Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
SIW Crohn’s disease
Содержание
- 1. SIW Crohn’s disease
- 2. Crohn's disease - is a multisystem disease
- 3. Слайд 3
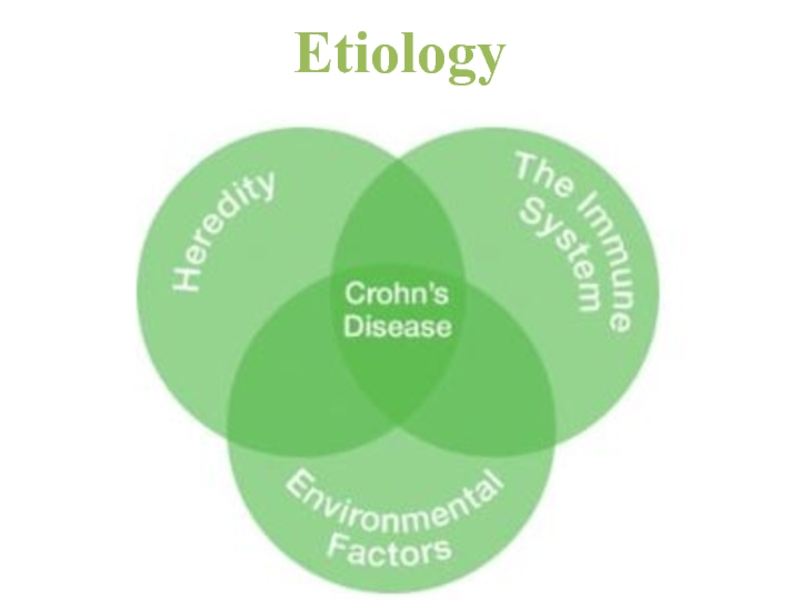
- 4. Etiology
- 5. EtiologyAccording to the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation
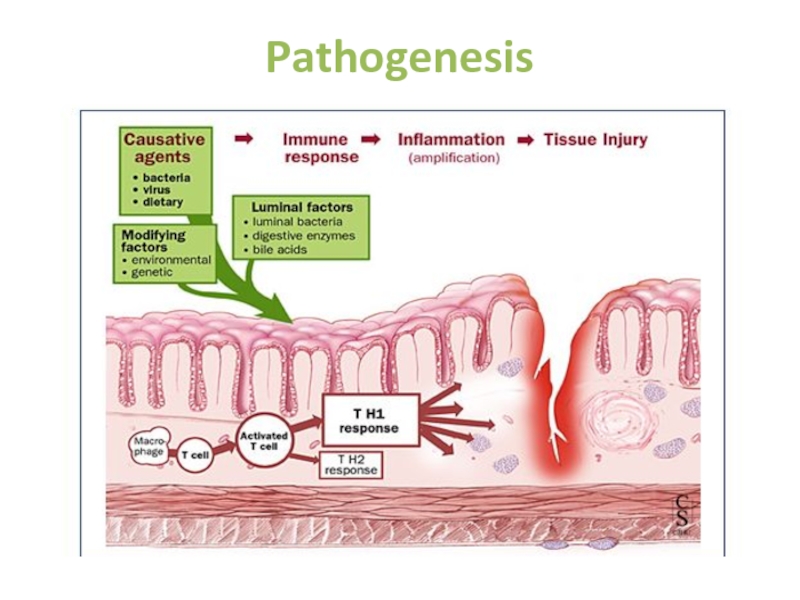
- 6. Pathogenesis
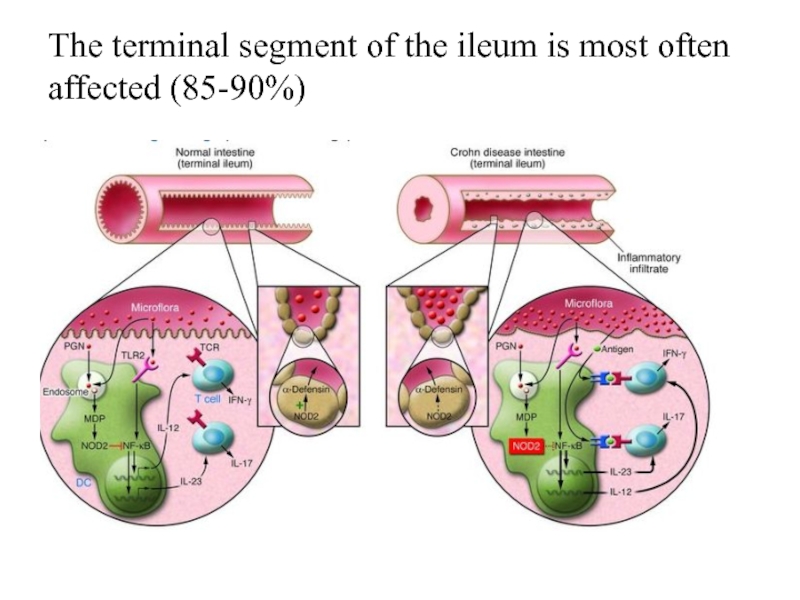
- 7. The terminal segment of the ileum is most often affected (85-90%)
- 8. Слайд 8
- 9. Clinical manifestations. intestinal manifestationsAcuteChronic1)growing pains in the
- 10. combined defeat of the small intestine and
- 11. extraintestinal
