Слайд 2CONTENTS
Introduction
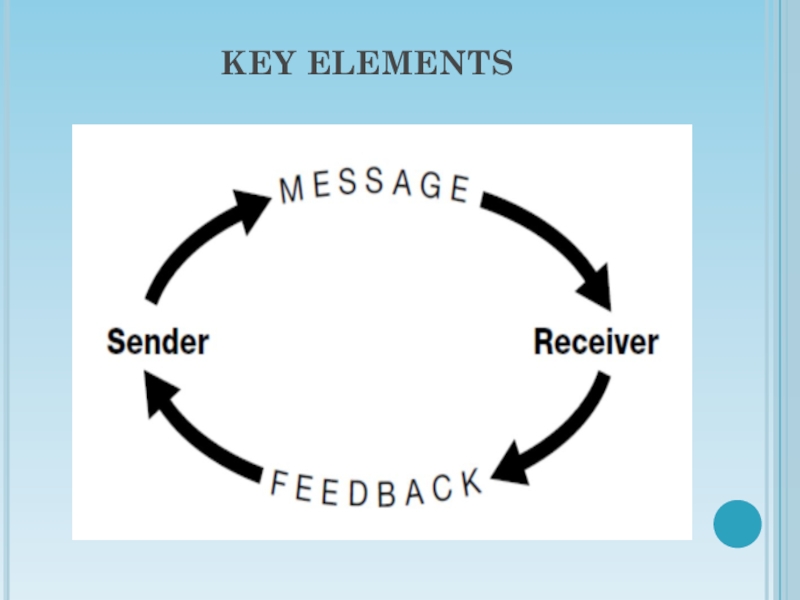
Elements
Communication Models
Слайд 3INTRODUCTION
Communication is an exchange of facts, ideas, opinions or emotions
by two or more persons (W. H. Norman & Summer).
The
English word “Communication” is derived from a Latin word “communis” which means common.
Communication is common understanding through communion of minds and hearts.
Communication is the process of sharing our ideas, thoughts, and feelings with other people and having those ideas, thoughts, and feelings understood by the people we are talking with. When we communicate we speak, listen, and observe.
Слайд 4Effective Communication
is to share meaning and understanding between the person
sending the message and the person receiving the message.
The
key element is understanding.”
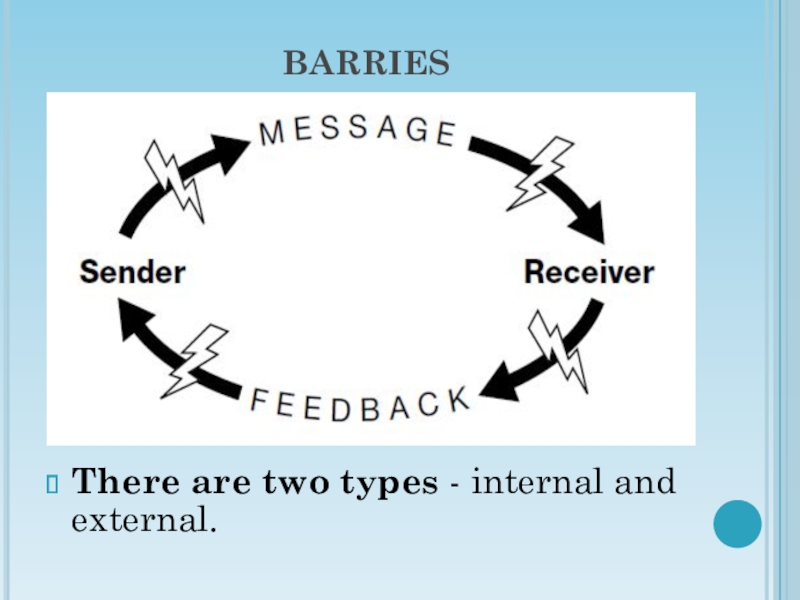
Слайд 6BARRIES
There are two types - internal and external.
