Слайд 1Ministry education and Science of Republic of Kazakhstan
Karaganda State University
named after academician Ye.A. Buketov
Biological and geographical faculty
Botany Department
Course – Botany
Specialty - 5В011300 – «Biology»
Lecture № 7
Types of inflorescences. Role of inflorescences in plants’ life
(1 hour)
Lecturer: candidate of biological science, associated professor
Ishmuratova Margarita Yulaevna
Слайд 2Plan of lecture:
1 Definition and biological role of inflorescences.
2 Simple
inflorescences.
3 Compound inflorescences.
4 Pollination.
Слайд 3Basic literatures:
1 Бавтуто Г.А. Практикум по анатомии и морфологии
растений. – Минск: Новое знание, 2002. – 185 с.
2 Родман
А.С. Ботаника. – М.: Колос, 2001. - 328 с.
Additional literatures:
1 Ишмуратова М.Ю. Ботаника. Учебно-методическое пособие. - Караганда: РИО Болашак-Баспа, 2015. - 331 с.
2 Тусупбекова Г.Т. Основы естествознания. Ч. 1. Ботаника. – Астана: Фолиант, 2013. – 321 с.
3 Байтулин И.О. Основы ризологии. - Алматы: Гылым, 2001. – 210 с.
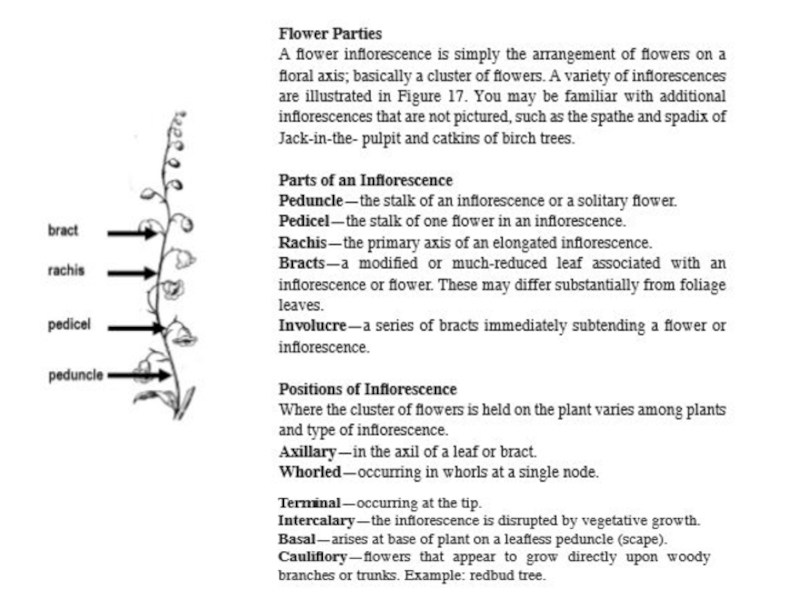
Слайд 4Inflorescence is an isolated generative shoot (shoot bearing FU).Together, inflorescences
make generative shoot system. Its diverse structure is of not
lesser importance than the structure of vegetative shoot system.
Biological role of inflorescences – to attract insects – pollinators.