- 12. DiagnosticsComplaints of patientAnamnesisPhysical examinationLaboratory and instrumental research
- 13. Laboratory research GBA; GUA;A biochemical blood test;
- 14. Changes
- 15. Endoscopic examination of the upper sections of
- 16. a - single aphthous lesions of the
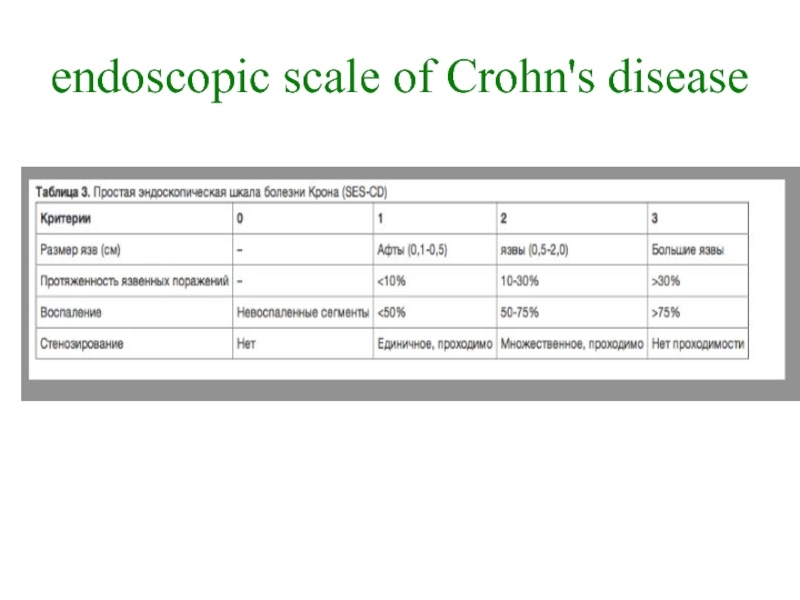
- 17. endoscopic scale of Crohn's disease
- 18. microscopic examinationgranuloma with Langhans cellsNB! One of
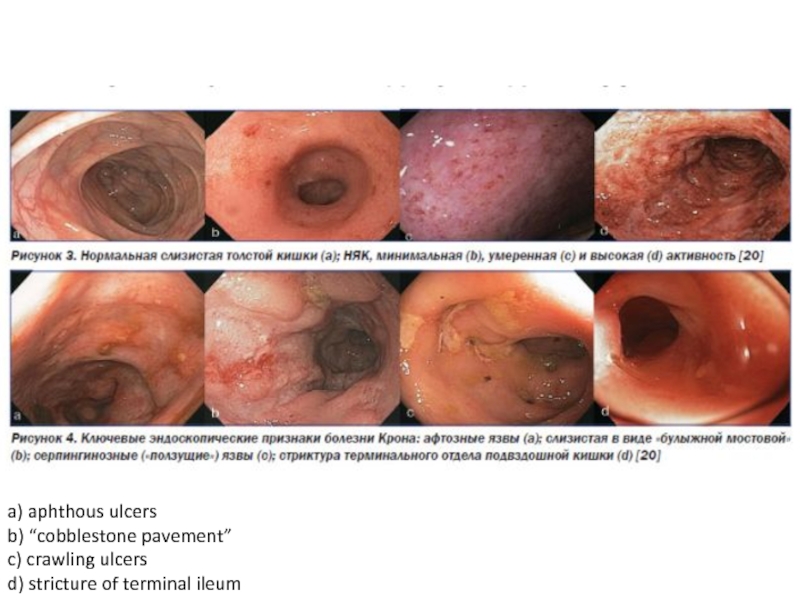
- 19. a) aphthous ulcersb) “cobblestone pavement”c) crawling ulcersd) stricture of terminal ileum
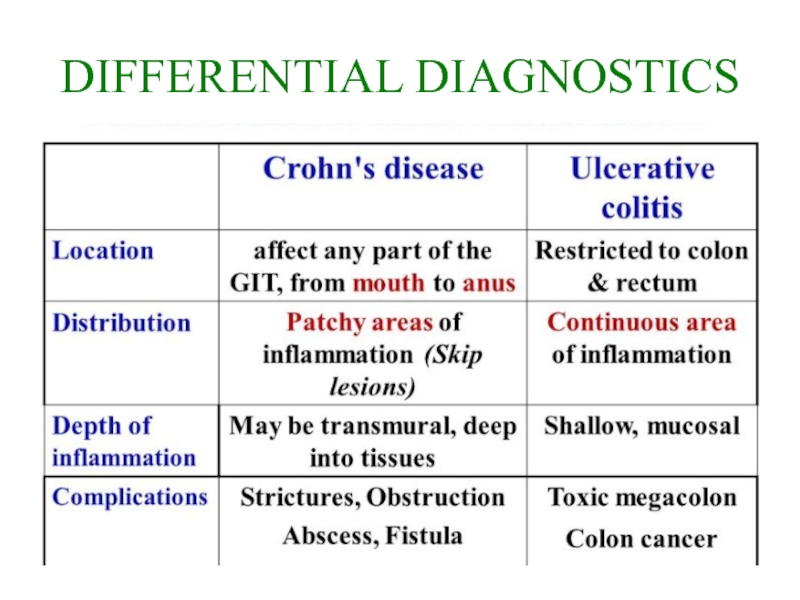
- 20. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSTICS
- 21. Слайд 21
- 22. Слайд 22
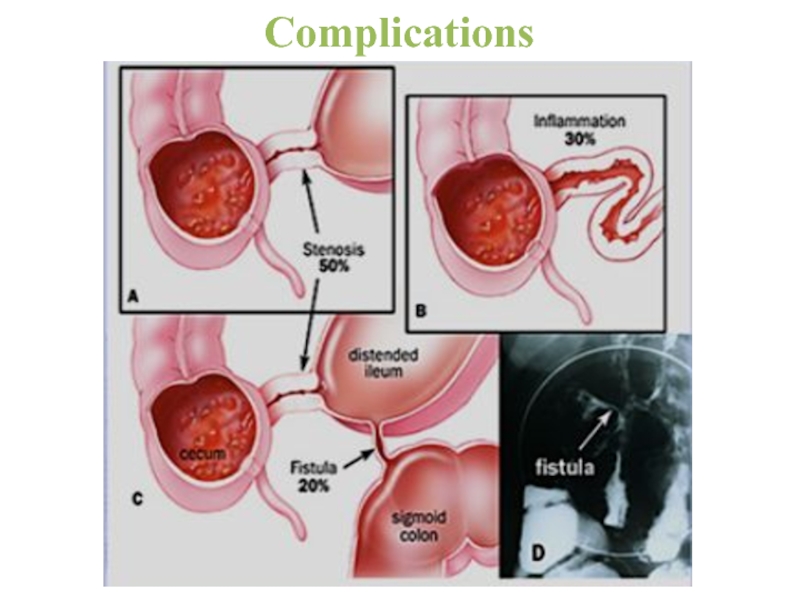
