Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
TEM Transmision Electrom Microscope Construction and Application
Содержание
- 1. TEM Transmision Electrom Microscope Construction and Application
- 2. Plan of presentationIntroduction,Selected parts of construction,Electron gun,Lenses,Specimen holder,Image registration,Detectors – different types
- 3. Initial informationSample image is magnified at formed
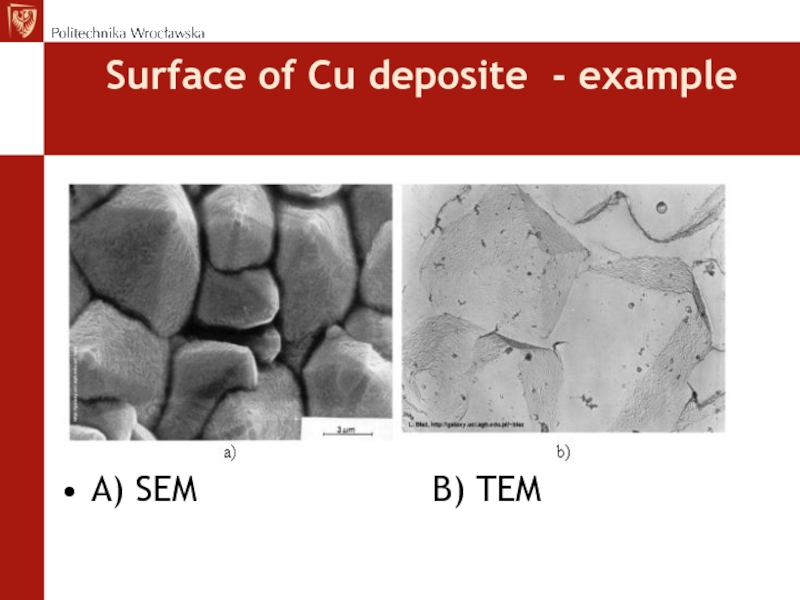
- 4. Surface of Cu deposite - example A)
- 5. Application Presentation of specimens internal structureImages are
- 6. Basic construction of TEMColumn:Electron gunLenses SpecimenScreen /
- 7. TEM situation at laboratory room
- 8. Слайд 8
- 9. Electron gun Aim: electron beam emision and
- 10. Electron gun
- 11. Properties of electron guns different types
- 12. Electron gun - thermoemission
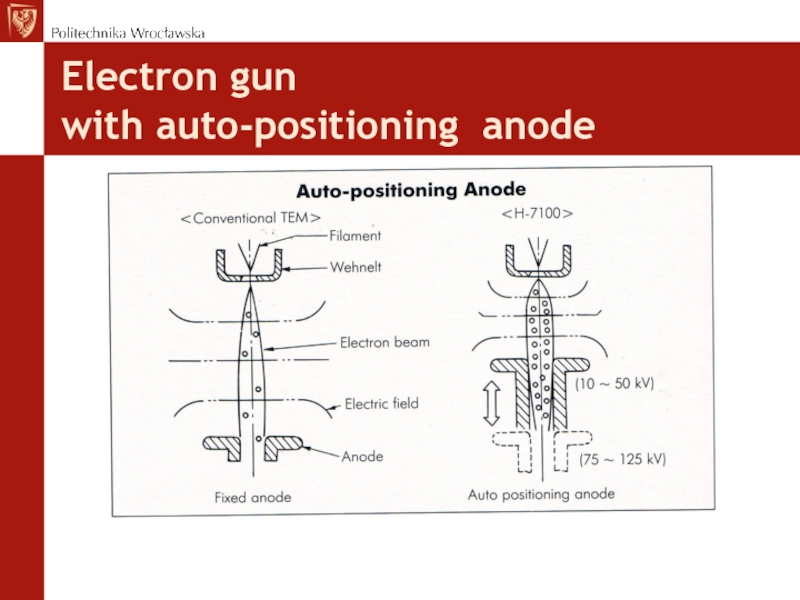
- 13. Electron gun with auto-positioning anode
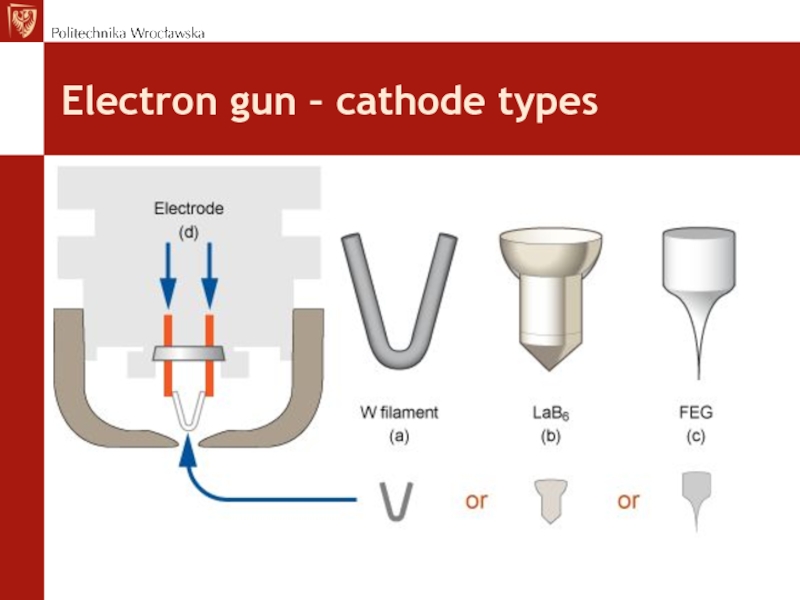
- 14. Electron gun – cathode types
- 15. Electromagnetic lenses at TEMAre used for changing
- 16. Condensor systemForms electron beam, changing their brightness
- 17. Condenser lensesLens C1:Decreaese beam diameterControl the electron
- 18. Condenser apertureEliminate electrons dispersed to muchProtect the specimen against excessive radiation
- 19. Specimen chamberVery high precission of specimen movement,
- 20. Specimen chamber – obiective polepiece
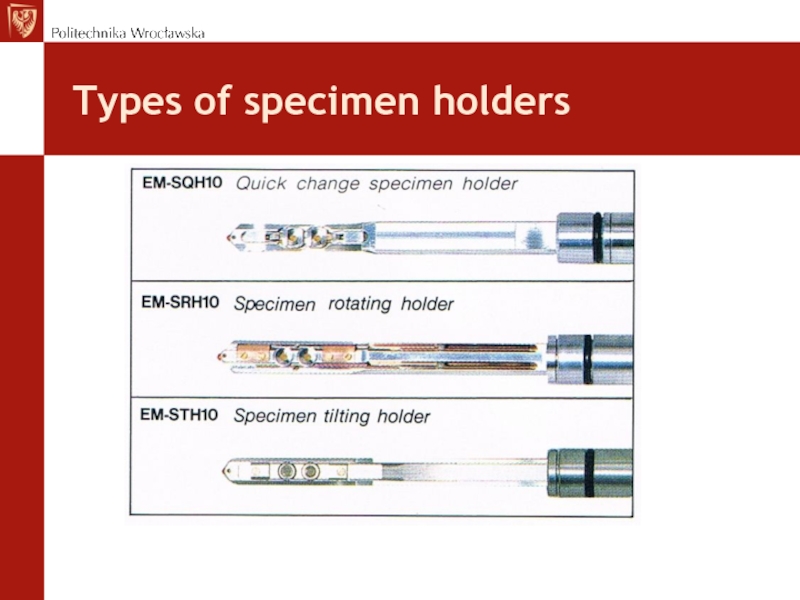
- 21. Types of specimen holders
- 22. Types of specimen holders
- 23. Specimens storage
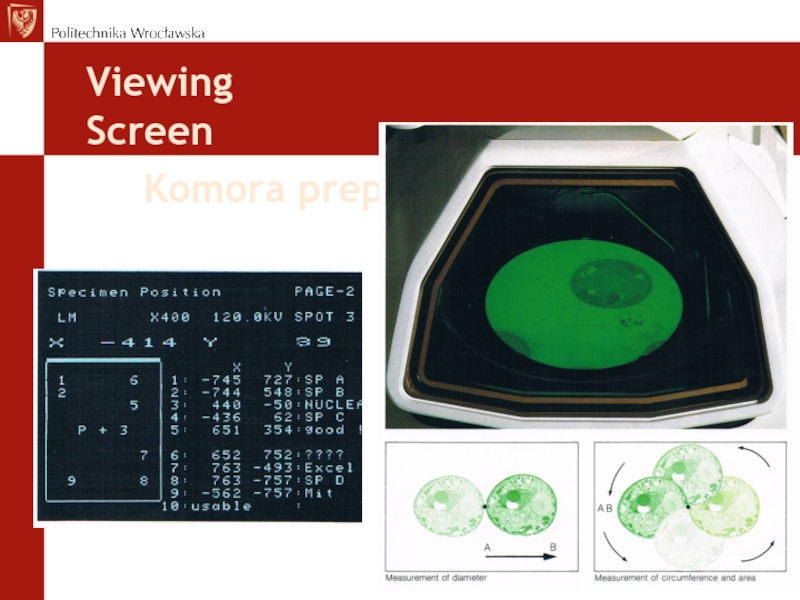
- 24. Komora preparatuViewingScreen
- 25. Contamination Negative phenomenon – the rest