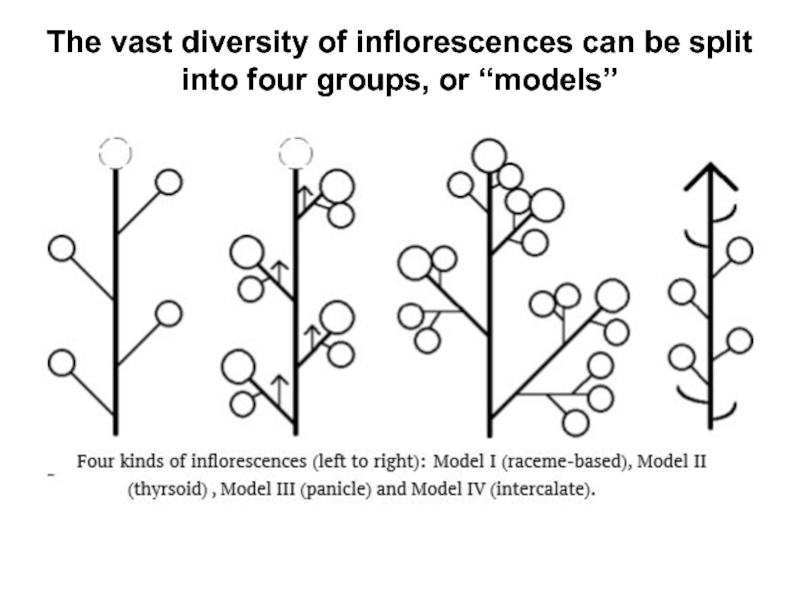
Слайд 5The vast diversity of inflorescences can be split into four
groups, or “models”
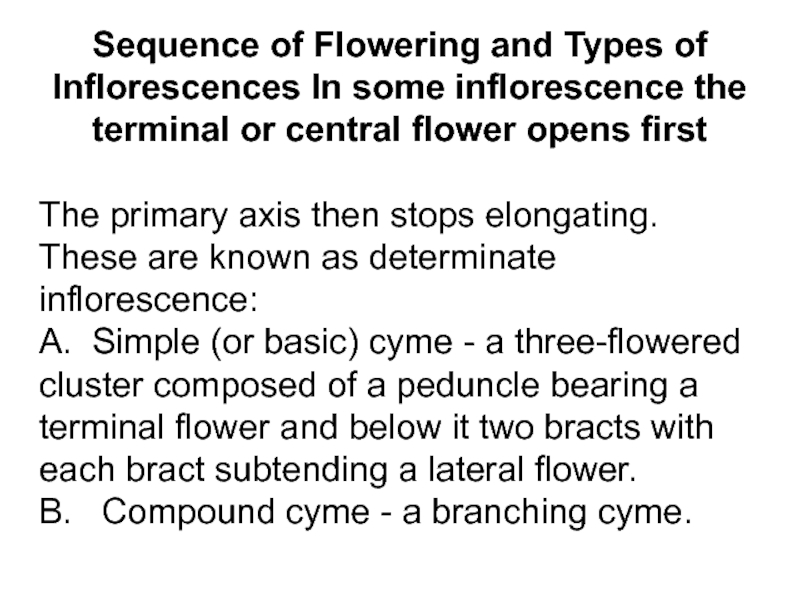
Слайд 7Sequence of Flowering and Types of Inflorescences In some inflorescence
the terminal or central flower opens first
The primary axis then
stops elongating. These are known as determinate inflorescence:
A. Simple (or basic) cyme - a three-flowered cluster composed of a peduncle bearing a terminal flower and below it two bracts with each bract subtending a lateral flower.
B. Compound cyme - a branching cyme.
Слайд 8 In some plants the inflorescence primary axis continues to
grow as the flowers develop. These are called indeterminate inflorescence.
The lowermost or outermost flowers open first; usually no terminal flower is produced.
C. Panicle - similar to a raceme but greatly branched.
D. Raceme - stalked flowers arranged along an elongate central axis.
E. Spike - sessile flowers arranged along an elongate central axis.
F. Corymb - short, broad, and flattopped.
G. Simple umbel - several branches radiating from the same point and terminated by single flowers.
H. Compound umbel - same as above with additional secondary umbels.
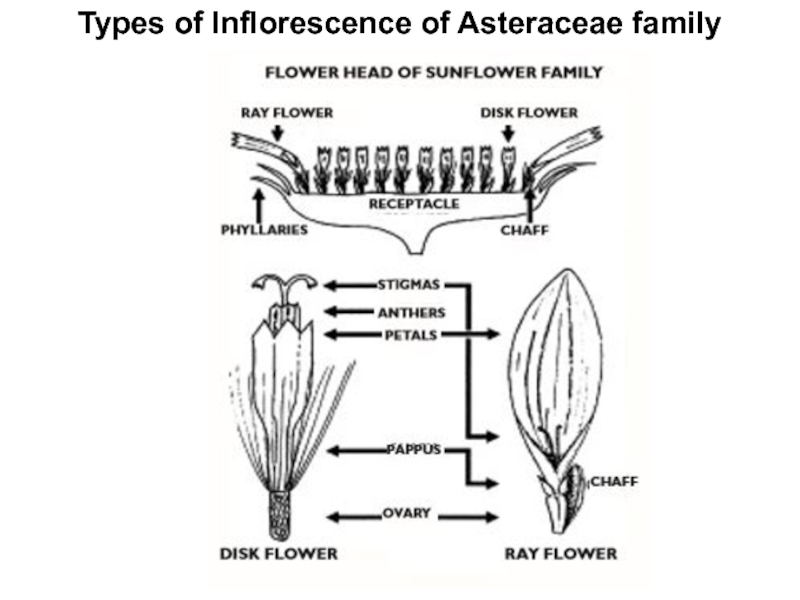
I. Head (capitulum) - a compact inflorescence composed of a very short axis and usually sessile flowers; characteristic of sunflower family.
