Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
SIW Theme : “Visual diagnostics of glomerulonephritis”
Содержание
- 1. SIW Theme : “Visual diagnostics of glomerulonephritis”
- 2. Plan:IntroductionMethods of diagnosticsUltrasoundRadionuclide methodProcedure for conducting the NRHMethods of conducting DRMGConclusionReferences
- 3. IntroductionGlomerulonephritis is an immunoinflammatory disorder with predominant
- 4. Of the methods of radiation studies use
- 5. At the second stage of the survey,
- 6. Слайд 6
- 7. Renal hemodynamics, in the case of glomerulonephritis,
- 8. Слайд 8
- 9. Based on the results of the NRR
- 10. Ultrasound examination of blood flow in the vessels of the kidneys - dopplerography of renal vessels.
- 11. Procedure for conducting the NRRThe patient is
- 12. Слайд 12
- 13. Methods of conducting DRMGPreparation of the patient
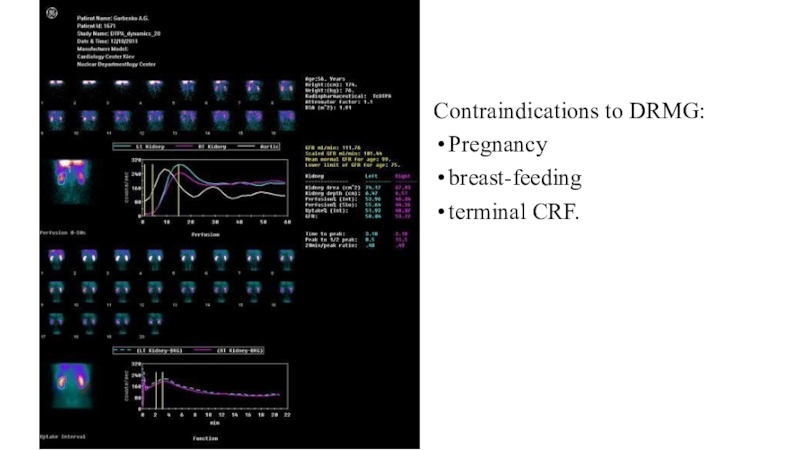
- 14. Contraindications to DRMG:Pregnancybreast-feeding terminal CRF.
- 15. The obtained data are analyzed in several
- 16. ConclusionIn the case of glomerulonephritis, the diagnosis
- 17. Referenceshttp://www.sweli.ru/zdorove/meditsina/analizy/radionuklidnaya-vizualizatsiya-skeleta.htmlhttp://vmede.org/sait/?page=12&id=Onkilogiya_trufanov_t1_2010&menu=Onkilogiya_trufanov_t1_2010http://www.krasotaimedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_urology/glomerulonephritishttp://impotencija.net/glomerulonefrit/simptomy-i-formy/
- 18. Скачать презентанцию
Plan:IntroductionMethods of diagnosticsUltrasoundRadionuclide methodProcedure for conducting the NRHMethods of conducting DRMGConclusionReferences
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Plan:
Introduction
Methods of diagnostics
Ultrasound
Radionuclide method
Procedure for conducting the NRH
Methods of conducting
DRMG
Слайд 3Introduction
Glomerulonephritis is an immunoinflammatory disorder with predominant glomerular lesion
The diagnosis
of glomerulonephritis is established on the basis of clinical and
laboratory data. Distinguish between acute and chronic glomerulonephritis.Acute glomerulonephritis is characterized by proteinuria, edema, hematuria, renal insufficiency and hypertension.
Chronic is a slowly progressive disease that leads to irreversible renal failure and can be primary and secondary (due to systemic diseases).
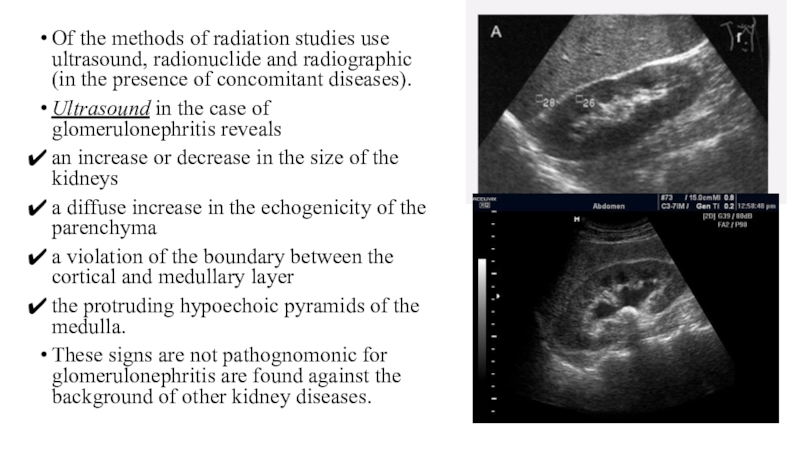
Слайд 4Of the methods of radiation studies use ultrasound, radionuclide and
radiographic (in the presence of concomitant diseases).
