Слайд 1Ministry education and Science of Republic of Kazakhstan
Karaganda State University
named after academician Ye.A. Buketov
Biological and geographical faculty
Botany Department
Course – Botany
Specialty - 5В011300 – «Biology»
Lecture № 8
Fruits and their classification. Spreading of fruits and seeds
(1 hour)
Lecturer: candidate of biological science, associated professor
Ishmuratova Margarita Yulaevna
Слайд 2Plan of lecture:
1 Fruit and seed. Functions of fruits and
seeds.
2 Morphology of fruits. Types of fruits.
3 Spreading of fruits
and seeds. Practical uses.
Слайд 3Basic literatures:
1 Бавтуто Г.А. Практикум по анатомии и морфологии
растений. – Минск: Новое знание, 2002. – 185 с.
2 Родман
А.С. Ботаника. – М.: Колос, 2001. - 328 с.
Additional literatures:
1 Ишмуратова М.Ю. Ботаника. Учебно-методическое пособие. - Караганда: РИО Болашак-Баспа, 2015. - 331 с.
2 Тусупбекова Г.Т. Основы естествознания. Ч. 1. Ботаника. – Астана: Фолиант, 2013. – 321 с.
3 Байтулин И.О. Основы ризологии. - Алматы: Гылым, 2001. – 210 с.
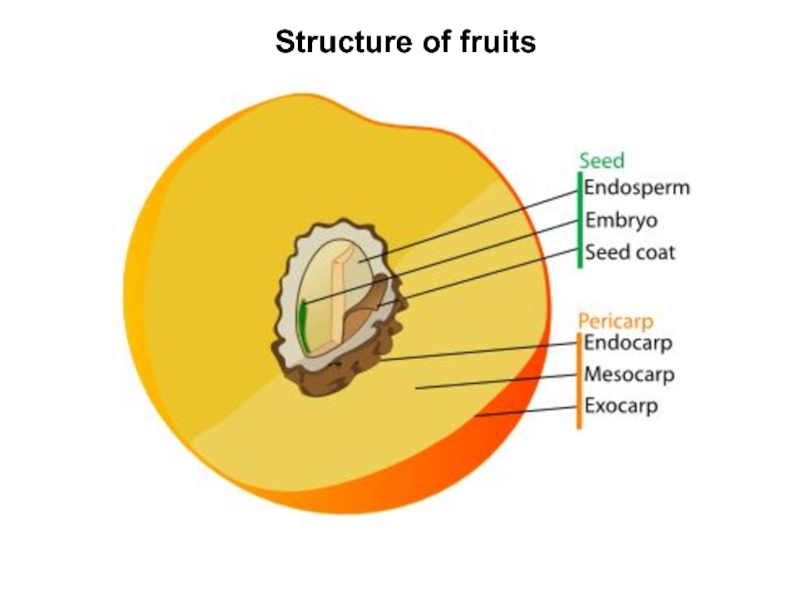
Слайд 4A fruit is defined as ripened ovary, flower, or whole
inflorescence. The origins of the fruit coat and the pericarp
which is comprised of the exocarp, mesocarp, and endocarp, are mostly from the wall of the pistil.
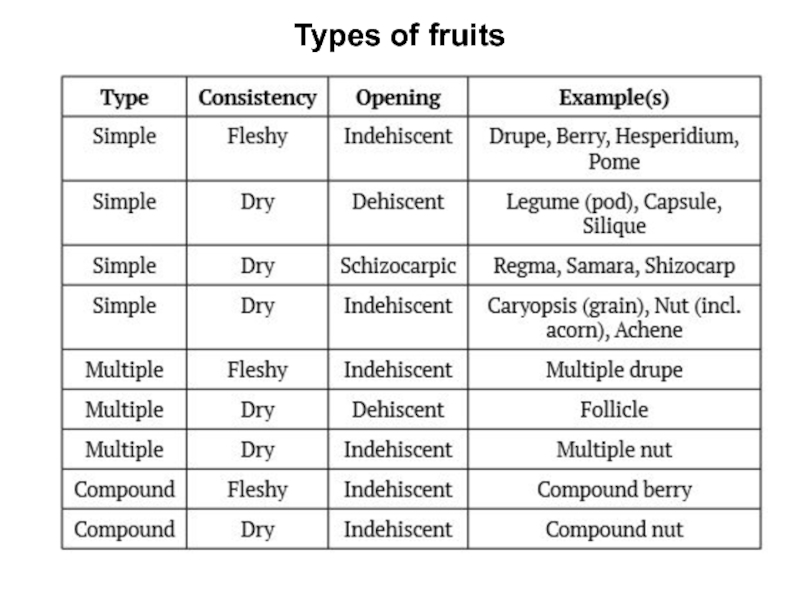
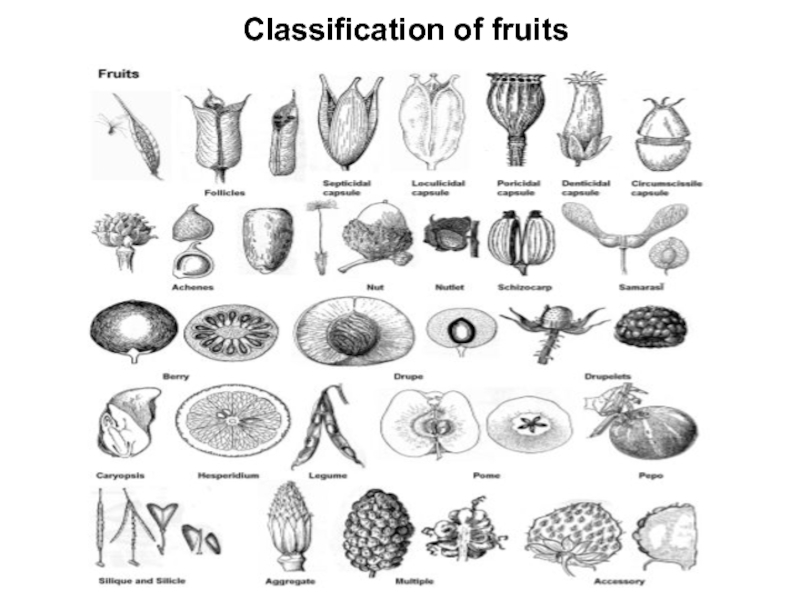
Слайд 5Fruits can be simple, multiple, or compound. Simple fruits come
from a single pistil (like cherry, Prunus). Multiple fruits are