- 26. Contamination
- 27. Position of „Cold Finger” in respect to specimen holder
- 28. Pouring liquid nitrogen
- 29. Vacuum systemVacuum is necessary that gas molecules
- 30. Vacuum system - valves
- 31. Vacuum system - rotary pumpReached vacuum:10-2 Pa
- 32. Vacuum system – diffusion pumpReached vacuum:10-5 Pa
- 33. Vacuum system – Ion Getter Pump
- 34. Vacuum system – Turbo Molecular Pump
- 35. Penning vacuum gaugeVacuum glow gaugeThe measure is
- 36. Penning vacuum gauge
- 37. Pirani vacuum gaugeVacuum thermal-conductive gauge.The special wire
- 38. Lens system forming imageTypically it consists of
- 39. Obiective lensThe lens of the greatest importanceGenerates
- 40. Obiective apertureImproves contrast of final imageBy changing
- 41. Intermediate LensIt enables to obtain:magnification of initial imagediffraction pattern of the selected area SAED
- 42. Diffraction apertureUsed to obtain a diffraction pattern of the selected area - SAED
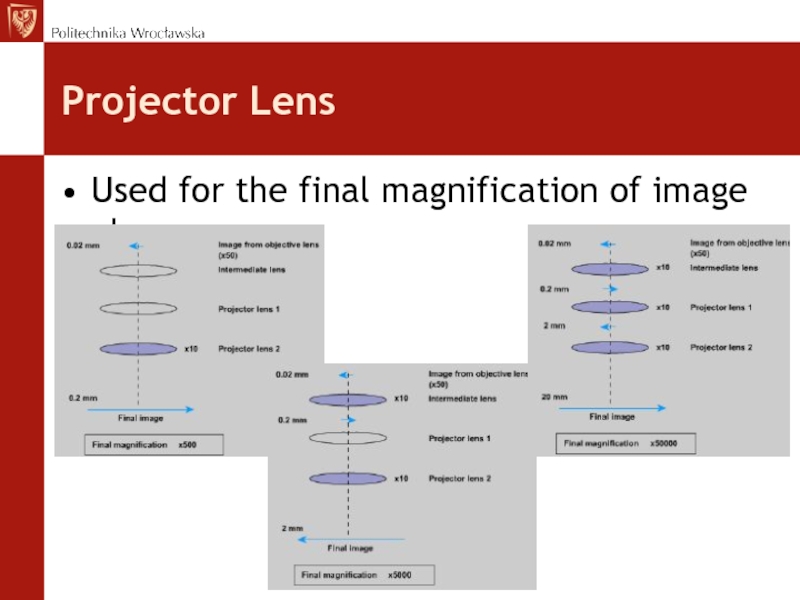
- 43. Projector LensUsed for the final magnification of image obrazu
- 44. Registration of imagesVisualization of the images is
- 45. CCD Camera
- 46. Visualisation equipment
- 47. Power Supply To ensure production of appropriate
- 48. Control System
- 49. Control System
- 50. Control System
- 51. Control system
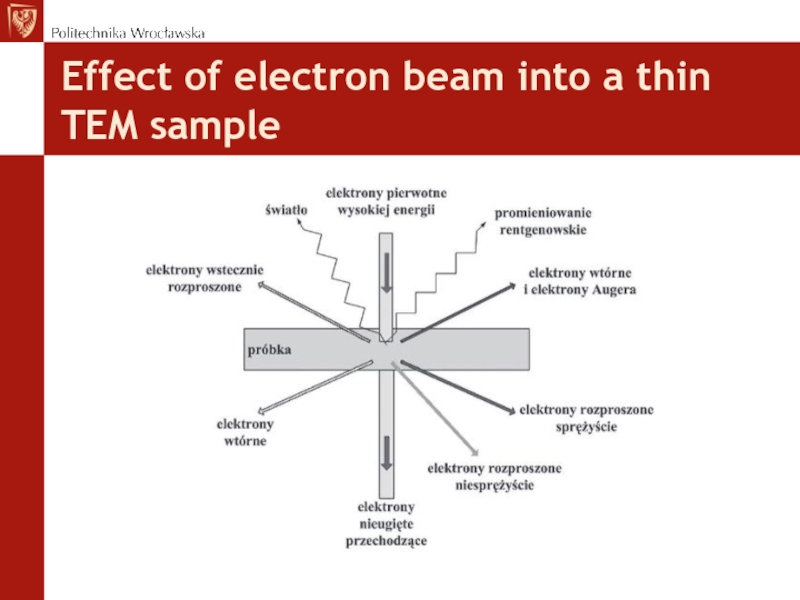
- 52. Effect of electron beam into a thin TEM sample
- 53. Scanning Transmission Microscope - STEMTransmission electron microscope
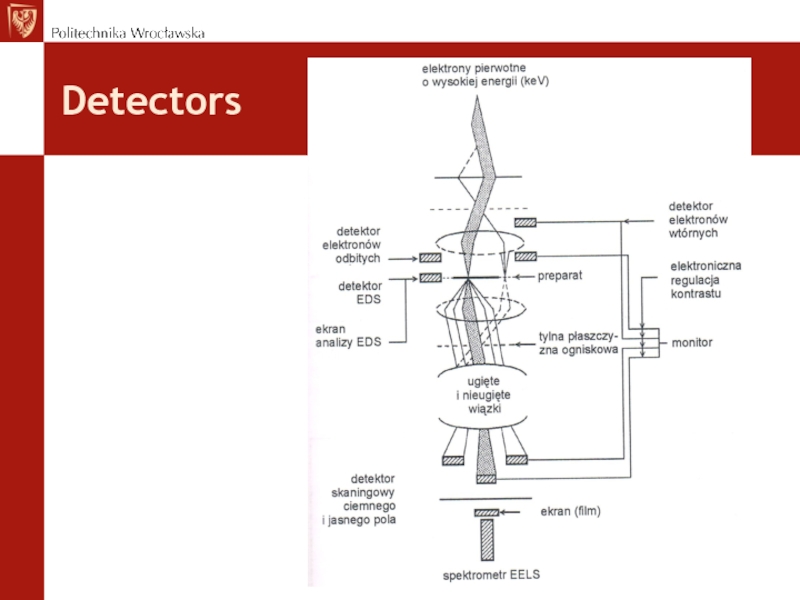
- 54. Detectors
- 55. HVTEM / HRTEMHVTEM – High Voltage TEM
- 56. HVTEM/HRTEM
- 57. HVTEM The amorphous carbon coated with sprayed Li4Ti5O12.