Ultrasound in the
case of glomerulonephritis reveals an increase or decrease in the size of the kidneys
a diffuse increase in the echogenicity of the parenchyma
a violation of the boundary between the cortical and medullary layer
the protruding hypoechoic pyramids of the medulla.
These signs are not pathognomonic for glomerulonephritis are found against the background of other kidney diseases.
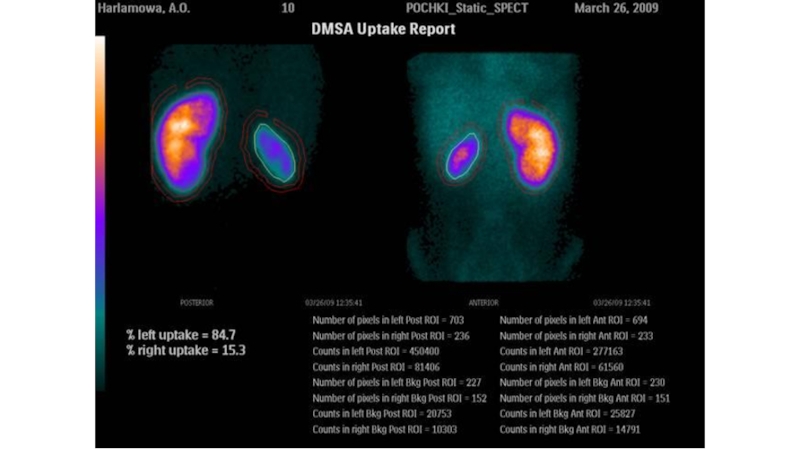
Слайд 5At the second stage of the survey, a radionuclide method
is used to assess the function of the kidneys and
the extent to which it is disturbed. The most informative methods are the IRPH (indirect radionuclide radiography is a technique for assessing the temporal and quantitative parameters of renal hemodynamics using radiopharmaceuticals.) And DRМG (dynamic reno-scintigraphy is a technique for visualizing the kidneys and urinary tracts with a scintigraphy method and a gamma camera to determine the parameters of accumulation and secretion Nephrotropic radiopharmaceuticals of tubular and glomerular elimination mechanisms) with ⁹⁹ᵐTc-DTPO (technetium complex with precipitate).Слайд 7Renal hemodynamics, in the case of glomerulonephritis, is characterized by
a slowing of the arterial and venous phases of the
blood flow (Ta. Tv), an increase in the time of aortic transit (Tar).DRМG with ⁹⁹ᵐТс-DTPО allows to define symmetric retardations of filtration-excretory processes in kidneys - renograms of the parenchymal type. In the case of glomerulonephritis, the kidneys are clearly visualized on scintiphotos. Changes in renal circulation and functional state of the organ are more significant in the presence of clinically unfavorable variants of the disease (nephrotic syndrome with hematuria, elevated blood pressure, disturbance of the renal nitrogen function).
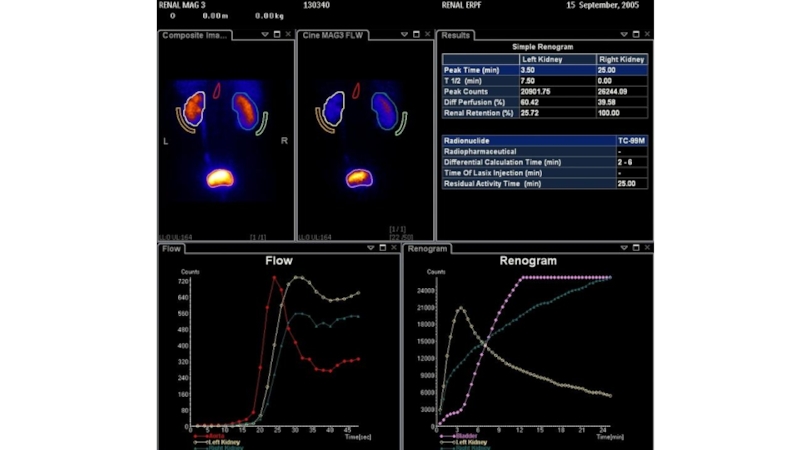
Слайд 9Based on the results of the NRR and DRMG obtained
before the beginning of the program therapy of glomerulonephritis, it
is possible to predict the course of the disease.In case of chronicization of the pathological process in the kidneys or its further progression with the development of CRF
by slowing down of Ta and Tar, glomerular filtration rate, Tmax (the time of maximum accumulation of RFP in the kidneys)
an increase in the percentage of excretion of RFP is possible in comparison with the control group (intact kidneys)
the elongation of Ta is possible in the absence of the effect of treatment (progression) in comparison with the results characteristic of patients with complete clinical and laboratory remission.
