeability → injury of arteries
endothelium → accumulation of VLDLP and LDLP in the arteries intima → proliferation of unstriped muscle cells and macrophages and their transformation into foam cells.Слайд 10Morphology and morphogenesis:
Macroscopic and microscopic stages of atherosclerosis
have to be distinguished.
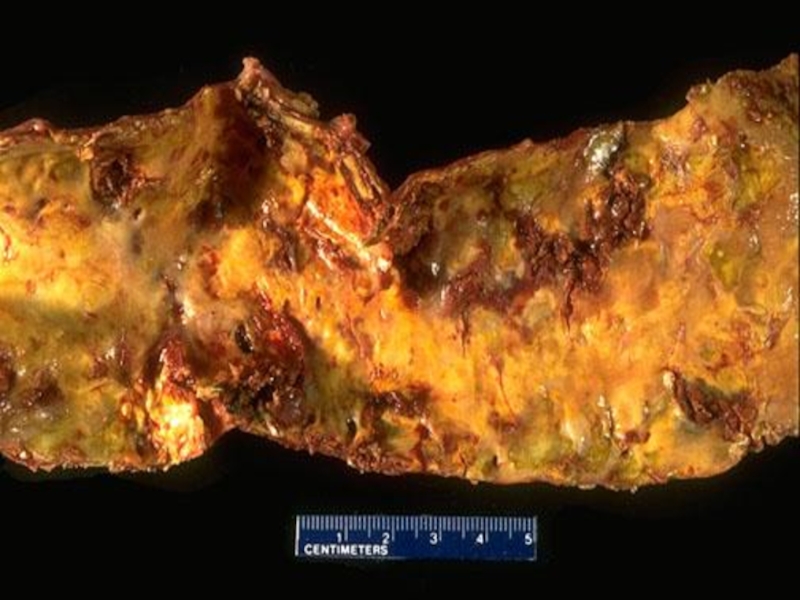
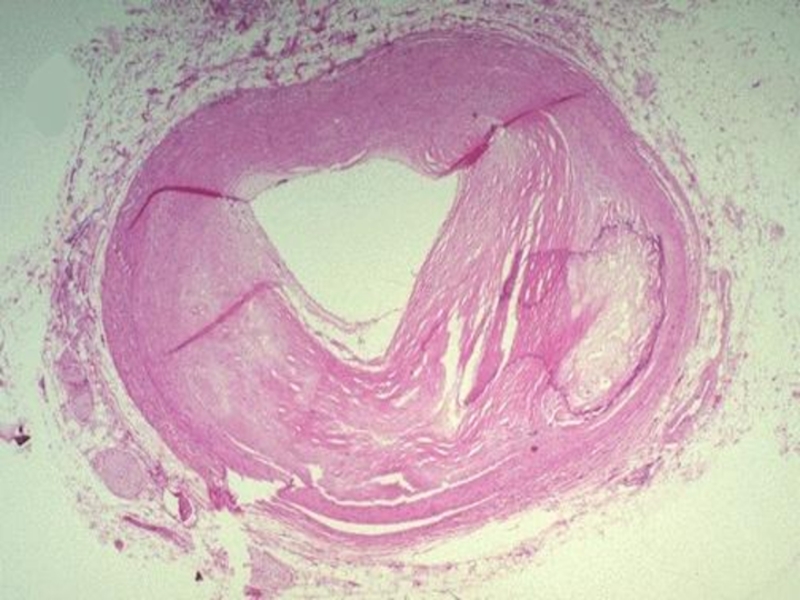
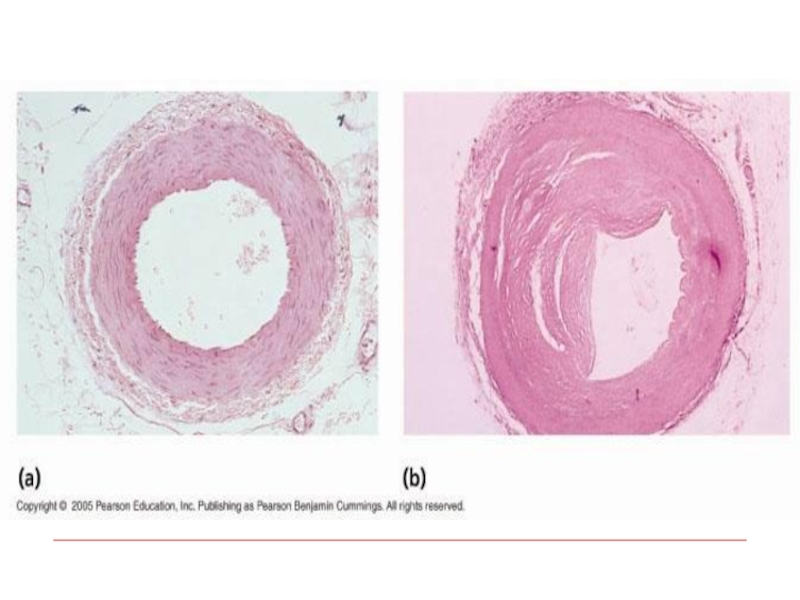
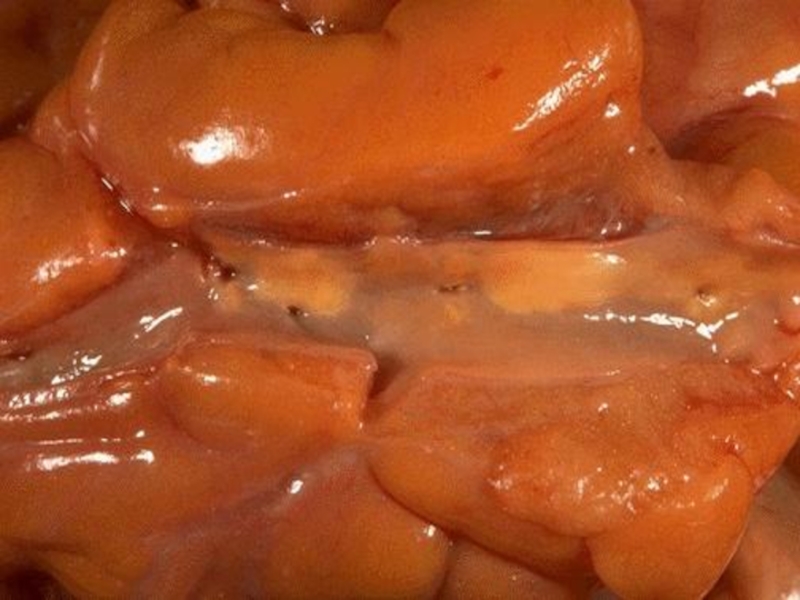
Слайд 11Stages of atherosclerosis (macroscopic):
Fat stains and stripes (stains and stripes
of yellow color, not raised above the intima surface)
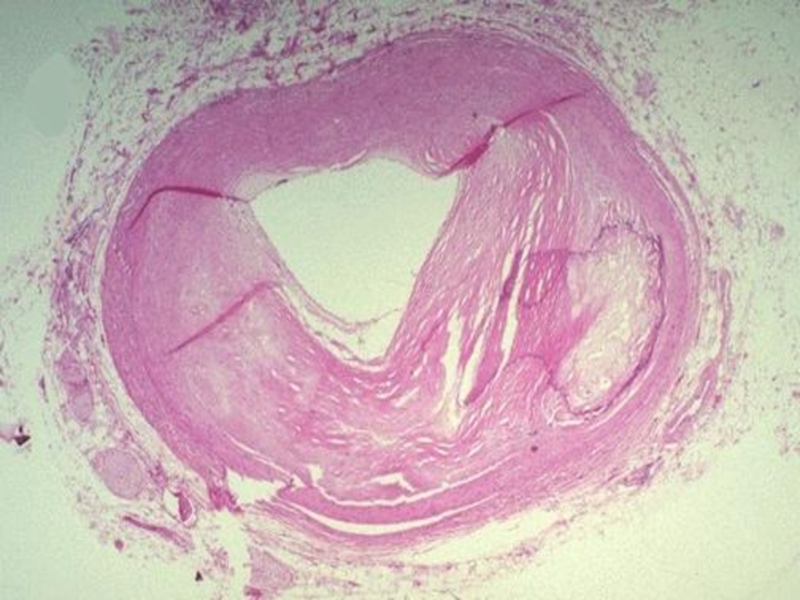
