Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
THE BASIC STRUCTURES OF GOVERNMENT THE PLAN discussion of political
Содержание
- 1. THE BASIC STRUCTURES OF GOVERNMENT THE PLAN discussion of political
- 2. THE BASIC STRUCTURES OF GOVERNMENT Political institution:
- 3. THE BASIC STRUCTURES OF GOVERNMENT the problem
- 4. THE BASIC FORMS OF GOVERNMENTThe first division
- 5. question: how can the European countries
- 6. The second division : Unitary and Federal
- 7. UNITARY SYSTEMS center exerts significant control over
- 8. Cases of decentralization in unitary systems devolution
- 9. Слайд 9
- 10. FEDERAL SYSTEMS in federalism, composing units have
- 11. However, in federal regimes composing units (states)
- 12. Слайд 12
- 13. Слайд 13
- 14. Слайд 14
- 15. Слайд 15
- 16. Слайд 16
- 17. Слайд 17
- 18. Слайд 18
- 19. Слайд 19
- 20. Слайд 20
- 21. Слайд 21
- 22. Слайд 22
- 23. Слайд 23
- 24. Скачать презентанцию
THE BASIC STRUCTURES OF GOVERNMENT Political institution: it connotes flamboyant buildings representing the might of the state they are also the things relevant to the established and durable relationships of power
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2THE BASIC STRUCTURES OF GOVERNMENT
Political institution:
it connotes flamboyant
buildings representing the might of the state
they are also
the things relevant to the established and durable relationships of power and authority (tangible and intangible)Constitutional Court
National Security Council
constitution of the Republic of Turkey
division of pre-institutional and institutional
it relates to the method of politics
it relates to multi-level accountability
the problem of consolidation/institutionalization
Слайд 3THE BASIC STRUCTURES OF GOVERNMENT
the problem of consolidation/institutionalization
it
is relevant to the codification (laws)
it erodes the role
and influence of personal actors (although they might play a pivotal role in the emergence of political institutions) (Ataturk)it is relevant to longitude (historical context)
it is relevant to the extent of internalization and accommodation (in the absentee of a clear codified rules) (co-habitation in France)
it is relevant to the usage of governmental power (by whom and until when)
hence it is relevant to the interruptedly continuation of government
Question
What does ‘consolidation of democracy’ mean?
Слайд 4THE BASIC FORMS OF GOVERNMENT
The first division : Monarchy or
Republic
all but few countries in the world are republics.
it does not necessarily mean, all republics are good and democratic.Britain, Norway, Sweden, Denmark, Holland and Belgium are restricted monarchies, whereas, the monarchies in the Arabian peninsula befit to the definition of traditional monarchies.
