Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Organizational Structure and Design
Содержание
- 1. Organizational Structure and Design
- 2. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 3. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 4. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 5. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 6. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 7. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 8. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall9–Exhibit 9–2 The Five Common Forms of Departmentalization
- 9. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall9–Exhibit 9–2 (cont’d) Geographical Departmentalization
- 10. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall9–Exhibit 9–2 (cont’d) Product Departmentalization
- 11. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 12. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 13. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 14. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 15. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 16. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall9–Exhibit 9–3 Contrasting Spans of Control
- 17. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 18. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 19. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 20. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 21. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 22. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 23. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 24. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 25. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 26. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 27. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 28. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 29. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 30. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall9–Exhibit 9–8 Contemporary Organizational Designs
- 31. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 32. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 33. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 34. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 35. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 36. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 37. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 38. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 39. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Organizational
Structure and Design
editionСлайд 2Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Learning
Outcomes Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this
chapter.9.1 Defining Organizational Structure
Discuss the traditional and contemporary views of work specialization, chain of command, and span of control.
Describe each of the five forms of departmentalization.
Differentiate, authority, responsibility, and unity of command.
Explain how centralization – decentralization and formalization are used in organizational design.
Слайд 3Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Learning
Outcomes
9.2 Mechanistic and Organic Structures
Contrast mechanistic and organic organizations.
Explain the
contingency factors that affect organizational design.9.3 Common Organizational Designs
Contrast the three traditional organizational designs.
Describe the contemporary organizational designs.
Discuss the organizational design challenges facing managers today.
Слайд 4Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Designing
Organizational Structure
Organizing
Arranging and structuring work to accomplish an organization’s goals.
Organizational
StructureThe formal arrangement of jobs within an organization.
Organizational Design
A process involving decisions about six key elements:
Work specialization
Departmentalization
Chain of command
Span of control
Centralization and decentralization
Formalization
Слайд 5Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Exhibit
9–1 Purposes of Organizing
Divides work to be done into specific jobs
and departments.Assigns tasks and responsibilities associated with individual jobs.
Coordinates diverse organizational tasks.
Clusters jobs into units.
Establishes relationships among individuals, groups, and departments.
Establishes formal lines of authority.
Allocates and deploys organizational resources.
Слайд 6Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Organizational
Structure
Work Specialization
The degree to which tasks in the organization are
divided into separate jobs with each step completed by a different person.Overspecialization can result in human diseconomies from boredom, fatigue, stress, poor quality, increased absenteeism, and higher turnover.
Слайд 7Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
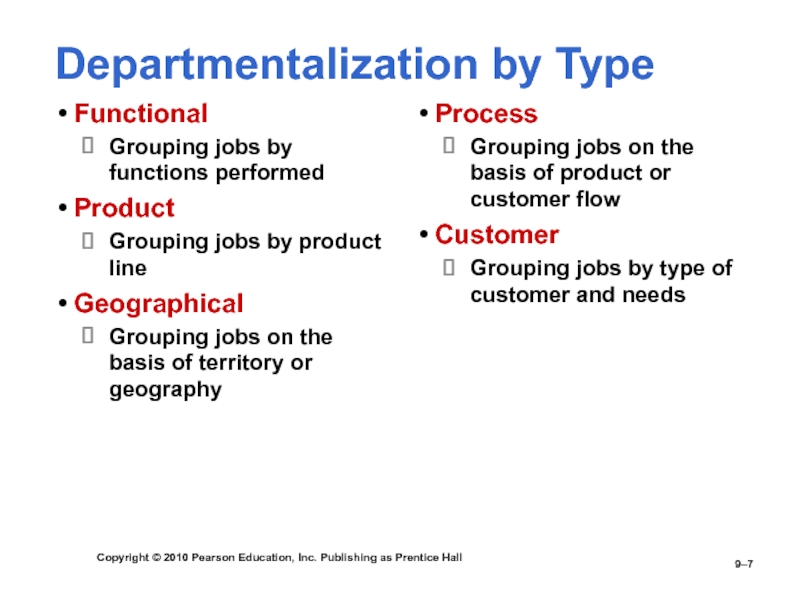
Departmentalization
by Type
Functional
Grouping jobs by functions performed
Product
Grouping jobs by product
lineGeographical
Grouping jobs on the basis of territory or geography
Process
Grouping jobs on the basis of product or customer flow
Customer
