Слайд 1Monohybrid Crosses
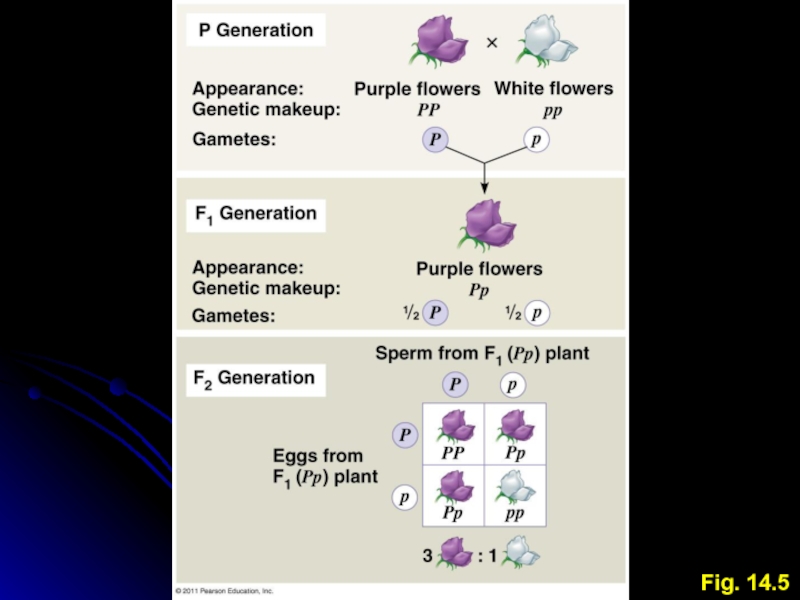
Simple cross
Cross two individuals with different alleles at a
particular locus
Individual may have one or two copies of allele
Both
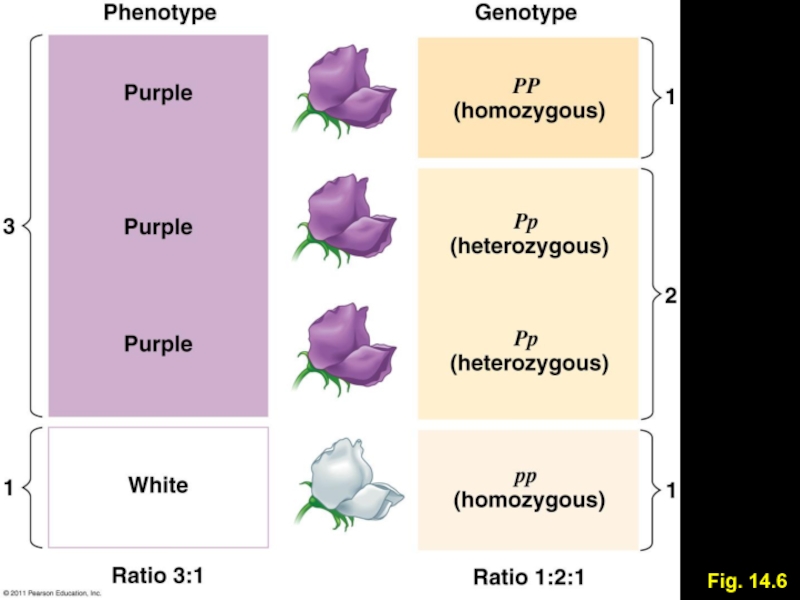
copies identical = homozygous
Different copies = heterozygous
One allele may be dominant, the other recessive
Слайд 4Monohybrid Crosses
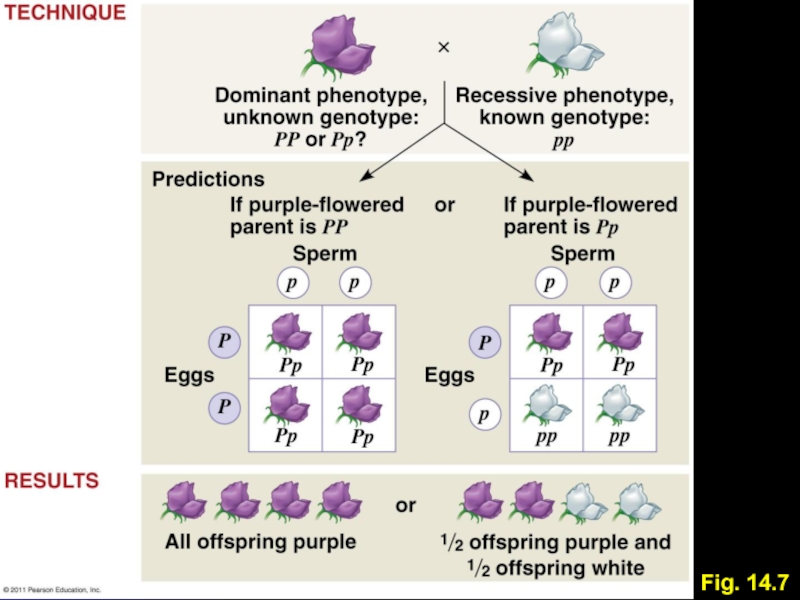
Testcross
Individual with known phenotype but unknown genotype
Ex: Pea with
purple flowers – homozygous or heterozygous?
