Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Theme: Bronchitis
Содержание
- 1. Theme: Bronchitis
- 2. Plan What is the bronchitis? The types
- 3. .Bronchitis is an inflammation or swelling of
- 4. •There are two types of bronchitis:•Acute Bronchitis:
- 5. The primary bronchi, in each lung, which are
- 6. Who can get bronchitis?•People of all ages
- 7. CausesBronchitis is caused by the inflammation of
- 8. What is Affected by Bronchitis? Bronchitis affects
- 9. What are symptoms of bronchitis?For both types
- 10. What diagnostic methods are available?•Chest x –ray •Sputum test •Pulmonary function test •Pulse oximetry
- 11. What treatments are available?•For acute bronchitis, most
- 12. Side effects of treatment :Different types of
- 13. Is the bronchitis curable? What is the
- 14. References :Retrieved from http://www.emedicinehealth.com/Bronchitis - Causes, Symptoms,
- 15. Thank’s for your attention
- 16. Скачать презентанцию
Plan What is the bronchitis? The types of bronchitis Anatomy of the bronchioles Who can get bronchitis? Causes What is Affected by Bronchitis? What are symptoms of bronchitis? What diagnostic methods
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1By: Turkumbaeva Aliya
Berkimbaev Daulet
Sarsikei Dayana
Theme: «Bronchitis»
Independent work of a student
Слайд 3.
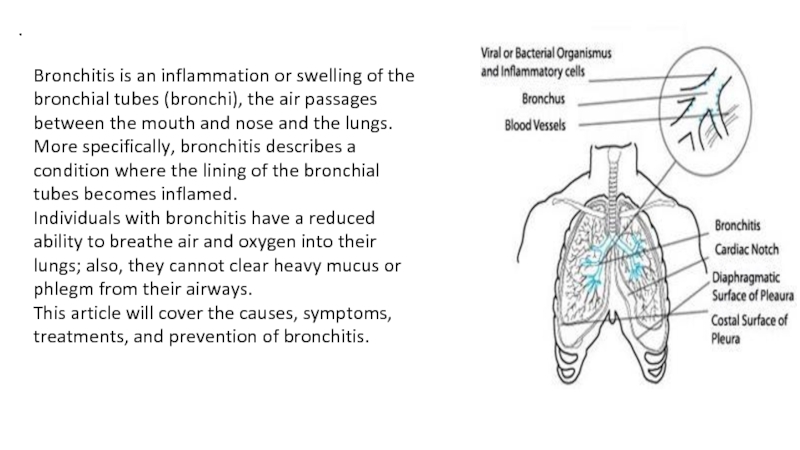
Bronchitis is an inflammation or swelling of the bronchial tubes
(bronchi), the air passages between the mouth and nose and
the lungs. More specifically, bronchitis describes a condition where the lining of the bronchial tubes becomes inflamed.Individuals with bronchitis have a reduced ability to breathe air and oxygen into their lungs; also, they cannot clear heavy mucus or phlegm from their airways.
This article will cover the causes, symptoms, treatments, and prevention of bronchitis.