- 58. HVTEM Atomic resolution
- 59. HVHRTEM Atomic resolution:Grain boundaries orientationInterphase boundaries, subgrains,
- 60. EDS – X-ray radiationX-ray - formed
- 61. Energy Distribution Spectrum - EDS
- 62. EELS – Electron Energy Loss SpectroscopySpectroscopy
- 63. Detector EELS
- 64. EELS - equipment
- 65. The influence of the sample thickness on research capabilities TEM
- 66. Selected Area Electron DiffractionThe need to remove
- 67. Diffraction image formation Mikrodiffraction (SAED – selected
- 68. Electron Diffraction – Bragg’s model Bragg’s
- 69. Geometry of electron diffraction in TEM Location
- 70. Interpretation of electron diffraction patternsIdentification of the
- 71. Application of electron diffraction in materials investigationDiffraction
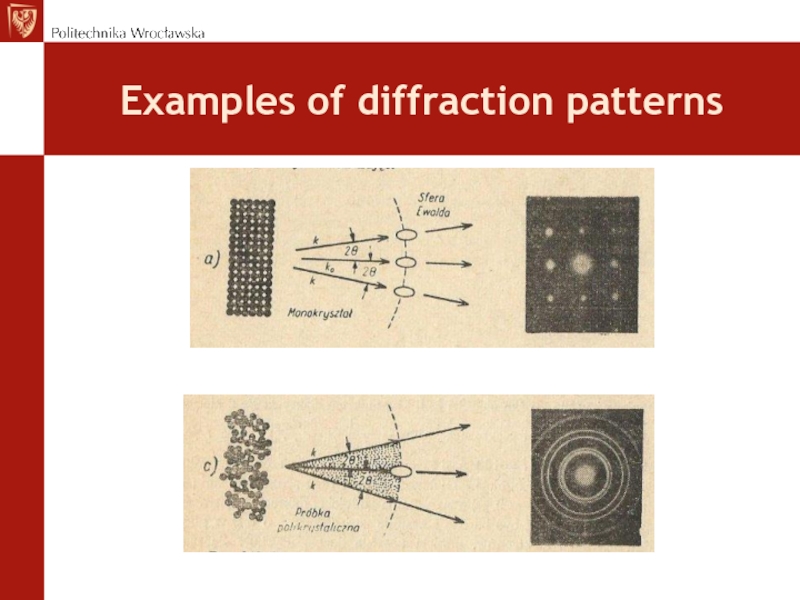
- 72. Examples of diffraction patterns
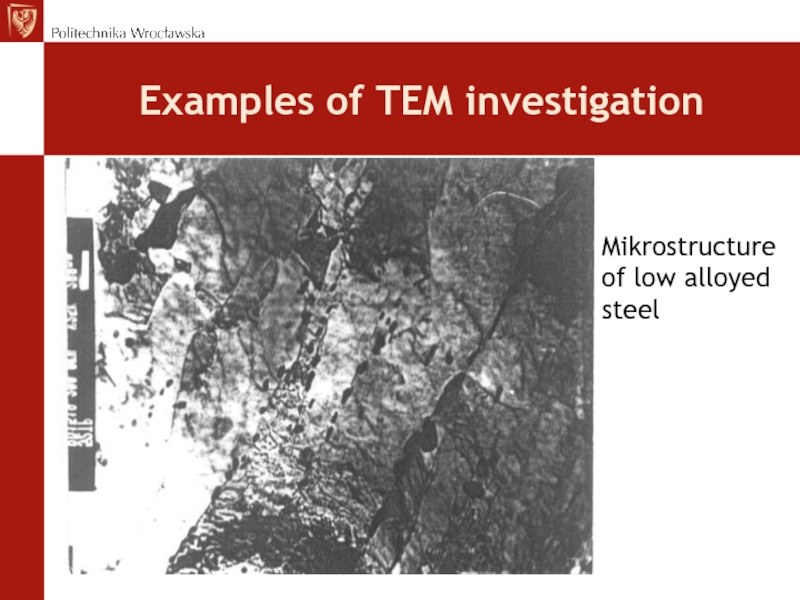
- 73. Examples of TEM investigationMikrostructure of low alloyed steel
- 74. Imperfections in the crystal structure (dislocations and grain boundary between the two polycrystal).Image obtained by TEM.
- 75. Martensite inside structure of steel 35SG grade
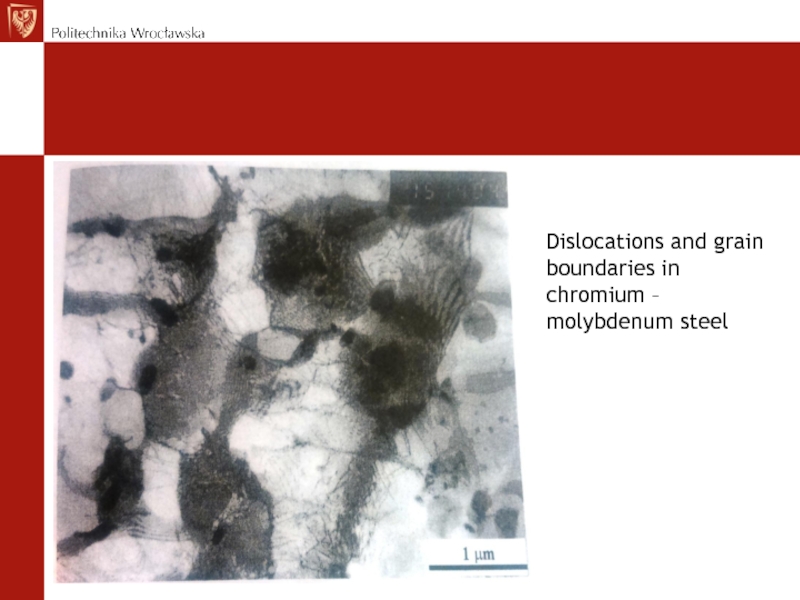
- 76. Dislocations and grain boundaries in chromium – molybdenum steel
- 77. Structure of the two-phase polymer
- 78. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iiJuG636PfQ
- 79. Hitachi
- 80. JEOL
- 81. LiteraturaG. Schimmel, Metodyka mikroskopii elektronowej, PWN, Warszawa
- 82. Скачать презентанцию
Plan of presentationIntroduction,Selected parts of construction,Electron gun,Lenses,Specimen holder,Image registration,Detectors – different types
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1TEM
Transmision Electrom Microscope
Construction and Application
Prof. dr habil. ing. Włodzimierz Dudziński
Слайд 2Plan of presentation
Introduction,
Selected parts of construction,
Electron gun,
Lenses,
Specimen holder,
Image registration,
Detectors –
different types
Слайд 3Initial information
Sample image is magnified at formed by electron beam
It
is used for investigation of specime internal structure
Maximale thicknes
of specimen can be 0,1 µmApplied acceleration voltages are from 100kV up to 3 mV ( 3 milion V)
