Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Introduction to SYMLOG ® SYMLOG is an acronym. Multiple Level Observation
Содержание
- 1. Introduction to SYMLOG ® SYMLOG is an acronym. Multiple Level Observation
- 2. Introduction to SYMLOG®It is also a system
- 3. SYMLOG®In a systematic way, the theoretical model
- 4. SYMLOG®The power of the method is its
- 5. SYMLOG®The SYMLOG method is used to evaluate
- 6. SYMLOG®The method is especially powerful because it
- 7. SYMLOG®The SYMLOG Consulting Group has refined over
- 8. The following demonstration displays important images that
- 9. Famous PeopleThis striking and important picture reflects
- 10. You, of course, have your own perceptions
- 11. Survey ResearchParticipants use SYMLOG to answer survey
- 12. Take a moment to review the DESCRIPTIVE
- 13. The SYMLOG 26 Descriptive Items
- 14. A profile is produced which displays
- 15. Comparing the average profile for an image
- 16. Comparing the average profile for an image
- 17. Plotting the location of the “most effective
- 18. Plotting onto the SYMLOG Field Diagram…
- 19. Introducing the SYMLOG Field DiagramIn order to
- 20. The three-dimensional fieldThe horizontal axis represents Values
- 21. The three-dimensional fieldThe vertical axis represents Values
- 22. The three-dimensional fieldThe third dimension of Values
- 23. The three-dimensional fieldThere are
- 24. The Overlay DesignVALUES ON ACCEPTING TASK ORIENTATION
- 25. The Overlay DesignThe large circle in the
- 26. The Values Orientation OverlayVALUES ON ACCEPTING TASK
- 27. The Values Orientation OverlayIt also indicates the
- 28. Behavior is strongly influenced by values, especially
- 29. “In general, what kinds of values do
- 30. “In general, what kinds of values do
- 31. “In general, what kinds of values do
- 32. At the organizational level, to assess ideal
- 33. The responses to these team and organizational
- 34. In contrast, when individuals are asked about
- 35. “In general, what kinds of values do
- 36. “In general, what kinds of values do
- 37. “In general, what kinds of values do
- 38. Additionally, when asked about values which inhibit
- 39. LEP = least productiveOnce again, the results
- 40. “In general, what kinds of values does
- 41. “In general, what kinds of values do
- 42. In contrast, when asked about the actual situation in their own organization, respondents answer the question:
- 43. “In general, what kinds of values are CURRENTLY shown in the culture of your organization?” (CUR)
- 44. “In general, what kinds of values are
- 45. “In general, what kinds of values are
- 46. “In general, what kinds of values are
- 47. And when asked in particular about the
- 48. CUR = current cultureThe perceptions of values
- 49. “In general, what kinds of values are
- 50. A summary view of common polarizations and
- 51. What are some of the implications in
- 52. ImplicationsTeamwork will never take the place of
- 53. ImplicationsMost organizations have serious design flaws.The vision
- 54. ImplicationsOrganizations need and thrive on feedback.Most organizations
- 55. Samples drawn from over 1,000,000 ratings
- 56. SYMLOG -"Improving Performance Through Effective Feedback"18580 Polvera
- 57. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Introduction to SYMLOG®
It is also a system that can measure
the effectiveness of social interaction in an elegantly simple yet
comprehensive way.It is a theory of social interaction.
Слайд 3SYMLOG®
In a systematic way, the theoretical model allows for the
integration of organizational change efforts for organizational culture, team, and
individual development efforts.In addition to providing a model of planned change, SYMLOG has an associated measurement system.
Слайд 4SYMLOG®
The power of the method is its ability to measure
and feedback useful, valid, and reliable results using one comprehensive
framework.The system measures three dimensions of social interaction important to effective leadership, team work, and organizational culture.
Слайд 5SYMLOG®
The SYMLOG method is used to evaluate the current situation
and to compare these results with an assessment of what
is needed to be most effective.This most effective profile has been demonstrated to apply cross-culturally and further shown to be the location where organizational effectiveness is optimum, and employee productivity and satisfaction are maximized.
Слайд 6SYMLOG®
The method is especially powerful because it also encourages the
use of repeated measures. These repeated measures provide continuing direction
to support development efforts, and allows for ongoing assessment of the effectiveness of change programs.This comparison between current and desired future conditions provides strategic guidance to needed changes in organizational development, team building, and leadership training efforts.
Слайд 7SYMLOG®
The SYMLOG Consulting Group has refined over fifty years of
continuous research by Robert F. Bales, Professor Emeritus of Harvard
University, to make SYMLOG available in twelve languages worldwide.The displays in this demonstration are based on very large random samples drawn from the SYMLOG Data Bank which contains over 1,000,000 profiles.
Слайд 8The following demonstration displays important images that affect leadership, teamwork,
and organizational productivity.
Watch the movement of images and you
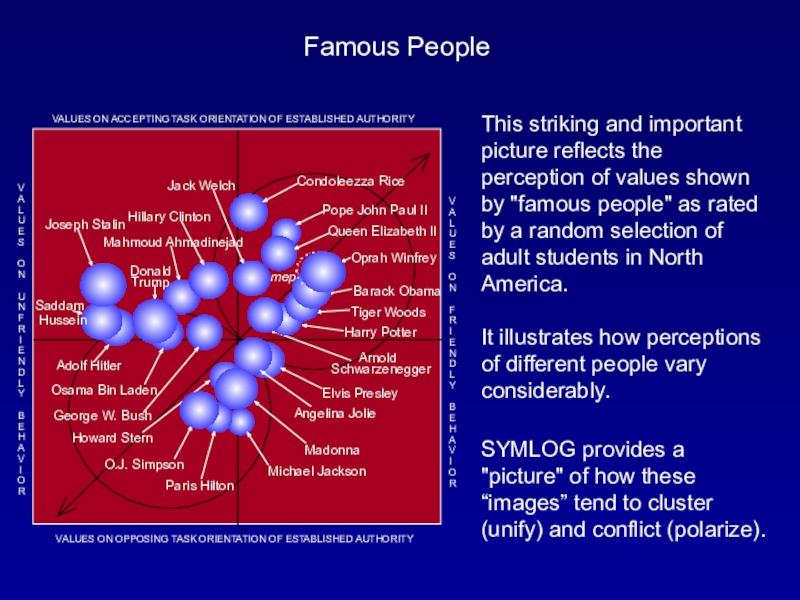
will see the SYMLOG theory of polarization and unification in action.Слайд 9Famous People
This striking and important picture reflects the perception of
values shown by "famous people" as rated by a random
selection of adult students in North America.It illustrates how perceptions of different people vary considerably.
SYMLOG provides a "picture" of how these “images” tend to cluster (unify) and conflict (polarize).
