Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION
Содержание
- 1. MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION
- 2. Monopolistic Competition1. Monopolistic Competition Definition2. The monopolistic
- 3. 1. Monopolistic Competition DefinitionA monopolistically competitive industry
- 4. Now we encounter a differentiated product for
- 5. If the buyer doesn't differentiate among the
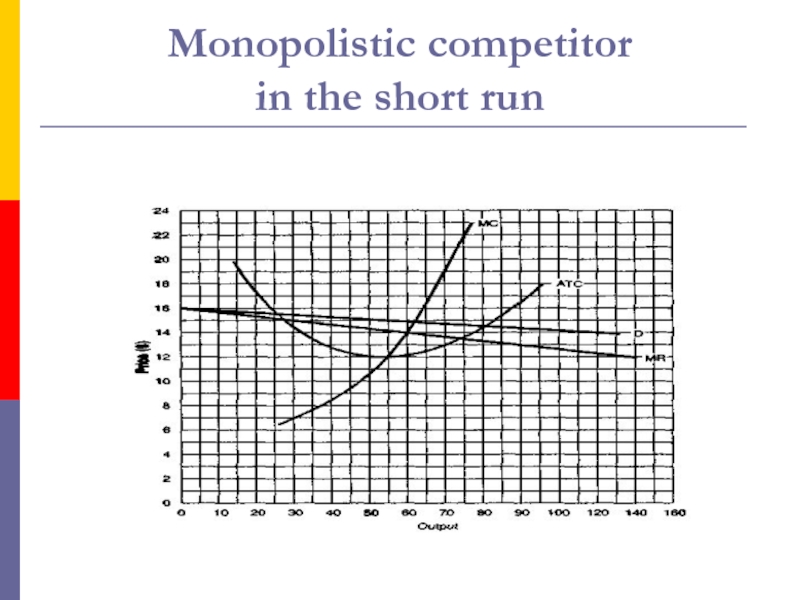
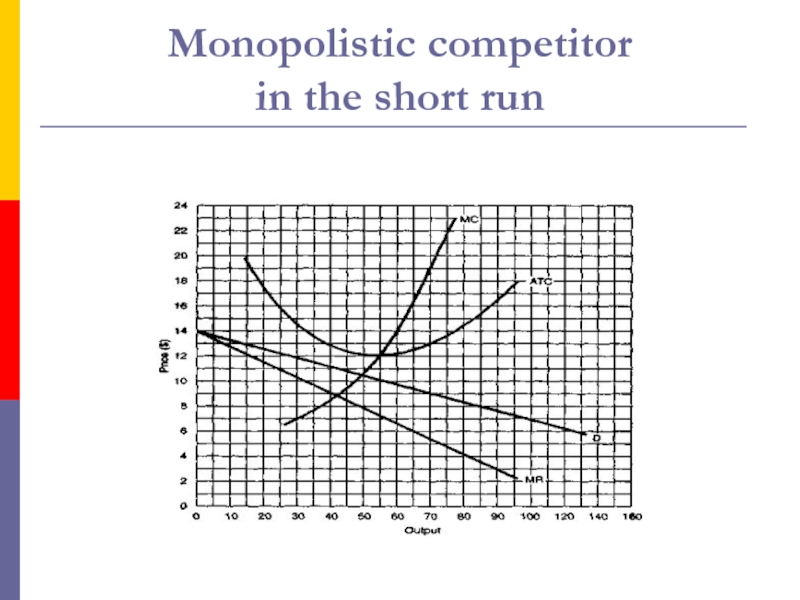
- 6. The monopolistic competitor in the short
- 7. Monopolistic competitor in the short run
- 8. Monopolistic competitor in the short run
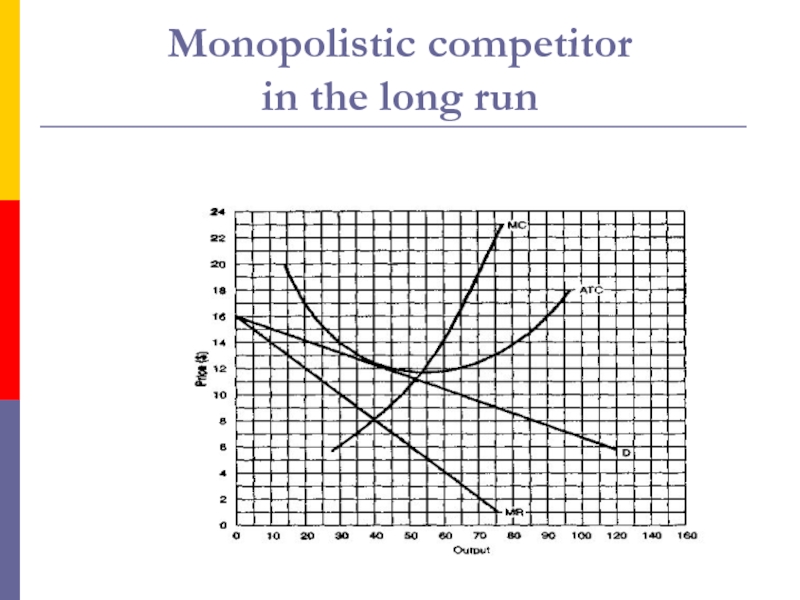
- 9. The monopolistic competitor in the long runIn
- 10. Monopolistic competitor in the long run
- 11. To sum up, both the monopolistic competitor
- 12. 3. Product DifferentiationProduct differentiation is crucial to
- 13. Who’s got the Flatter Demand Curve?The monopolistic
- 14. Слайд 14
- 15. Слайд 15
- 16. Слайд 16
- 17. 4. Price DiscriminationPrice discrimination occurs when a
- 18. The firm that practices price discrimination needs
- 19. To practice price discrimination you need to
- 20. Perfect Price DiscriminationIf price discrimination were carried
- 21. Monopolistic competitors do compete with respect to
- 22. Скачать презентанцию
Monopolistic Competition1. Monopolistic Competition Definition2. The monopolistic competitor in the short and long runs3. Product differentiation4. Price discrimination
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Monopolistic Competition
1. Monopolistic Competition Definition
2. The monopolistic competitor in the
short and long runs
Слайд 31. Monopolistic Competition Definition
A monopolistically competitive industry has many firms
selling a differentiated product. How many is many?
So many
that no one firm has any significant influence over price. Although this is our working definition, monopolistic competitors do have some influence over price because their products are differentiated. But it's a very small influence.Слайд 4Now we encounter a differentiated product for the first time.
Notice that the definition of monopolistic competition differs from that
of perfect competition only in that now we have a differentiated product. You'll remember that under perfect competition, all the sellers sold an identical product.
Слайд 5If the buyer doesn't differentiate among the various products sold,