- 23. perforationtoxic colon dilatationintestinal bleedingfistulasstrictureComplications
- 24. Complications
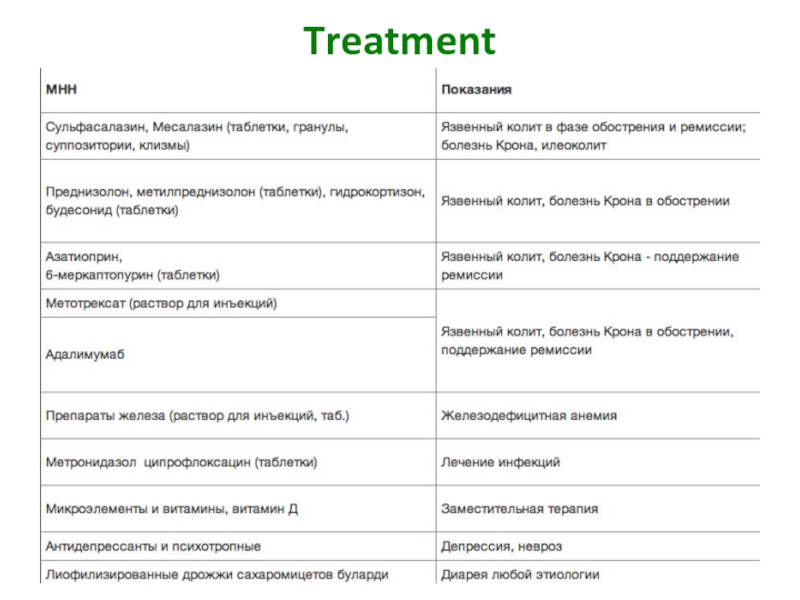
- 25. Treatment
- 26. Слайд 26
- 27. Treatment
- 28. Secondary prevention of Crohn's disease Measures
- 29. BibliographyПротокол № 23 от «25» мая 2017
- 30. Скачать презентанцию
Crohn's disease - is a multisystem disease with a specific clinical picture, characterized by focal, asymmetric, transmural granulomatous inflammation, which affects primarily the gastrointestinal tract; but can also be manifested by
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1SIW
Crohn’s disease
Smagulova Aida, 463 GM
JSC Astana Medical University
