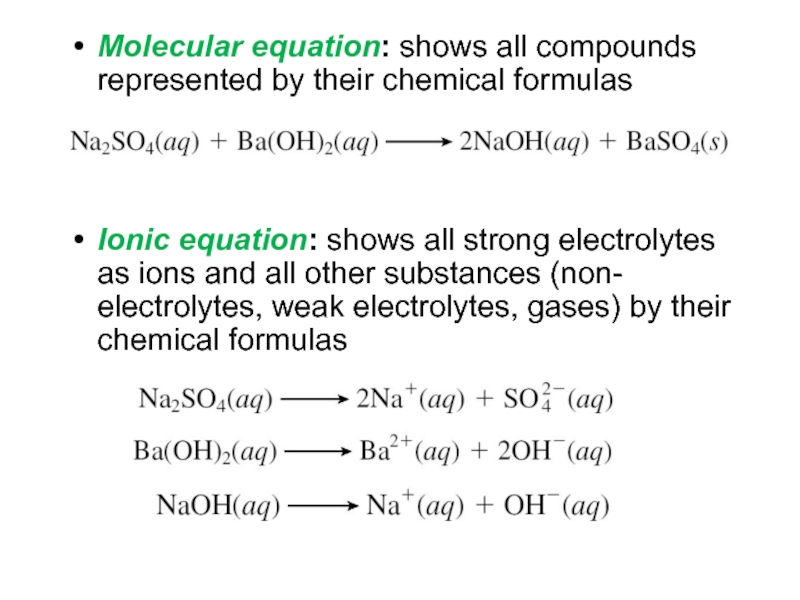Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
1 Electrolytes. Reactions in Aqueous Solutions
Содержание
- 1. 1 Electrolytes. Reactions in Aqueous Solutions
- 2. Name the compounds:CuSO4 NaOH HNO3 NH4NO3
- 3. General Properties of Aqueous SolutionsSolution - a
- 4. Electrolytes and NonelectrolytesElectrolyte: substance that, when dissolved
- 5. Dissociation - ionic compounds separate into constituent
- 6. Hydration: process by which water molecules remove and surround individual ions from the solid.
- 7. ACIDSBASESNaOH (s) → Na+ (aq) +
- 8. Strong Electrolytes: 100% dissociationAll water soluble ionic
- 9. Degree of dissociationThe fraction of total number
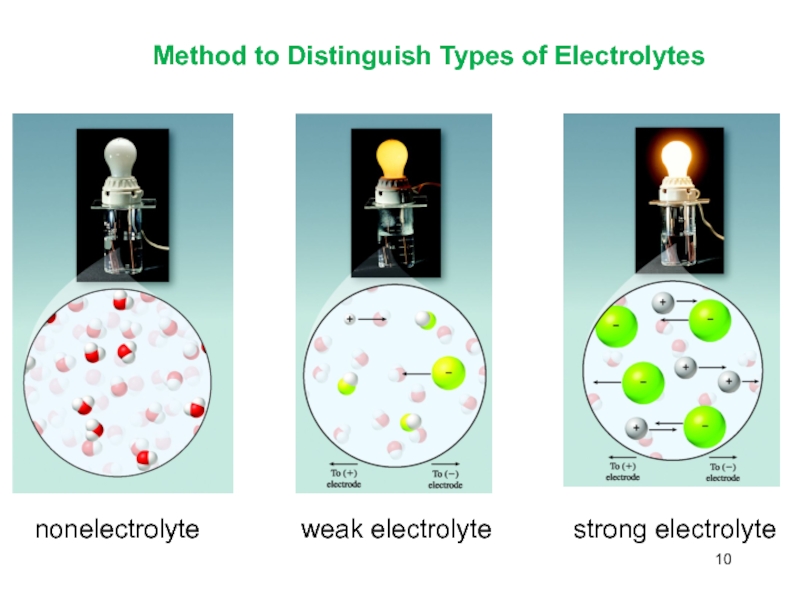
- 10. Method to Distinguish Types of Electrolytesnonelectrolyteweak electrolytestrong electrolyte
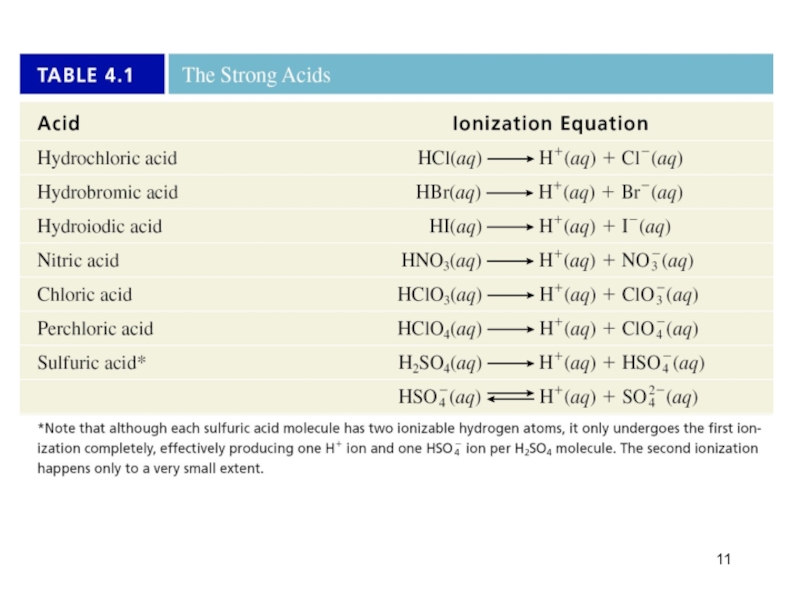
- 11. Слайд 11
- 12. Examples of weak electrolytesWeak acids
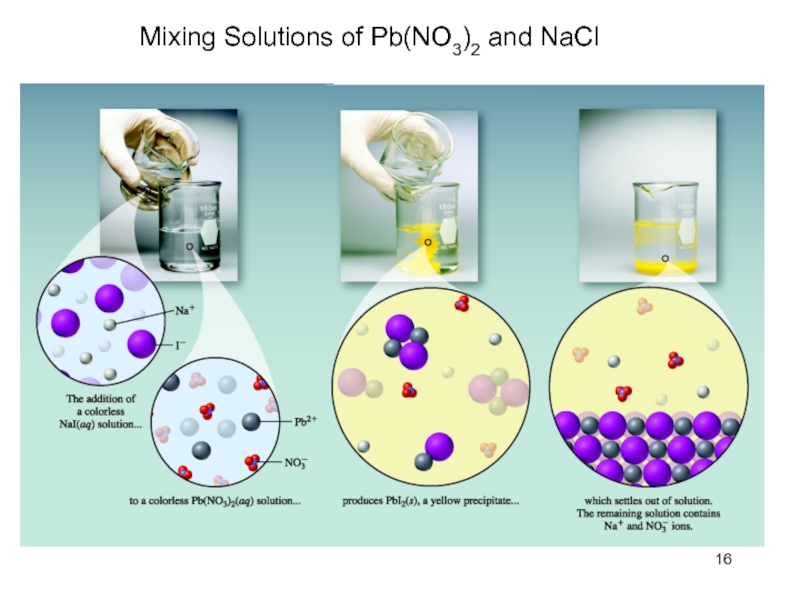
- 13. Precipitation ReactionsPrecipitation (formation of a solid from
- 14. Simple Rules for SolubilityMost nitrate (NO3) salts
- 15. Identify the PrecipitatePb(NO3)2(aq) + 2NaI(aq) 2NaNO3 + PbI2 (s)(aq)(?) (?)