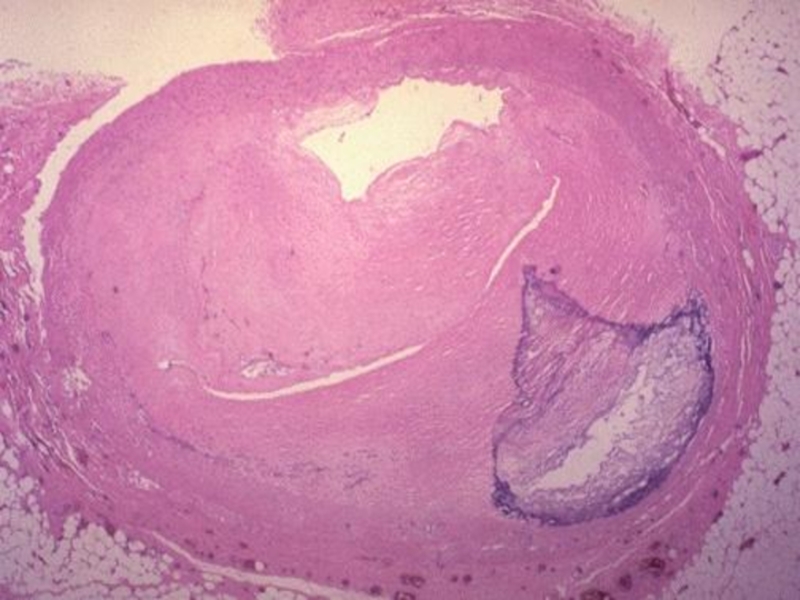
Fibrous plaques
(solid, whitish formations, raised above the intima surface – atherosclerotic plaques)Complicated affections/lesions (atheromatosis, hemorrhages in the plaque, formation of thrombi)
Atherocalcinosis (solid, white as a stone)
Слайд 14Stages of atherosclerosis (microscopic):
Prelipidic stage
Lipoidosis (corresponds to fat stains
and stripes)
Liposclerosis (corresponds to fibrous plaques)
Atheromatosis (corresponds to the 3rd
stage macro)Atherocalcinosis (corresponds to the 4th stage macro)
Слайд 15Stages of atherosclerosis (microscopic):
Prelipidic stage (macro: no changes, increase
