Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
MOTIVATION
Содержание
- 1. MOTIVATION
- 2. Nature of Motivation Motivation is the
- 3. Слайд 3
- 4. Nature of MotivationAbilityMotivationEnvironmentalConditionsPerformance=xX
- 5. Intrinsic Motivation: A person’s internal desire to
- 6. Needs theoriesNeed theories argue that we behave
- 7. Слайд 7
- 8. Physiological Needs: Hunger, thirst and bodily needs.Safety
- 9. 2. Two-factor theory (Herzberg)Herzberg’s theory that hygiene factors
- 10. Motivators: factors seeming to make individuals feel
- 11. AchievementResponsibilityWork itselfRecognitionGrowthAdvancementPayWorking ConditionsSupervisorsCompany PoliciesFringe benefitsHygiene factorsMotivatorsThese factors
- 12. Слайд 12
- 13. 3. ERG theory (Clayton Alderfer)Alternative to Maslow’s hierarchy
- 14. Existence needsPhysiological (food, water)PayBenefitsWorking conditionsRelatedness needsRelationships with family,work and professionalgroupsGrowth needsCreativityInnovationProductivityProductive impact on surroundingsNeed theoriesERG theory
- 15. 4. Acquired needs theory (David McClelland)Theory stating that
- 16. Acquired needs theoryDeveloped by David McClelland —
- 17. Need for Achievement (nAch): Is the desire
- 18. Need for Power (nPow): The need to
- 19. Need for Affiliation (nAff): Is the desire
- 20. A Comparison of the Need TheoriesMaslow(need hierarchy)Self-actualizationEsteemBelongingness,social,
- 21. 5. Reinforcement theory (B.F. Skinner) Theory arguing that our
- 22. Types of reinforcement:Extinction Stopping previously available positive
- 23. Questions
- 24. Thank You
- 25. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Nature of Motivation
Motivation is the force energising behaviour,
giving direction to behaviour, and underlying the tendency to persist.
Слайд 5Intrinsic Motivation: A person’s internal desire to do something due
to interest, challenge personal satisfaction.
Extrinsic Motivation: Motivation that comes
from outside the person such as pay, bonus, and other tangible awards. Types of Motivation
Слайд 6Needs theories
Need theories argue that we behave as we do
due to the internal needs we attempt to fulfil.
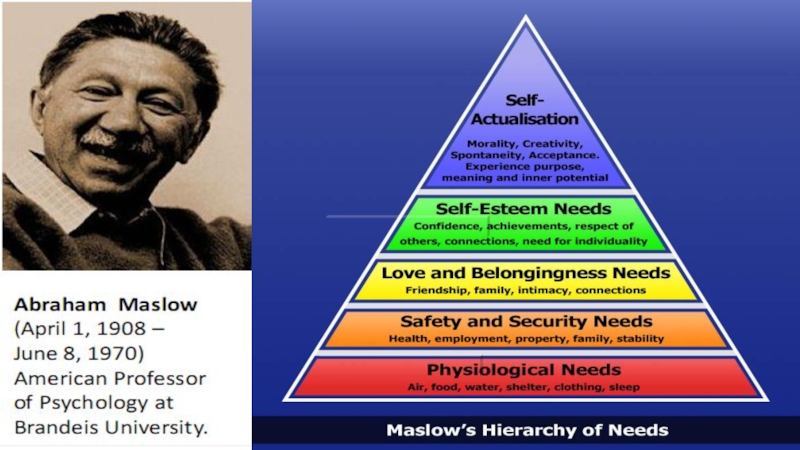
Hierarchy of
needs theory (Maslow):Theory arguing that individual needs form a five-level hierarchy.
Слайд 8Physiological Needs: Hunger, thirst and bodily needs.
Safety Needs: Security and
protection.
Social Needs: Affection, belongingness and friendship.
Esteem Needs: Includes internal esteem
factors, such as self respect, autonomy, achievement and external esteem factors such as status recognition and attention.Self-actualization: The drive to become what one is capable of becoming; it includes growth and achieving one’s potential.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Слайд 92. Two-factor theory (Herzberg)
Herzberg’s theory that hygiene factors are necessary to
keep workers from feeling dissatisfied but, only motivators can lead
workers to feel satisfied and motivated.Need theories
Слайд 10Motivators: factors seeming to make individuals feel satisfied with their
jobs.
Hygiene Factors: factors seeming to make individuals feel dissatisfied with
their job.Two-factor theory (Herzberg)
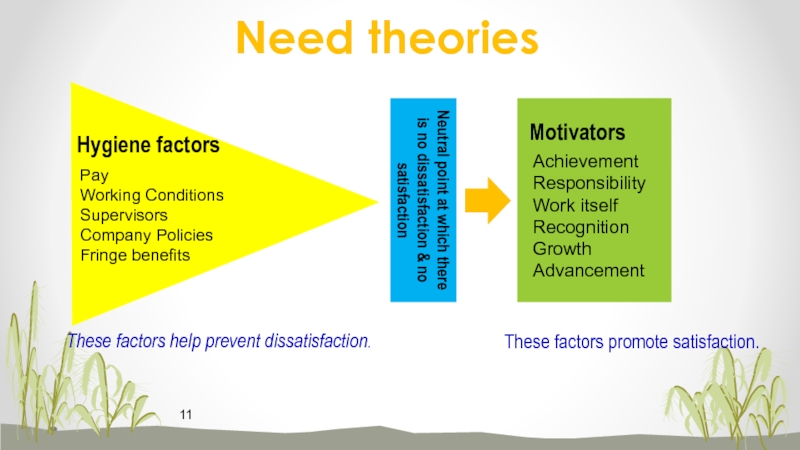
Слайд 11Achievement
Responsibility
Work itself
Recognition
Growth
Advancement
Pay
Working Conditions
Supervisors
Company Policies
Fringe benefits
Hygiene factors
Motivators
These factors help prevent dissatisfaction.