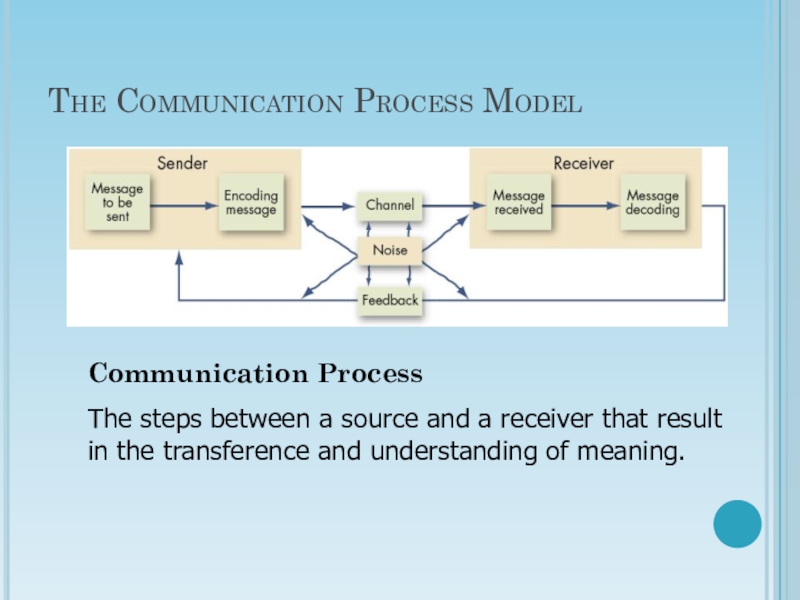
Слайд 7The Communication Process Model
Communication Process
The steps between a source and
a receiver that result in the transference and understanding of
meaning.
Слайд 8Sender-
Communication process starts with the sender, the person who wants
to transmit the message to another person.
He must be clear
about the purpose and the receiver (intended communication has a purpose)
The sender’s functions are clarifying the objectives, encoding the message, choosing the medium and sending the message
Слайд 9Message-
Messages can be verbal(spoken or written), non- verbal ( photograph,
an illustration, a symbol, facial expression)
The physical form of the
idea or information conveyed which can be understood through receiver’s sensory receptors.
Messages are not the meanings but indicative of meanings.
Слайд 10Encoding-
To change into a system of sending messages secretly or
to represent in a simple or brief way.
Symbols (words, signs,
pictures, sounds) stand for ideas
Symbols must be understood by the receiver
Sender and receiver, both must assign the same meaning to the symbols used
Слайд 11Channel-
Medium or Channel used for conveying the encoded message to
the receiver.
The choice of medium depends on factors like:
Urgency
of the message
Availability and effectiveness of a medium
Relationship between the two communicants
Слайд 12
Receiver-
Decodes the message on the basis of personal experience and
characteristics.
The sender should be aware of receivers attitude and perception.
The
meaning that a receiver gives to the message is influenced by …….
*His/her knowledge
*Intelligence
*Relation with the sender
Слайд 13Decoding-
The process of converting words or symbols of received message
into ideas is called decoding.
Even if message is received,
it is possible that it is not understood in the same sense and spirit, because the receiver decodes it differently.
Слайд 14Feedback-
It is the reversal of communication process in which receiver
expresses the response to the sender’s message.
Whatever the response of
a receiver to a sender is ..its a feedback.
Some feedbacks are non-verbal: smiles, sighs, nods.
Ultimately the success and failure of the communication is decided by the feedback.
Слайд 15Types of Communication
A. Self-Action or One-Way Communication:
In one –way communication
, there is no feedback from the receiver to the
sender.
The sender is not sure of the receipt of information as well as its understanding by the recipient.
MESSAGE
ENCODE
CHANNEL
RECEIVER
Слайд 16
Types of Communication
B. Interaction or Two-Way Communication.
This approach recognizes
the role of the receiver as a communicator through feedback.
It is message centered and is a very simplistic view of the communication process.
Feedback allows senders to see if their message got across.
ENCODE
MESSAGE
CHANNEL
RECEIVER
DECODE AS RECEIVER
CHANNEL
MESSAGE
ENCODE AS SENDER
Слайд 17Types of Communication
C. Transaction.
This approach focuses on meaning and
sharing by accounting for all other factors in the communication
process.
It is concerned with the barriers that might affect the communication.
Transaction is best described as effective communication.
This is when the communication process is applied and carried out completely. The sender gives a message that is passed on to the receiver. In return, the receiver can give clear feedback that allows the sender to know whether or not the message was perceived as intended. If the message wasn’t received as intended, then the sender will continue the communication process again in order to ensure effective communication.