Exploitation is very expensive kosztów
Слайд 5Application
Presentation of specimens internal structure
Images are not coloured
Application at
materials science, biology, medicine and geology
Microstructure, crystalographic orientation, atomic resolution,
chemical composition of different phases can be investigated (HREM, EDX, EELS)3D imaging of specimen is possible (STEM)
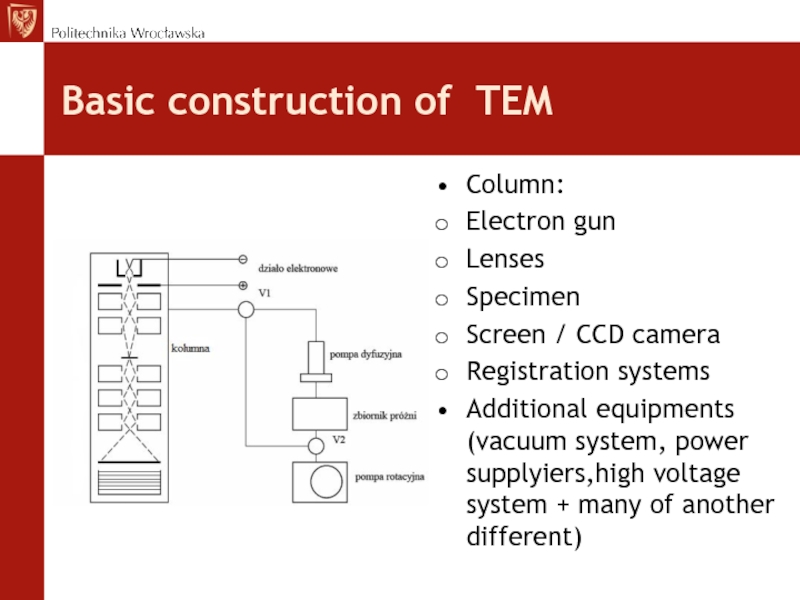
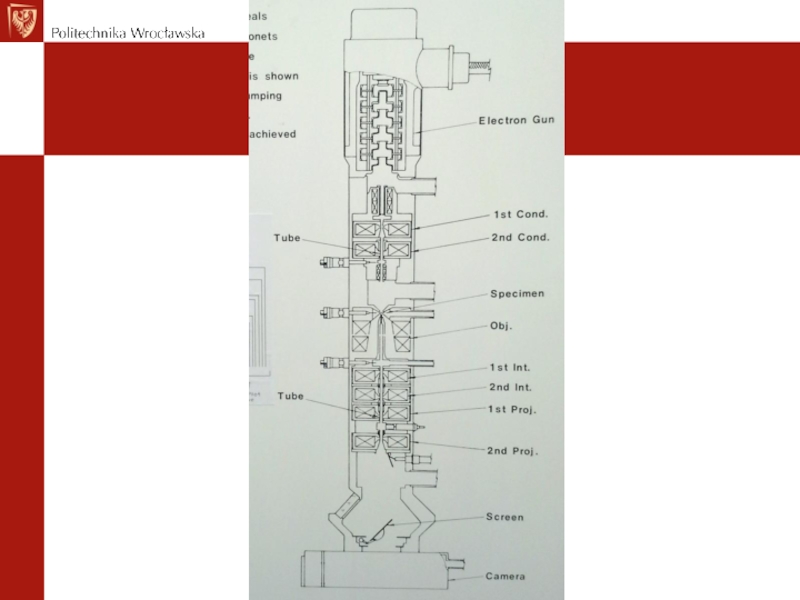
Слайд 6Basic construction of TEM
Column:
Electron gun
Lenses
Specimen
Screen / CCD camera
Registration systems
Additional
equipments (vacuum system, power supplyiers,high voltage system + many of
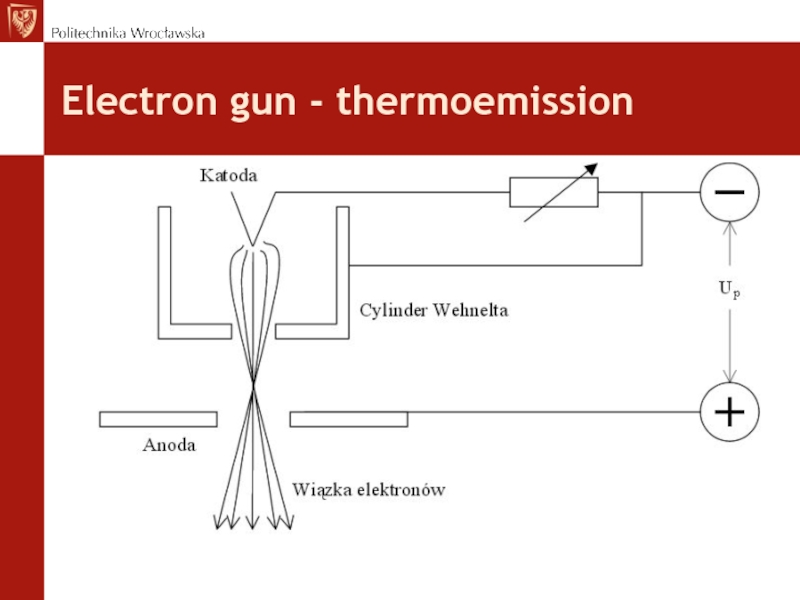
another different)Слайд 9Electron gun
Aim: electron beam emision and initial formation
Acceleration
voltage : typical 100 – 400 kV (up to 3
MV –HVTEM)Слайд 15Electromagnetic lenses at TEM
Are used for changing characteristic of electron
beam
Brightness
Concentration
Focusing
Are constructed like coils of coper wires
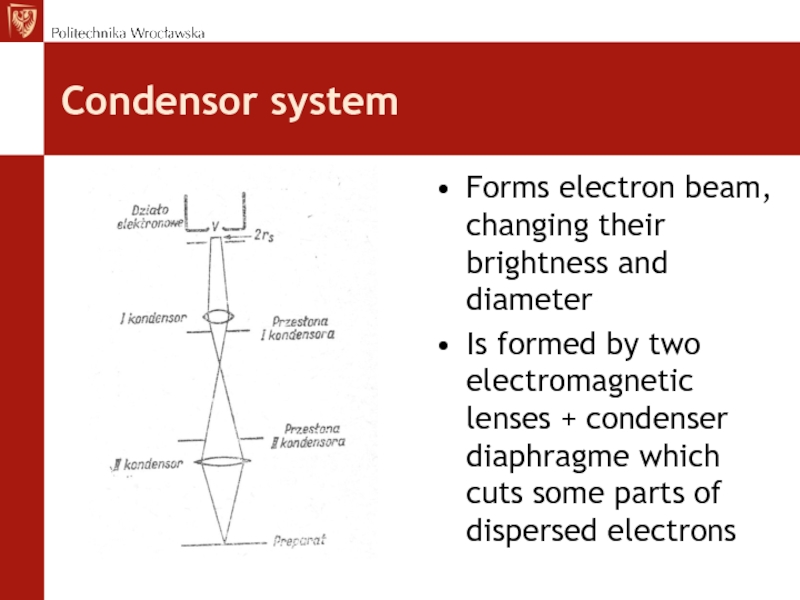
Слайд 16Condensor system
Forms electron beam, changing their brightness and diameter
Is formed
by two electromagnetic lenses + condenser diaphragme which cuts some
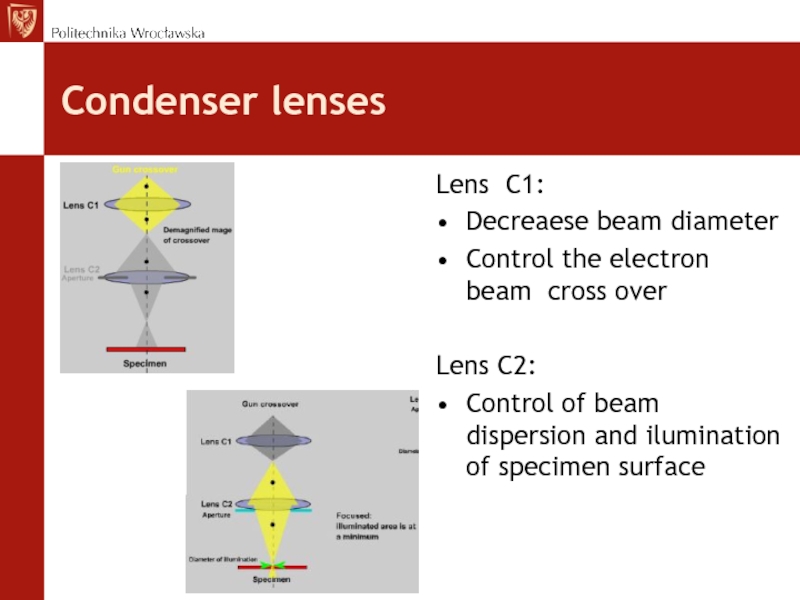
parts of dispersed electronsСлайд 17Condenser lenses
Lens C1:
Decreaese beam diameter
Control the electron beam cross over
Lens
C2:
Control of beam dispersion and ilumination of specimen surface
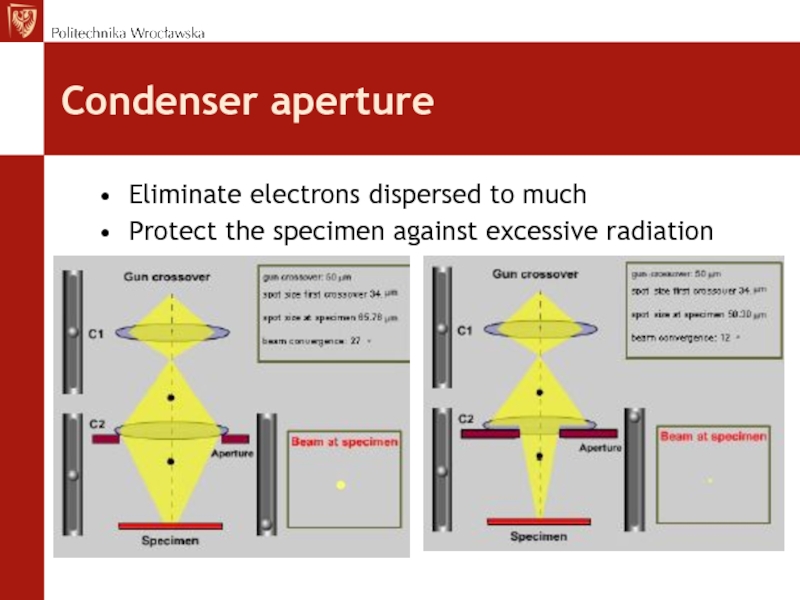
Слайд 18Condenser aperture
Eliminate electrons dispersed to much
Protect the specimen against excessive
radiation
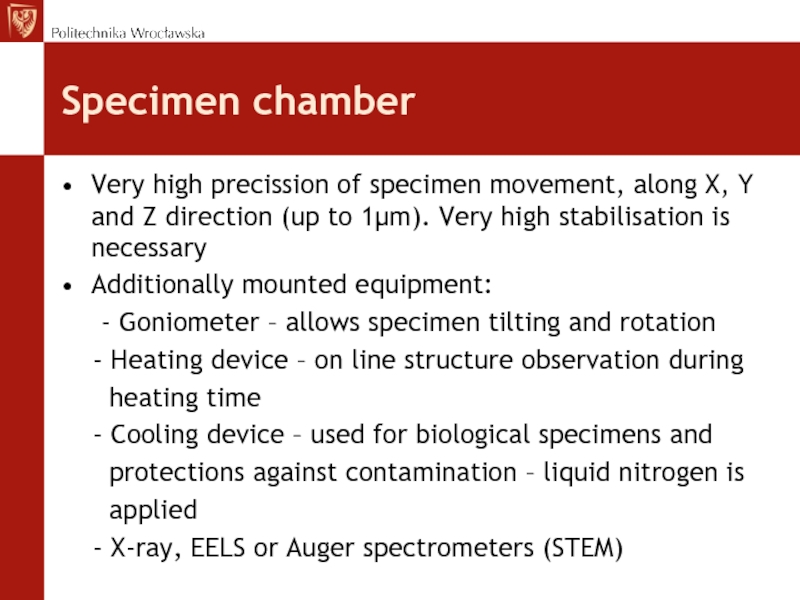
Слайд 19Specimen chamber
Very high precission of specimen movement, along X, Y
and Z direction (up to 1µm). Very high stabilisation is
necessaryAdditionally mounted equipment:
- Goniometer – allows specimen tilting and rotation
- Heating device – on line structure observation during
heating time
- Cooling device – used for biological specimens and
protections against contamination – liquid nitrogen is
applied
- X-ray, EELS or Auger spectrometers (STEM)
Слайд 25Contamination
Negative phenomenon – the rest of silicon oil