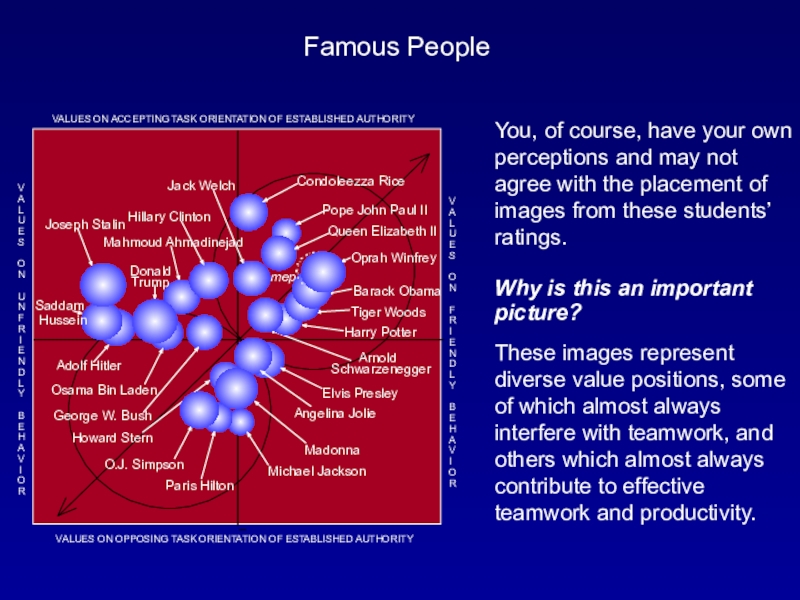
Слайд 10You, of course, have your own perceptions and may not
agree with the placement of images from these students’ ratings.
Famous People
Why is this an important picture?
These images represent diverse value positions, some of which almost always interfere with teamwork, and others which almost always contribute to effective teamwork and productivity.
Слайд 11Survey Research
Participants use SYMLOG to answer survey questions associated with
key images that influence effective leadership, teamwork, and organizational productivity.
For
example:"In general, what kinds of values does the MOST EFFECTIVE LEADER of a task-oriented group you have known show in behavior?"
or
“In general, what kinds of values does your team CURRENTLY show in behavior?”
Слайд 12Take a moment to review the DESCRIPTIVE ITEMS
1 U Individual financial success,
personal prominence and power
2 UP Popularity and social success, being liked
and admired3 UPF Active teamwork toward common goals, organizational unity
4 UF Efficiency, strong impartial management
5 UNF Active reinforcement of authority, rules, and regulations
6 UN Tough-minded, self-oriented assertiveness
7 UNB Rugged, self-oriented individualism, resistance to authority
8 UB Having a good time, releasing tension, relaxing control
9 UPB Protecting less able members, providing help when needed
10 P Equality, democratic participation in decision making
11 PF Responsible idealism, collaborative work
12 F Conservative, established, "correct" ways of doing things
13 NF Restraining individual desires for organizational goals
14 N Self-protection, self-interest first, self-sufficiency
15 NB Rejection of established procedures, rejection of conformity
16 B Change to new procedures, different values, creativity
17 PB Friendship, mutual pleasure, recreation
18 DP Trust in the goodness of others
19 DPF Dedication, faithfulness, loyalty to the organization
20 DF Obedience to the chain of command, complying with authority
21 DNF Self-sacrifice if necessary to reach organizational goals
22 DN Passive rejection of popularity, going it alone
23 DNB Admission of failure, withdrawal of effort
24 DB Passive non-co-operation with authority
25 DPB Quiet contentment, taking it easy
26 D Giving up personal needs and desires, passivity
To answer a question, a respondent considers the question as it relates to each of the 26 descriptive phrases.
Слайд 13The SYMLOG 26 Descriptive Items
RARELY
SOMETIMES OFTEN
Individual financial success, personal
prominence and power Popularity and social success, being liked and admired
Active teamwork toward common goals, organizational unity
Efficiency, strong impartial management
Active reinforcement of authority, rules, and regulations
Tough-minded, self-oriented assertiveness
Rugged, self-oriented individualism, resistance to authority
Having a good time, releasing tension, relaxing control
Protecting less able members, providing help when needed
Equality, democratic participation in decision making
Responsible idealism, collaborative work
Conservative, established, "correct" ways of doing things
Restraining individual desires for organizational goals
Self-protection, self-interest first, self-sufficiency
Rejection of established procedures, rejection of conformity
Change to new procedures, different values, creativity
Friendship, mutual pleasure, recreation
Trust in the goodness of others
Dedication, faithfulness, loyalty to the organization
Obedience to the chain of command, complying with authority
Self-sacrifice if necessary to reach organizational goals
Passive rejection of popularity, going it alone
Admission of failure, withdrawal of effort
Passive non-co-operation with authority
Quiet contentment, taking it easy
Giving up personal needs and desires, passivity
They mark their answers using Rarely, Sometimes, or Often.
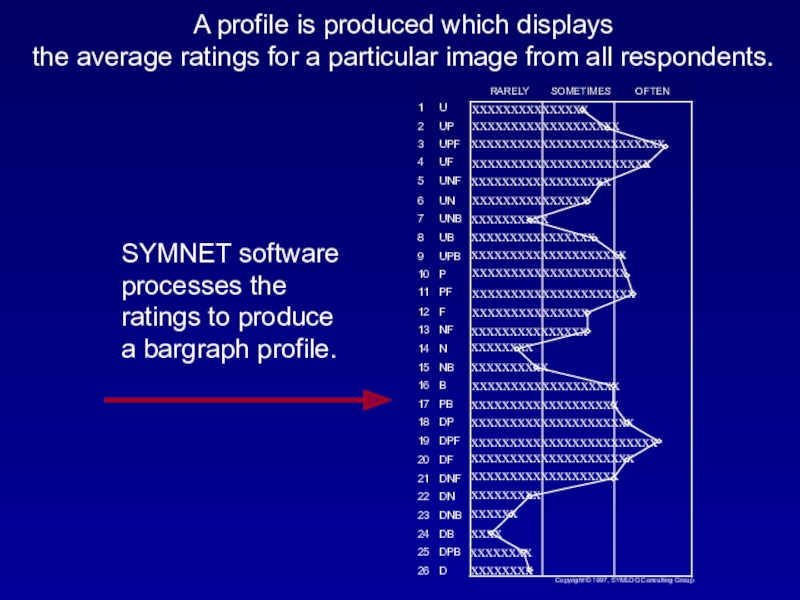
Слайд 14A profile is produced which displays
the average ratings for a particular image from all respondents.
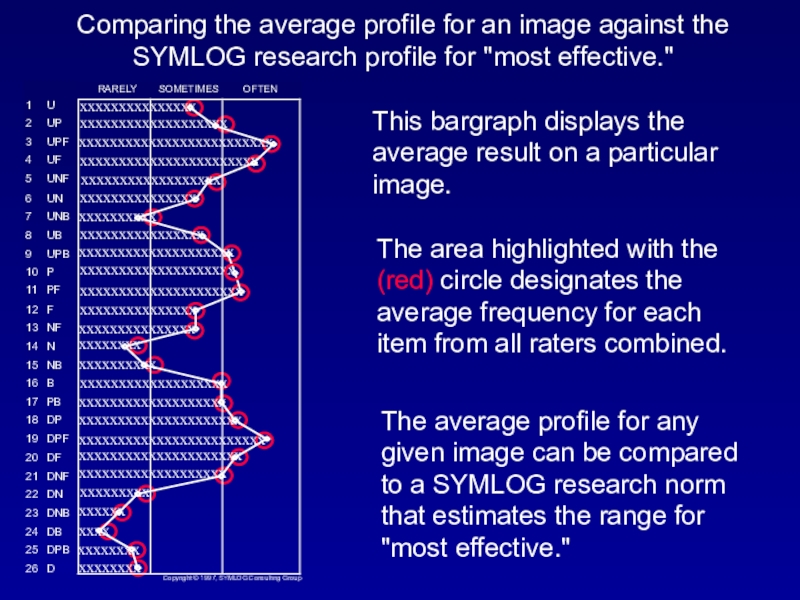
Слайд 15Comparing the average profile for an image against the SYMLOG
research profile for "most effective."