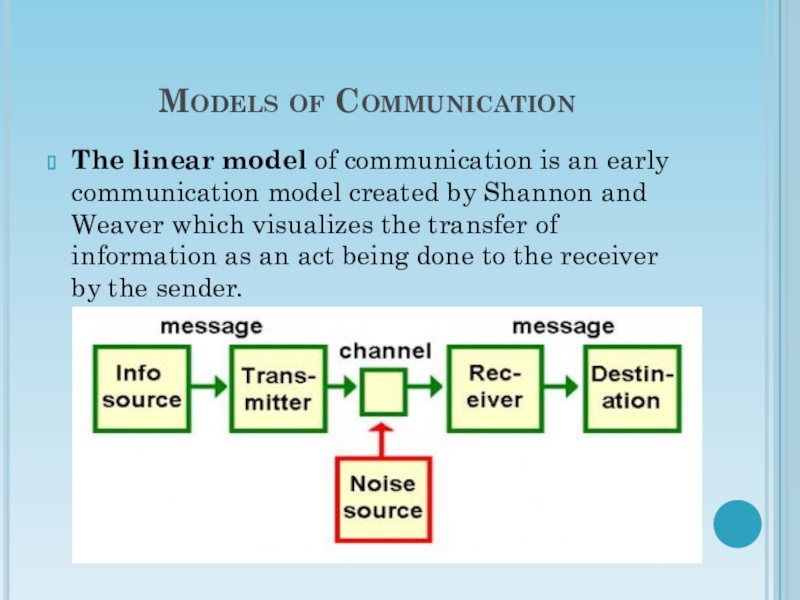
Слайд 18Models of Communication
The linear model of communication is an early
communication model created by Shannon and Weaver which visualizes the
transfer of information as an act being done to the receiver by the sender.
Слайд 19Linear Model of Communication
Understanding several key terms is important in
order to follow the model. These terms are:
Sender: the message
creator.
Encoding: the process of putting thoughts into messages through the creation of content and symbols.
Decoding: the process of interpreting and assigning meaning to a message.
Message: the transmitted information.
Channel: the medium through which the message passes.
Receiver: the target of the sender and collector of the message.
Noise: those distractions which interfere with the transmission of the message.
Слайд 20Advantages and Problems
of Linear Model
This linear model is
great for electronic media, such as radio and television, because
of its one way nature, but it encounters several problems when looking at other channels.
Conversations with your friends and others are never one way, but rather they are back-and-forth, which is a problem with the linear model.
A second problem is that encoding is typically done unconsciously.
A third problem is that other factors like culture, environment, and relational history often come in play to affect the message.
Due to these problems, a better model was created: the transactional model of communication.
Слайд 21Transactional Model of Communication
The transactional model, unlike the linear, recognizes
that communication is a simultaneous process and therefore switched both
the terms “sender” and “receiver” to “communicator.”
It also adds “environment,” which embraces not only physical location, but also personal experiences and cultural backgrounds.
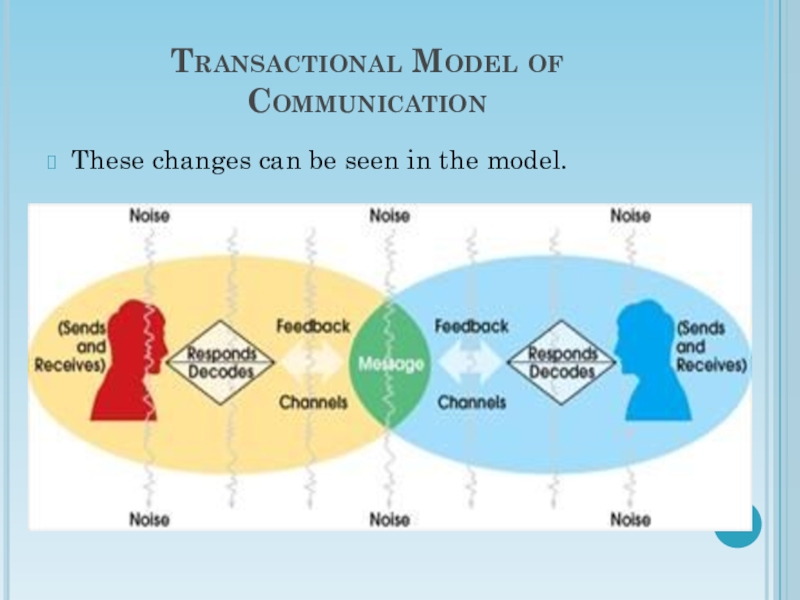
Слайд 22Transactional Model of Communication
These changes can be seen in the
model.
Слайд 23Transactional Model of Communication
Another change you will notice in the
transactional model is the overlap between each communicator. This recognizes
similarities between each communicator’s environment. The model displays how communication becomes more difficult when communicator’s have less in common.
In addition, the transactional model recognizes how the type of channel can affect meaning. For example, the words “I love you” have a much different meaning if they are said through a billboard than through a voicemail.
Слайд 24Transactional Model of Communication
In the linear model, noise is solely
external noise; for example, loud music while trying to converse.
The transactional model says that two other types of noise exist:
Physiological Noise: biological factors that interfere with communication (i.e. illness, fatigue, etc.)
Psychological Noise: the forces within that interfere with communication (i.e. an unwillingness to listen)
Overall, the transactional model realizes that it is not what we do to each other as senders and receivers, but it is what we do with each other as communicators.
Слайд 25 THANK YOU
“Your ability to communicate effectively is closely tied to
your ability to perform effectively to get the results….”