vapeurs deriving from cacuum pumps are sedimented on the specimen
surface and borders of apertures. This phenomenon can heavy decrease contrast and resolution of images.Protection:
Instalation of anti contamination device inside TEM column – i.e. ring or „cold fingers” sourrounded specimen - cooled by liquid nitrogene
Increasing of vacuum quality by application „Cold Trap” and „oil free” pomps like: Ion Getter Pump (IGP) or Turbo Molecular Pump (TMP).
Слайд 29Vacuum system
Vacuum is necessary that gas molecules do not interfere
with the course of the electron beam
Necessary condition: high vacuum
(10-4 - 10-5 Pa),Vaccum is obtained by the system of rotary (RP) and oil diffusion pomps (DP) or TMP or IGP.
Turbo Molecular Pumps (TMP) and Ion Getter Pumps (IGP) don’t contain oilacji)
The lock is used to paste samples into specimen chamber without column aeration
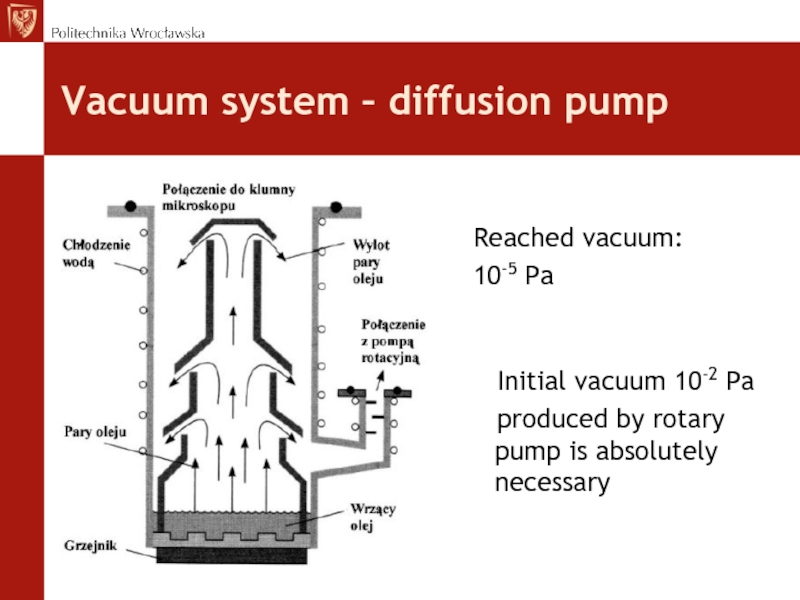
Слайд 32Vacuum system – diffusion pump
Reached vacuum:
10-5 Pa
Initial vacuum 10-2 Pa
produced by rotary pump is
absolutely necessary
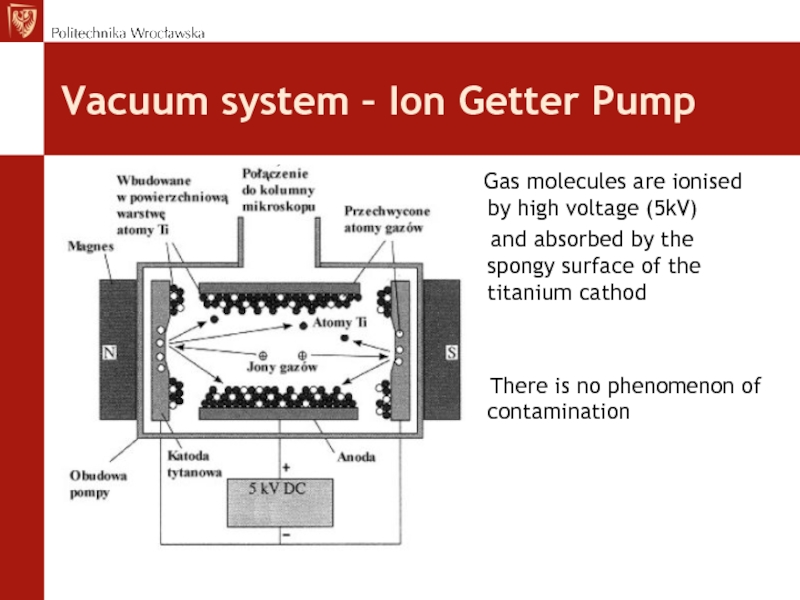
Слайд 33Vacuum system – Ion Getter Pump
Gas molecules
are ionised by high voltage (5kV)
and absorbed
by the spongy surface of the titanium cathodB There is no phenomenon of contamination
Слайд 34Vacuum system –
Turbo Molecular Pump
It works on the
principle of centrifugal pump.
Thanks generated by the rotary
pump an initial vacuum, the turbine can reach very high ultrasonic speeds. This causes the mechanical expulsion of the gas molecules.
There is no phenomenon of contamination.
Слайд 35Penning vacuum gauge
Vacuum glow gauge
The measure is the current vacuum
glow discharge
Electrodes are placed in the external permanent magnet, it
prevents stalling discharge.Electrode head is applied high voltage (1000 - 2000V).
Is used in the pressure range from approx. 10-2 do 10-7 Pa
Слайд 37Pirani vacuum gauge
Vacuum thermal-conductive gauge.
The special wire end located in
the vacuum test is heated by electric current
When the vacuum
is better, the worse the heat is extracted from the wire, which increases its temperature. As a result, the wire resistance is increased.applies to vacuum measurement in the range from 0,5 up to 10-3 Pa.