- 16. Mixing Solutions of Pb(NO3)2 and NaCl
- 17. Molecular equation: shows all compounds represented by
- 18. Net Ionic equation: shows only the reacting
- 19. Steps in writing a net ionic equation
- 20. Aqueous solutions of silver nitrate and sodium
- 21. Aqueous Reactions and Chemical AnalysisTypes of quantitative
- 22. Gravimetric AnalysisOne form: isolation of a precipitate
- 23. A 0.825 g sample of an ionic
- 24. Steps in solution: Find the % of
- 25. Слайд 25
- 26. Volumetric analysisCommonly accomplished by titration Addition of
- 27. Apparatus for Titration
- 28. A student measured exactly 15.0 mL of
- 29. Calculate the molarity of 25.0 mL of
- 30. Home taskRead and memorize:Pp. 282-285, pp. 286-291Write
- 31. Скачать презентанцию
Name the compounds:CuSO4 NaOH HNO3 NH4NO3 Ca(OH)2 H2SiO3 H3BO3 KMnO4 Na[Al(OH)4] NaH2PO4 Na2HPO4PbI2 HNO2
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 3General Properties of Aqueous Solutions
Solution - a homogeneous mixture
Solute: the
component that is dissolved
Solvent: the component that does the
dissolvingGenerally, the component present in the greatest quantity is considered to be the solvent. Aqueous solutions are those in which water is the solvent.