Grouping jobs by type of customer and needs
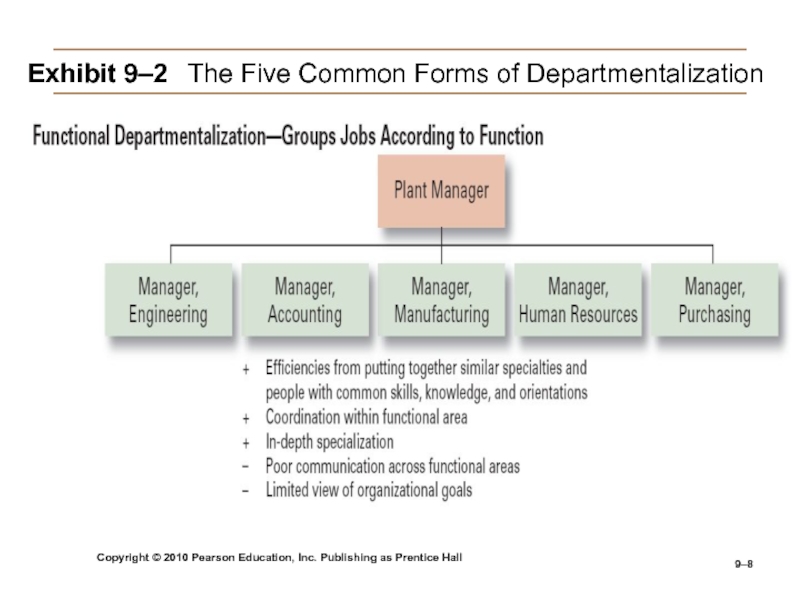
Слайд 8Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Exhibit
9–2 The Five Common Forms of Departmentalization
Слайд 9Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Exhibit
9–2 (cont’d) Geographical Departmentalization
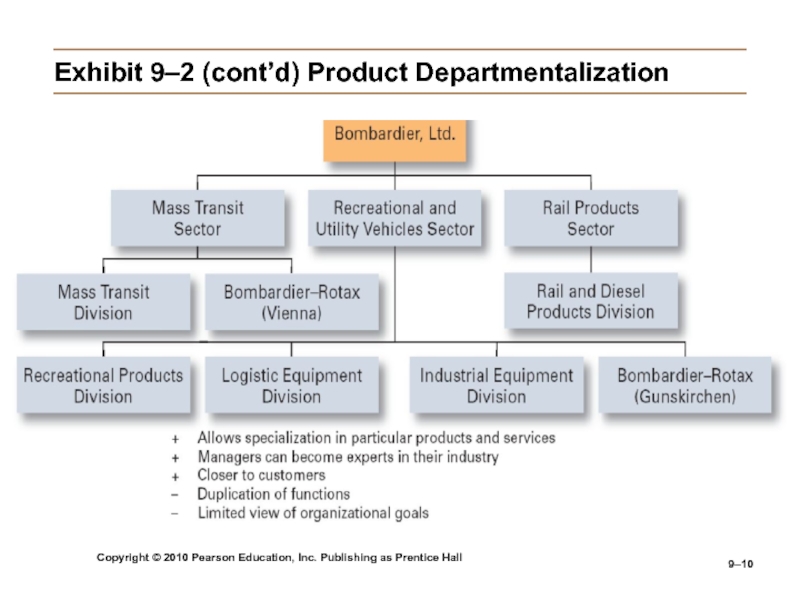
Слайд 10Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Exhibit
9–2 (cont’d) Product Departmentalization
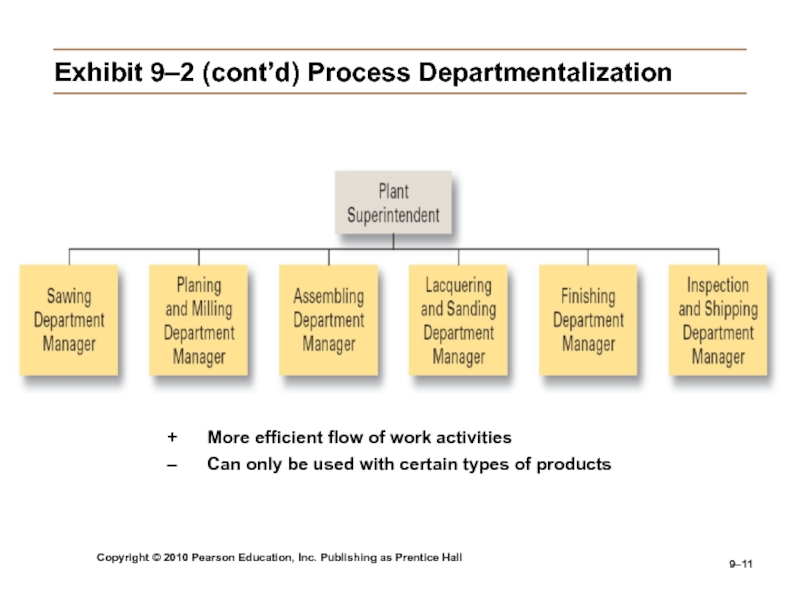
Слайд 11Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Exhibit
9–2 (cont’d) Process Departmentalization
+ More efficient flow of work activities
– Can only
be used with certain types of productsСлайд 12Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Exhibit
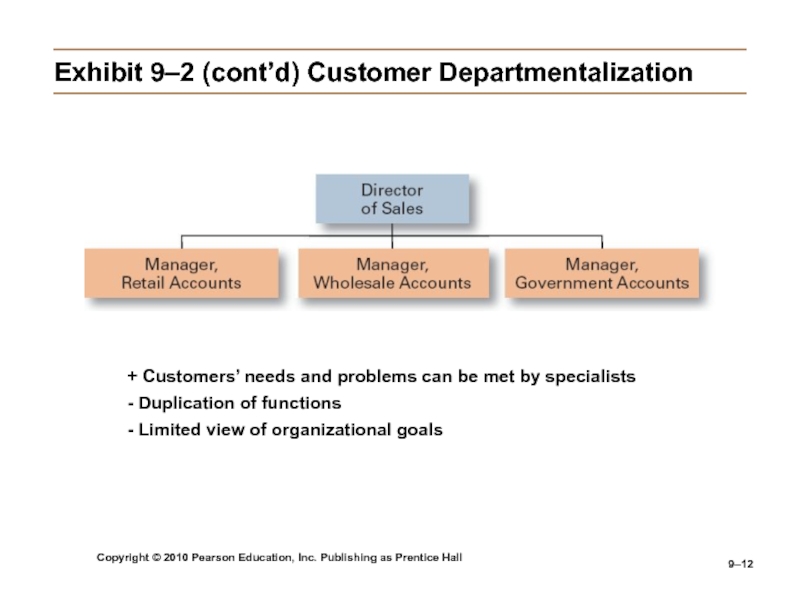
9–2 (cont’d) Customer Departmentalization
+ Customers’ needs and problems can be
met by specialists- Duplication of functions
- Limited view of organizational goals
Слайд 13Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Organizational
Structure (cont’d)
Chain of Command
The continuous line of authority that extends
from upper levels of an organization to the lowest levels of the organization and clarifies who reports to whom.Слайд 14Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Organizational
Structure (cont’d)
Authority
The rights inherent in a managerial position to tell
people what to do and to expect them to do it.Responsibility
The obligation or expectation to perform.
Unity of Command
The concept that a person should have one boss and should report only to that person.
Слайд 15Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Organizational
Structure (cont’d)
Span of Control
The number of employees who can be
effectively and efficiently supervised by a manager.Width of span is affected by:
Skills and abilities of the manager
Employee characteristics
Characteristics of the work being done
Similarity of tasks
Complexity of tasks
Physical proximity of subordinates
Standardization of tasks
Sophistication of the organization’s information system
Strength of the organization’s culture
Preferred style of the manager
Слайд 16Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
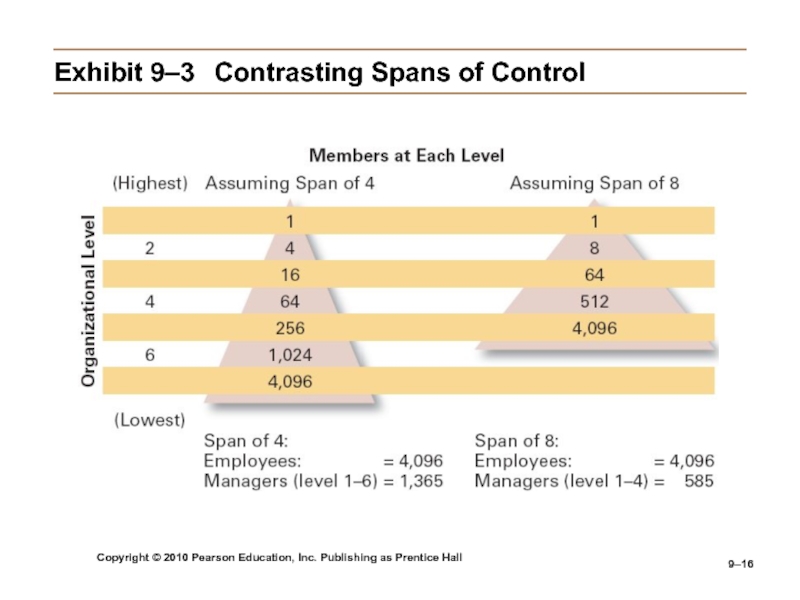
Exhibit
9–3 Contrasting Spans of Control
Слайд 17Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Organizational
Structure (cont’d)
Centralization
The degree to which decision making is concentrated at
upper levels in the organization.Organizations in which top managers make all the decisions and lower-level employees simply carry out those orders.
