Слайд 1Marketing II / Session 1
02.03.2015
Martin Samek
martin.samek@lbs.ac.at
Слайд 2Spring Term 2015
Written final exam in
Session 12; 1st of
June 2015:
90 Minutes, open-ended questions,
40% contribution to
final grade
Two written (groups of two) assignments until:
Session 8; 7th of May 2015
Session 12; 1st of June 2015
30% contribution per assignment
Groups of two students each need to discuss in form of an essay a given question per assignment.
Assignment a) Product and Price
Assignment b) Place and Promotion
Each essay needs to be structured in introduction, main text and conclusion (a deeper structure/chapters of 2nd and 3rd level are also allowed). A minimum of 15 pages (fonts and layout according to LBS standards) is required per essay. You will be asked to elaborate on an example of your choice about the applicable concepts of pricing and product strategies respectively distribution channels and networks a s well as integrated marketing communication (promotion).
Marketing II/ Session 1
Слайд 3Product
Marketing II/ Session 1
Слайд 4What is a PRODUCT?
Marketing II / Session 1
The term
product can refer to
- both goods and services
- the full
product profile (4Ps)
- part of the customer-company exchange
Remember: A Company offers something (a flight), and the customer offers something in return (payment).
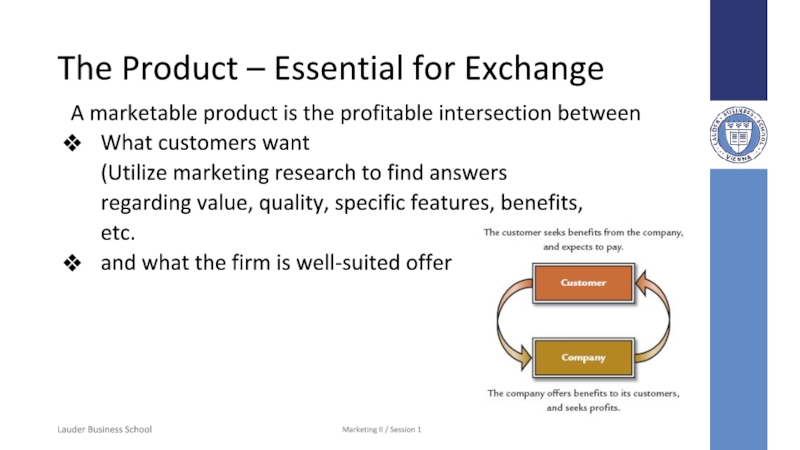
Слайд 5The Product – Essential for Exchange
Marketing II / Session 1
A
marketable product is the profitable intersection between
What customers want
(Utilize marketing
research to find answers
regarding value, quality, specific features, benefits,
etc.
and what the firm is well-suited offer
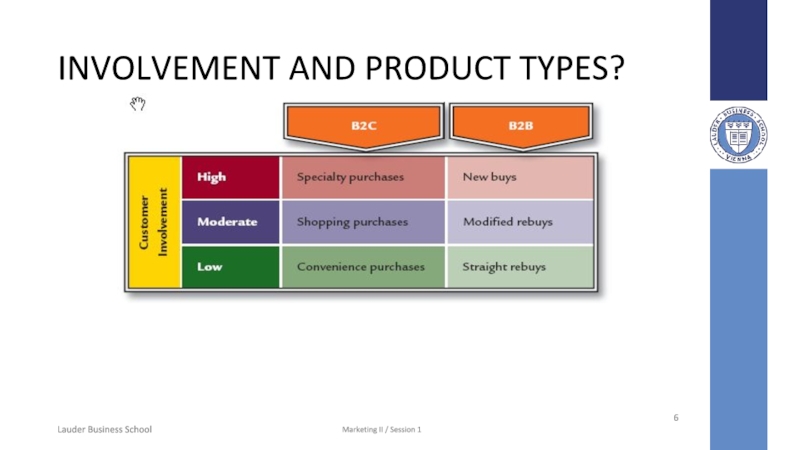
Слайд 6INVOLVEMENT AND PRODUCT TYPES?