Department of Internal
Diseases № 1
Слайд 2Crohn's disease - is a multisystem disease with a specific
clinical picture, characterized by focal, asymmetric, transmural granulomatous inflammation, which
affects primarily the gastrointestinal tract; but can also be manifested by systemic and extraintestinal complications.Слайд 5Etiology
According to the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation of America, between
5 and 20 percent of people who
have an IBD
have a first – degree relative with one. the risk is higher in Crohn’s than ulcerative colitis,and higher when both parents are affected.
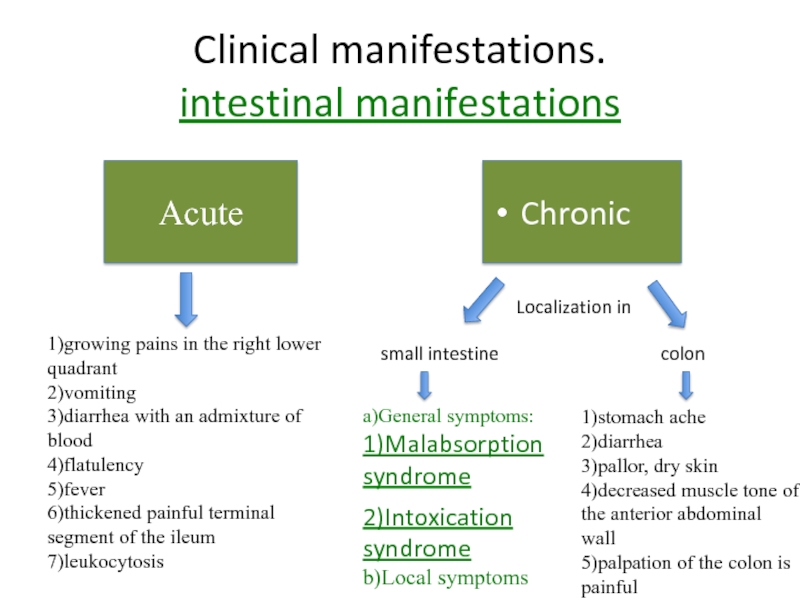
Слайд 9Clinical manifestations.