of endothelium permeability)
Lipoidosis (lipids infiltrate the intima)
Liposclerosis (in the plaque
center – lipids and proteins, on the periphery– connective tissue and newly formed vessels)Atheromatosis (lipoprotein detritus, fibers destruction, arrosion of plaque vessels tissue)
Atherocalcinosis (lime in the form of granules and plates of violet color when stained with hematoxylin/eosin)
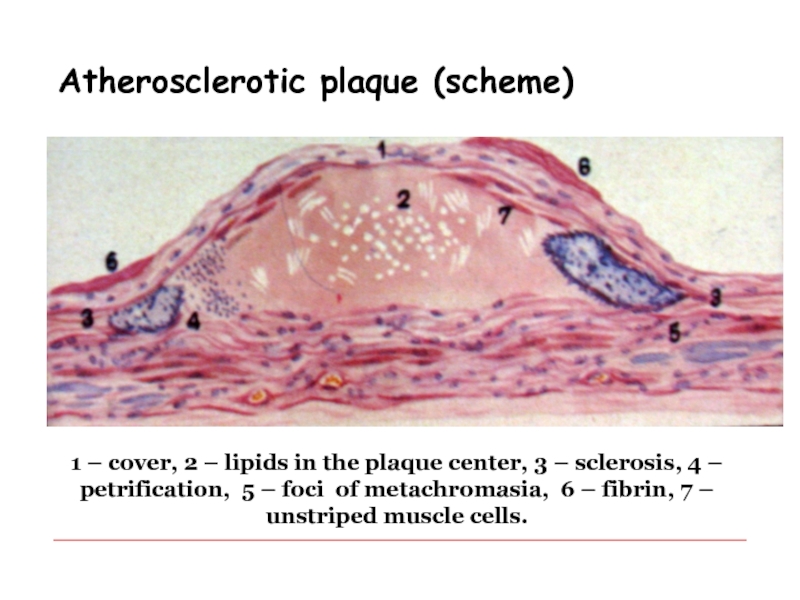
Слайд 22Atherosclerotic plaque (scheme)
1 – cover, 2 – lipids in the
plaque center, 3 – sclerosis, 4 – petrification, 5 –
foci of metachromasia, 6 – fibrin, 7 – unstriped muscle cells.Слайд 23Clinicopathologic forms of atherosclerosis:
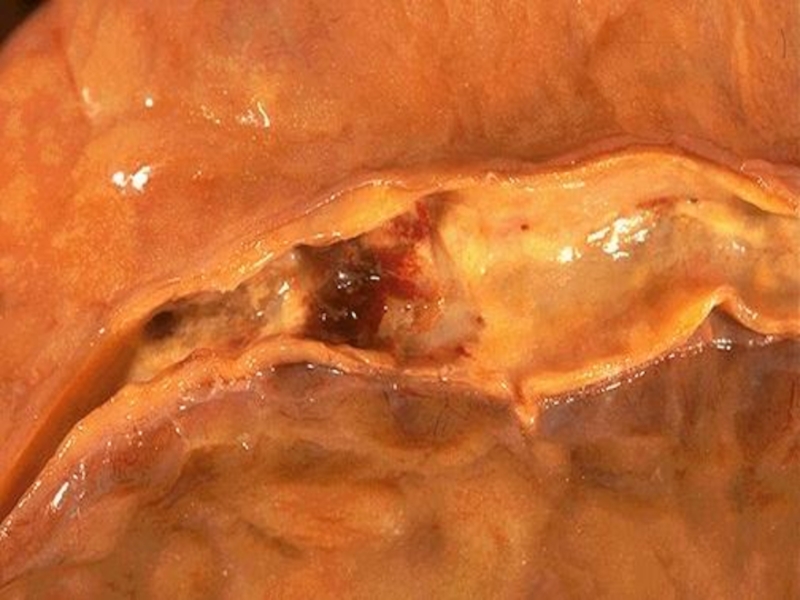
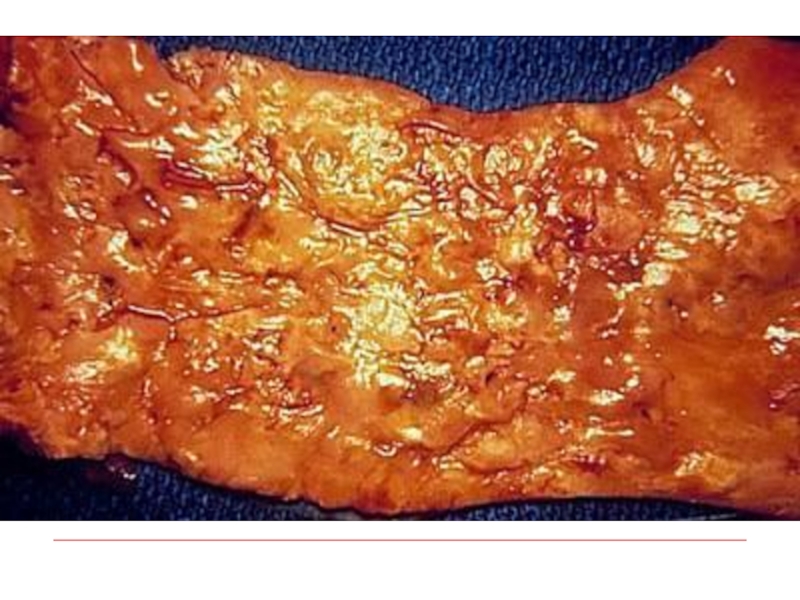
Atherosclerosis of aorta
Atherosclerosis of coronary arteries
Atherosclerosis of
cerebral arteries
Atherosclerosis of renal arteries
Atherosclerosis of intestinal arteries
Atherosclerosis of arteries of low extremities
Слайд 24In case of atherosclerosis of any localization the manifestations can
be dual:
If the atherosclerotic plaque does not block the artery
lumen fully – chronic ischemia is appearing → dystrophy, atrophy of parenchyma and stroma sclerosisIf the plaque is blocking the artery lumen fully – acute ischemia and necrosis (infarction) appear in the tissue