This bargraph displays the average result
on a particular image.The area highlighted with the (red) circle designates the average frequency for each item from all raters combined.
The average profile for any given image can be compared to a SYMLOG research norm that estimates the range for "most effective."
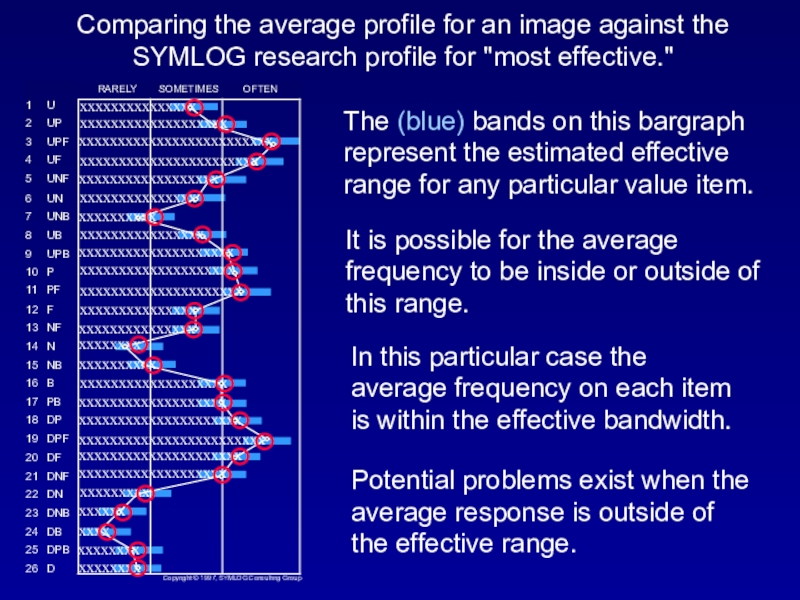
Слайд 16Comparing the average profile for an image against the SYMLOG
research profile for "most effective."
The (blue) bands on this bargraph
represent the estimated effective range for any particular value item. It is possible for the average frequency to be inside or outside of this range.
In this particular case the average frequency on each item is within the effective bandwidth.
Potential problems exist when the average response is outside of the effective range.
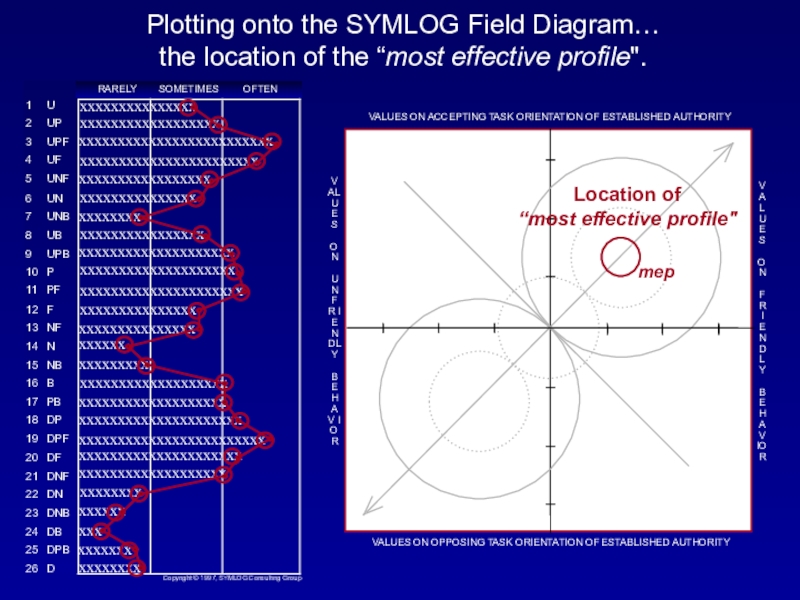
Слайд 17Plotting the location of the “most effective profile” onto the
field diagram …
This particular profile has been demonstrated and researched
to be "most effective."When this profile is plotted on a field diagram, it is located in a very strategic position.
In fact, research indicates it is indeed the "most effective profile" (mep), over time and across situations and cultures, to unify diverse groups, resulting in high quality outcomes.
Слайд 18Plotting onto the SYMLOG Field Diagram…
the location of the “most effective profile".
VALUES ON ACCEPTING TASK ORIENTATION OF ESTABLISHED AUTHORITY
VALUES ON OPPOSING TASK ORIENTATION OF ESTABLISHED AUTHORITY
V ALUES
ON
UNFR I ENDLY
BEHAV I
OR
V ALUES
ON
FR I ENDLY
BEHAV IOR
Location of “most effective profile"
mep
Слайд 19Introducing the SYMLOG Field Diagram
In order to understand the scenarios
you are about to view, let us take a brief
tour of the ways in which the values are displayed.The SYMLOG Individual and Organizational Values Field is characterized by three bipolar dimensions:
3. Values on Dominance vs. Submissiveness
Values on Individualistic vs. Group-oriented Behavior
2. Values on Accepting vs. Opposing Authority
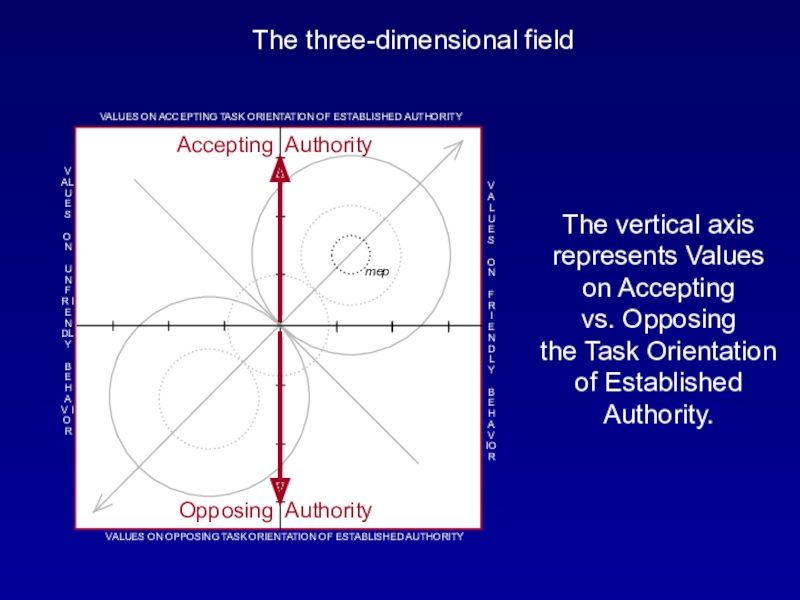
Слайд 20The three-dimensional field
The horizontal axis represents Values on Unfriendly (Individualistic)
Behavior vs. Friendly (Group-oriented) Behavior.