intestinal manifestations
Acute
Chronic
1)growing pains in the right lower quadrant
2)vomiting
3)diarrhea with
an admixture of blood
4)flatulency
5)fever
6)thickened painful terminal segment of the ileum
7)leukocytosis
Localization
insmall intestine
colon
a)General symptoms:
1)Malabsorption
syndrome
2)Intoxication syndrome
b)Local symptoms
1)stomach ache
2)diarrhea
3)pallor, dry skin
4)decreased muscle tone of the anterior abdominal wall
5)palpation of the colon is painful
Слайд 10combined defeat of the small intestine and colon
localization in the
upper gastrointestinal tract
symptoms of terminal ileitis and
colon damage
ulcerative syndrome
clinic
of chronic gastritis and esophagitisСлайд 12Diagnostics
Complaints of patient
Anamnesis
Physical examination
Laboratory and instrumental research
Слайд 13Laboratory research
GBA;
GUA;
A biochemical blood test;
Coprogramme; admixture
of blood and mucus
Definition of HIV (differential diagnosis of diarrheal
syndrome)Immunological status;
Fecal calprotectin can be recommended
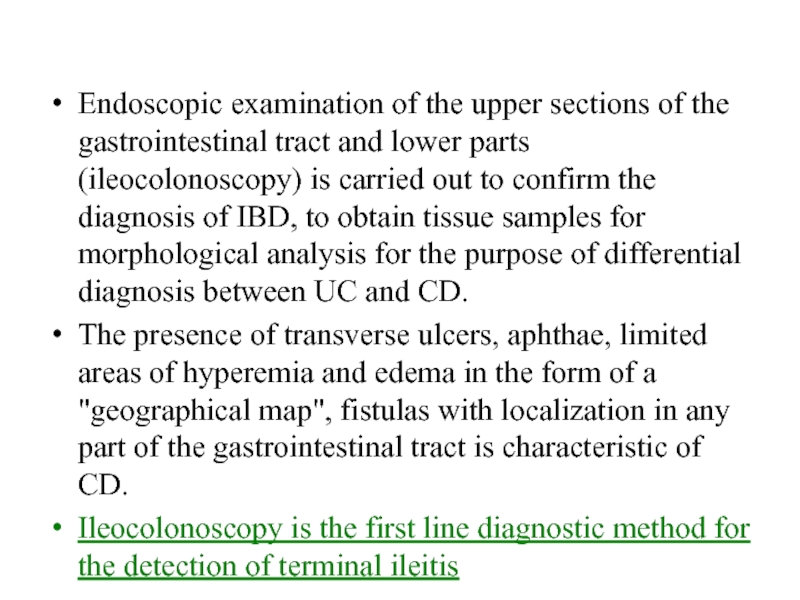
Слайд 15Endoscopic examination of the upper sections of the gastrointestinal tract
and lower parts (ileocolonoscopy) is carried out to confirm the
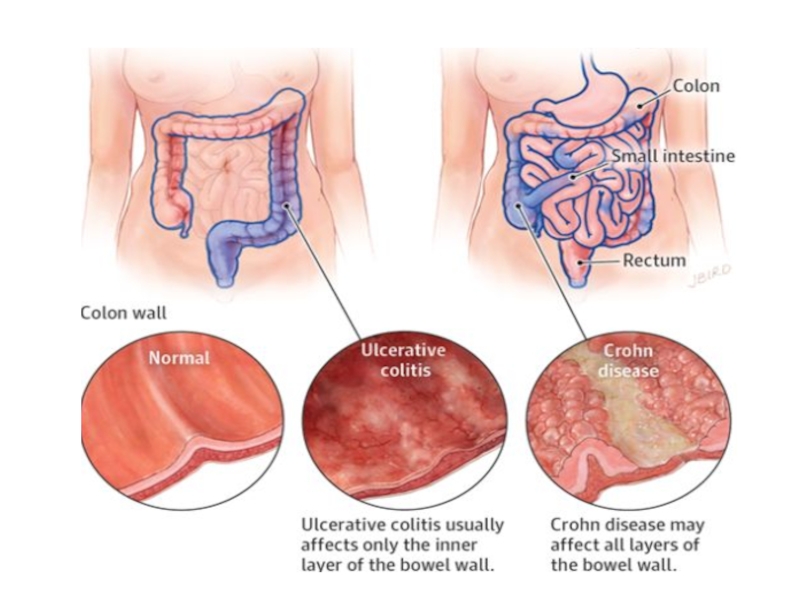
diagnosis of IBD, to obtain tissue samples for morphological analysis for the purpose of differential diagnosis between UC and CD.The presence of transverse ulcers, aphthae, limited areas of hyperemia and edema in the form of a "geographical map", fistulas with localization in any part of the gastrointestinal tract is characteristic of CD.