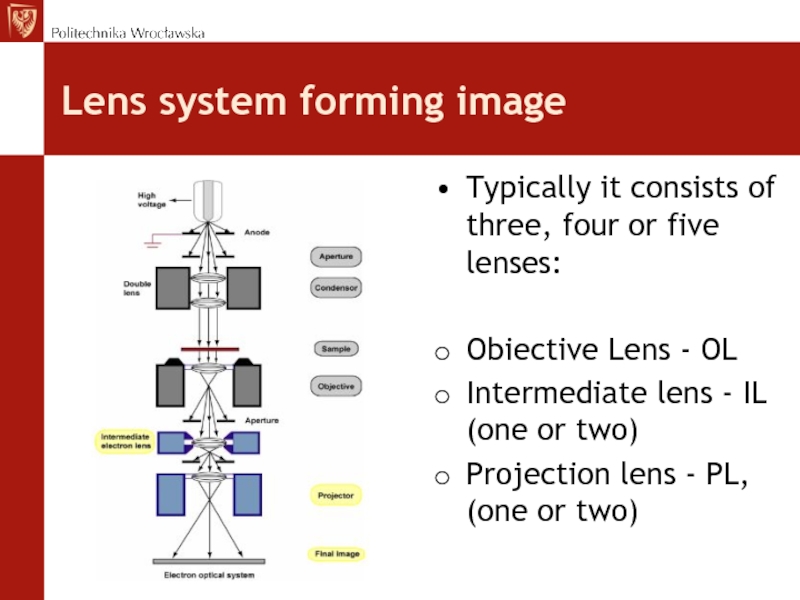
Слайд 38Lens system forming image
Typically it consists of three, four or
five lenses:
Obiective Lens - OL
Intermediate lens - IL (one or
two)Projection lens - PL, (one or two)
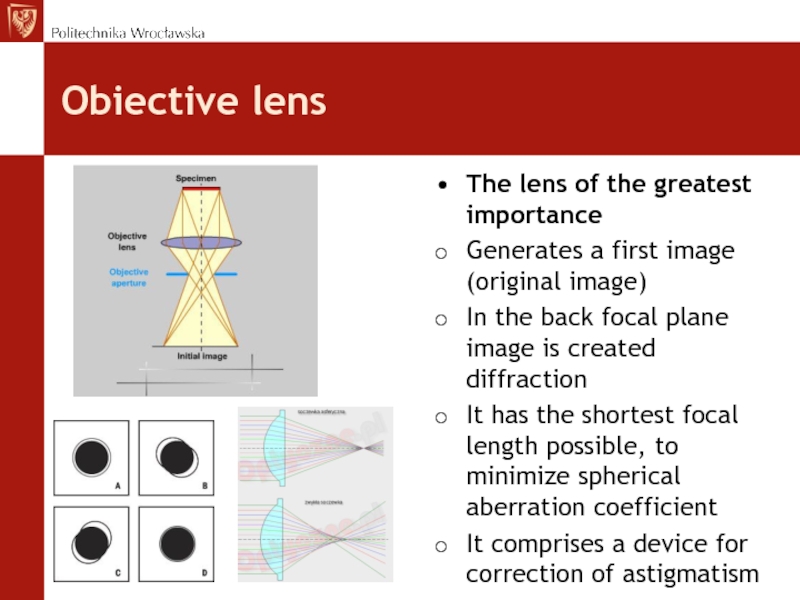
Слайд 39Obiective lens
The lens of the greatest importance
Generates a first image
(original image)
In the back focal plane image is created diffraction
It
has the shortest focal length possible, to minimize spherical aberration coefficientIt comprises a device for correction of astigmatism
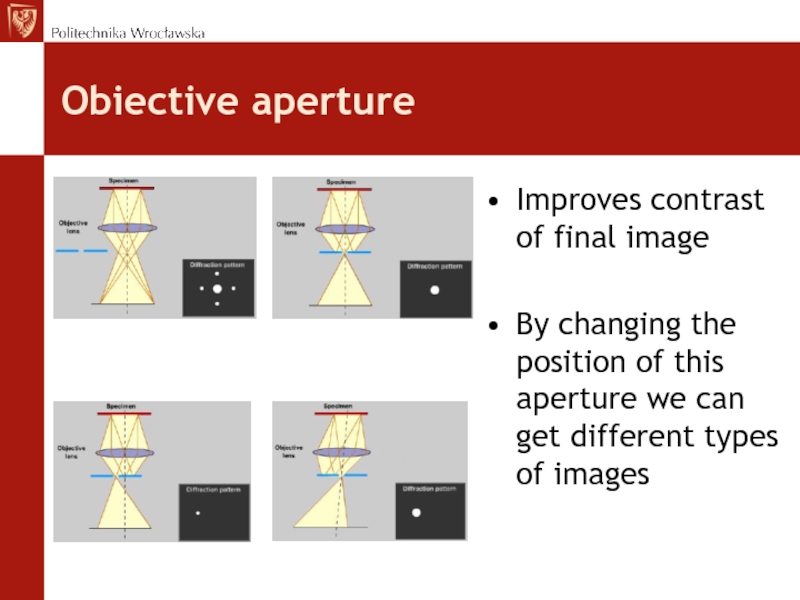
Слайд 40Obiective aperture
Improves contrast of final image
By changing the position of
this aperture we can get different types of images
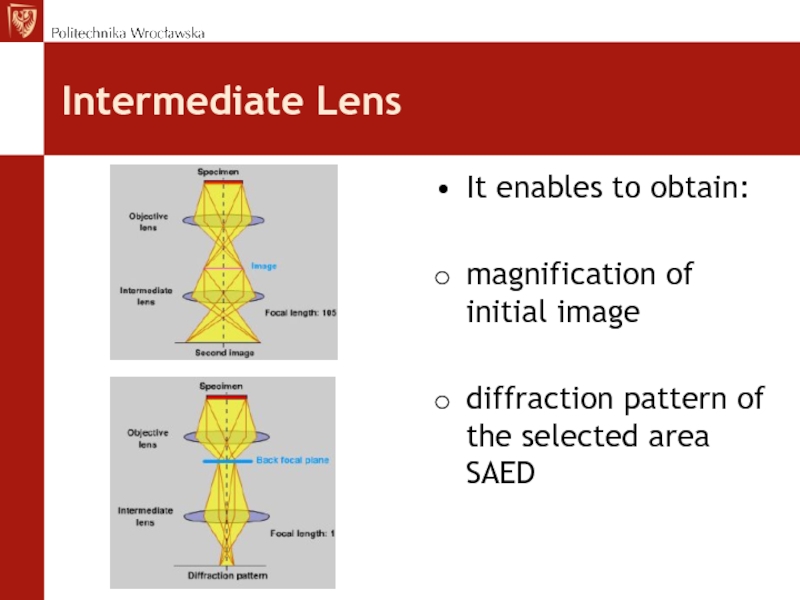
Слайд 41Intermediate Lens
It enables to obtain:
magnification of initial image
diffraction pattern of
the selected area SAED
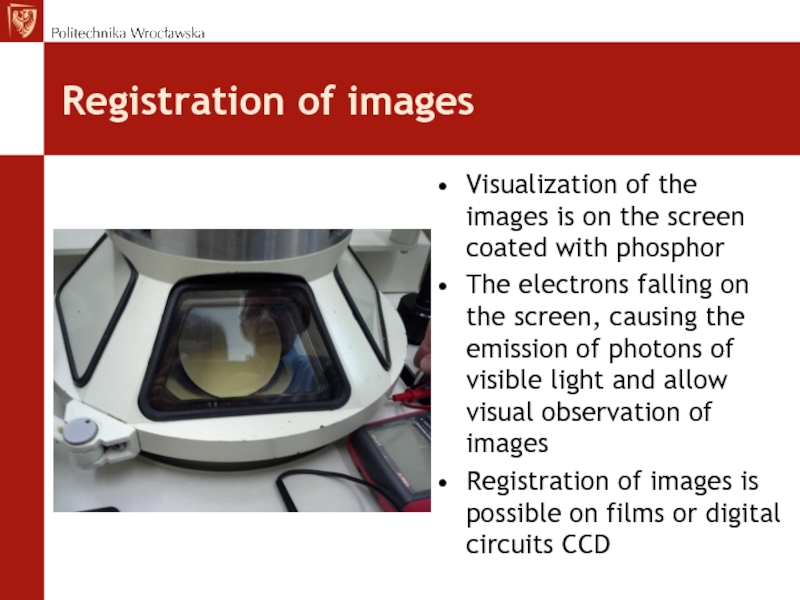
Слайд 44Registration of images
Visualization of the images is on the screen
coated with phosphor
The electrons falling on the screen, causing the
emission of photons of visible light and allow visual observation of imagesRegistration of images is possible on films or digital circuits CCD
Слайд 47Power Supply
To ensure production of appropriate voltages used for:
cathode
heating, accelerating movement of electrons,
excitation systems of lenses
powering auxiliary
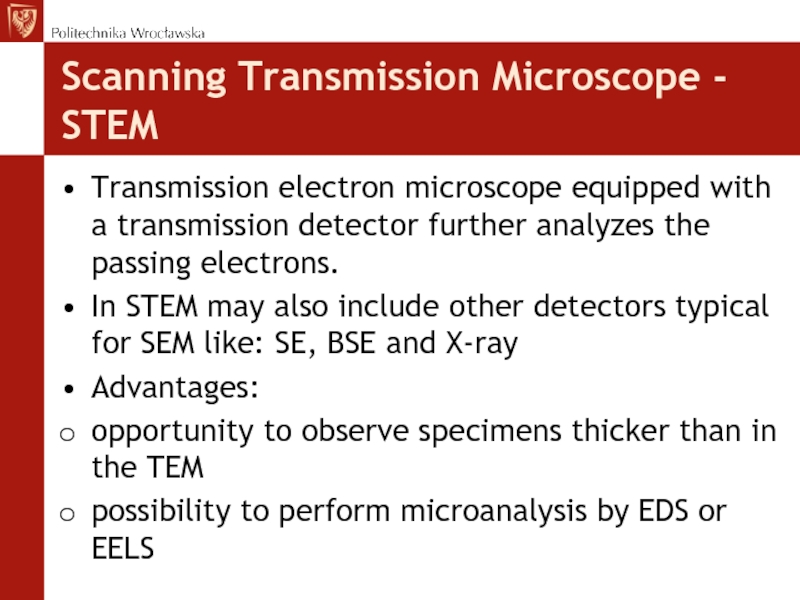
systemСлайд 53Scanning Transmission Microscope - STEM
Transmission electron microscope equipped with a
transmission detector further analyzes the passing electrons.
