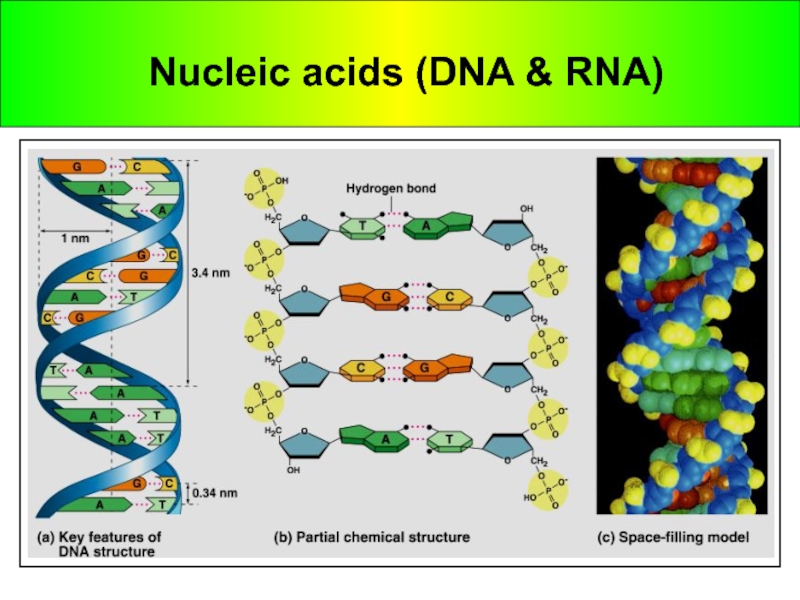
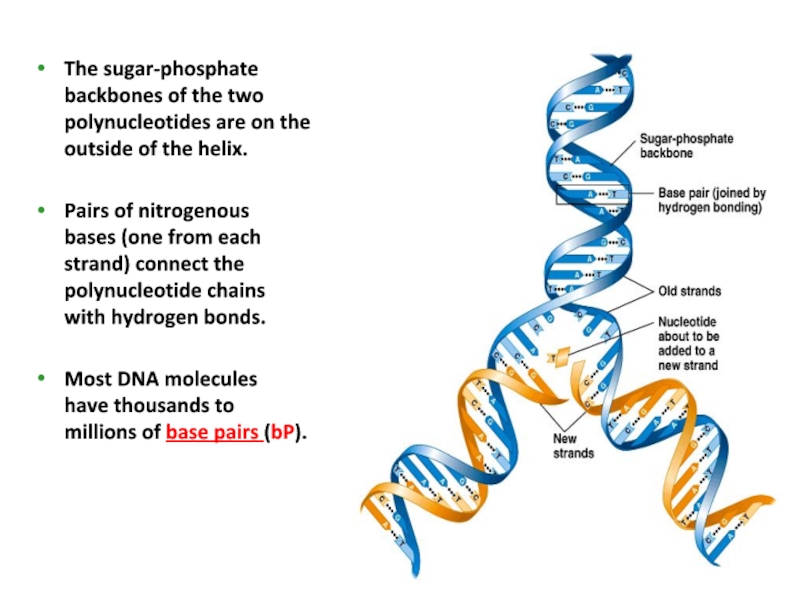
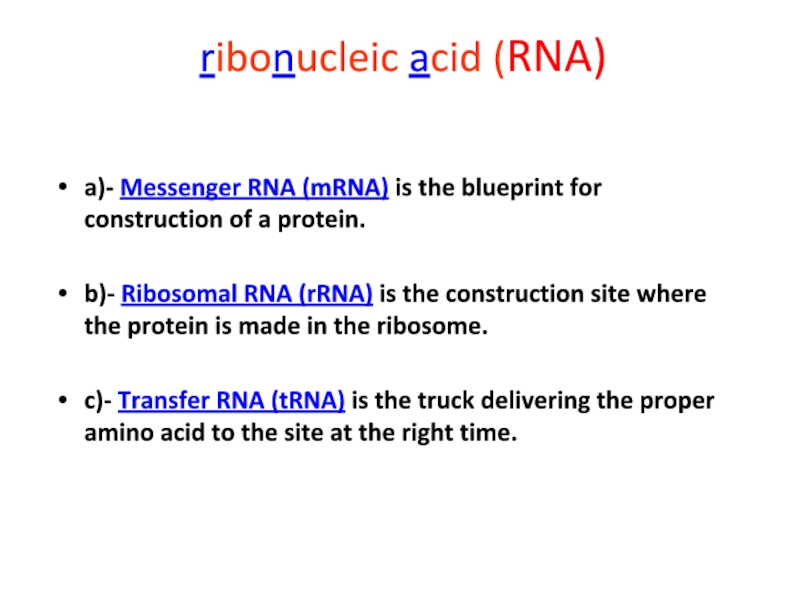
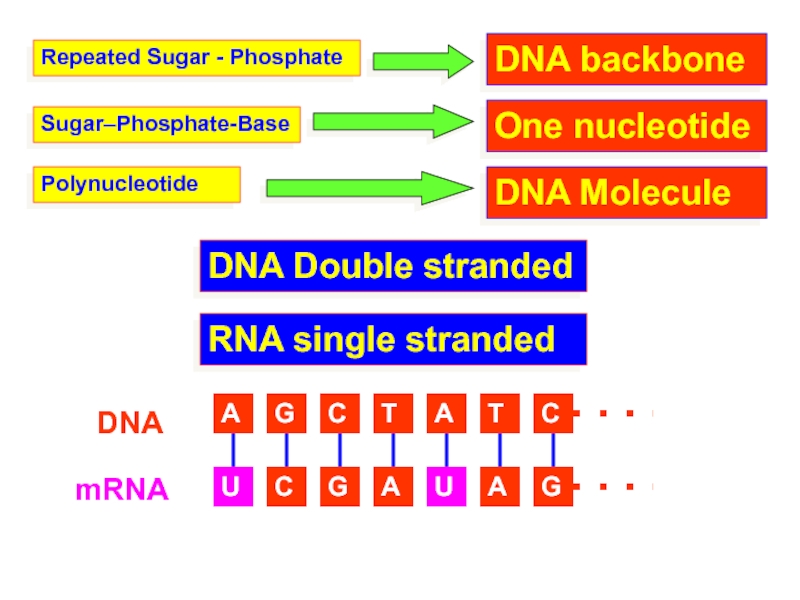
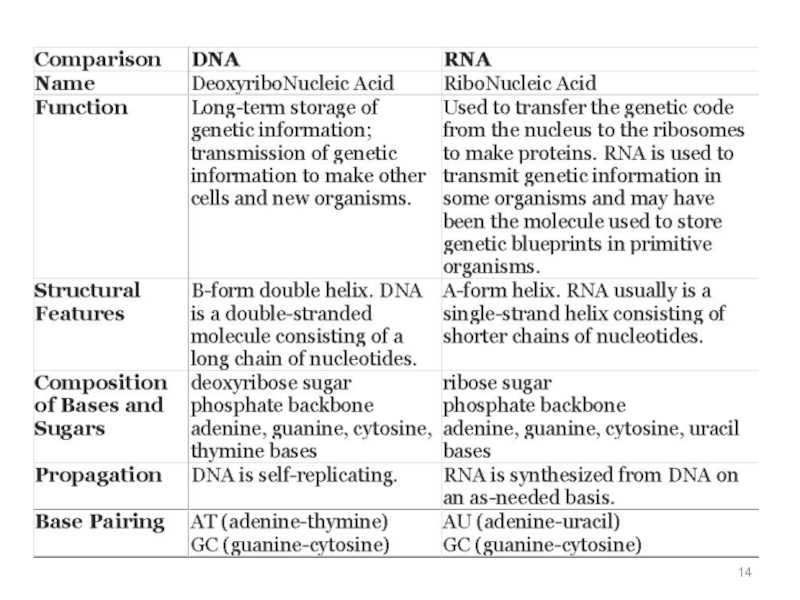
to conform to X-ray data
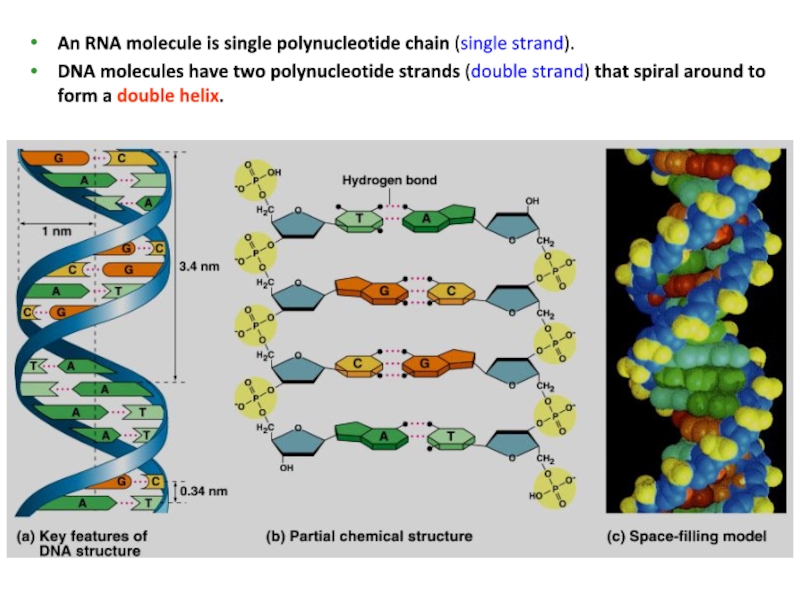
In April 1953, James Watson and
Francis Crick shook the scientific world with an elegant double-helical model or the structure of deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA.Watson and Crick began to work on a model of DNA with two strands, the double helix.