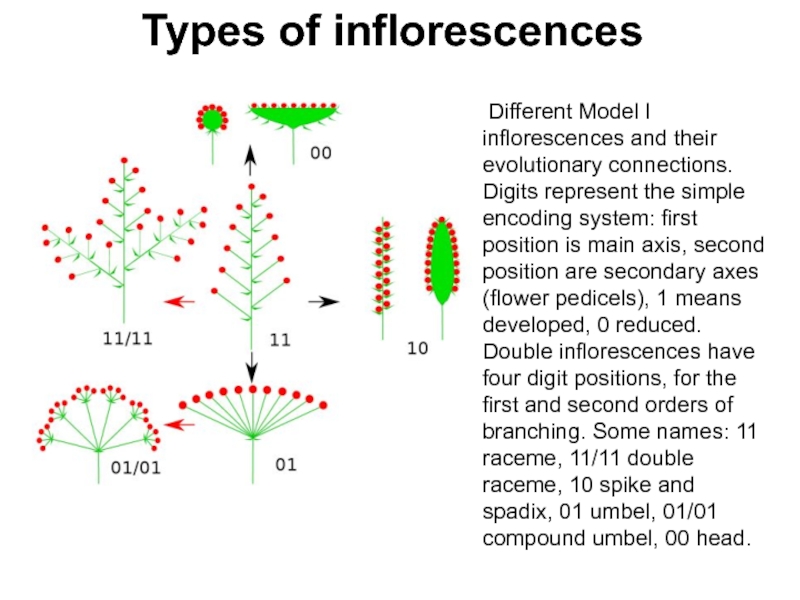
Слайд 9Types of inflorescences
Different Model I inflorescences and their evolutionary
connections. Digits represent the simple encoding system: first position is
main axis, second position are secondary axes (flower pedicels), 1 means developed, 0 reduced. Double inflorescences have four digit positions, for the first and second orders of branching. Some names: 11 raceme, 11/11 double raceme, 10 spike and spadix, 01 umbel, 01/01 compound umbel, 00 head.
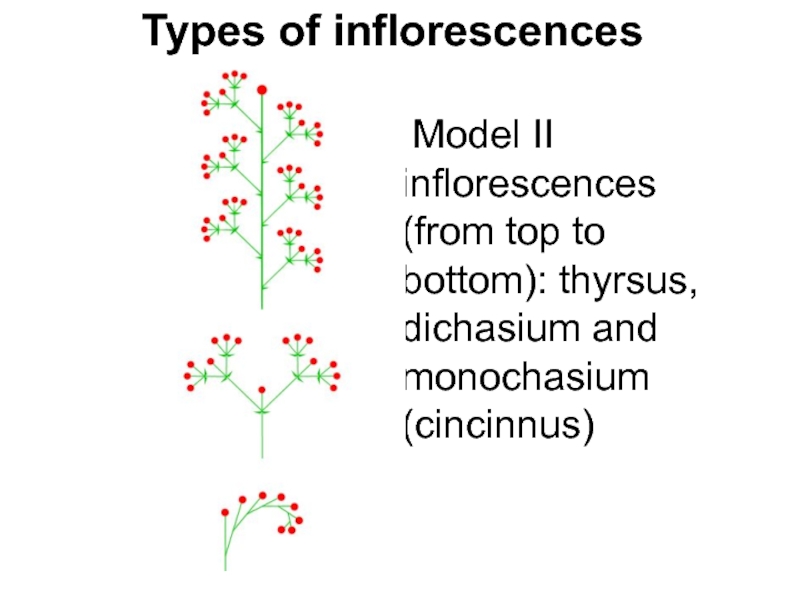
Слайд 10Types of inflorescences
Model II inflorescences (from top to bottom):
thyrsus, dichasium and monochasium (cincinnus)
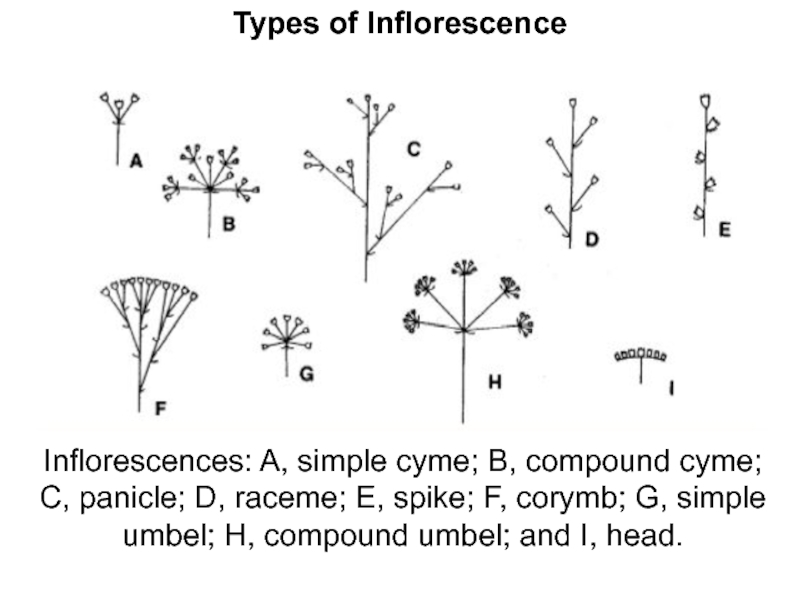
Слайд 11Types of Inflorescence
Inflorescences: A, simple cyme; B, compound cyme; C,
panicle; D, raceme; E, spike; F, corymb; G, simple umbel;
H, compound umbel; and I, head.
Слайд 12Types of Inflorescence of Asteraceae family
Слайд 13Pollination could be of two types: self- and cross-pollination. Cross-pollination
can happen in both abiotic and biotic ways. Abiotic would
be represented by gravity, wind, or water; biotic would be performed by agents like insects, birds, bats, or in some cases tree mammals like possums. Wind-pollination is seen as being wasteful and unintelligent due to the fact that the plant needs to produce so much more pollen without any precise targeting.
Adaptation to the particular pollination agent results in different pollination syndromes. For example, cup-shaped flowers are usually pollinated with massive animals like beetles and even bats. Funnel-shaped flowers as well as labiate flowers (with lips), are adapted to flies and bees. Flowers with long spurs attract butterflies and birds (like hummingbirds or sugarbirds).
