Слайд 1Ministry education and Science of Republic of Kazakhstan
Karaganda State University
named after academician Ye.A. Buketov
Biological and geographical faculty
Botany Department
Course – Botany
Specialty - 5В011300 – «Biology»
Lecture № 29
Bases of phytocenology
(1 hour)
Lecturer: candidate of biological science, associated professor
Ishmuratova Margarita Yulaevna
Слайд 2Plan of lecture:
1 Definition of phytocenology, or plant geography.
2 Flora.
Geographic elements of flora.
3 Phytocoenosis.
Слайд 3Main literatures:
1 Еленевский А.Г., Соловьев М.П., Тихомиров В.Н. Ботаника:
систематика высших, или наземных, растений. 2 изд. - М.: Academіa,
2000. - 440 с.
2 Родман А.С. Ботаника. – М.: Колос, 2001. - 328 с.
Additional literatures:
1 Билич Г.Л., Крыжановский В.А. Биология. Т. 2: Ботаника. - М.: Оникс 21 век, 2002. - 543 с.
2 Байтенов М.С. Флора Казахстана. - Алматы: Гылым, 1999. – 240 с.
3 Байтенов М.С. Флора Казахстана. - Алматы: Ғылым, 2001. - 198 с.
Слайд 4Geography of Vegetation
Plants are main components of terrestrial ecosystems, they
are primary producers, and almost all terrestrial life if based
on plants. Consequently, plants will determine how a particular territory might look, which could be,for example, grassland, tundra, or forest.
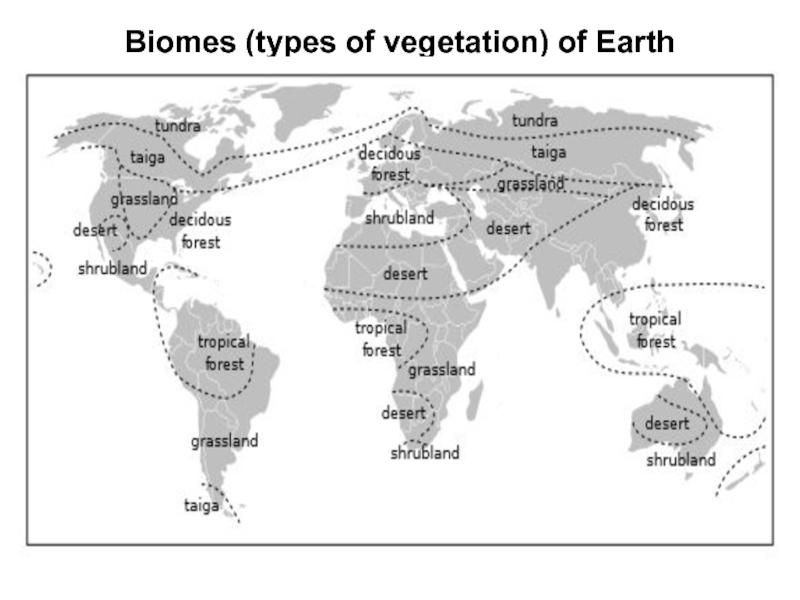
These types of vegetation (i.e., visually different plant communities) will have different occurrence on Earth. Below is the list of the most important types (they also called biomes):
Tundra
Small-sized plants adapted to the short season, wet soils and sometimes also permafrost
Taiga
Conifer forests
Слайд 5Geography of Vegetation
Deciduous forest
Broadleaved temperate forests. The other type
of deciduous forests are dry forests of tropical climates.
Grassland
Prairie(North
America),steppe (Eurasia), savanna (Africa and Australia), llanos (north South America), pampas (south South America)
Shrubland
Chaparral (North America), maquis (Mediterranean),fynbos (South Africa), bush (Australia)
Desert
Different from shrubl and by plants staying apart and soil surface visible
Tropical forest
Selva, tropical rain forest: humid and warm environment, the peak of Earth biodiversity
Слайд 6Biomes (types of vegetation) of Earth
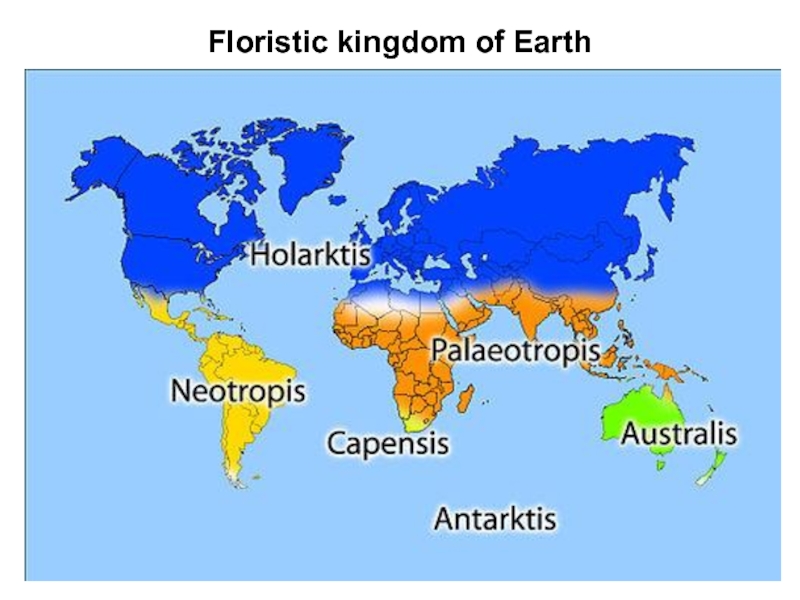
Слайд 7Geography of Vegetabilia
Floristic differences are due to the various
geological and biological histories of these places. Plant biogeography studies
them, explains the mand creates the floristic kingdoms classification.