Unfriendly (Individualistic) Behavior
Friendly
(Group-oriented)
BehaviorСлайд 21The three-dimensional field
The vertical axis represents Values on Accepting
vs. Opposing
the Task Orientation of Established Authority.Accepting Authority
Opposing Authority
Слайд 22The three-dimensional field
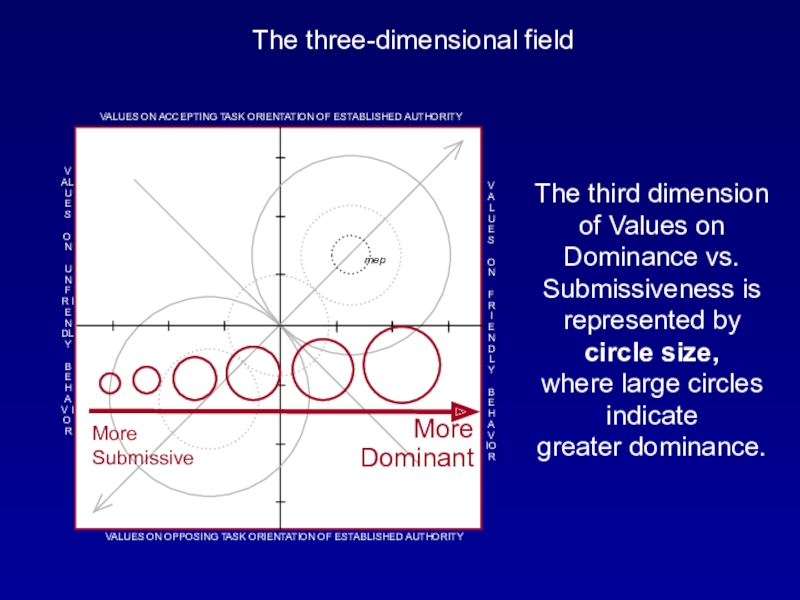
The third dimension of Values on Dominance vs.
Submissiveness is represented by circle size,
where large circles indicate greater dominance.More Submissive
More Dominant
Слайд 23The three-dimensional field
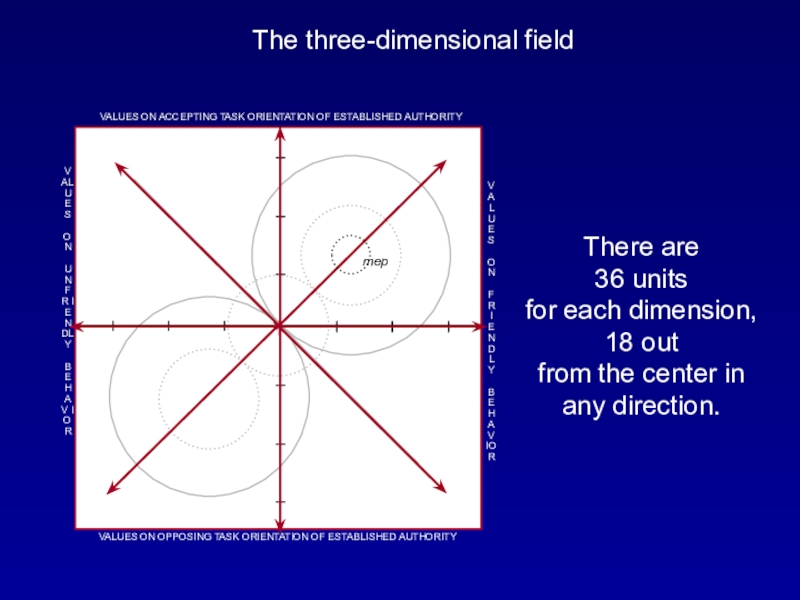
There are
36 units
for each dimension, 18 out from the center in any direction.Слайд 24The Overlay Design
VALUES ON ACCEPTING TASK ORIENTATION OF ESTABLISHED AUTHORITY
VALUES
ON OPPOSING TASK ORIENTATION OF ESTABLISHED AUTHORITY
V ALUES
ON
UNFR
I ENDLYBEHAV I
OR
V ALUES
ON
FR I ENDLY
BEHAV IOR
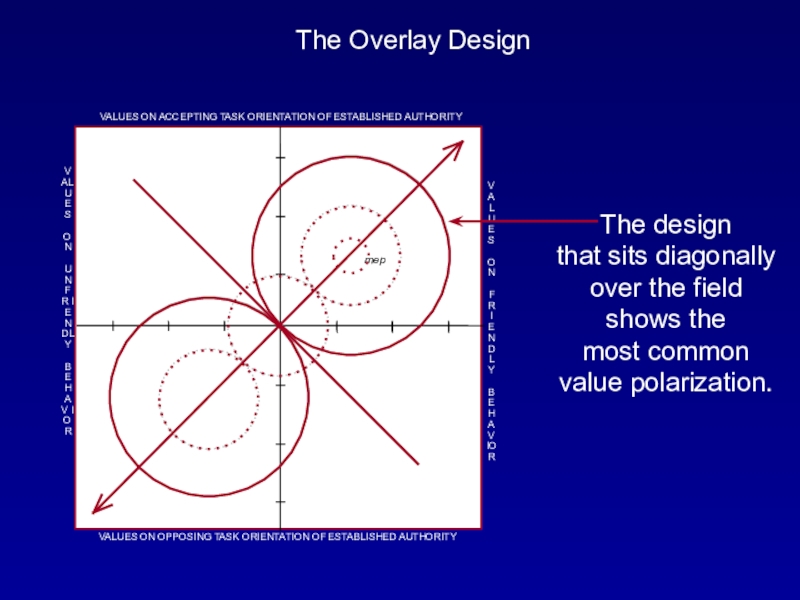
The design that sits diagonally over the field shows the most common value polarization.
Слайд 25The Overlay Design
The large circle in the upper right surrounds
the position of "Most Effective Teamwork Core"
which is in
opposition to the lower left circle surrounding the position of "Radical Opposition Core.""Most Effective Teamwork Core"
"Radical Opposition Core"
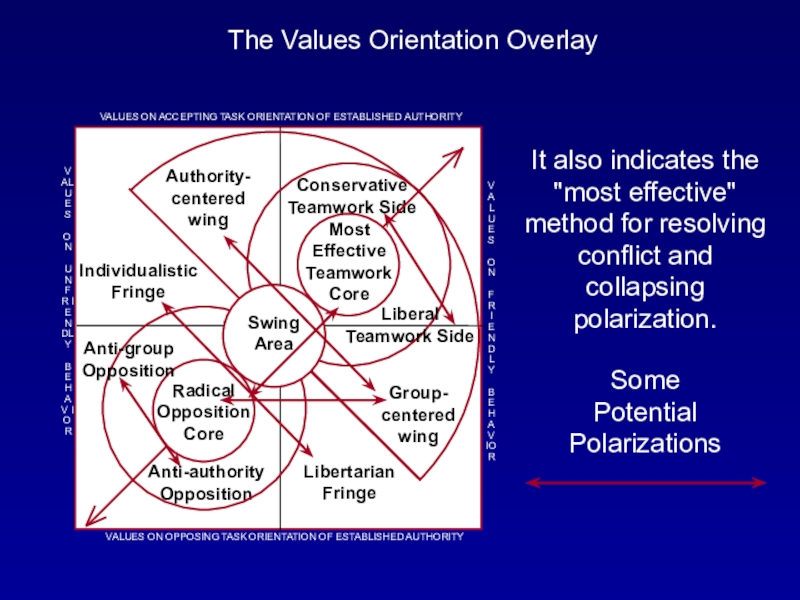
Слайд 26The Values Orientation Overlay
VALUES ON ACCEPTING TASK ORIENTATION OF ESTABLISHED
AUTHORITY
VALUES ON OPPOSING TASK ORIENTATION OF ESTABLISHED AUTHORITY
V ALUES
ON
UNFR I ENDLYBEHAV I
OR
V ALUES
ON
FR I ENDLY
BEHAV IOR
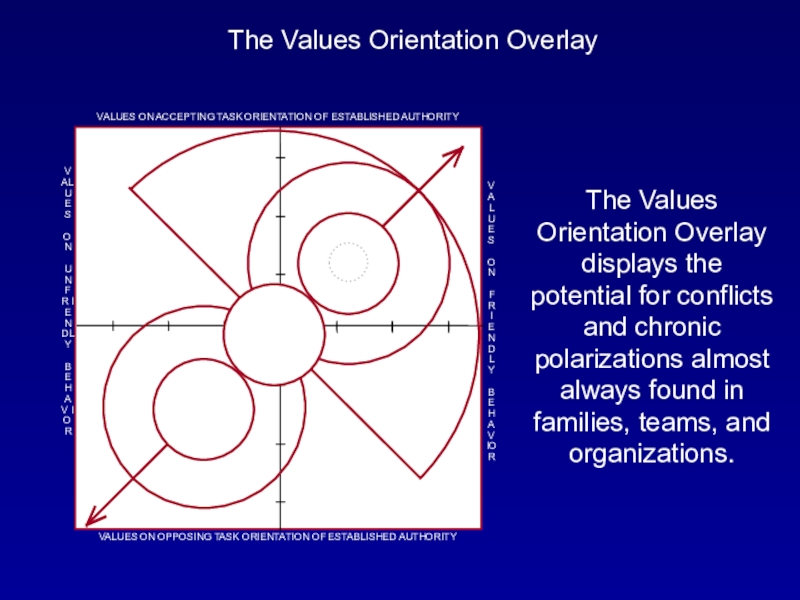
The Values Orientation Overlay displays the potential for conflicts and chronic polarizations almost always found in families, teams, and organizations.