In STEM may also
include other detectors typical for SEM like: SE, BSE and X-rayAdvantages:
opportunity to observe specimens thicker than in the TEM
possibility to perform microanalysis by EDS or EELS
Слайд 55HVTEM / HRTEM
HVTEM – High Voltage TEM
HRTEM – High
Resolution TEM
Used for studies crystalline samples
It enables observation of atoms
and atomic planesZoom up to several million times
It enables observation of crystal structure, crystal defects, the interphase boundaries.
It enables testing of thicker samples
Слайд 59HVHRTEM
Atomic resolution:
Grain boundaries orientation
Interphase boundaries, subgrains, stacking faults, t
microtwins, polytype structure
Defects of atoms distribution inside crystallline and amorphous
phasesGold particle on carbon film
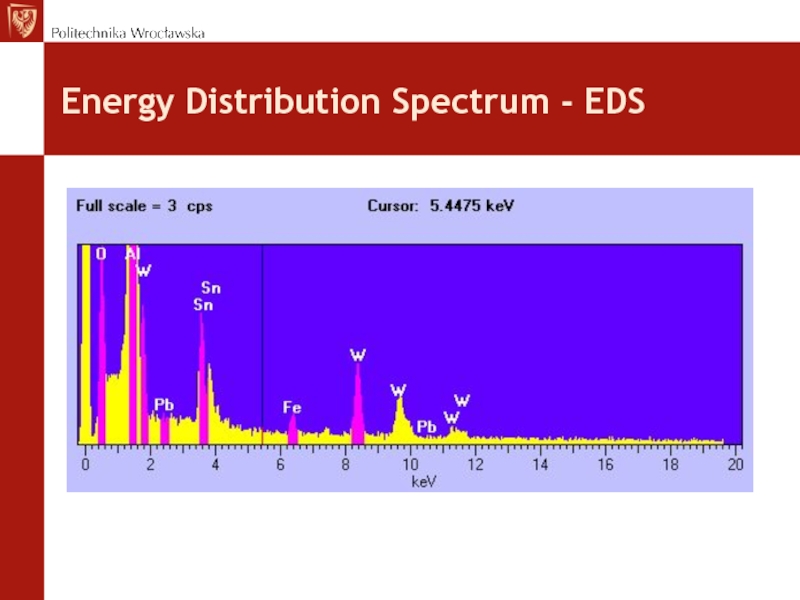
Слайд 60EDS – X-ray radiation
X-ray - formed in the electron
beam column takes an electron from an inner shell of
the atom in the test sample. His place is taken by an electron from a higher energy shell emitting quantum characteristic energyThe radiation energy is characteristic of the element
Possible chemical composition - microanalysis (detection of elements)
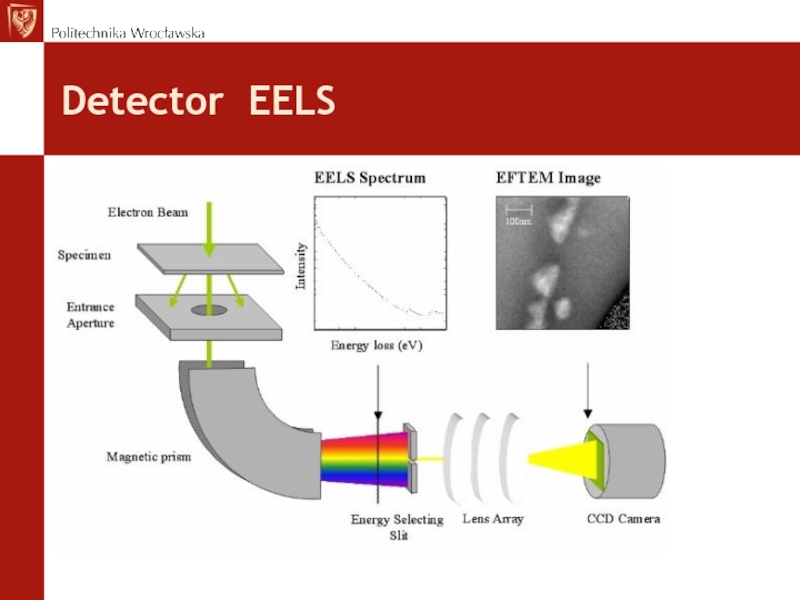
Слайд 62EELS –
Electron Energy Loss Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy (EELS) - is based
on the analysis of the energy distribution of scattered electrons.
With such a collision the electron loses some part of their kinetic energy - the energy of the primary electrons E0 is reduced by the value characteristic for the materialIt is possible microanalysis chemical composition.