Marketing II / Session 1
Слайд 7INVOLVEMENT AND PRODUCT TYPES
Marketing II / Session 1
Low Involvement
Convenience
and straight re-buys
Customers are inclined to
engage in limited, if
any, word-of-mouth
exert minimum effort retrieving the product
be more price sensitive
Marketers are inclined to
offer price-related loyalty programs
engage in extensive distribution
try to capture customers’ attention
Слайд 8INVOLVEMENT AND PRODUCT TYPES
Marketing II / Session 1
Low Involvement
Слайд 9INVOLVEMENT AND PRODUCT TYPES
Marketing II / Session 1
High Involvement
Products
Specialty and new buys
Customers are inclined to
engage in considerable
word-of-mouth
exert effort retrieving the product
be less price sensitive
Marketers are inclined to
offer community related loyalty programs
engage in selective distribution
offer much information about products
Слайд 10INVOLVEMENT AND PRODUCT TYPES
Marketing II / Session 1
High Involvement
Слайд 11INVOLVEMENT AND PRODUCT TYPES
Marketing II / Session 1
High Involvement
Offer
a lot of specific information about products!
Riedel HP
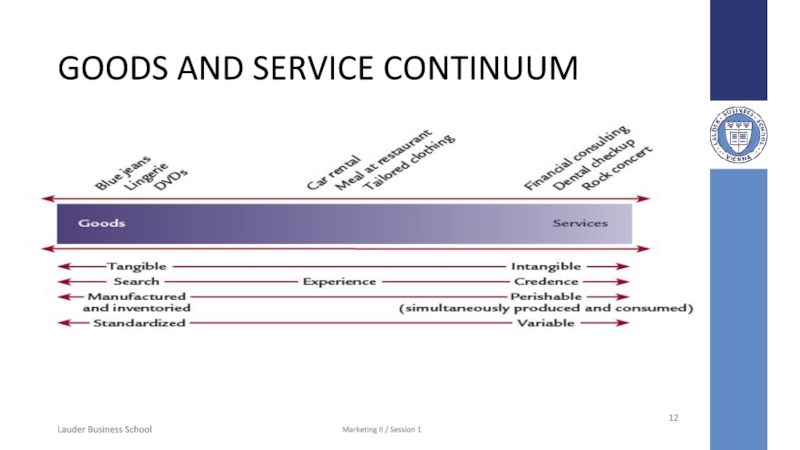
Слайд 12GOODS AND SERVICE CONTINUUM
Marketing II / Session 1
Слайд 13TANGIBILITY
Marketing II / Session 1
Goods are more tangible than
services
Pure goods are tangible
- socks
Pure service are intangible
- medical
procedure
A mix has tangible and intangible components
- rental cars
Слайд 14SEARCH, EXPERIENCE, CREDENCE
Marketing II / Session 1
Search Qualities
May be
evaluated prior to purchase
- socks
Experience Qualities
Require trial or consumption
before evaluation
- restaurants
Credence Qualities
Difficult to judge even post-consumption
- medical procedures
Слайд 15PERISABILITY & INSEPERABILITY
Marketing II / Session 1
Services are simultaneously produced
and consumed
Perishability: Services are more perishable than goods
Marketers must
try to even out demand
Inseparability: Services are more impacted by the interaction between the service provider and the customer than goods
Слайд 16VARIABILITY
Marketing II / Session 1
Services are more variable than goods
Due
to changing needs, abilities, etc. in the service provider and
customer
Self-service and equipment can decrease variability
Try to reduce bad variability
Errors in the system
Try to improve good variability
Customization for customers’ unique needs
Слайд 17GOODS & SERVICES
Marketing II / Session 1
Differences between goods and
services influence business decisions
- Advertising, branding, pricing, logistics, etc.