Слайд 27The Values Orientation Overlay
It also indicates the "most effective" method
for resolving conflict and collapsing polarization.
Most Effective Teamwork Core
Radical Opposition
CoreConservative Teamwork Side
Authority-centered wing
Group- centered wing
Individualistic Fringe
Libertarian Fringe
Anti-authority Opposition
Anti-group Opposition
Swing Area
Liberal Teamwork Side
Слайд 28Behavior is strongly influenced by values, especially those behaviors individuals
“wish to show”. When participants in leadership training are
asked about their own value preferences, they use the 26 SYMLOG items to answer the question:“In general, what kinds of values do you WISH to show in your own behavior, whether or not you are actually able to do so?” (WSH)
All survey results shown are from random samples drawn from over 1,000,000 ratings worldwide.
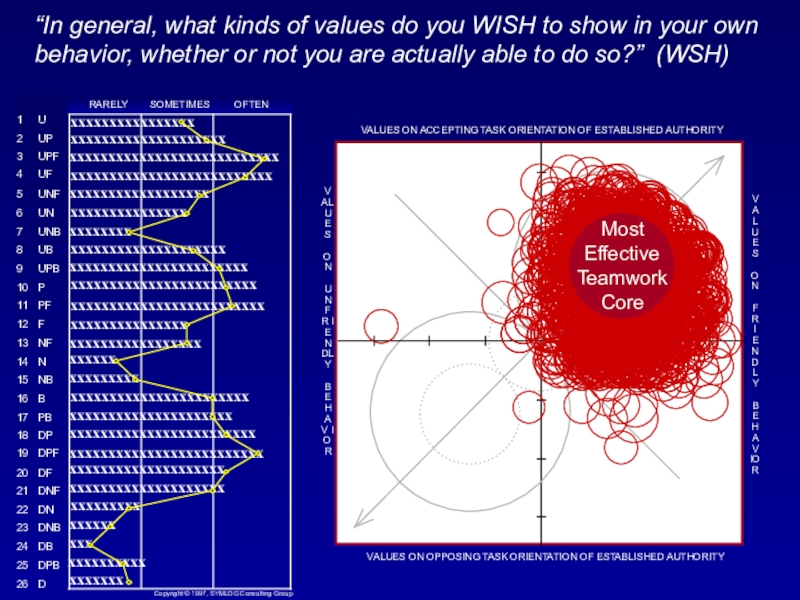
Слайд 29“In general, what kinds of values do you WISH to
show in your own behavior, whether or not you are
actually able to do so?” (WSH)Слайд 30“In general, what kinds of values do you WISH to
show in your own behavior, whether or not you are
actually able to do so?” (WSH)mep
WSH
The group average of these responses indicate a final location of ...
Слайд 31“In general, what kinds of values do you WISH to
show in your own behavior, whether or not you are
actually able to do so?” (WSH)WSH
The general characteristics of this location in the field are:
Active teamwork toward common goals, organizational unity.
Notice that almost every average on the bargraph is within the (blue) most effective bandwidth.
Given the opportunity, most people WISH to be effective.
mep
Слайд 32At the organizational level, to assess ideal conditions, members of
the organization are asked:
“In general, what kinds of values need
to be shown in the culture of your organization in the FUTURE in order to be most effective?” (FUT)To assess ideal conditions, members answer the question:
“In general, what kinds of values need to be shown by your team in the future in order to be most effective?” (FTM)
At the team level, for a measure of demonstrated effectiveness, team members answer the question:
“In general, what kinds of values does the MOST EFFECTIVE MEMBER of a task-oriented work team you have known show in behavior?” (MEM)
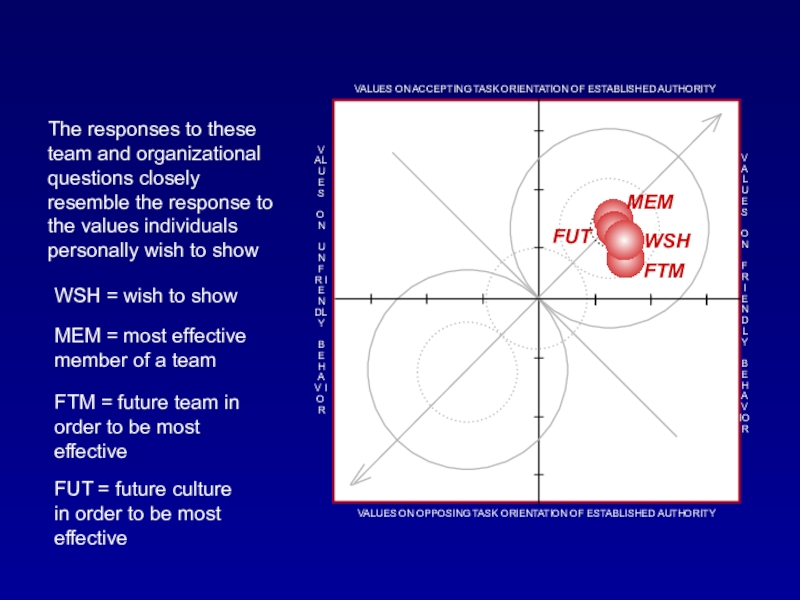
Слайд 33The responses to these team and organizational questions closely resemble
the response to the values individuals personally wish to show
WSH
= wish to showMEM = most effective member of a team
FTM = future team in order to be most effective
FUT = future culture in order to be most effective
Слайд 34In contrast, when individuals are asked about the values they
tend to oppose they use the same 26 SYMLOG items
to answer the question,“In general, what kinds of values do you tend to REJECT, either in yourself or in others?” (REJ)
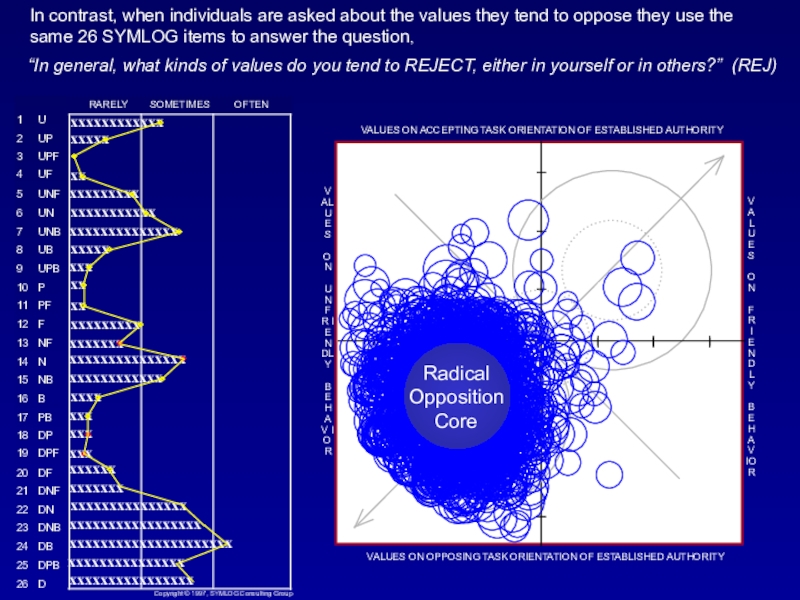
Слайд 35“In general, what kinds of values do you tend to
REJECT, either in yourself or in others?” (REJ)
REJ
The group average
of these responses indicate a final location of ...Слайд 36“In general, what kinds of values do you tend to
REJECT, either in yourself or in others?” (REJ)
mep
REJ
The general characteristics
of this location in the field are: Admission of failure, withdrawal of effort.