These
factors promote satisfaction.
Need theories
Neutral point at which there is no
dissatisfaction & no satisfactionСлайд 133. ERG theory (Clayton Alderfer)
Alternative to Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory,
which argues that there are three levels of individual needs.
Needs
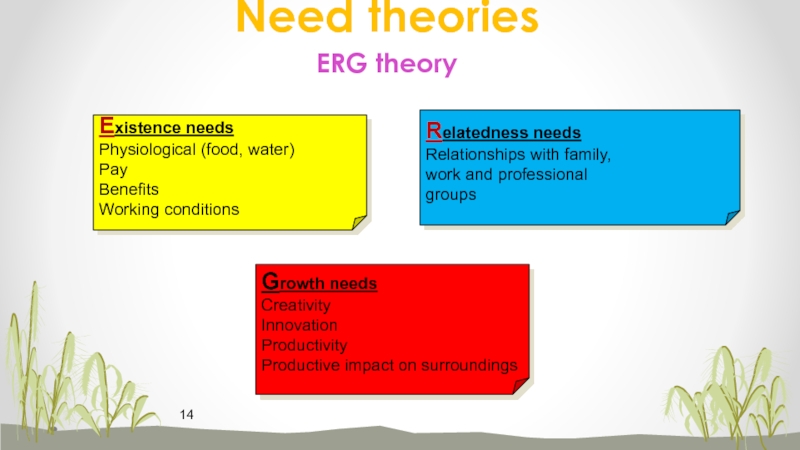
theoriesСлайд 14Existence needs
Physiological (food, water)
Pay
Benefits
Working conditions
Relatedness needs
Relationships with family,
work and professional
groups
Growth
needs
Creativity
Innovation
Productivity
Productive impact on surroundings
Need theories
ERG theory
Слайд 154. Acquired needs theory (David McClelland)
Theory stating that our needs are
acquired or learned on the basis of our life experiences.
Need
theoriesСлайд 16Acquired needs theory
Developed by David McClelland —
cites the need
for achievement, power,
and affiliation as major motives in work
Need
for achievement —drive to excelNeed for power—influence others behavior
Need for affiliation—desire for friendly
and close interpersonal relationships
Need theories
Слайд 17Need for Achievement (nAch): Is the desire to accomplish challenging
tasks and achieve a standard of excellence in one’s work.
McCelland
argues high-nAch individuals may not be motivated by money (as they get satisfaction mainly from achievement). Nevertheless, they may still see money as a source of feedback on their progress. Acquired need theory
Слайд 18Need for Power (nPow): The need to make others behave
in a way that they would not have behaved otherwise.
Personal
Power: Need for power in which individuals want to dominate others for the sake of demonstrating their ability to wield (administer) power.Institutional Power: Need for power in which individuals focus on working with other to solve problems and further organizational goals.
Acquired need theory
Слайд 19Need for Affiliation (nAff): Is the desire maintain warm, friendly
relationships with others.
High-nAff individuals tend to work in professions
demanding interaction with others, such as health care, teaching, sales and counseling. Such individuals can be assessed in situations needing high-level cooperation with and support of others.
Acquired need theory
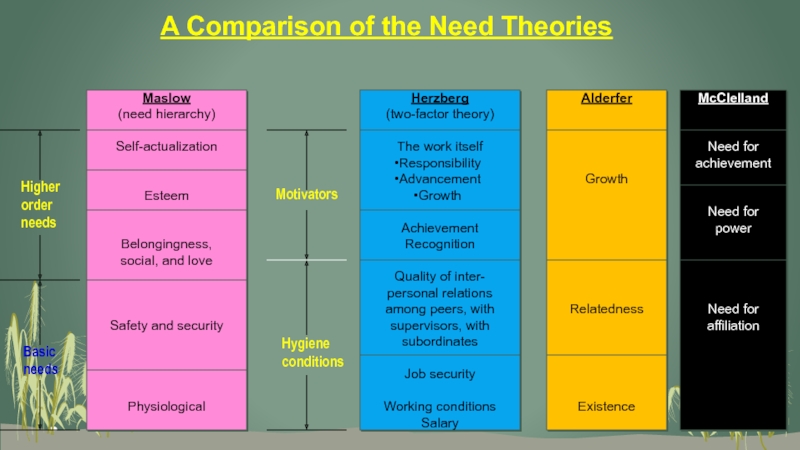
Слайд 20A Comparison of the Need Theories
Maslow
(need hierarchy)
Self-actualization
Esteem
Belongingness,
social, and love
Safety and
security
Physiological
Herzberg
(two-factor theory)
The work itself
Responsibility
Advancement
Growth
Achievement
Recognition
Quality of inter-
personal relations
among peers, with
supervisors, with
subordinates
Job
securityWorking conditions
Salary
Alderfer
Growth
Relatedness
Existence
McClelland
Need for
achievement
Need for
power
Need for
affiliation
Motivators
Hygiene
conditions
Higher
order
needs
Basic
needs
Слайд 215. Reinforcement theory (B.F. Skinner)
Theory arguing that our behaviour can be
explained by consequences in the environment.
Types of reinforcement:
Positive
Uses pleasant,
rewarding consequences to encourage desired behaviour. Use of shaping.Negative
(unpleasant) stimuli so an individual will engage in the desired behaviour to stop the stimuli.