настоящем времени, в придаточном предложении глагол употребляется в том же
времени, в котором он стоит в прямой речи.Direct and Indirect Speech
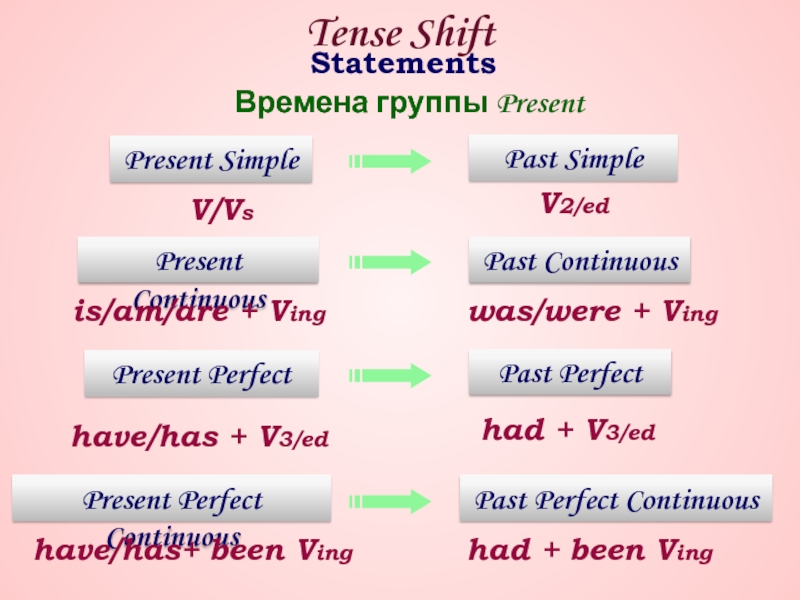
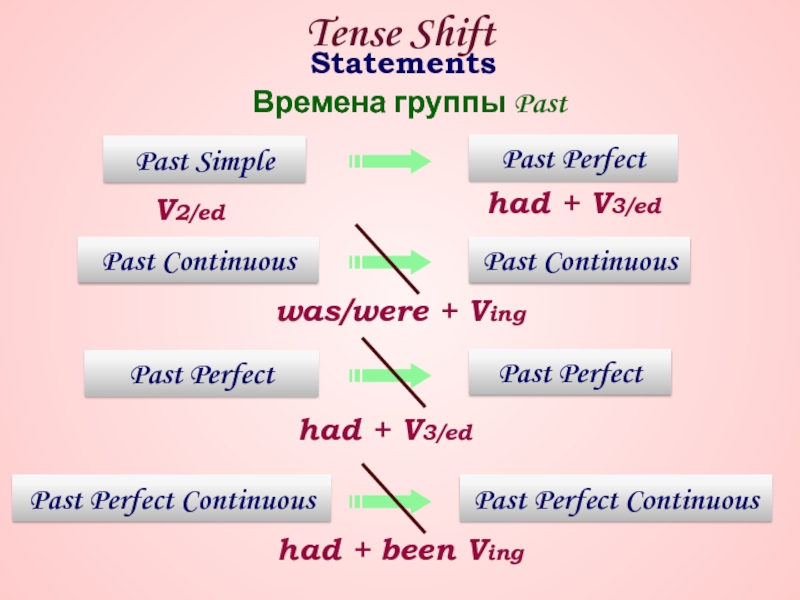
Если в косвенной речи в главном предложении глагол стоит в прошедшем времени, в придаточном предложении глагол употребляется в одном из прошедших времен: происходит сдвиг времён – глагол делает «шаг назад» (one step back)
Jane says that she is reading the Encyclopedia now.
Present
Past
Jane said that she was reading the Encyclopedia then.
Tom tells me that his sister lost her laptop yesterday.»
Tom told me that his sister had lost her laptop the day before.»
Jane says: «I’m reading the Encyclopedia now.»
Tom tells me: «My sister lost her laptop yesterday.»
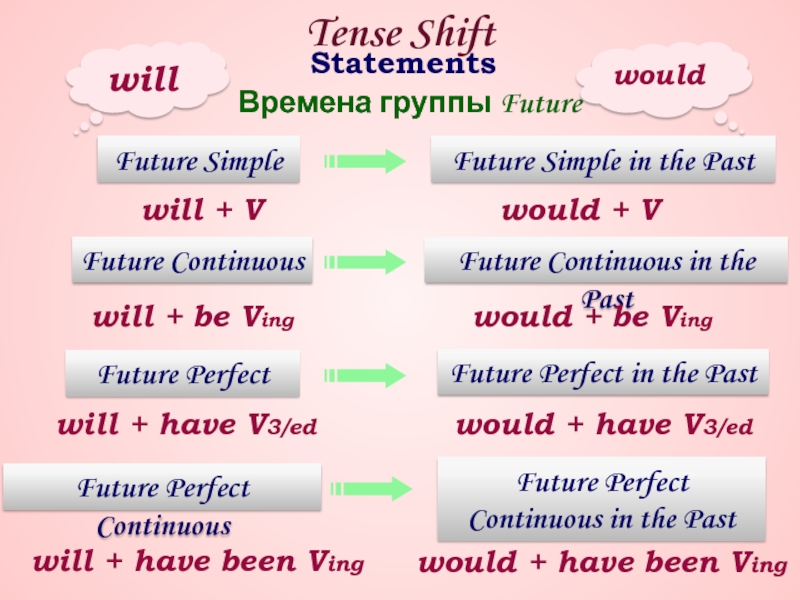
Rita thinks: «it will rain tomorrow.»
Rita thinks that it will rain tomorrow.
Rita thought that it would rain the next day.