Slowing Ta> 8 is a sign of significant changes in renal circulation and an unfavorable prognosis of the disease. On the background of treatment and after its completion, the majority of patients notice improvement in the parameters of NRH and DRSG, but in the history of renal dysfunction and slowing of renal hemodynamics remain in almost a quarter of patients with remission, which indicates the incompleteness of the pathological process in the kidneys and the need for a constant clinical and laboratory And radionuclide monitoring.
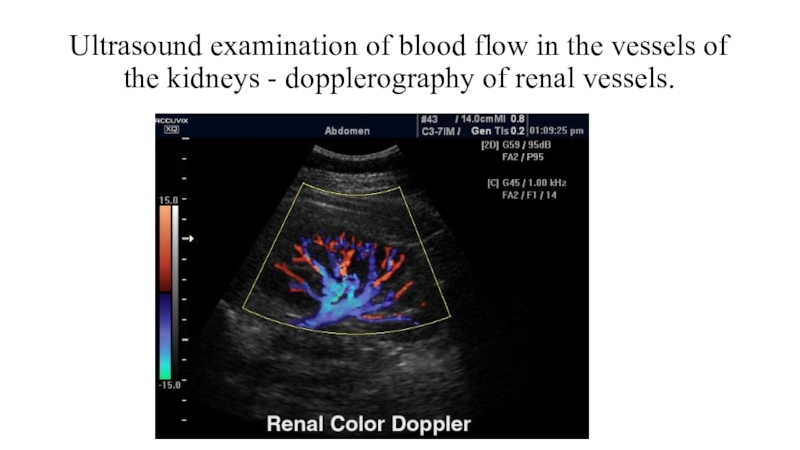
Слайд 10Ultrasound examination of blood flow in the vessels of the
kidneys - dopplerography of renal vessels.
Слайд 11Procedure for conducting the NRR
The patient is sitting in the
patient's position with his back to the gamma detector or
lying on his back. The middle of the detector is set at the level of the XII rib from behind.RFPs are administered bolus (0.3-0.5 ml) under a tourniquet, fast, with an activity of at least 3 MBq / kg.
After the injection, the tourniquet is removed and several movements are made by the patient's hand up and down for quick passage of the "bolus". Further, the program for recording information on a computer in the event that a heart image appears on the monitor for collecting information.
Angiographic examination is carried out with exposure 1 frame per 1s. The recommended time of the procedure is 30 s (for children) and 45 s (for adults).
After the study, several angiogram points are marked to determine the parameters of the NNRG. Such points are the beginning of the RFP entering the kidneys, the time of the maximum passage of the "bolus" and the time to reach a balanced concentration. Based on this, the time of the arterial phase (Ta) of renal blood flow (c), the time of the venous phase (Tv) of renal blood flow (c) and the time of arterial transit (Tar) (c) are calculated.
Слайд 13Methods of conducting DRMG
Preparation of the patient for the study
includes:
* Normal physiological regimen (light breakfast) and 100-200 ml of
tea or mineral water 30 min before the study;Empty bladder;
* Immobility of the patient during the study.
The study is conducted in the patient's position while sitting with his back to the gamma detector or lying on his back. The middle of the detector is set at the level of the XII rib from behind. RFP is administered in an amount of 0.3-0.5 ml, rapidly. After the introduction of the RFP, the computer program is launched and the information begins to be collected with the exposure of 1 frame per minute. The duration of the study is 20 min (children) and 30 min (adults).
Слайд 15The obtained data are analyzed in several stages:
1. Visual assessment
during the study gives primary information about the degree of
visualization of the kidneys at each minute, the presence of ureter imaging and the time of the appearance of the image of the bladder.2. Single-frame viewing of the kidney scintigraphy image gives preliminary information about the function of the parenchyma and the state of urodynamic.
3. Analysis of the "zone of interest".
4. Segment analysis.
5. Analysis of secretory-excretory and filtration-excretory functions of each kidney is carried out by calculating the basic parameters of its functional capacity.
Слайд 16Conclusion
In the case of glomerulonephritis, the diagnosis is based on
a combination of the definition of symptoms of the clinical
picture, the conduct of various types of laboratory diagnosis and various instrumental methods. For correct differential diagnosis, a combination of all available methods is necessary.The preliminary diagnosis is made on the basis of clinical manifestations of the disease, complaints and anamnesis, identification of diagnostic criteria during examination and physical examination.
Further the doctor appoints additional researches for specification of the form of disease and its etiology. To determine the primary or secondary form of glomerulonephritis, the connection with the transmitted infectious diseases, for example, with streptococcal infections, is taken into account.