Decentralization
Organizations in which decision making is pushed down to the managers who are closest to the action.
Employee Empowerment
Increasing the decision-making authority (power) of employees.
Слайд 18Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Exhibit
9–4 Factors that Influence the Amount of Centralization
and DecentralizationMore Centralization
Environment is stable.
Lower-level managers are not as capable or experienced at making decisions as upper-level managers.
Lower-level managers do not want to have a say in decisions.
Decisions are relatively minor.
Organization is facing a crisis or the risk of company failure.
Company is large.
Effective implementation of company strategies depends on managers retaining say over what happens.
Слайд 19Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Exhibit
9–4 (cont’d) Factors that Influence the Amount
of Centralization and DecentralizationMore Decentralization
Environment is complex, uncertain.
Lower-level managers are capable and experienced at making decisions.
Lower-level managers want a voice in decisions.
Decisions are significant.
Corporate culture is open to allowing managers to have a say in what happens.
Company is geographically dispersed.
Effective implementation of company strategies depends on managers having involvement and flexibility to make decisions.
Слайд 20Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Organizational
Structure (cont’d)
Formalization
The degree to which jobs within the organization are
standardized and the extent to which employee behavior is guided by rules and procedures.Highly formalized jobs offer little discretion over what is to be done.
Low formalization means fewer constraints on how employees do their work.
Слайд 21Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
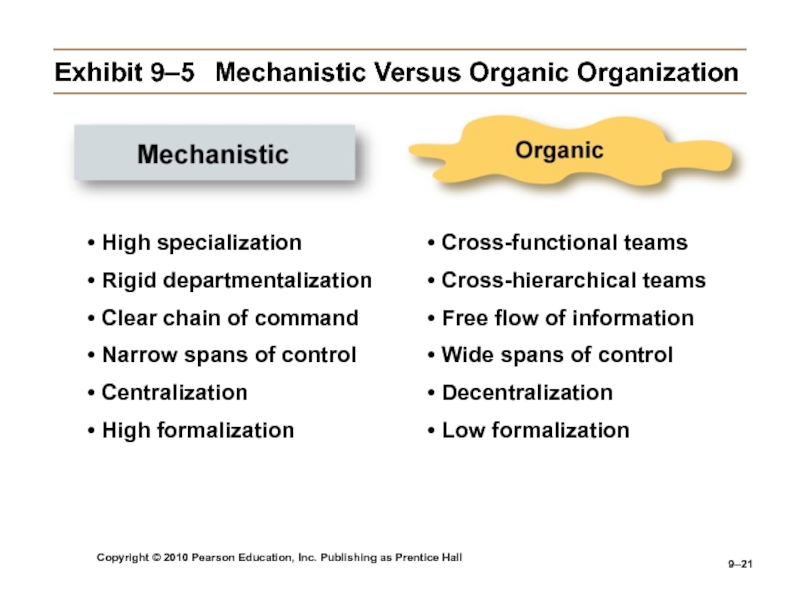
Exhibit
9–5 Mechanistic Versus Organic Organization
• High specialization
• Rigid departmentalization
• Clear chain
of command• Narrow spans of control
• Centralization
• High formalization
• Cross-functional teams
• Cross-hierarchical teams
• Free flow of information
• Wide spans of control
• Decentralization
• Low formalization
Слайд 22Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Contingency
Factors
Structural decisions are influenced by:
Overall strategy of the organization
Organizational structure
follows strategy.Size of the organization
Firms change from organic to mechanistic organizations as they grow in size.
Technology use by the organization
Firms adapt their structure to the technology they use.
Degree of environmental uncertainty
Dynamic environments require organic structures; mechanistic structures need stable environments.
