Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Reserves of the Republic of Bashkortostan
Содержание
- 1. Reserves of the Republic of Bashkortostan
- 2. A reserve is a territory where the
- 3. Shulgan-Tash (reserve)Shulgan-Tash is a state nature reserve
- 4. Shulgan-Tash
- 5. Bashkirian reserve The Bashkir State Nature Reserve
- 6. Bashkirian reserve
- 7. South Ural ReserveThe South Ural State Nature
- 8. Южно-Уральский заповедник
- 9. ZygalgaZygalga - the ridge of the Southern
- 10. Zygalga
- 11. YamantauYamantau (Bashka Yaman tau - "bad (evil)
- 12. Yamantau
- 13. InzerInzer (Bashin Inyur) is a river in
- 14. Inzer
- 15. Assinsky FallsAssinsky (Assinsky mirror, Abzanovsky) - a
- 16. Assinsky Falls
- 17. Atysh (waterfall)Atysh (from the bash Atysh -
- 18. Atysh
- 19. GadelshaThe Gadelsha waterfall is the largest waterfalls
- 20. Gadelsha
- 21. BathhouseBathhouse (Yaktykul, Yaktykul, Mauzyzy, Bashka, Yaty kul
- 22. Bathhouse
- 23. Ilmen Nature ReserveOn the border with Bashkiria,
- 24. Ilmen Nature Reserve
- 25. Скачать презентанцию
A reserve is a territory where the natural complex is preserved in its natural state, is completely excluded from economic activities. There are three reserves in Bashkortostan: • Shulgan-Tash Nature Reserve
Слайды и текст этой презентации
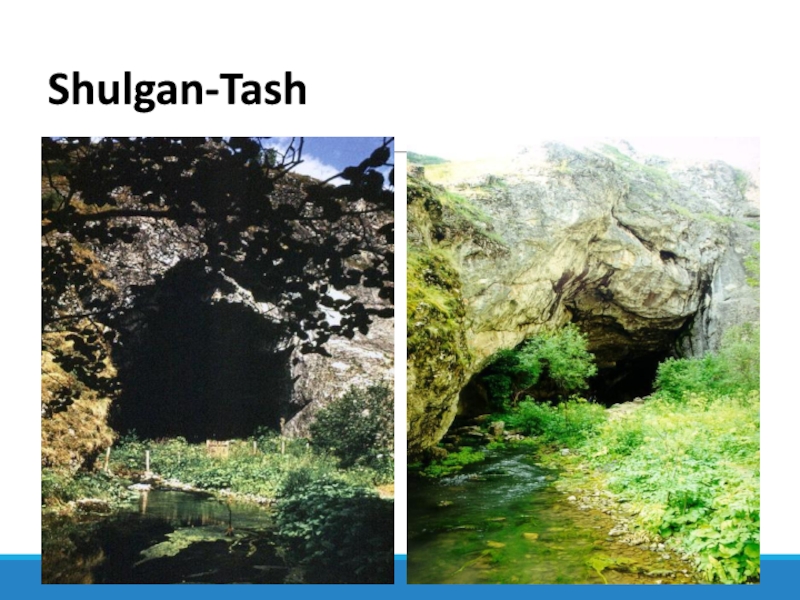
Слайд 3Shulgan-Tash (reserve)
Shulgan-Tash is a state nature reserve in Bashkortostan, which
has a federal status. It is located in the western
foothills of the Southern Urals, in the mountain-forest belt, within the Burzyan district. The total area is 22,531 hectares, or 225 square meters. Km.The name comes from the Bashkir words "Shulgan" ("dropped", "failed", "disappeared") and "Tash" ("stone").
Shulgan-Tash is a unique cultural and historical object. It is mentioned in many myths and legends of Bashkir. For example, in the epic of the Bashkir people Ural-batyr.
On the territory of the reserve there is a unique karstic Kapova Cave, or Shulgan-Tash. The length of all cave passages is more than 2.9 km. The cave has three tiers, inside the cave there is a river called Underground Shulgan, which formed this cave.
Слайд 5Bashkirian reserve
The Bashkir State Nature Reserve is located in the
Burzyan region of the Republic of Bashkortostan, on the spurs
of the Southern Urals. The reserve was organized on July 11, 1930.In 1951, by decision of the Council of Ministers of the Bashkir ASSR, the reserve was liquidated, and a leshoz was organized on its territory: intensive exploitation of the forest began.
Only in November 1958 the first reserve of Bashkortostan was restored . Until 1986, the reserve consisted of 3 sites: Ural-Tau, South Krak and Pribelsky.
The reserve was created to protect the intact ecosystems of the mountainous Ural region, primarily undisturbed forests. The main direction of scientific research of the reserve is a comprehensive study of natural ecosystems of the western slopes of the Southern Urals. About 700 species of herbaceous, shrubby and woody plants grow in the reserve; There are 51 species of mammals and 155 species of birds, 27 species of fish, 4 - amphibians, 6 - reptiles. In the forests of the reserve there is still a wild Bashkir beekeeper bee
Слайд 7South Ural Reserve
The South Ural State Nature Reserve is located
on the territory of the Beloretsk District of Bashkortostan and,
in part, the Chelyabinsk Region.Заповедник образован Постановлением ЦК КПСС и Совета Министров СССР № 487—152 от 19 июня 1978 г. для охраны и изучения горно-таежных экосистем Южного Урала. Заповедник расположен в центральной, наиболее высокой части Южного Урала на территории Республики Башкортостан и Челябинской области. Общая площадь 252,8 тыс. га.
На территории заповедника расположены несколько горных хребтов — Машак, Зигальга, Нары, Кумардак и Ямантау. Гора Большой Ямантау, имеющая высоту 1640 м, является самой высокой горой Южного Урала.