Слайд 4Electrolytes and Nonelectrolytes
Electrolyte: substance that, when dissolved in water, produces
a solution that conducts electricity
Contains ions
Nonelectrolyte: substance that, when dissolved
in water, produces a solution that does not conduct electricityDoes not contain ions
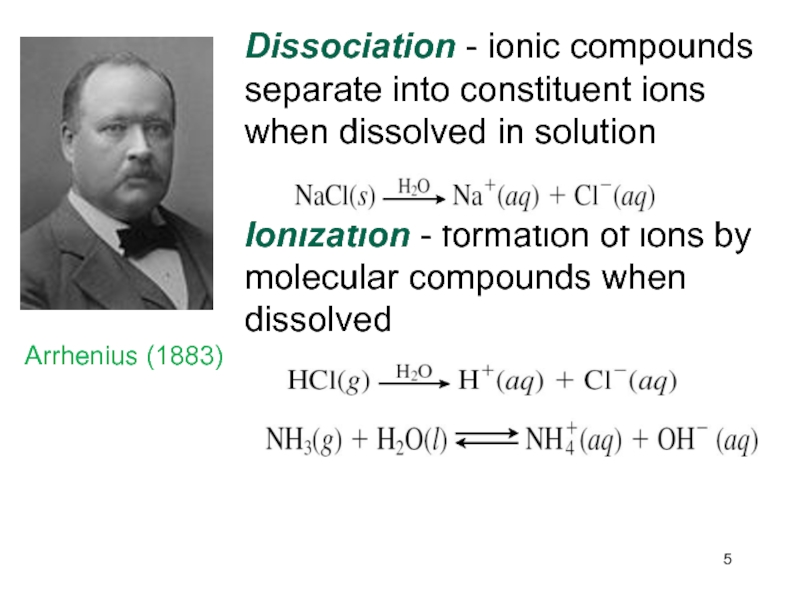
Слайд 5Dissociation - ionic compounds separate into constituent ions when dissolved
in solution
Ionization - formation of ions by molecular compounds
when dissolvedArrhenius (1883))
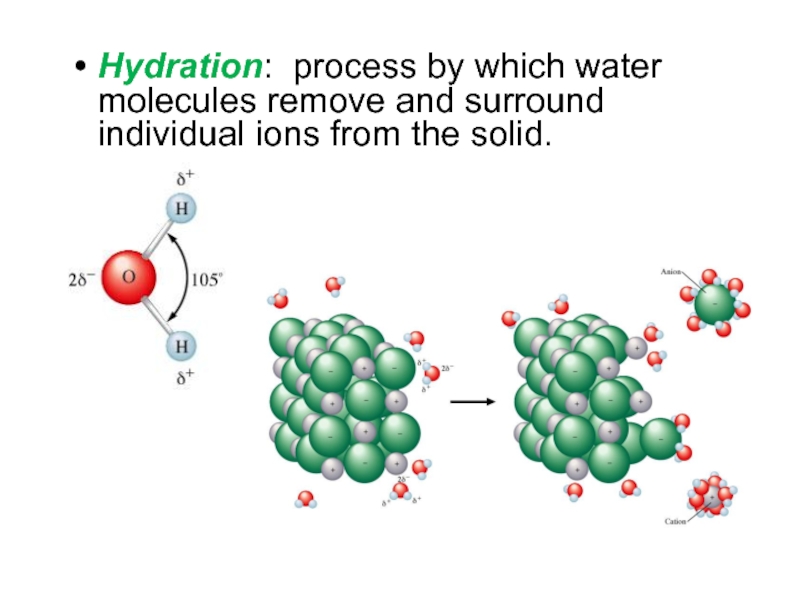
Слайд 6Hydration: process by which water molecules remove and surround individual
ions from the solid.