Слайд 23Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Contingency
Factors (cont’d)
Strategy Frameworks:
Innovation
Pursuing competitive advantage through meaningful and unique innovations
favors an organic structuring.Cost minimization
Focusing on tightly controlling costs requires a mechanistic structure for the organization.
Слайд 24Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Contingency
Factors (cont’d)
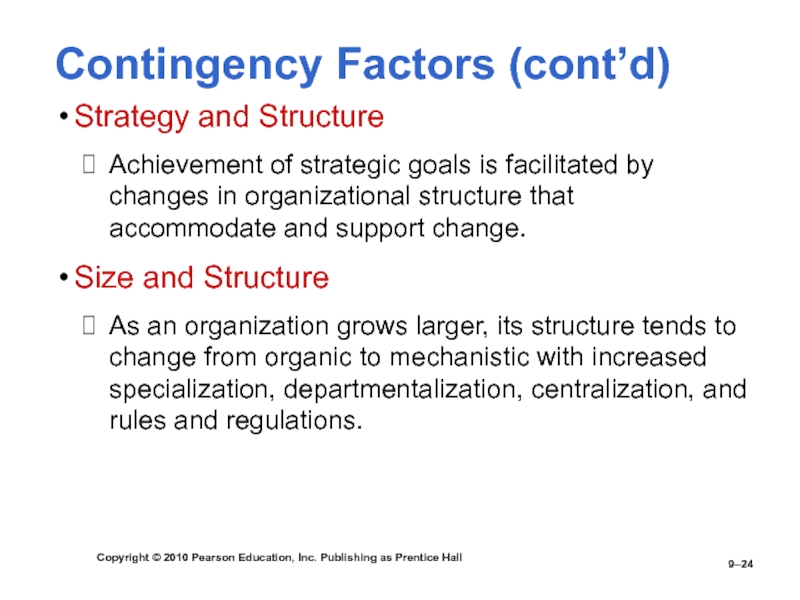
Strategy and Structure
Achievement of strategic goals is facilitated by
changes in organizational structure that accommodate and support change.Size and Structure
As an organization grows larger, its structure tends to change from organic to mechanistic with increased specialization, departmentalization, centralization, and rules and regulations.
Слайд 25Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Contingency
Factors (cont’d)
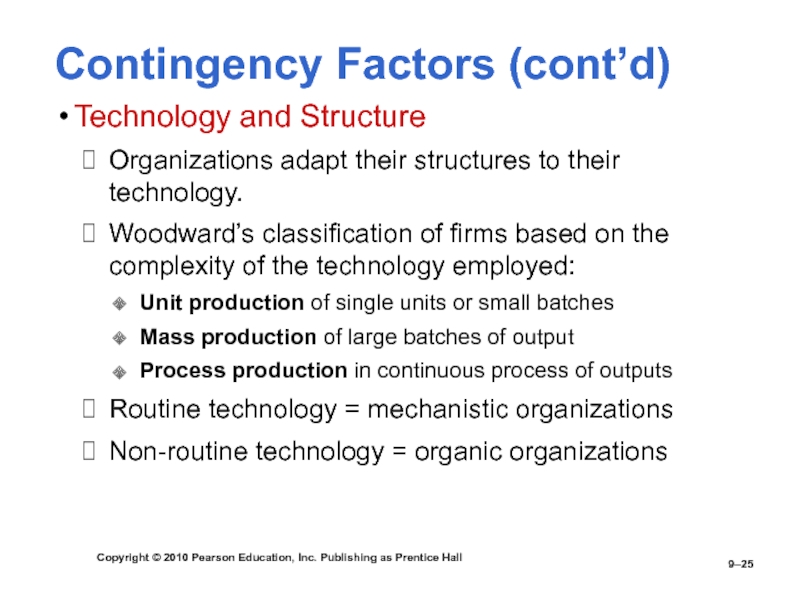
Technology and Structure
Organizations adapt their structures to their technology.
Woodward’s
classification of firms based on the complexity of the technology employed:Unit production of single units or small batches
Mass production of large batches of output
Process production in continuous process of outputs
Routine technology = mechanistic organizations
Non-routine technology = organic organizations
Слайд 26Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Exhibit
9–6 Woodward’s Findings on Technology,
Structure, and Effectiveness
Слайд 27Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Contingency
Factors (cont’d)
Environmental Uncertainty and Structure
Mechanistic organizational structures tend to be
most effective in stable and simple environments.The flexibility of organic organizational structures is better suited for dynamic and complex environments.