Слайд 11Areal – is a region of geographical spreading of systematic
unit (species, genus, family, etc).
Place of location – is a
concrete geographic point, where this species was observed.
Слайд 15All species from Red Book are separated into following categories:
1.
Ех - disappeared.
2. Е – dangerous of disappearing. Need special
activity for storage.
3. V – decreasing in amount.
4. R - rare. It is possible to decreasing in amount at non comfortable conditions.
5. Recover species. They early were included in categories Е, V or R, but present day recovered their populations. Need in constant control.
Слайд 16Control questions:
1 Take a definition for plant geography and
phytocenology.
2 Which living forms do grow in Kazakhstan?
3 Make a
list of basic types of vegetation for continent Eurasia.
4 How many types of vegetation can you separate for Kazakhstan?
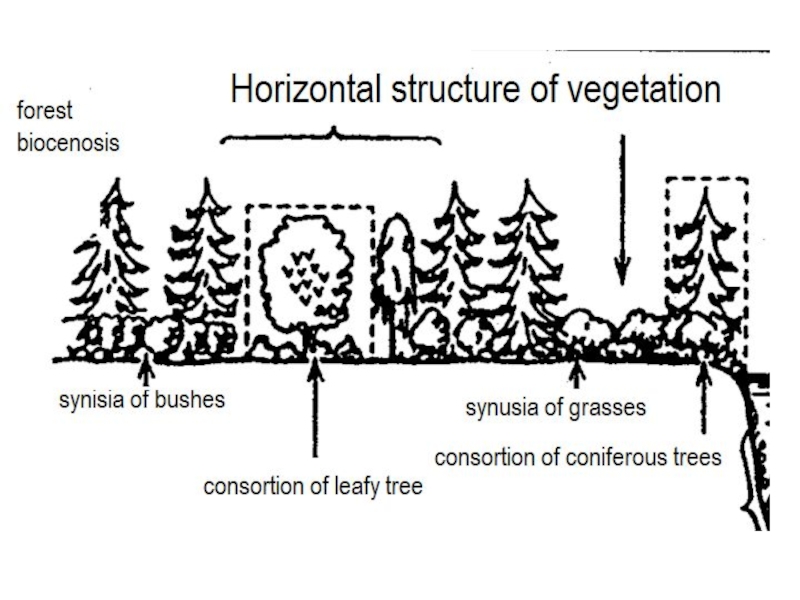
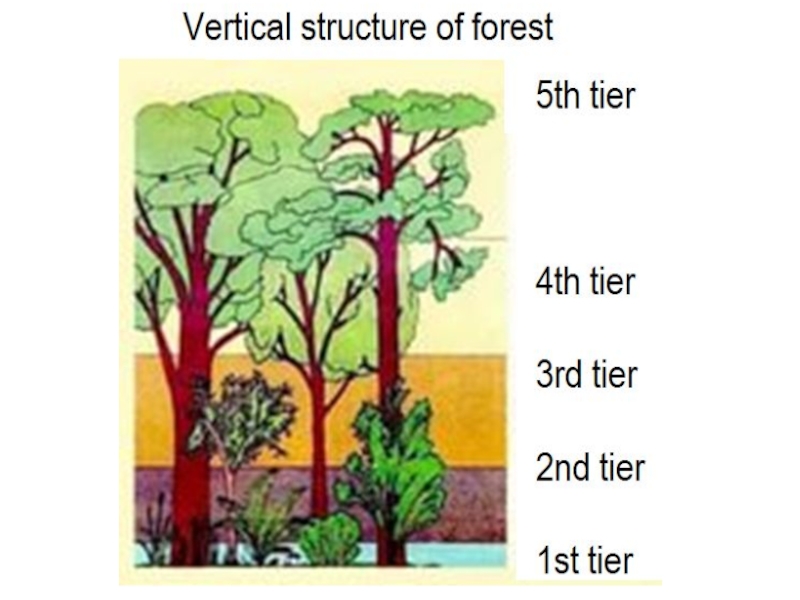
5 What is vertical and horizontal structure of vegetation? Take a examples.
Слайд 17Test question:
Wide spreading species with leading position in society:
A) mesophytes
B)
heliophytes
C) xerophytes
D) calsiphytes
E) heliophobes
F) Succulent
G) Dominant