Слайд 4•
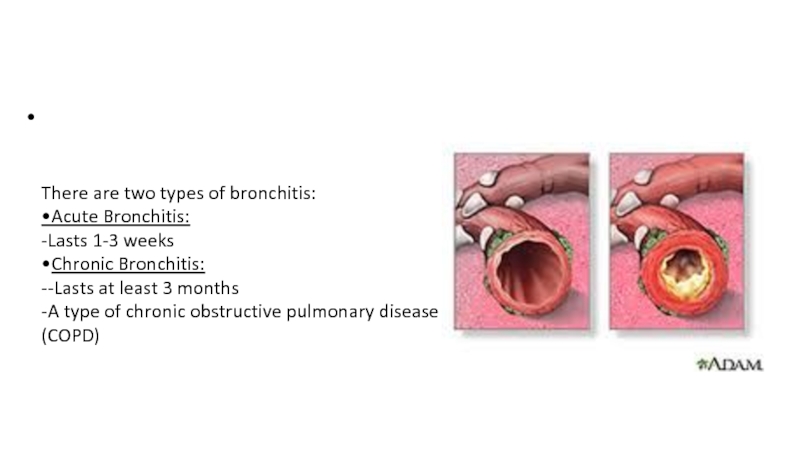
There are two types of bronchitis:
•Acute Bronchitis:
-Lasts 1-3 weeks
•Chronic
Bronchitis:
--Lasts at least 3 months
-A type of chronic obstructive pulmonary
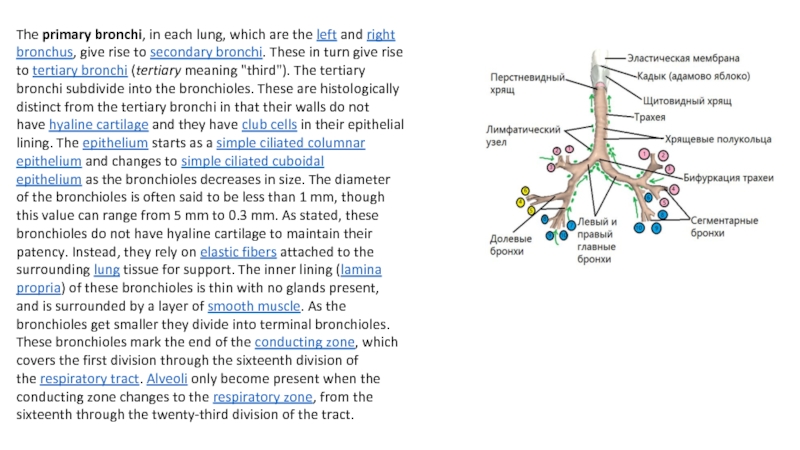
disease (COPD)Слайд 5The primary bronchi, in each lung, which are the left and right bronchus, give
rise to secondary bronchi. These in turn give rise to tertiary bronchi (tertiary meaning
"third"). The tertiary bronchi subdivide into the bronchioles. These are histologically distinct from the tertiary bronchi in that their walls do not have hyaline cartilage and they have club cells in their epithelial lining. The epithelium starts as a simple ciliated columnar epithelium and changes to simple ciliated cuboidal epithelium as the bronchioles decreases in size. The diameter of the bronchioles is often said to be less than 1 mm, though this value can range from 5 mm to 0.3 mm. As stated, these bronchioles do not have hyaline cartilage to maintain their patency. Instead, they rely on elastic fibers attached to the surrounding lung tissue for support. The inner lining (lamina propria) of these bronchioles is thin with no glands present, and is surrounded by a layer of smooth muscle. As the bronchioles get smaller they divide into terminal bronchioles. These bronchioles mark the end of the conducting zone, which covers the first division through the sixteenth division of the respiratory tract. Alveoli only become present when the conducting zone changes to the respiratory zone, from the sixteenth through the twenty-third division of the tract.Слайд 6Who can get bronchitis?
•People of all ages and ethnicity can
get chronic bronchitis but it’s most common in people over
45 years old and people who smoke•Women are twice as more likely to be diagnosed with chronic bronchitis
•Acute bronchitis is most common in elderly people, infants, and young children
Слайд 7Causes
Bronchitis is caused by the inflammation of the bronchial tubes.
Acute bronchitis is usually caused by viruses. Typically the same
viruses that cause colds and the flu.Chronic bronchitis is usually caused by smoking, air pollution, dust, or toxic gases.
Tonsillitis is similar to bronchitis except tonsillitis is the inflammation of the tonsils.
It is also caused by bacteria and viruses.