formed from many pistils of the same flower (strawberry, Fragaria). A compound fruit (infructescense) would be a pineapple (Ananas) or fig (Ficus) which comes from multiple flowers (inflorescence).
Fruits can be dry or fleshy. An example of dry fruit is a nut like peanut (Arachis) or walnut (Juglans). Examples of fleshy fruits include apples (Malus) or oranges (Citrus). (like papaya, Carica) will not open and will be dispersal units (diaspores) themselves. Schizocarp fruits (like in spurge, Euphorbia or maple, Acer) are in between: they do not open but break into several parts, and each of them contains seed inside. In addition, simple fruits could be monomerous (1-seeded) like nut or achene (sunflower, Helianthus), or bear multiple seeds (like follicle in tulip, Tulipa).
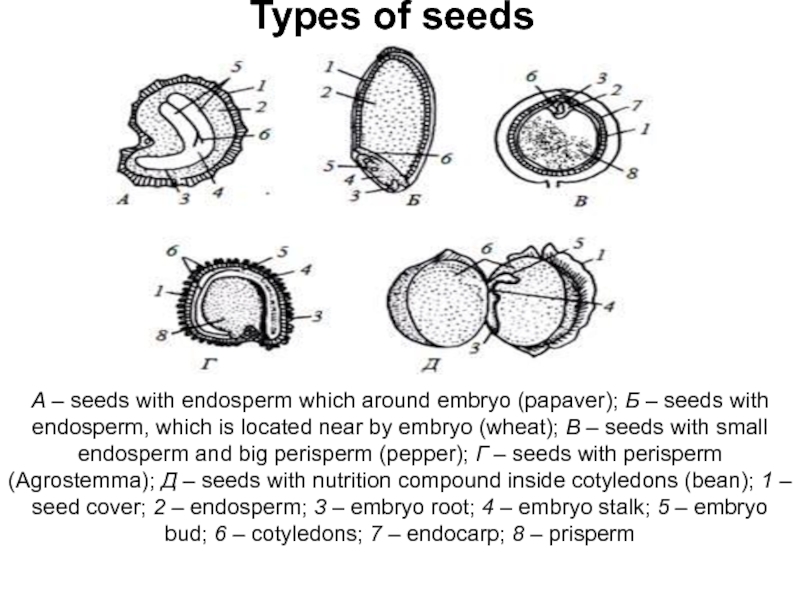
Слайд 9Types of seeds
А – seeds with endosperm which around embryo (papaver);
Б – seeds with endosperm, which is located near by embryo
(wheat); В – seeds with small endosperm and big perisperm (pepper); Г – seeds with perisperm (Agrostemma); Д – seeds with nutrition compound inside cotyledons (bean); 1 – seed cover; 2 – endosperm; 3 – embryo root; 4 – embryo stalk; 5 – embryo bud; 6 – cotyledons; 7 – endocarp; 8 – prisperm
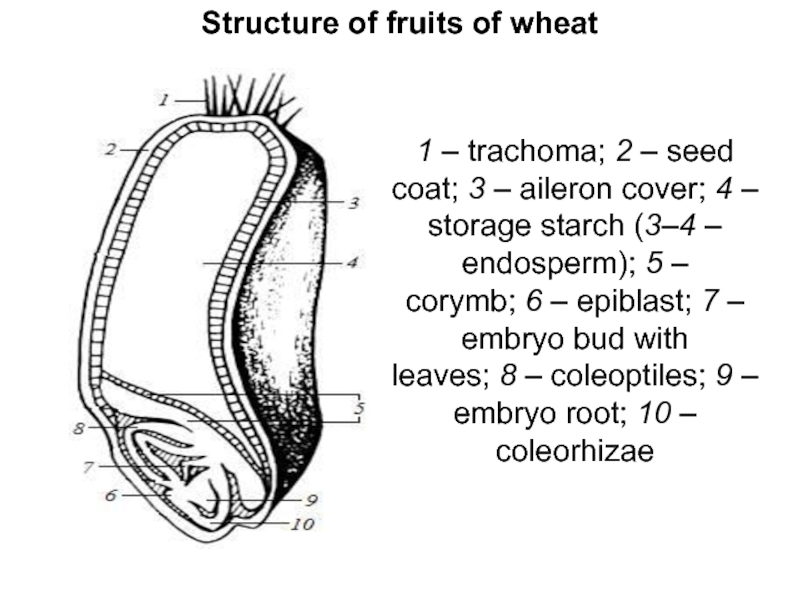
Слайд 11Structure of fruits of wheat
1 – trachoma; 2 – seed coat; 3 – aileron cover;
4 – storage starch (3–4 – endosperm); 5 – corymb; 6 – epiblast; 7 – embryo bud with
leaves; 8 – coleoptiles; 9 – embryo root; 10 – coleorhizae
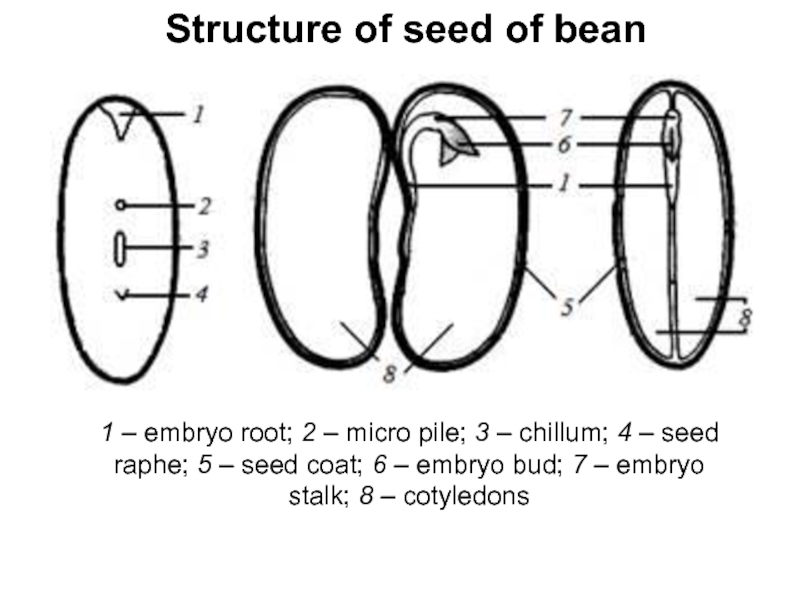
Слайд 12Structure of seed of bean