Notice that almost every average on the bargraph is outside (opposite) of the (blue) most effective bandwidth. This profile leads to conflict and polarization.
Слайд 37“In general, what kinds of values do you tend to
REJECT, either in yourself or in others?” (REJ)
In essence, people
tend to reject and avoid others who demonstrate values associated with: 7. Rugged, self-oriented individualism, resistance to authority
14. Self-protection, self-interest first, self sufficiency
22. Passive rejection of popularity, going it alone
23. Admission of failure, withdrawal of effort
24. Passive, non-cooperation with authority
25. Quiet contentment, taking it easy
Слайд 38Additionally, when asked about values which inhibit effective teamwork and
lower productivity, team members answer the questions:
“In general, what
kinds of values does the LEAST EFFECTIVE MEMBER of a task-oriented team you have known show in behavior?” (LEM)“In general, what kinds of values do members of your team show in behavior when the team is LEAST PRODUCTIVE? (LEP)
and
Слайд 39LEP = least productive
Once again, the results are strikingly similar
to what individuals reject
REJ = reject in self or others
LEM
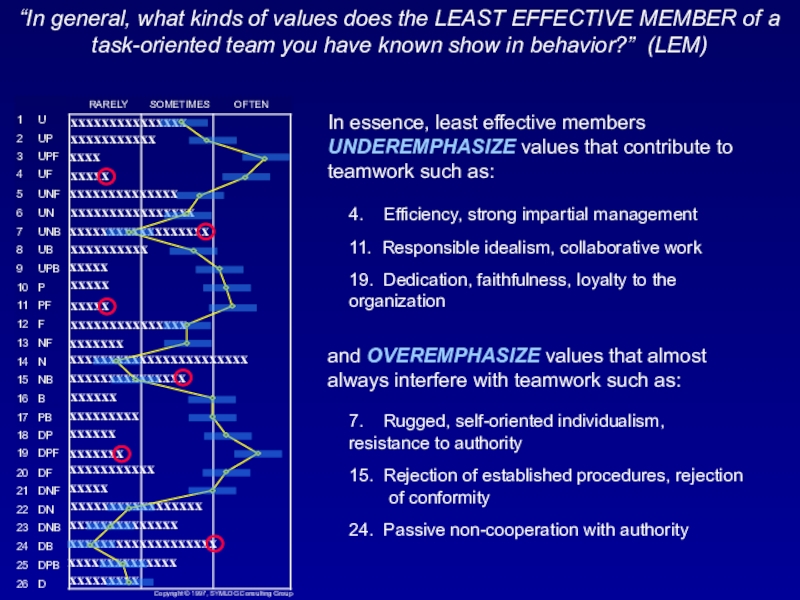
= least effective member knownСлайд 40“In general, what kinds of values does the LEAST EFFECTIVE
MEMBER of a task-oriented team you have known show in
behavior?” (LEM)In essence, least effective members UNDEREMPHASIZE values that contribute to teamwork such as:
4. Efficiency, strong impartial management
11. Responsible idealism, collaborative work
19. Dedication, faithfulness, loyalty to the organization
and OVEREMPHASIZE values that almost always interfere with teamwork such as:
7. Rugged, self-oriented individualism, resistance to authority
15. Rejection of established procedures, rejection of conformity
24. Passive non-cooperation with authority
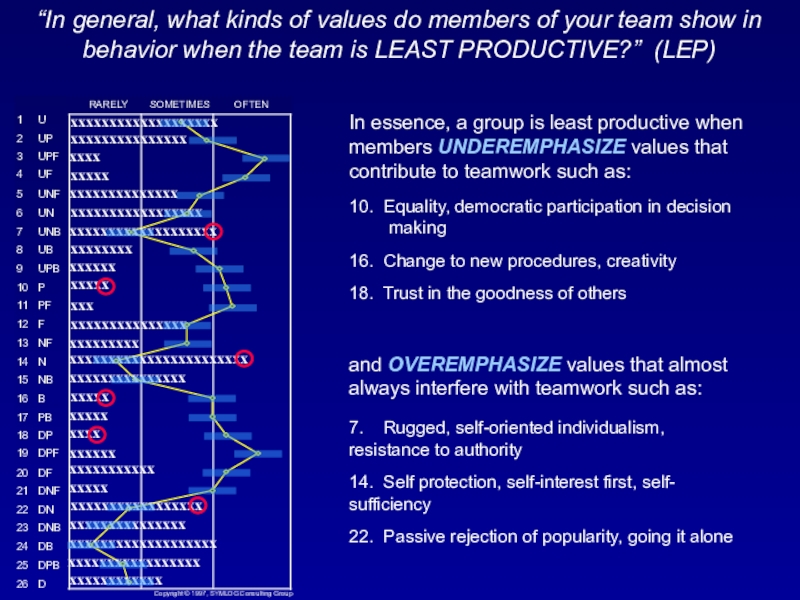
Слайд 41“In general, what kinds of values do members of your
team show in behavior when the team is LEAST PRODUCTIVE?”