Слайд 28Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Common
Organizational Designs
Traditional Designs
Simple structure
Low departmentalization, wide spans of control, centralized
authority, little formalizationFunctional structure
Departmentalization by function
Operations, finance, marketing, human resources, and product research and development
Divisional structure
Composed of separate business units or divisions with limited autonomy under the coordination and control the parent corporation.
Слайд 29Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Exhibit
9–7 Strengths and Weaknesses of Traditional
Organizational Designs
Слайд 30Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Exhibit
9–8 Contemporary Organizational Designs
Слайд 31Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Exhibit
9–8 (cont’d ) Contemporary Organizational
DesignsСлайд 32Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Organizational Designs (cont’d)
Contemporary Organizational Designs
Team structures
The entire organization is made
up of work groups or self-managed teams of empowered employees.Matrix and project structures
Specialists from different functional departments are assigned to work on projects led by project managers.
Matrix and project participants have two managers.
In project structures, employees work continuously on projects; moving on to another project as each project is completed.
Слайд 33Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Organizational
Designs (cont’d)
Contemporary Organizational Designs (cont’d)
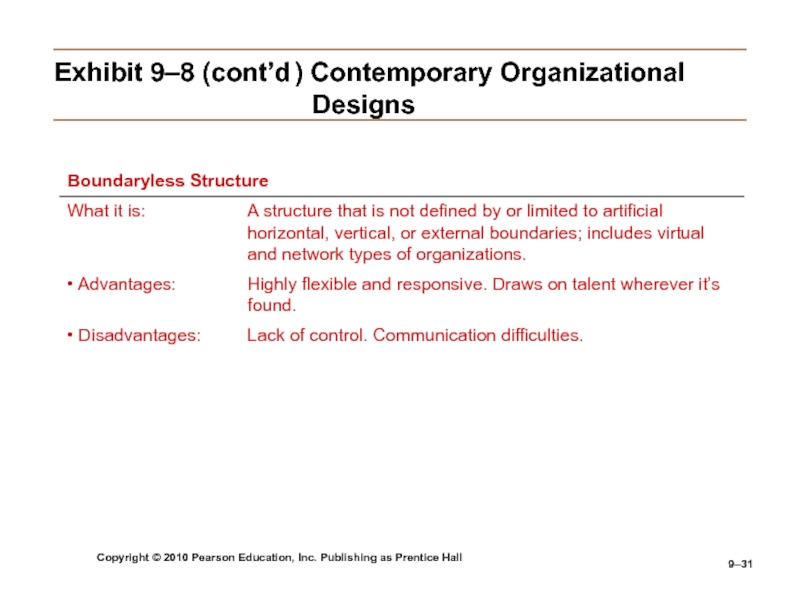
Boundaryless Organization
An flexible and unstructured organizational
design that is intended to break down external barriers between the organization and its customers and suppliers.Removes internal (horizontal) boundaries:
Eliminates the chain of command
Has limitless spans of control
Uses empowered teams rather than departments
Eliminates external boundaries:
Uses virtual, network, and modular organizational structures to get closer to stakeholders.
Слайд 34Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Removing
External Boundaries
Virtual Organization
An organization that consists of a small core
of full-time employees and that temporarily hires specialists to work on opportunities that arise.Network Organization
A small core organization that outsources its major business functions (e.g., manufacturing) in order to concentrate on what it does best.
Modular Organization
A manufacturing organization that uses outside suppliers to provide product components for its final assembly operations.
Слайд 35Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Today’s
Organizational Design Challenges
Keeping Employees Connected
Widely dispersed and mobile employees
Building a
Learning OrganizationManaging Global Structural Issues
Cultural implications of design elements
Слайд 36Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Organizational
Designs (cont’d)
The Learning Organization
An organization that has developed the capacity
to continuously learn, adapt, and change through the practice of knowledge management by employees.Characteristics of a learning organization:
An open team-based organization design that empowers employees
Extensive and open information sharing
Leadership that provides a shared vision of the organization’s future.
A strong culture of shared values, trust, openness, and a sense of community.
Слайд 37Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
9–
Terms
to Know
organizing
organizational structure
organizational chart
organizational design
work specialization
departmentalization
cross-functional teams
chain of command
authority
responsibility
unity of
commandspan of control
centralization
decentralization
employee empowerment
formalization
mechanistic organization
organic organization
unit production
mass production
process production
simple structure
functional structure
divisional structure
team structure
matrix structure
project structure
boundaryless organization
virtual organization
network organization
learning organization