Thinking beyond
traditional services…
- Professional services
- Purchase experiences
- On-line shopping
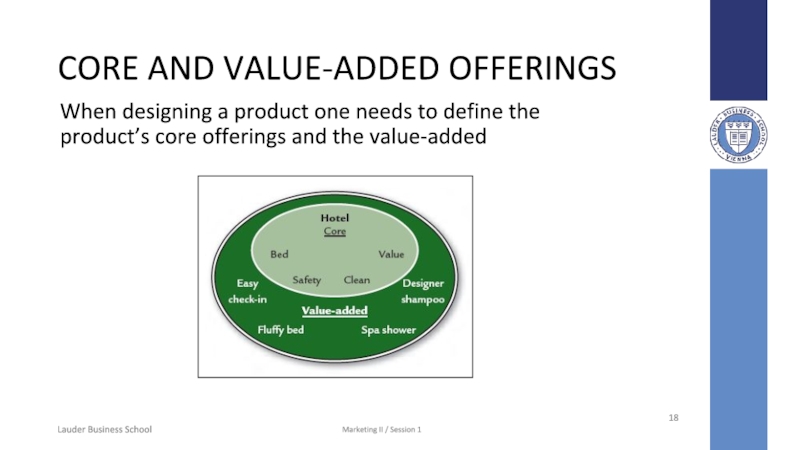
Слайд 18CORE AND VALUE-ADDED OFFERINGS
Marketing II / Session 1
When designing a
product one needs to define the product’s core offerings and
the value-added
Слайд 19CORE AND VALUE-ADDED OFFERINGS
Marketing II / Session 1
Core is essential
to the product offering
Core elements are expected by customers
If core
elements are substandard, dissatisfaction can be triggered
Value-added is supplemental and can be used for differentiation
Marketers can affect level of satisfaction through value-addeds
For example, luxurious rooms may lead to high satisfaction
Слайд 20DYNAMIC STRATEGIES
Marketing II / Session 1
Core businesses might change as
the industry changes or as the firm’s competencies change
Ask…
What
business are we in?
What benefits do we want to provide to the
consumer?
Who is our competition?
Example: IBM
Слайд 21PRODUCT MIX
Marketing II / Session 1
Product mix
A company’s product lines
Breadth
Number
of product lines
Depth
Number of products in a line
Слайд 22PRODUCT MIX
Marketing II / Session 1
Example:
Example: Samsung
Faber-Castell
Слайд 23PRODUCT MIX
Marketing II / Session 1
Product line manager can prune
or supplement existing lines
Extensions into breadth and depth must be
done for strategic reasons
Shouldn’t try to be all things to all people
Are the new launches consistent with brand’s/company’s positioning?
If not, can the brands be directed to different target segments without diluting the existing position?
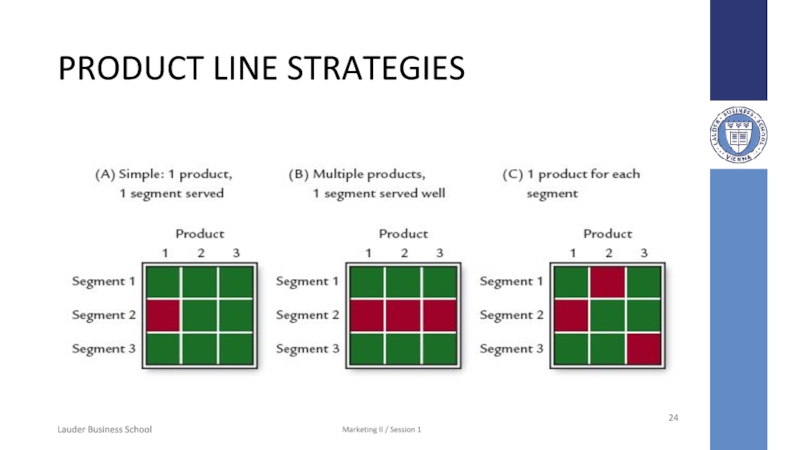
Слайд 24PRODUCT LINE STRATEGIES
Marketing II / Session 1