(LEP)In essence, a group is least productive when members UNDEREMPHASIZE values that contribute to teamwork such as:
10. Equality, democratic participation in decision making
16. Change to new procedures, creativity
18. Trust in the goodness of others
and OVEREMPHASIZE values that almost always interfere with teamwork such as:
7. Rugged, self-oriented individualism, resistance to authority
14. Self protection, self-interest first, self- sufficiency
22. Passive rejection of popularity, going it alone
Слайд 42In contrast, when asked about the actual situation in their
own organization, respondents answer the question:
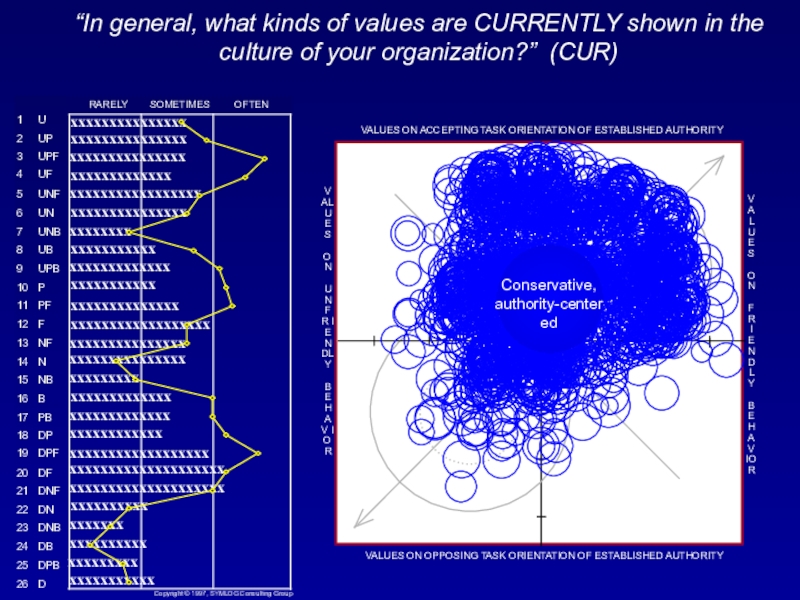
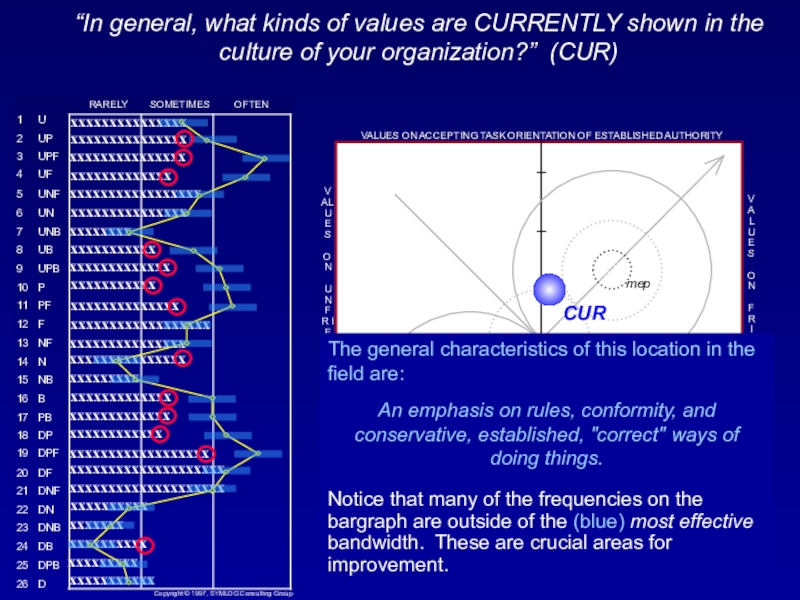
Слайд 43“In general, what kinds of values are CURRENTLY shown in
the culture of your organization?” (CUR)
Слайд 44“In general, what kinds of values are CURRENTLY shown in
the culture of your organization?” (CUR)
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
The group average of these
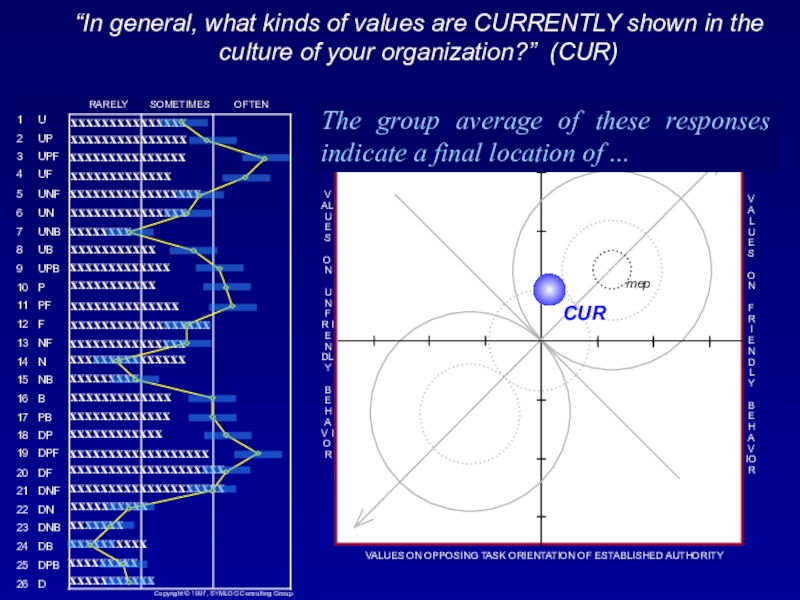
responses indicate a final location of ...Слайд 45“In general, what kinds of values are CURRENTLY shown in
the culture of your organization?” (CUR)
The general characteristics of this
location in the field are: An emphasis on rules, conformity, and conservative, established, "correct" ways of doing things.
Notice that many of the frequencies on the bargraph are outside of the (blue) most effective bandwidth. These are crucial areas for improvement.
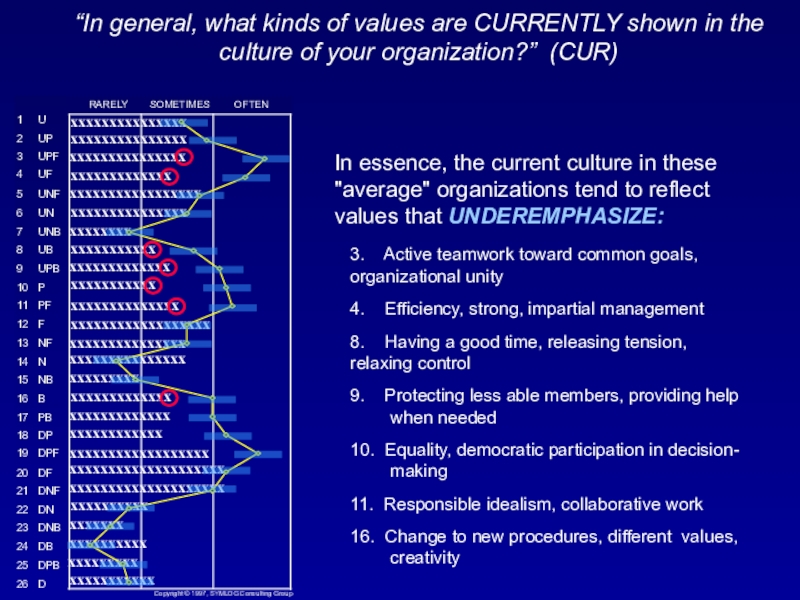
Слайд 46“In general, what kinds of values are CURRENTLY shown in
the culture of your organization?” (CUR)
In essence, the current culture
in these "average" organizations tend to reflect values that UNDEREMPHASIZE:3. Active teamwork toward common goals, organizational unity
4. Efficiency, strong, impartial management
8. Having a good time, releasing tension, relaxing control
9. Protecting less able members, providing help when needed
10. Equality, democratic participation in decision- making
11. Responsible idealism, collaborative work
16. Change to new procedures, different values, creativity
Слайд 47And when asked in particular about the reward structures in
their organization, respondents answer the question:
“In general, what kinds of
values are members of your organization actually REWARDED for showing in behavior now?” (REW)Similarly, teams are asked:
“In general, what kinds of values does your team CURRENTLY show in behavior?” (CTM)
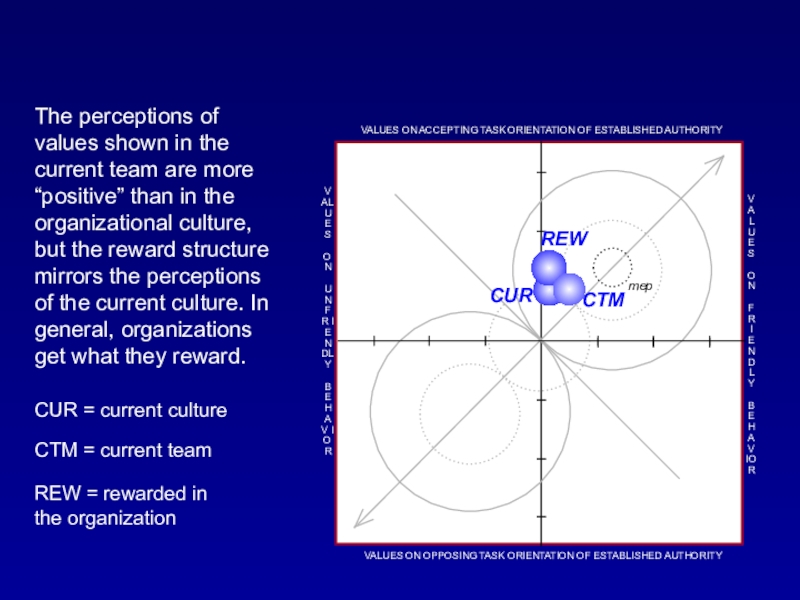
Слайд 48CUR = current culture
The perceptions of values shown in the
current team are more “positive” than in the organizational culture,
but the reward structure mirrors the perceptions of the current culture. In general, organizations get what they reward.CTM = current team
REW = rewarded in the organization
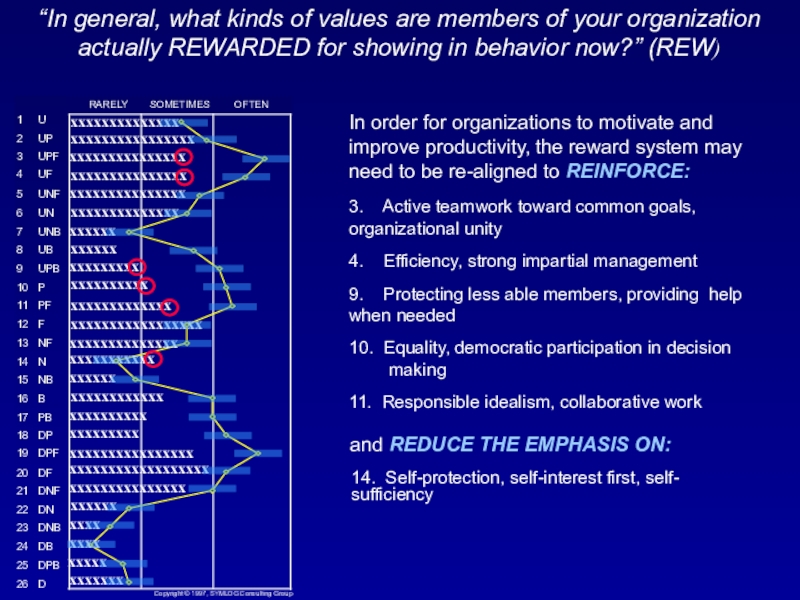
Слайд 49“In general, what kinds of values are members of your
organization actually REWARDED for showing in behavior now?” (REW)