the products are identical. If he or she does differentiate,
the product is then differentiated.Слайд 6The monopolistic competitor
in the short run
Like the perfect competitor,
the monopolistic competitor can make a profit or take a
loss in the short run;Слайд 9
The monopolistic competitor in the long run
In the long run,
the firm will break even. The reason the monopolistic competitor
makes zero economic profits in the long run is the same as that under perfect competition.In the long run, if firms are losing money, many will leave the industry, lowering industry supply and raising market price.
And if, in the long run, firms are realizing substantial profits, new firms will be attracted to the industry, thus raising supply and lowering market price. But we're getting ahead of ourselves since we're only beginning the short run.
Слайд 11To sum up, both the monopolistic competitor and the perfect
competitor make zero economic profits in the long run.
The
monopolistic competitor charges a higher price and has a lower output than the perfect competitor and the perfect competitor is a more efficient producer than the monopolistic competitor.Слайд 123. Product Differentiation
Product differentiation is crucial to monopolistic competition. In
fact, product differentiation is really what stands between perfect competition
and the real world. People differentiate among many similar products.What makes one good or service differ from another? We need only for the buyer to believe it's different, because product differentiation takes place in the buyer's mind. In the real world, however, buyers generally do differentiate. We're always differentiating, and it doesn't have to be based on taste, smell, size, or even any physical differences among the products.
Слайд 13Who’s got the Flatter Demand Curve?
The monopolistic competitor faces a
more elastic, or flatter, demand curve than the monopolist.
Слайд 174. Price Discrimination
Price discrimination occurs when a seller charges two
or more prices for the same good or service.
Слайд 18The firm that practices price discrimination needs to be able
to distinguish between two or more separate groups of buyers.
In addition to distinguishing among separate groups of buyers, the price discriminator must be able to prevent buyers from reselling the product (i.e., stop those who buy at a low price from selling to those who would otherwise buy at a higher price).