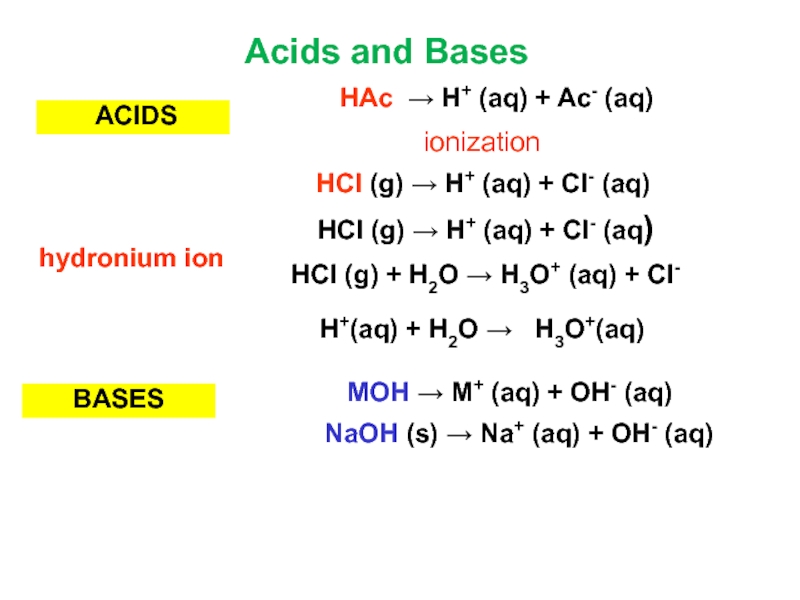
Слайд 7 ACIDS
BASES
NaOH (s) → Na+ (aq) + OH- (aq)
MOH →
M+ (aq) + OH- (aq)
HCl (g) → H+ (aq) +
Cl- (aq)HAc → H+ (aq) + Ac- (aq)
ionization
Acids and Bases
HCl (g) → H+ (aq) + Cl- (aq)
H+(aq) + H2O → H3O+(aq)
HCl (g) + H2O → H3O+ (aq) + Cl- (aq)
hydronium ion
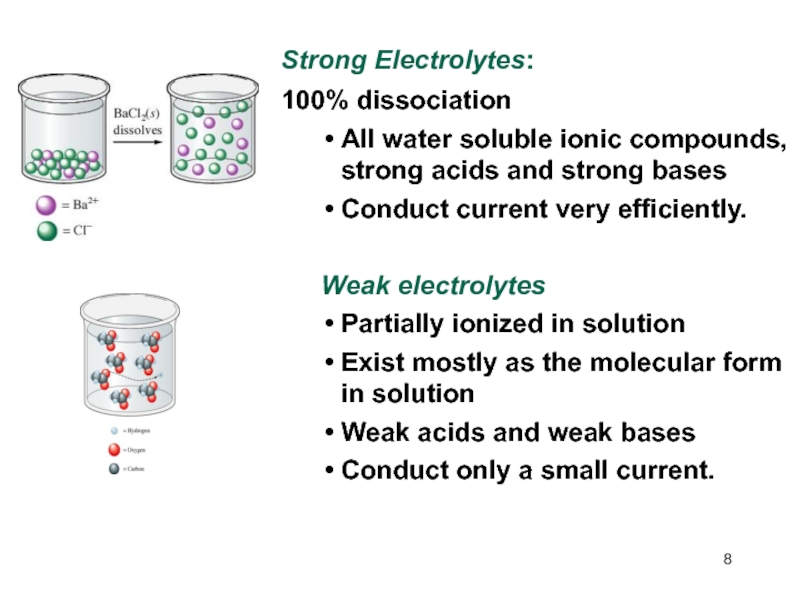
Слайд 8Strong Electrolytes:
100% dissociation
All water soluble ionic compounds, strong acids
and strong bases
Conduct current very efficiently.
Weak electrolytes
Partially ionized in solution
Exist
mostly as the molecular form in solution Weak acids and weak bases
Conduct only a small current.
Слайд 9Degree of dissociation
The fraction of total number of total number
of molecules of electrolytes dissolved, that ionizes at equilibrium is
known as degree of dissociation or degree of ionization.Degree of dissociation (DOD) α=amount of substance of the reactant dissociated/amount of substance of the reactant present initially
In case of very strong acids and bases, degree of dissociation will be close to 1. Less powerful acids and bases will have lesser degree of dissociation.