In order
for organizations to motivate and improve productivity, the reward system may need to be re-aligned to REINFORCE:3. Active teamwork toward common goals, organizational unity
4. Efficiency, strong impartial management
9. Protecting less able members, providing help when needed
10. Equality, democratic participation in decision making
11. Responsible idealism, collaborative work
and REDUCE THE EMPHASIS ON:
14. Self-protection, self-interest first, self- sufficiency
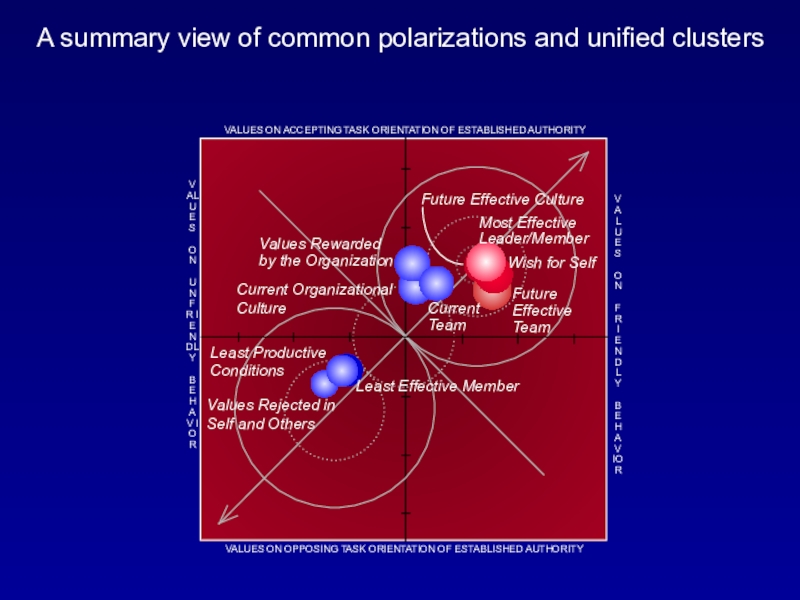
Слайд 50A summary view of common polarizations and unified clusters
Future Effective
Culture
Most Effective Leader/Member
Values Rewarded
by the Organization
Current
Team
Слайд 51What are some of the implications in these displays?
People have
powerful images of themselves and others.
These images dramatically influence the
way people behave and whether they will unify or polarize with others as they work together. SYMLOG helps leaders and members to clarify and understand these images and to guide strategic changes towards more effective behavior.Слайд 52Implications
Teamwork will never take the place of technical competence.
However, competent
individuals working within groups that are in constant conflict find
it very difficult to produce superior results. Chronic polarization is corrosive and undermines both work quality and personal satisfaction. SYMLOG feedback helps groups to understand and appreciate their diversity, point out areas of common values, and implement ways to work more effectively together.Слайд 53Implications
Most organizations have serious design flaws.
The vision and mission call
for creative teamwork but the system actually rewards individual turf-building
and self-sufficiency. Few organizations are able to promote, much less reward, effective teamwork. Simply "restructuring" and focusing on technical quality does not necessarily motivate people to perform effectively. Teams, as well as individuals, need ongoing feedback that is valid and reliable as well as rewards for superior performance.Слайд 54Implications
Organizations need and thrive on feedback.
Most organizations cannot live without
regular status reports from finance, yet very few have an
ongoing feedback system in place to tell them how their espoused values are, or are not, being lived out. SYMLOG provides such a system, on a regular and repeated basis, to strengthen individual leadership, support productive teamwork, and develop organizational competence.Thank you for viewing this demonstration,
Robert J. Koenigs, Ph.D.
President, SYMLOG Consulting Group
Слайд 55Samples drawn from over 1,000,000 ratings
worldwide.
Contact us today to discuss how
SYMLOG may benefit you and your organization.Слайд 56SYMLOG -"Improving Performance Through Effective Feedback"
18580 Polvera Drive
San Diego, CA 92128
phone:
(858) 673-2098 fax: (858) 674-1593
e-mail: staff@symlog.com
web site: www.symlog.com
©1999, 2009 SYMLOG Consulting Group