1 – embryo root; 2 – micro pile; 3 – chillum;
4 – seed raphe; 5 – seed coat; 6 – embryo bud; 7 – embryo stalk; 8 –
cotyledons
Слайд 13There are two basic types of spreading of seed. The
first way is realized without using of external agents; the
second way – by using different external factors: wind, water, animals and human.
The first way is caled autochoria (from Greek «autos» - self, «choreo» - spreading, going), second method - allochoria (from Greek word «allos» - another). So, these plants are called autochores and allochores.
Слайд 14There are four main methods of allochoria. They are: anemochoria
(from Greek word «anemos» – wind), zoochoria («zoon» – animal),
hydrochoria («hydro» – water) and antropochoria («antropos» – human). The most wide group of plants with anemochria. So, units of spreading, seeds or whole fruits are spreaded by wind.
Слайд 15Control questions:
1 How scientists make a scheme of parts
of flowers and fruits?
2 Which signs belong higher plants to
leading positions in world?
3 How do produce simple and compound fruits?
4 Note the differences between seeds of monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants.
5 Make a classification of fruits and seeds.
6 Prepare the scheme of seed of bean and wheat.
7 Why did zoochoria appear after anemochoria?
Слайд 16Test questions:
Compound fruits has:
А) sycamine
В) broad tree
С) apple tree
Д) ananas
Е) cherry
F) banana
Type of spreading of seeds and fruits by
using of insects:
А) antropochoria
В) zoochoria
С) hydrochoria
Д) entomochoria
Е) anemochoria