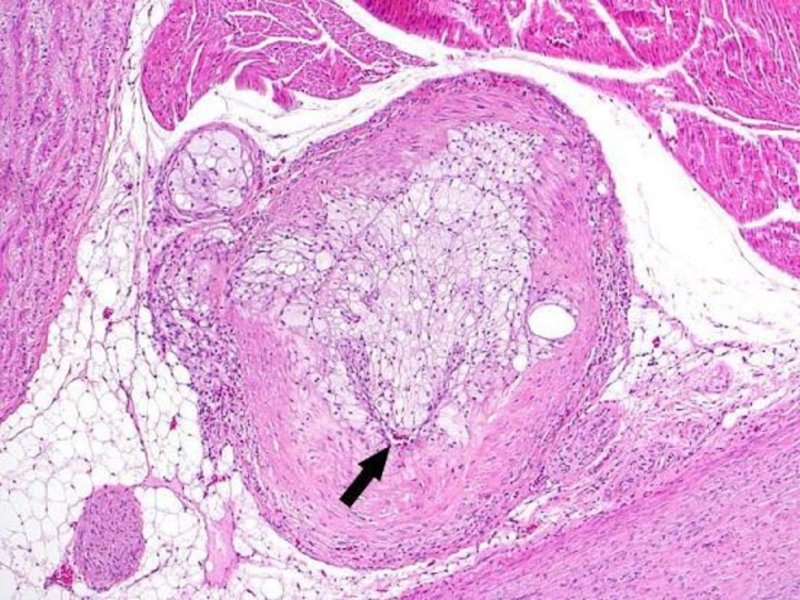
Слайд 33Atherosclerosis of arteries of heart and cerebral arteries
underlies the coronary
heart disease (CHD) and cerebrovascular disease (CVD) correspondingly.
Слайд 35
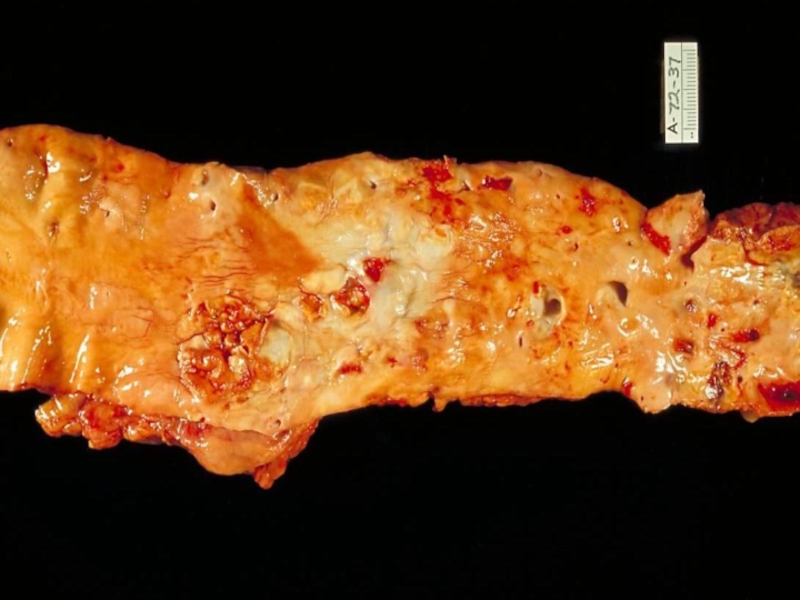
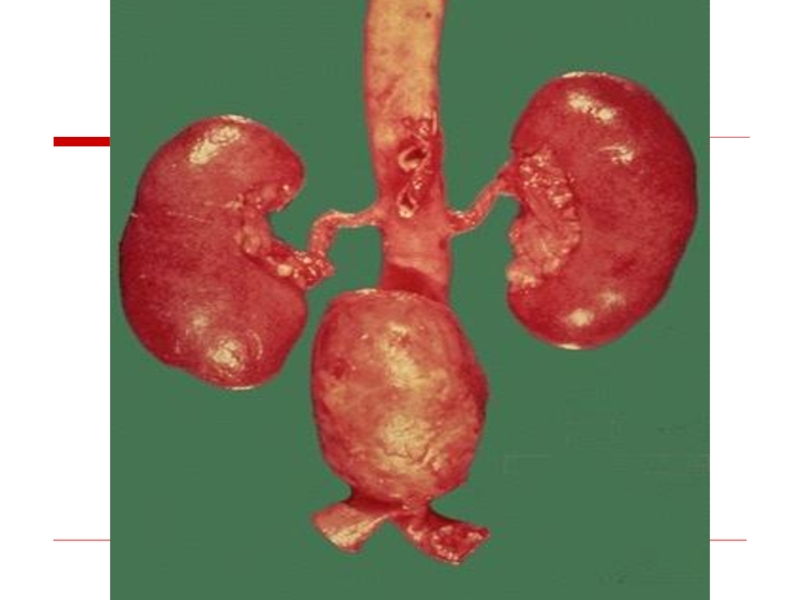
Atherosclerosis of renal arteries leads to the development of atherosclerotic
macrotuberous kidney
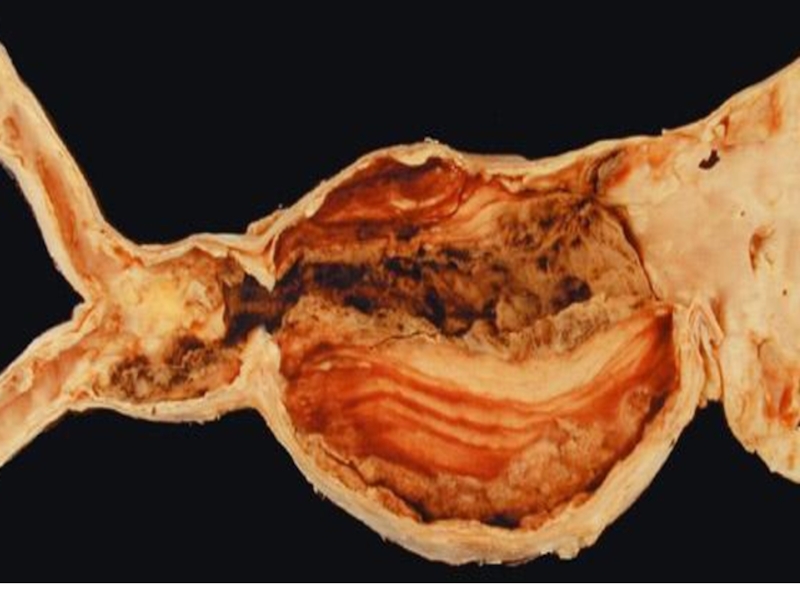
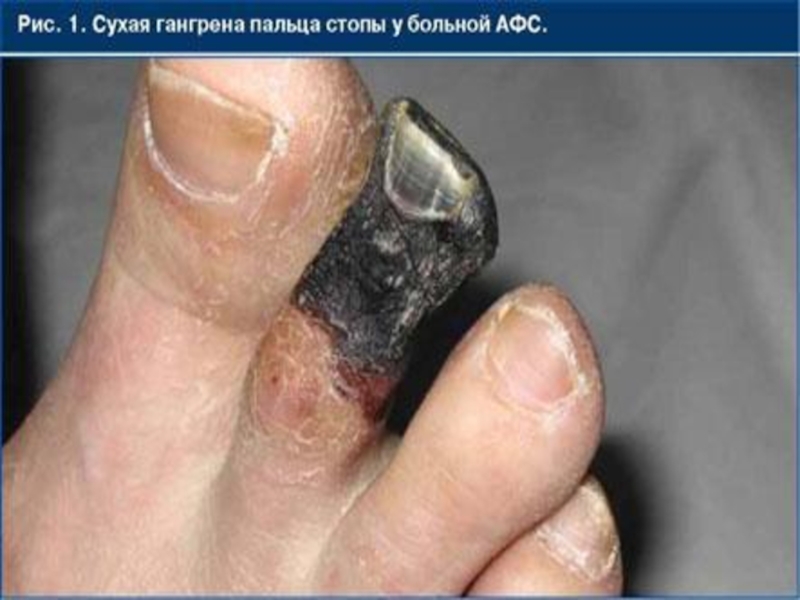
Слайд 37Atherosclerosis of arteries of low extremities
leads to intermittent claudication
(partial blocking of artery by the plaque) or to gangrene