the role played by the monarchs are different yet. (British king is just a figurehead whereas in Spain, the king has still important location in politics –even he is one of the founding fathers of democracy in Spain.)
in those countries, monarchies are individually political institutions on their own.
Edmund Burke criticized the French Revolution because the French monarcy was a reliable political institution distilled through the history.
Слайд 5 question:
how can the European countries with monarchic governments
be the most democratic regimes in the world?
monarchies assume
a political integration role between the traditional segments of society (particularly in Britain)monarchies may even assume the role of democratizing agent (Spanish case)
they are already established political institutions and when they act in democratic fashion, the outcome may change
however, in democratic monarchies (constitutional monarchies) monarchs plays a very symbolic role in political life
in democratic regimes (parliamentarian regimes particularly, the President fulfill what a traditional monarch does)
monarchs and republical presidents (in parliamentarian systems) are the head of state, whereas Premiers are head of government
particularly, the third world suffers from the lack of deeply institutionalized political mechanisms or institutions themselves
the third world lacks some efficient means to consolidate democracy
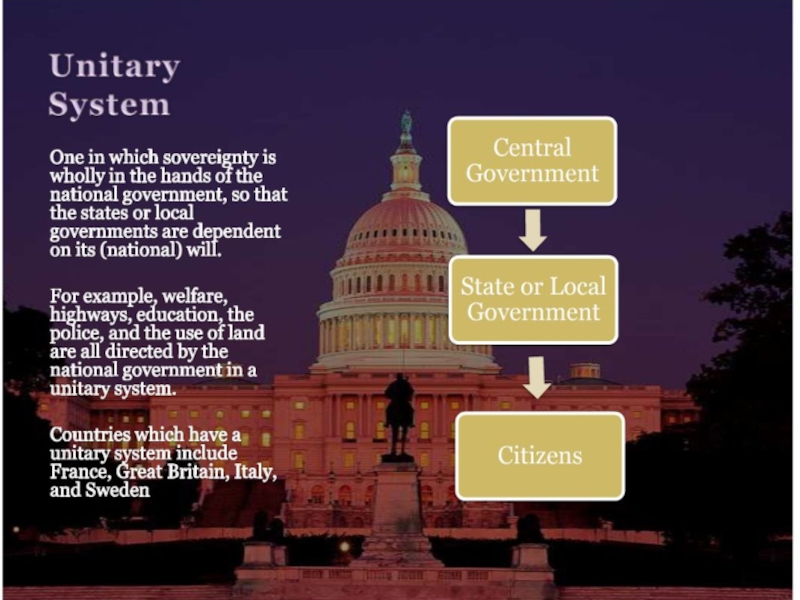
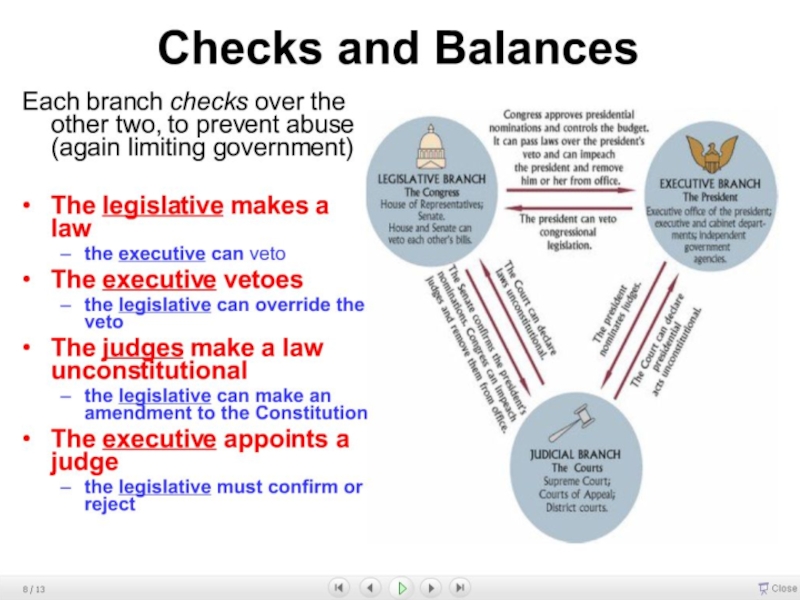
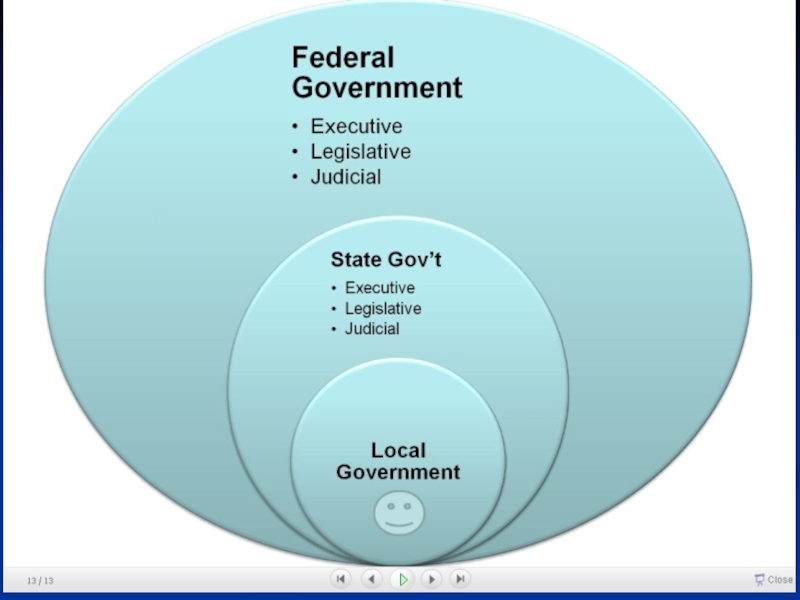
Слайд 6The second division : Unitary and Federal Systems
it is
relevant to the territorial structuring of the nation
unitary system
highly centralizedits subdivisions (departments in France, provinces in Italy, counties in Sweden, vilayets in Turkey, prefectures in Japan) are largely for administrative convenience
federal system
highly decentralized
its subdivisions are largely the representation of territorial division of political power (German lander, Swiss cantons, Yugoslavia Republics, US, Brazilian, Indian states)
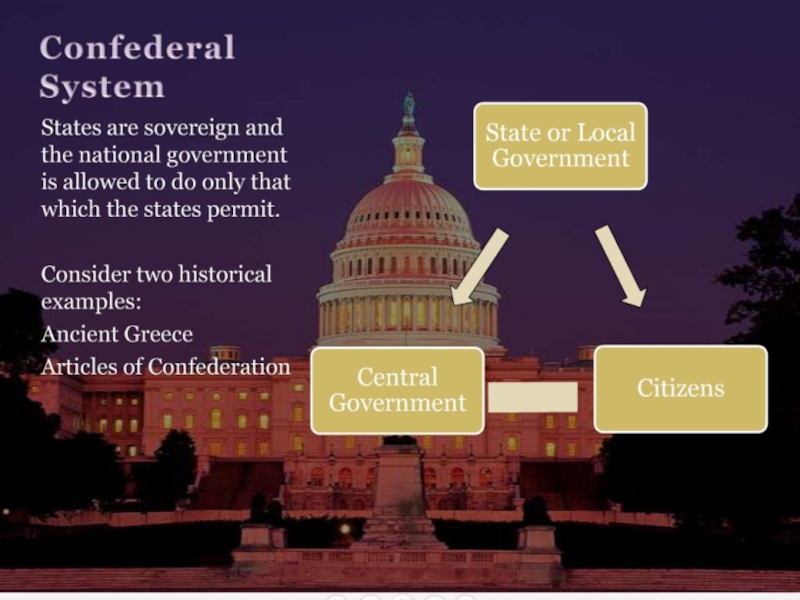
confederation (highly loosed federation)
it is the highest decentralized system
it is so loosely formed that components (states, republics) can override the center (present Montenegro-Serbia or EU)
it tends to disintegrating or forming a more formidable federation)
Слайд 7UNITARY SYSTEMS
center exerts significant control over local authorities
for
instance, the scholl curricula is determined by the central ministry
in Ankaracenter has a national police force and control over local police force