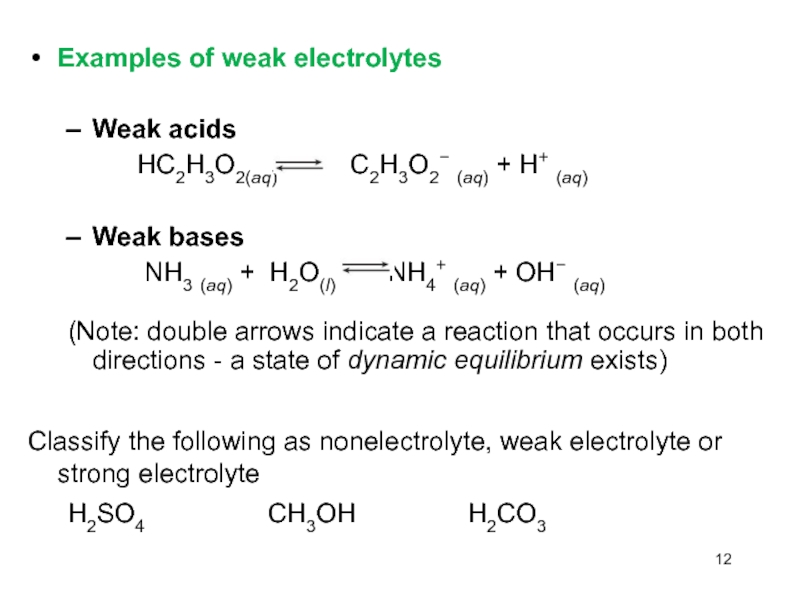
Слайд 12Examples of weak electrolytes
Weak acids
HC2H3O2(aq)
C2H3O2 (aq) + H+ (aq)
Weak bases
NH3 (aq) + H2O(l) NH4+ (aq) + OH (aq) (Note: double arrows indicate a reaction that occurs in both directions - a state of dynamic equilibrium exists)
Classify the following as nonelectrolyte, weak electrolyte or strong electrolyte
H2SO4 CH3OH H2CO3
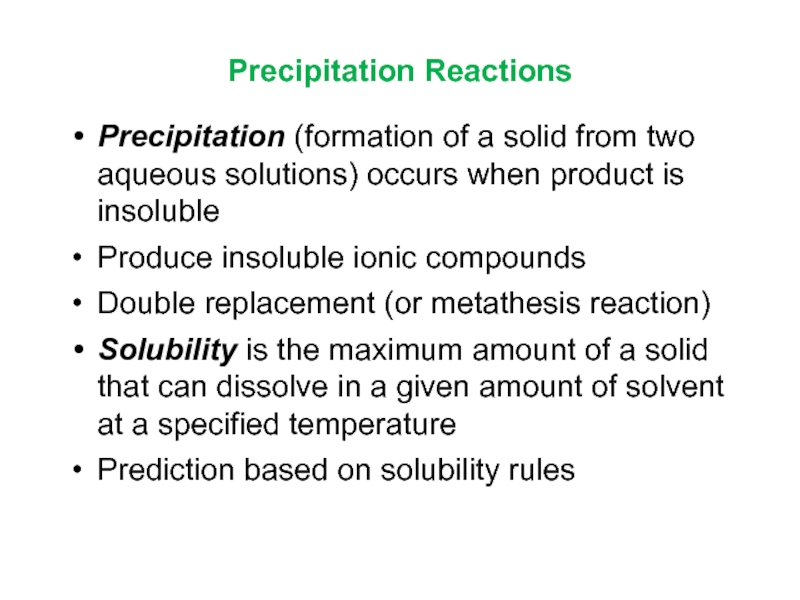
Слайд 13Precipitation Reactions
Precipitation (formation of a solid from two aqueous solutions)
occurs when product is insoluble
Produce insoluble ionic compounds
Double
replacement (or metathesis reaction)Solubility is the maximum amount of a solid that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a specified temperature
Prediction based on solubility rules
Слайд 14Simple Rules for Solubility
Most nitrate (NO3) salts are soluble.
Most alkali
metals (group 1A) salts and NH4+ are soluble.