(fully blocking of femoral artery by the plaque or thrombus)Слайд 43Essential hypertension
is a chronic disease, characterized by the stable
rise of arterial pressure of neurogenic nature, not connected with
the primary injury of any organAP= 120 and 80 mm of mercury
Слайд 44Risk factors:
Stress, psychoemotional overstrain
Heredity
Increased use of sodium chloride
(table salt)
Слайд 46
Malignant hypertension:
Diastolic pressure – 120 mm of mercury
More often
in young men (30-35 years old)
Renal form is dominant
In
kidneys – fibrinoid necrosis of arterioles and capillary loops of glomeruli. Renal insufficiency is appearing fastNo stages observed
Death cause – renal insufficiency, cerebral hemorrhages
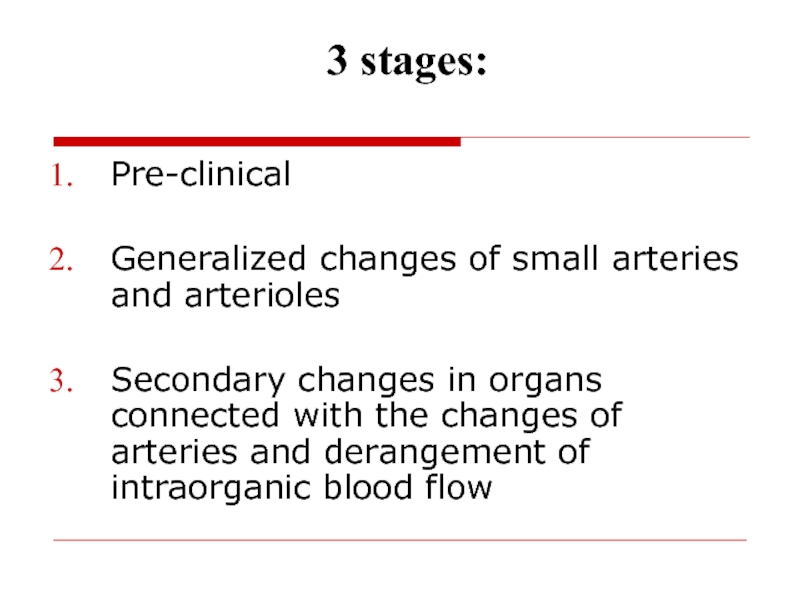
Слайд 513 stages:
Pre-clinical
Generalized changes of small arteries and arterioles
Secondary changes in
organs connected with the changes of arteries and derangement of
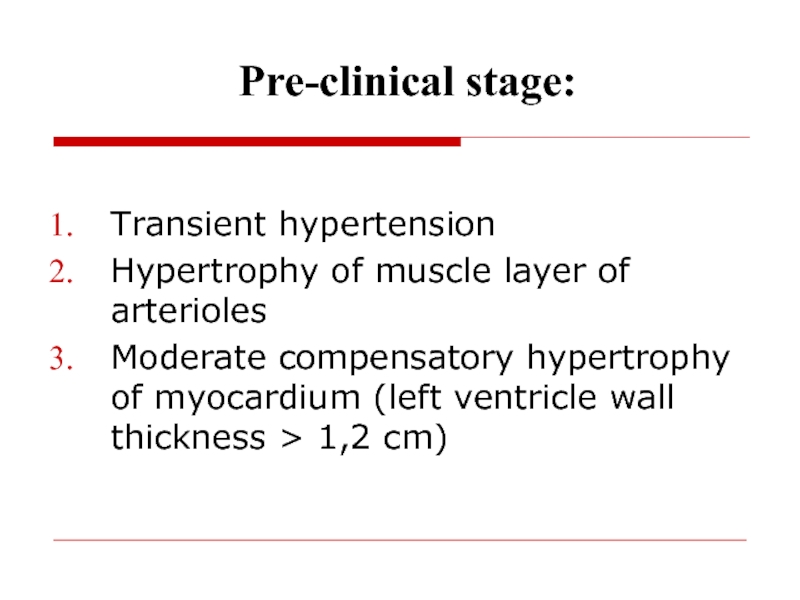
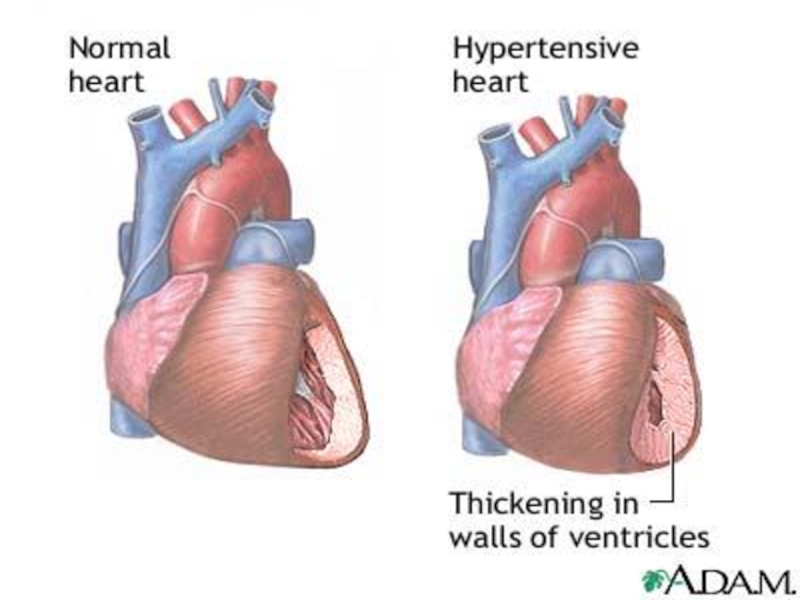
intraorganic blood flowСлайд 52Pre-clinical stage:
Transient hypertension
Hypertrophy of muscle layer of arterioles
Moderate compensatory
hypertrophy of myocardium (left ventricle wall thickness > 1,2 сm)
Слайд 54Stage of the generalized changes of arteries:
Stable rise of arterial
pressure
In the small arteries – plasma transudation, hyalinosis
Elastosis, elastofibrosis –
hyperplasia and splitting of internal elastic membrane, followed by sclerosis (fibrosis)Myocardial hypertrophy is increasing
! In case of hypertension combination with atherosclerosis the fibrous plaques are forming even in small arteries!
Слайд 58
Stage of organ changes
Dystrophy of parenchyma
Atrophy of parenchyma and stroma
sclerosis
Arteries occlusion (spasm, thrombosis, fibrinoid necrosis, infarctions, hemorrhages)
Cerebral hemorrhages are
dangerous In kidneys – arteriolosclerotic nephrosclerosis – “primary wrinkled kidneys”