the court system is also central, and body of laws are enforced in every part of the country
however, there are municipalities which assume some functions that the centre can not fulfill healthily, yet, they are still under firm scrutiny of the central government
on the other side, the trend is decentralization as much as possible
Слайд 8Cases of decentralization in unitary systems
devolution in Britain
as
a response to the growing Scottish and Welsh nationalisms British
parliament passed in 1997 devolution bills endowing political powerdecentralization in France
France has distinctive regional subcultures: the Celtic Bretons, the southerners of Midi, Corsicans
Paris govern the departments (provinces) through a appointed prefect (governer-vali)
In Mitterand era (1980s), Paris endowed transferred some competences to those departments regarding local economic and financial affairs (thereby reversing about five century long centralization)
autonomy in Spain
Basque and Catalans regions are proud of their distinct cultures from Castillian majority (Euzkadi ta Askatasuna-ETA) demanded full independence to the Basque region
it is organized as ‘autonomies’ having rights to say in taxation matters, language and education through their own institutions (regional parliaments)
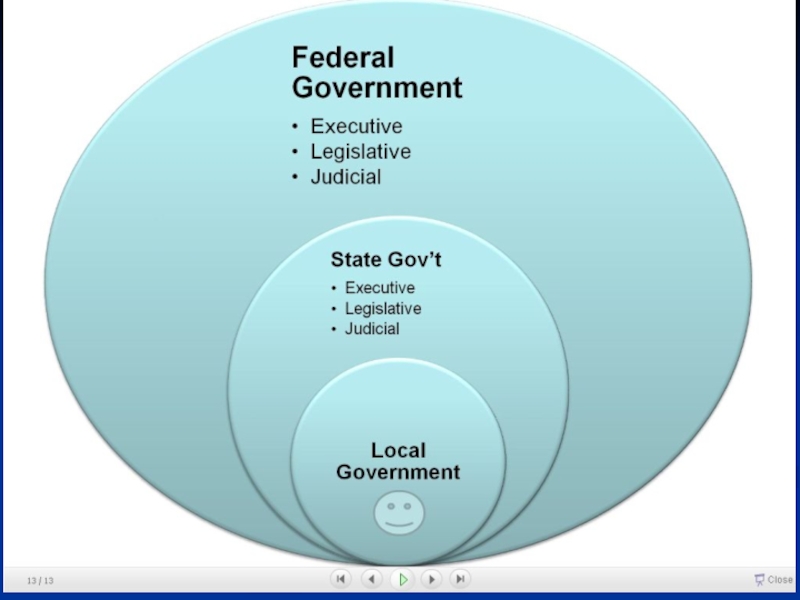
Слайд 10FEDERAL SYSTEMS
in federalism, composing units have a specific degree
(changing from regime to regime) political authority on the territorial
basisalthough USSR was a federal state, it was considerably different from other Western federal states like Germany or even from Yugoslavia
in a federal state composing units (states) have
their own constitution
their own body of law (accorded with the federal laws of course)
their own parliament, government and courts
their own parties (mostly offshots of federal level political parties)
their own local police forces (not army)
they are represented in federal bodies (generally bicameral parliaments)
their own rights regarding language and culture
Слайд 11However, in federal regimes composing units (states)
depended on the
federal (central) authorities regarding macro level economic decisions, security matters
and foreign relations issuesfederal decisions are based on check-balance between proportionality and delegative representation (upper house and house of representatives)
federal states are established
to unite against common enemies or rivals (Yugoslavia is surrounded by brigama (fears)
for economic reasons
to buttress the central government (as in the case of EU-US-India)
to weaken the central government (as in Yugoslavia)
-both of them for the sake of preserving national unity-
the right of secession from federal state is a disputable matter