Cross with known homozygous recessive
Слайд 6Dihybrid Crosses
Cross two individuals with different alleles at two loci
If
alleles at different loci on non-homologous chromosomes, traits should assort
independently
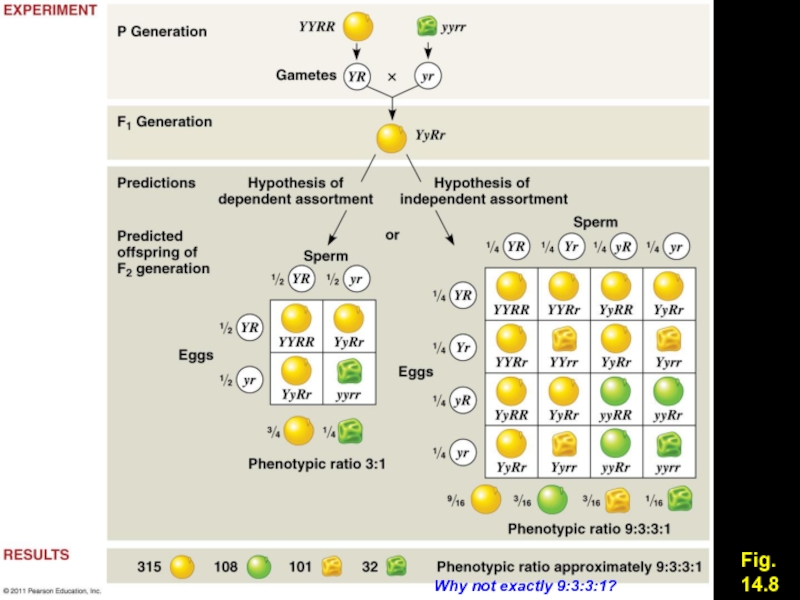
Слайд 7Fig. 14.8
Why not exactly 9:3:3:1?
Слайд 8Dihybrid Crosses
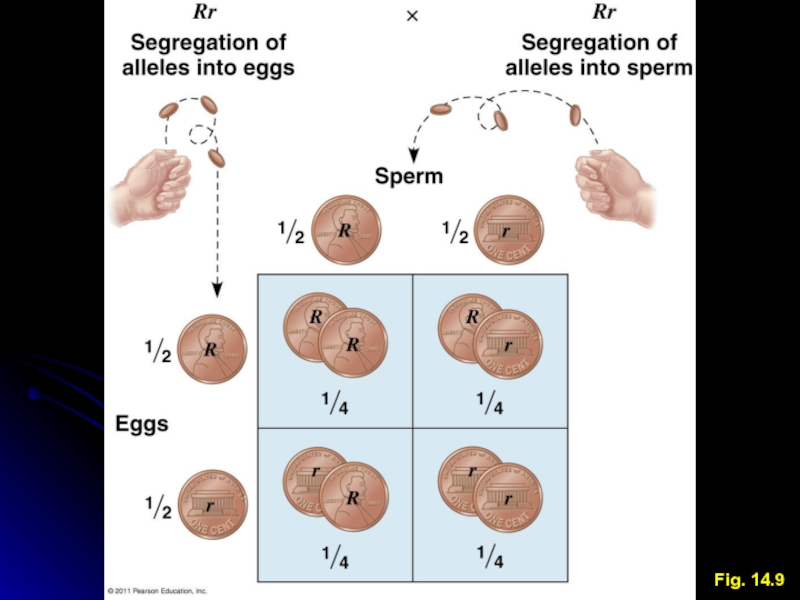
Law of Independent Assortment
Pairs of alleles segregate independently of
other pairs of alleles during gamete formation
Understanding principles of inheritance
permits prediction of cross outcomes
Слайд 9Probability
Product Rule
Predicts combined probability of independent events
Probability of multiple independent
events all occurring is product of probabilities for each
Sum Rule
Predicts
combined probability of mutually exclusive events
Probability of multiple exclusive events all occurring is sum of probabilities for each
Слайд 11Probability
Examples
Eye color in humans determined by one gene with two
alleles – B (Brown) & b (blue)
Two parents with brown
eyes are heterozygous for eye color (Bb)
Four children
Probability of a child having blue eyes?