The EELS spectrometer is placed under the screen
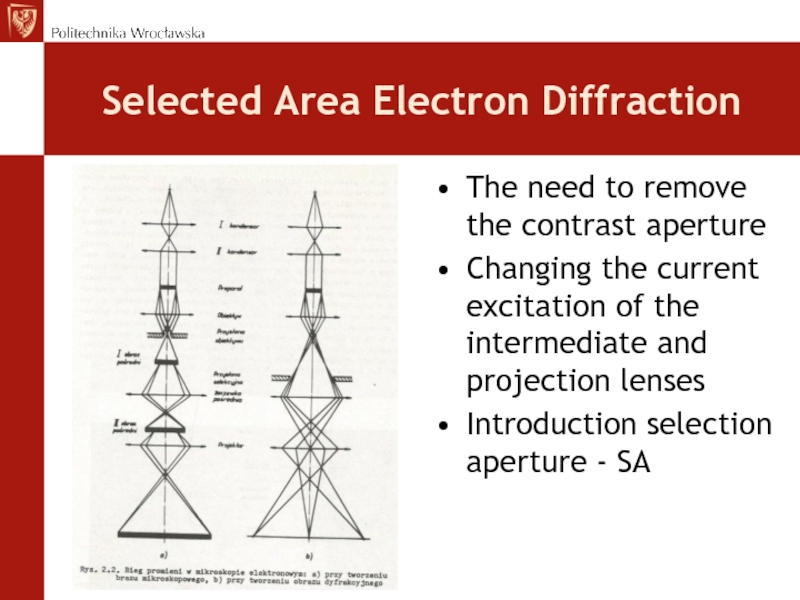
Слайд 66Selected Area Electron Diffraction
The need to remove the contrast aperture
Changing
the current excitation of the intermediate and projection lenses
Introduction selection
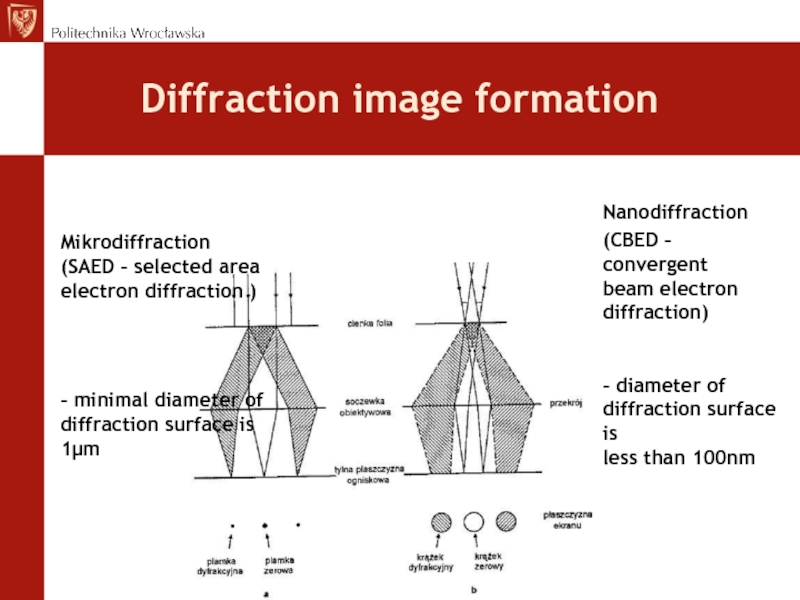
aperture - SAСлайд 67Diffraction image formation
Mikrodiffraction
(SAED – selected area electron diffraction )
– minimal diameter of diffraction surface is 1μm
Nanodiffraction
(CBED – convergent
beam electron
diffraction)
– diameter of
diffraction surface is
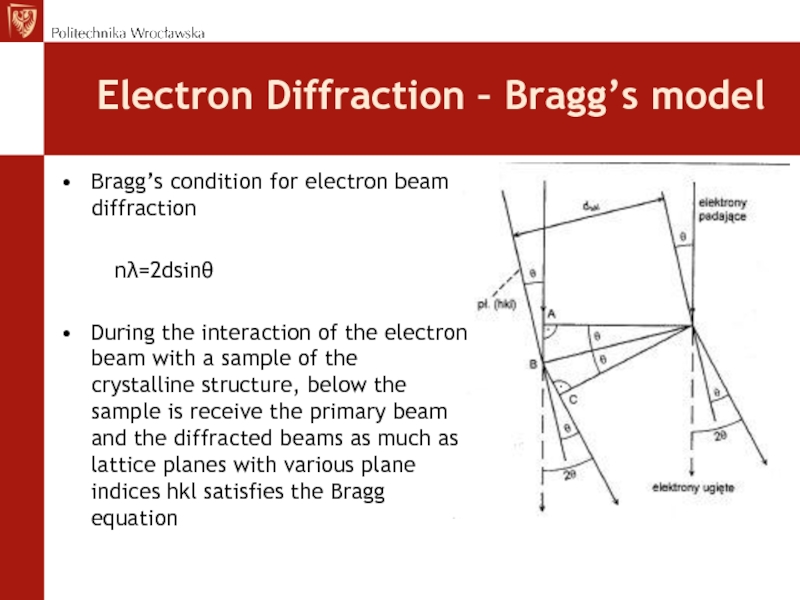
less than 100nmСлайд 68Electron Diffraction – Bragg’s model
Bragg’s condition for electron beam
diffraction
nλ=2dsinθ
During the interaction of the electron
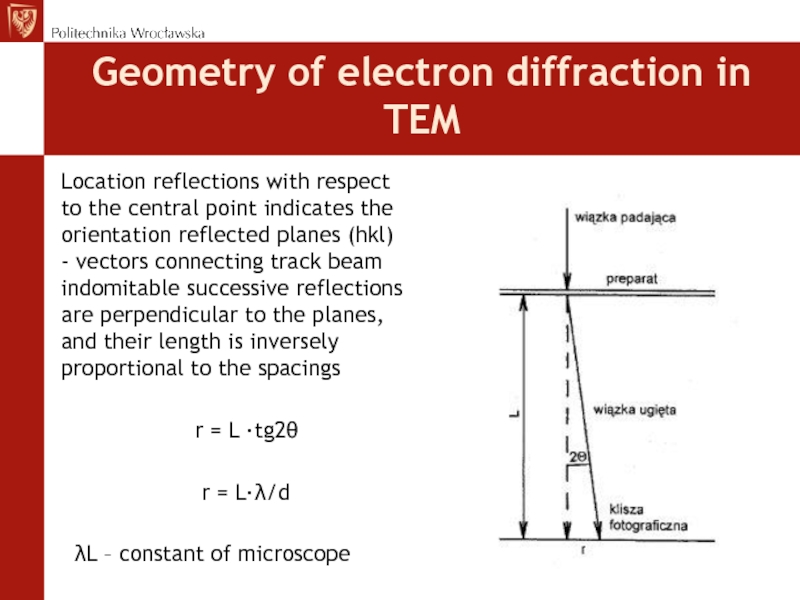
beam with a sample of the crystalline structure, below the sample is receive the primary beam and the diffracted beams as much as lattice planes with various plane indices hkl satisfies the Bragg equationСлайд 69Geometry of electron diffraction in TEM
Location reflections with respect to
the central point indicates the orientation reflected planes (hkl) -
vectors connecting track beam indomitable successive reflections are perpendicular to the planes, and their length is inversely proportional to the spacingsr = L ·tg2θ
r = L·λ/d
λL – constant of microscope
Слайд 70Interpretation of electron diffraction patterns
Identification of the structure of the
investigated crystal from which the reflections were formed
Indexing (specify indexes
of atom planes)Crystallographic analysis based on the diffraction image (SAED)
Applying the structure of the sample on the basis of the shape of elementary lattice and intensity of reflections
Слайд 71Application of electron diffraction in materials investigation
Diffraction studies enable the
identification of the observed phase
Identification of a polycrystal on the
basis of the diffraction pattern is compared with the calculated measurement of the interplanar spacings with values contained in the databases of crystallographic data and determining the indices indices of {hkl} atom planes forming a diffraction patternIn the case of a single crystal identification is a comprehensive solution diffraction pattern - defining indexes of atomic planes (hkl), zone axis [uvw] and their mutual crystallographic orientation
Слайд 74Imperfections in the crystal structure (dislocations and grain boundary between
the two polycrystal).
Image obtained by TEM.
Слайд 81Literatura
G. Schimmel, Metodyka mikroskopii elektronowej, PWN, Warszawa 1976
Ian M. Wat,
The principles and practice of electron microscopy, second edition, Cambridge
University Press, 1997Peter J. Goodhew, John Humphreys, Richard Beanland, Electron microscophy and analysis, third edition, Taylor & Francis Inc, London 2001
Andrzej Barbacki, Mikroskopia elektronowa, Wydawnictwo Politechniki Poznańskiej, Poznań 2005
Leszek A. Dobrzański, Eugeniusz Hajduczek, Mikroskopia świetlna i elektronowa, Wydawnictwa Naukowo-Techniczne, Warszawa 1987
Pod red. W. Dudzińskiego, Materiały konstrukcyjne w budowie maszyn, Oficyna Wydawnicza Politechniki Wrocławskiej, Wrocław 1994
Jan Kozubowski, Metody transmisyjnej mikroskopii elektronowej, Wydawnictwo Śląsk, Katowice 1975
Ludwig Reimer, Transmission Electron Microscopy, Spinger Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg-New York-Tokyo 1984