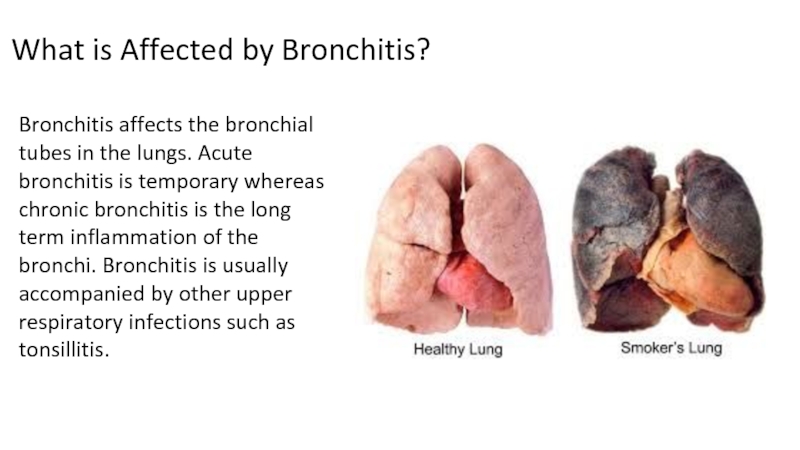
Слайд 8What is Affected by Bronchitis?
Bronchitis affects the bronchial tubes in
the lungs. Acute bronchitis is temporary whereas chronic bronchitis is
the long term inflammation of the bronchi. Bronchitis is usually accompanied by other upper respiratory infections such as tonsillitis.Слайд 9What are symptoms of bronchitis?
For both types of bronchitis the
symptoms are:
•Coughing
•Production of mucous
•Shortness of breath and wheezing
•Slight fever
and chills•Tiredness
•Sore throat/chest
Слайд 10What diagnostic methods are available?
•Chest x –ray
•Sputum test
•Pulmonary
function test
•Pulse oximetry
Слайд 11What treatments are available?
•For acute bronchitis, most cases are resolved
without medical treatment in 2 weeks
•Doctors may prescribe:
-Antibiotics
-Cough medicine
-An
inhaler•Chronic bronchitis cannot be cured but the treatments available are:
-Antibiotics
-Pulmonary rehabilitation
-Pneumonia and flu shot
-Lung volume reduction surgery
Слайд 12Side effects of treatment :
Different types of antibiotics have different
side effects. Common side effects include:
•Nausea, vomiting, and upset stomach.
•Dizziness
or headache.•Severe watery diarrhea and abdominal cramps.
•Persistent cough, which may produce mucus
•Wheezing
•Low fever and chills
•Sore throat
•Body aches
•Breathlessness
•Blocked nose and sinuses.
Слайд 13Is the bronchitis curable? What is the probable outcome after
treatment?
Bronchitis is a curable disease.
Outcome after treatment :
A dry,
hacking cough may however be present for several months . Acute bronchitis usually heals completely, therefore leading to an excellent prognosis.
What lifestyle changes would be recommended?
• Stop Smoking
Avoid Airborne Irritants
Wear a Mask
Stay Active
Manage Your Weight
Rest as Needed
Learn to Relax
Слайд 14References :
Retrieved from http://www.emedicinehealth.com/
Bronchitis - Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Diagnosis -
Flu (Seasonal) - C-Health. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://chealth.canoe.ca/channel_condition_info_details.asp?disease_id=222&channel_id=2113&relation_id=96004
Bronchitis and Tonsillitis
? Causes and diagnose | Sore Throat No Fever. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.sorethroatnofever.net/bronchitis-and-tonsillitis-causes-and-diagnose/Bronchitis Causes - Diseases and Conditions - Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bronchitis/basics/causes/con-20014956
Bronchitis Definition - Diseases and Conditions - Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bronchitis/basics/definition/con-20014956
Care During Chemotherapy and Beyond, Chemocare.com. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://chemocare.com/
Chronic Bronchitis Treatment | Conditions & Treatments | UCSF Medical Center. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.ucsfhealth.org/conditions/chronic_bronchitis/treatment.html
Dunlop, J. (2010). McGraw-Hill Ryerson Biology 11. Toronto: McGraw-Hill Ryerson.
How Is Bronchitis Diagnosed? - NHLBI, NIH. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/brnchi/diagnosis.html
Symptom Checker, Health Information and Medicines Guide | Patient.co.uk. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.patient.co.uk/
WebMD - Better information. Better health. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.webmd.com/
What Is Bronchitis? Acute and Chronic Causes, Picture, and Overview. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/understanding-bronchitis-basics
What is bronchitis? What causes bronchitis? - Medical News Today. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/8888.php