Ileocolonoscopy is the first line diagnostic method for the detection of terminal ileitis
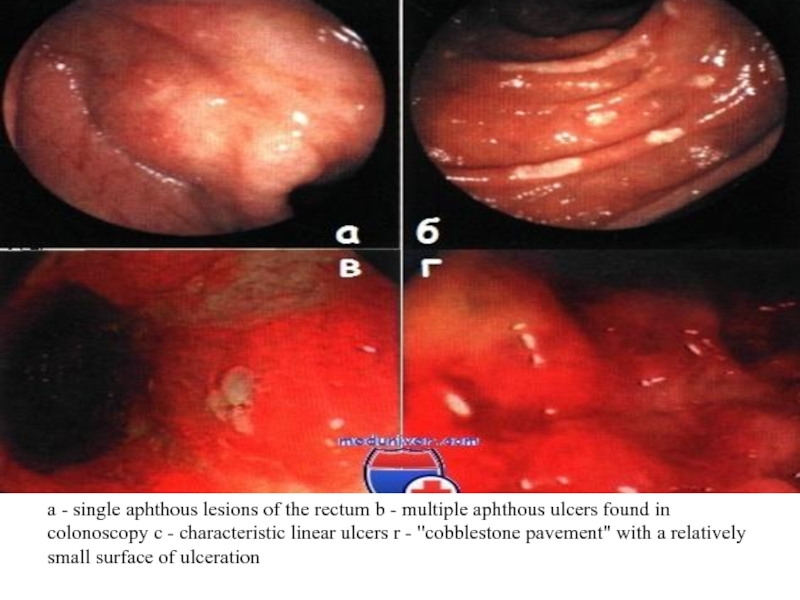
Слайд 16a - single aphthous lesions of the rectum b -
multiple aphthous ulcers found in colonoscopy c - characteristic linear
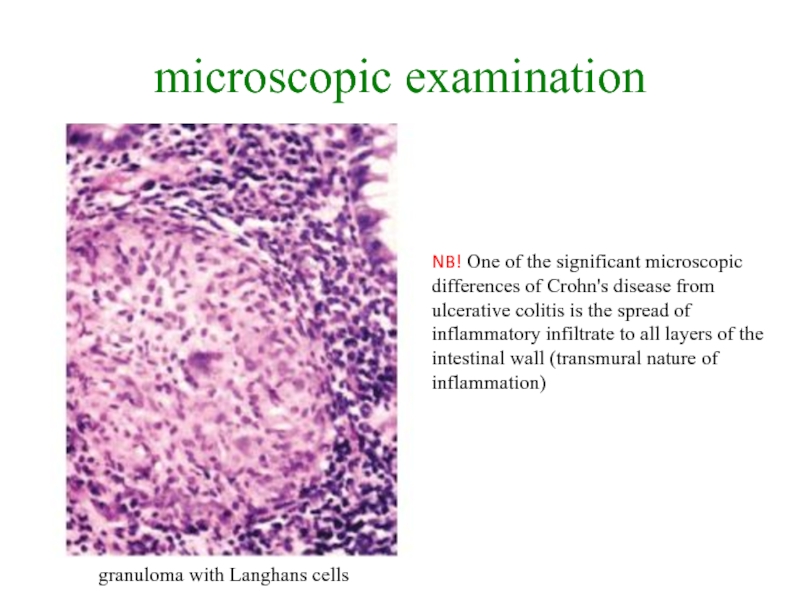
ulcers r - "cobblestone pavement" with a relatively small surface of ulcerationСлайд 18microscopic examination
granuloma with Langhans cells
NB! One of the significant microscopic
differences of Crohn's disease from ulcerative colitis is the spread
of inflammatory infiltrate to all layers of the intestinal wall (transmural nature of inflammation)Слайд 28Secondary prevention of Crohn's disease
Measures of primary prevention of
IBD have not been developed.
The patient should follow the diet
throughout life. Also, such patients are advised to stop smoking and treat infectious diseases of the intestine.With the preventive purpose, the same medicines are used, which are used to treat exacerbations of the disease, but in smaller doses (mesalazine at 2 grams per day, etc.).
Regular consultations of the gastroenterologist. Should be visited every 3 to 6 months.
Timely treatment of relapse of the disease.
Слайд 29Bibliography
Протокол № 23 от «25» мая 2017 года. Болезнь крона
[регионарный энтерит] (K50), Язвенный колит неуточненный (K51.9)
Диагностика болезней внутренних органов:
Т. 1. Диагностика болезней органов пищеварения: - М.: Мед. Лит., 2003 – 560 сhttps://www.crohnsandcolitis.com/tools-and-support/newly-diagnosed
https://www.halstedsurgery.org/GDL_Disease.aspx?CurrentUDV=31&GDL_Cat_ID=83F0F583-EF5A-4A24-A2AF-0392A3900F1D&GDL_Disease_ID=291F2209-F8A9-4011-8094-11EC9BF3100E












![SIW Crohn’s disease BibliographyПротокол № 23 от «25» мая 2017 года. Болезнь крона [регионарный BibliographyПротокол № 23 от «25» мая 2017 года. Болезнь крона [регионарный энтерит] (K50), Язвенный колит неуточненный (K51.9)Диагностика](/img/thumbs/732610eda35ca1de068077af53f08211-800x.jpg)