Self-pollination of ten exists like a “plan B”, in case cross-pollination is, for some reason, impossible. Sometimes, self-pollinated flowers even do not open; these flowers are called cleistogamous.
If pollination needs to be avoided, apomixis will prevent it. Apomixis requires reproductive organs, but there is no fertilization. One type of apomixis is apospory when an embryo develops from the maternal diploid tissue, but does not go through the meiosis stage. In this process, asexual reproduction will have become vegetative. Another type of apomixis would be apogamy (parthenogenesis) when embryo develops from an unfertilized gamete after diploidization has occurred. Here, vegetative reproduction evolved from sexual reproduction.

Слайд 14Control questions:
1 What is biological role of inflorescences?
2 Which
principles did use for classification of inflorescences?
3 Describe general characteristics
of simple and compound inflorescences.
4 Which inflorescences are characterized for Asteraceae family?
5 Which inflorescences are characterized for Apiaceae family?
6 Why inflorescences are important diagnostic signs for classification of plants?
Слайд 15Test questions:
Type of simple inflorescences:
А) simple spike
В) compound spike
С) head
Д)
compound umbel
Е) compound cyme
F) Panicle
Type of inflorescence for Asteraceae
family:
А) simple spike
В) anthodium
С) head
Д) umbel
Е) panicle