Most Cl, Br,
and I salts are soluble (NOT Ag+, Pb2+, Hg22+)
Most sulfate salts are soluble (
NOT BaSO4, PbSO4, HgSO4, CaSO4)
Most bases are only slightly soluble (NaOH, KOH are soluble, Ba(OH)2, Ca(OH)2 are marginally soluble
6. Most S2, CO32, CrO42, PO43 salts are only slightly soluble.
Слайд 17Molecular equation: shows all compounds represented by their chemical formulas
Ionic
equation: shows all strong electrolytes as ions and all other
substances (non- electrolytes, weak electrolytes, gases) by their chemical formulasСлайд 18
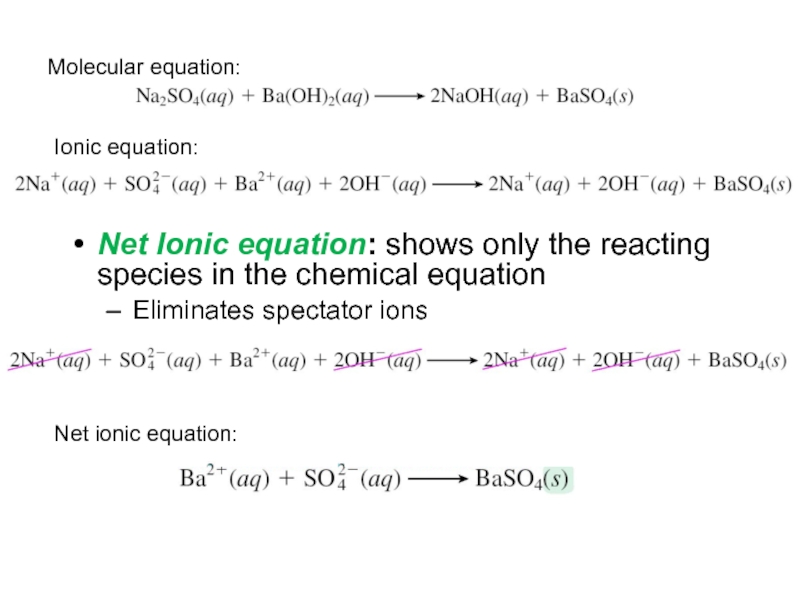
Net Ionic equation: shows only the reacting species in the
chemical equation
Eliminates spectator ions
Molecular equation:
Ionic equation:
Net ionic equation:
Слайд 19Steps in writing a net ionic equation
Write the balanced
molecular equation.
Predict products by exchanging cations and anions in reactants.
Separate
strong electrolytes into ions.Cancel spectator ions.
Use the remaining species to write the net ionic equation.
Слайд 20Aqueous solutions of silver nitrate and sodium sulfate are mixed.
Write the net ionic reaction.
2AgNO3(aq)+Na2SO4(aq) 2NaNO3(?)+Ag2SO4(?)
All nitrates are soluble
but silver sulfate is insoluble.2Ag+(aq) + 2NO3(aq) + 2Na+(aq) + SO42(aq)
2Na+(aq) + 2NO3(aq) + Ag2SO4(s)
Cancel spectators.
2Ag+(aq) + 2NO3(aq) + 2Na+(aq) + SO42(aq)
2Na+(aq) + 2NO3(aq) + Ag2SO4(s)
Write the net ionic reaction.