Реки — Большой Инзер, Малый Инзер, Тюльма, Юрюзань.
Доступ на территорию заповедника ограничен. Есть предположения что заповедник был основан в целях ограничения доступа к секретным объектам, расположенным в ЗАТО городе Межгорье и на прилегающей территории.
Слайд 9Zygalga
Zygalga - the ridge of the Southern Urals, on the
left bank of the river Juruzan. Zigalga is one of
the most powerful and extended ridges of the Southern Urals. Refers to the central Taganay-Yamantau belt. The Zigalginsky suite is named on the ridge.The most significant peaks, from the south to the north: the highest point of Zigalga and the third highest in the Southern Urals - Bolshoe Shelom (1427 m.), Third Shelom (1293), Merslah Utes (Mörzlaya) (1237), Transverse (1389), Eulactus 1310).
Слайд 11Yamantau
Yamantau (Bashka Yaman tau - "bad (evil) mountain") - a
mountain massif in Bashkortostan. It stretches to the northwest, width
- 3 km, length - 5 km. The main peaks are Bolshoy Yamantau (1640 m) and Maly Yamantau (1510 m). The peak of the "Big Yamantau" is the highest point of the Southern Urals. Located in the territory of the South Ural Reserve, it is located in the Beloretsk District of Bashkortostan. Bashkirs often invested an applied meaning in the name of geographical objects. The name "wicked mountain" probably came into use, as the slopes of the mountain massif are swamped and flooded with a kurumnik, which did not allow grazing cattle. Also there exist the beliefs of local Bashkirs that horses died during the campaign to this mountain, and on the slopes of the mountain there were many bears.Слайд 13Inzer
Inzer (Bashin Inyur) is a river in Bashkortostan, the left
tributary of the Sim river (Kama basin). It starts from
the merger of the Big and Small Inzers. The last few years, the river has become increasingly shallow. There is a quarry adjacent to the river, where there is an active industrial extraction of stones and gravel. On the banks of grazing cattle - cows, bulls, horses, sheep. Near the roads there are uncovered congresses where people wash their cars constantly, polluting the river.Слайд 15Assinsky Falls
Assinsky (Assinsky mirror, Abzanovsky) - a waterfall in the
Urals, near the Inzer River, on the Rock of Weeping.
It is administratively located in the Arkhangelsk district of Bashkortostan. The monument of nature since 1965 (Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the BASSR of August 17, 1965 No. 465). The height is about 6 meters.Tourist and scientific landmark
The Weeping Stone is composed of carbonate rocks, abundantly overgrown with moss, there are trees. The waterfall is on its southern side, which descends steeply to Inzeru. From the back, the northern part, the mountain canopy and covered with steppe vegetation.
Слайд 17Atysh (waterfall)
Atysh (from the bash Atysh - beating, shooting) -
a waterfall in the Southern Urals, in the Arkhangelsk region
of the Republic of Bashkortostan. The waterfall is the exit from the grotto of Atish on the surface of the underground river, also called Atish. The grotto itself (the same Atysh cave) is located in the mountain Yash-Kuz-tash. The age of the waterfall is very large. The mountain, where the waterfall Atysh is located, is composed of limestone with an age of 570 million years. Waters of the rivers Agui and Atysh protruded limestone in the upper part of the mountain, and passed down to the southern slope of the mountain, which forms the indigenous shore of the river valley of the river Lemesa.At present, the waterfall Atysh is one of the most popular places for connoisseurs of Bashkir natural beauties. In this connection, there was a very unsightly ecological situation around the waterfall. Piles of rubbish are visible everywhere, including across the waterfall itself.
Слайд 19Gadelsha
The Gadelsha waterfall is the largest waterfalls in the Republic
of Bashkortostan. He has several names - Ibragimovsky, Tuyalas, Khudolaz.
But still the most common is Gadelsha, from the nearby village of the same name.Слайд 21Bathhouse
Bathhouse (Yaktykul, Yaktykul, Mauzyzy, Bashka, Yaty kul - "light lake")
- a lake in Bashkortostan, the basin of the Ural
RiverThe area of the mirror is 7.7 km²; The catchment area is 36.3 km ²; Length - 4170 m, average width - 1880 m; Maximum depth 85 m [source is not specified 593 days], average - 10.6 m, water volume - 81.7 million m3 of the catchment area - 36.3 km²
The lake is located in the middle part of the Bashkir Trans-Ural region between the peaks of Kutukai (664 m), Karanyalyk (620 m) and spurs of the Yamankaya Range, 28 km [1] to the northeast of the village of Askarovo, the district center of the Abzelilovsky District of Bashkortostan, 45 km to the north Magnitogorsk.
Слайд 23Ilmen Nature Reserve
On the border with Bashkiria, in the Chelyabinsk
region is located one of the oldest in our country.
It was created in 1920 by decree of Lenin. Even then, in the country destroyed by the long civil war, the question of protecting these unique places was acute. Currently, the reserve occupies 34 place among other nature protection complexes.Despite the fact that the territory of the reserve is only slightly more than 34 thousand hectares, there are deep-sea lakes of the Southern Urals: Savelkul, Baraus, Bolshoy Ishkul, Big and Small Kisegachi, Terenkul and others. The water of these lakes is characterized by cleanliness and a special mineral composition.
Almost the whole territory of the Ilmen Reserve is forests with the richest vegetation, the distinctive feature of which is its mosaic. Here pine forests are mixed with birch forests, oak forests with small glades. Uniform forest in the reserve you will not meet, and this is its peculiarity.
Animal world of the reserve is typical for the Southern Urals. Most species are listed in the Red Book of the country and are protected at the federal level. Here, spotted deer and beaver, moose and roe deer, fox and wolf, marten and lynx feel great here.