Probability of child #4 having blue eyes?
Probability of all four children having blue eyes?
Probability of at least one child having blue eyes?
Слайд 12Inheritance
Relationship between genotype and phenotype may be simple or complex
Single
pair of alleles may regulate single trait
Single pair of alleles
may regulate multiple traits
Multiple alleles collectively may regulate single trait
Multiple alleles collectively may regulate multiple traits
Phenotype also may be influenced by environment
Complete Dominance
Codominance
Both alleles expressed independently
Ex: Reddish-coated stallion x white-coated mare Roan
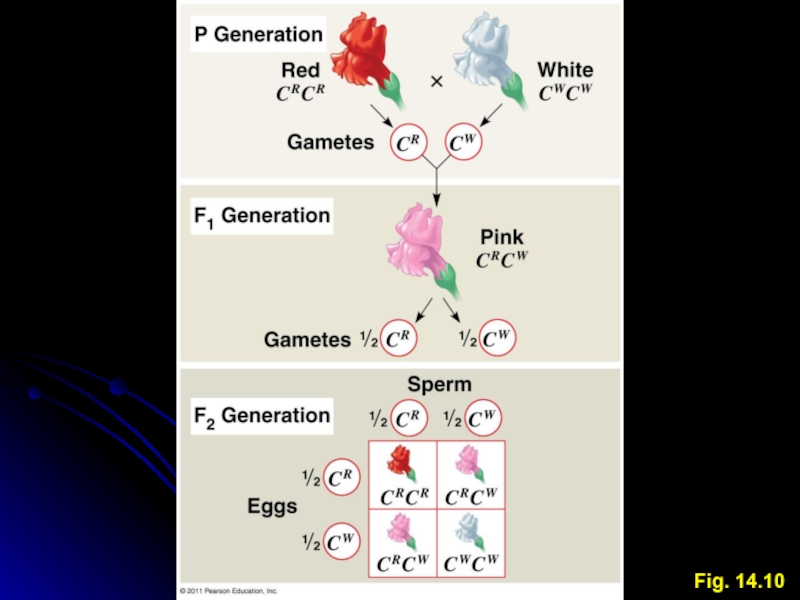
Incomplete Dominance
Intermediate phenotype
Слайд 14Inheritance
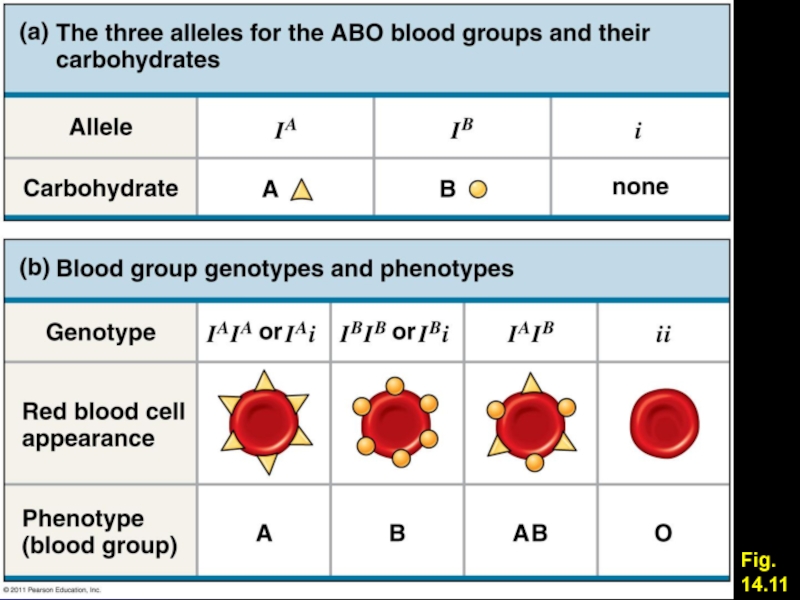
Multiple Alleles
Single individual has two alleles for each locus
Population may
contain more than two alleles at a locus
Three+ alleles at
a locus = multiple alleles
Ex: Blood type (three alleles) – IA, IB, i
Слайд 16Inheritance
Pleiotropy
Single gene may affect multiple traits
Single gene products may affect
many cells or cell types in different ways
Ex: Cystic fibrosis,
sickle cell disease
Epistasis
Presence of certain alleles at one locus can alter expression of alleles at different locus
Ex: Coat color in dogs
Color regulated by one allele pair (B = Black, b = brown)
Second allele pair (E = active, e = inactive) regulates deposition of color in hair
EE and Ee dogs are pigmented, ee dogs are yellow
Gene for pigment deposition is epistatic to gene that codes for Black or brown pigment