2Ag+(aq) + SO42(aq) Ag2SO4(s)
Слайд 21Aqueous Reactions and Chemical Analysis
Types of quantitative analysis
Gravimetric analysis (mass
analysis)
Example: precipitation reaction
Volumetric analysis (volume analysis)
Example: titration
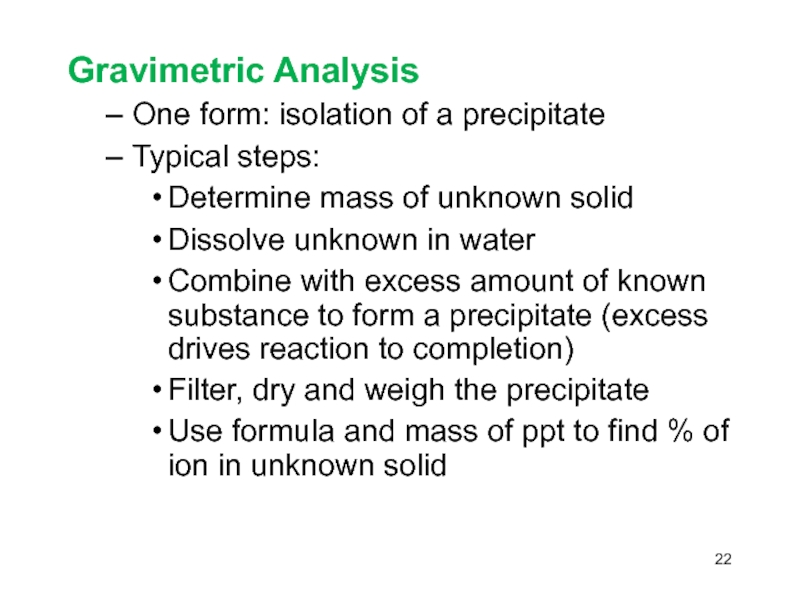
Слайд 22Gravimetric Analysis
One form: isolation of a precipitate
Typical steps:
Determine
mass of unknown solid
Dissolve unknown in water
Combine with excess
amount of known substance to form a precipitate (excess drives reaction to completion) Filter, dry and weigh the precipitate
Use formula and mass of ppt to find % of ion in unknown solid
Слайд 23A 0.825 g sample of an ionic compound
containing chloride ions
and an unknown
metal is dissolved in water and treated
with excess
silver nitrate. If 1.725 g ofAgCl precipitate forms, what is the
percent by mass of Cl in the original
sample?
Слайд 24Steps in solution:
Find the % of Cl in AgCl
Multiply the % of Cl by the mass of the
precipitate to obtain the Cl in the sampleDivide the mass of Cl in sample by total mass of sample (multiply by 100 for %)
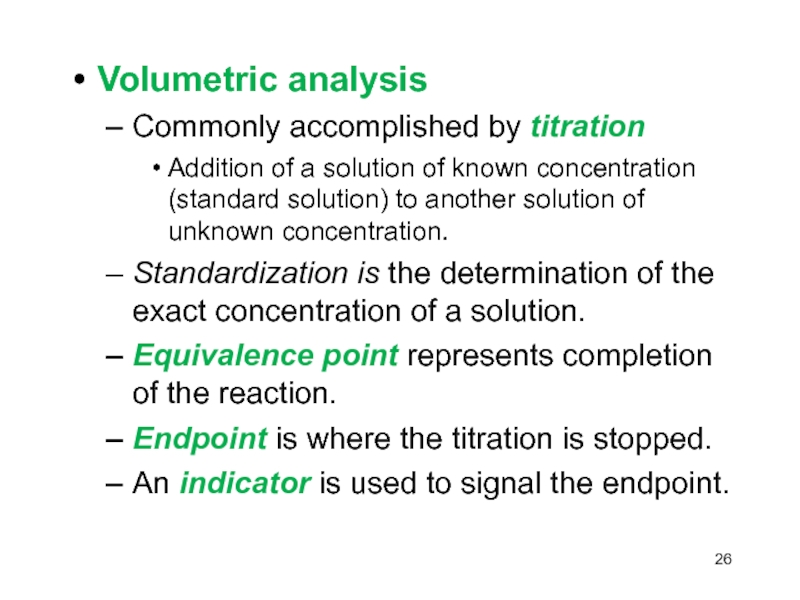
Слайд 26Volumetric analysis
Commonly accomplished by titration
Addition of a solution of
known concentration (standard solution) to another solution of unknown concentration.
Standardization
is the determination of the exact concentration of a solution.Equivalence point represents completion of the reaction.
Endpoint is where the titration is stopped.
An indicator is used to signal the endpoint.
Слайд 28A student measured exactly 15.0 mL of
an unknown monoprotic
acidic solution
and placed in an Erlenmeyer flask. An indicator
was added
to the flask. At the end of thetitration the student had used 35.0 mL of 0.12 M
NaOH to neutralize the acid. Calculate the
molarity of the acid.

![1
Electrolytes. Reactions in Aqueous Solutions Name the compounds:CuSO4 NaOH HNO3 NH4NO3 Ca(OH)2 H2SiO3 H3BO3 Name the compounds:CuSO4 NaOH HNO3 NH4NO3 Ca(OH)2 H2SiO3 H3BO3 KMnO4 Na[Al(OH)4] NaH2PO4 Na2HPO4PbI2 HNO2](/img/thumbs/b40aaf19f0e69e0d59891afb540c221b-800x.jpg)